Timer 是一个定时器,代表未来的一个单一事件,你可以告诉 timer 你要等待多长时间,它
提供一个 channel,在将来的那个时间那个 channel 提供了一个时间值。
Timer
创建方法<font style="color:rgb(0,0,0);">timer := time.NewTimer(...)</font><font style="color:rgb(0,0,0);">time.After(...)</font>
time.NewTimer(…)
基本执行语法
- 语法:
- 设置时间
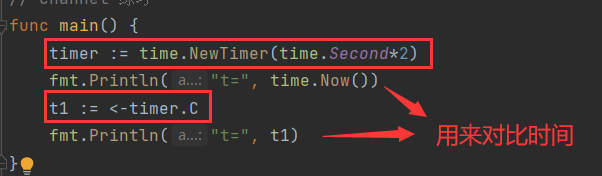
<font style="color:rgb(0,0,0);">timer := time.NewTimer(time.Second*n)</font> - 执行
<font style="color:rgb(0,0,0);"><-timer.C</font>
- 设置时间
- 目的:实现一个等待,且返回实时时间
结果: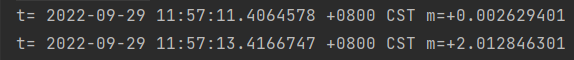
- 解释:
变量timer包含一个管道C(channel的简写) - NOTE:如果只是单纯等待,不返回实时时间
- 可以
<font style="color:rgb(0,0,0);">time.Sleep(time.Second*3)</font>等待3秒 - 或者把上面改一下
<font style="color:rgb(0,0,0);"><-timer.C</font>
- 可以
停止定时器
- 语法:
- 设置
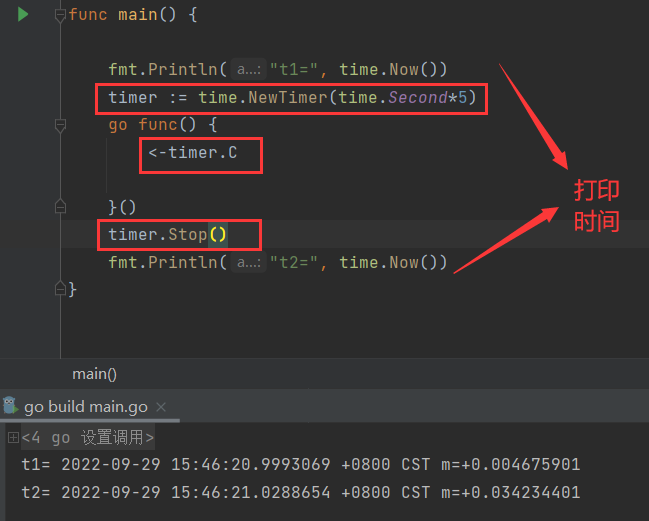
<font style="color:rgb(0,0,0);">timer := time.NewTimer(time.Second*n)</font> - 执行
<font style="color:rgb(0,0,0);"><-timer.C</font> - 停止
<font style="color:rgb(0,0,0);">timer.Stop()</font>
- 设置
- 目的:停止之前设置的定时器
- 实例
1. 实例1
 2. 实例3
2. 实例3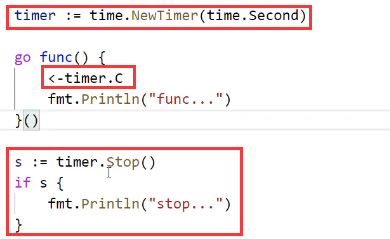
<font style="color:#E8323C;">timer.Stop()</font>执行了,执行成功还给true,执行不成功返回false
重置定时器
- 语法:
<font style="color:rgb(0,0,0);">timer := time.NewTimer(time.Second*n)</font>- 重置时间为m秒
<font style="color:rgb(0,0,0);">timer.Reset(time.Second*m)</font> - 执行
<font style="color:rgb(0,0,0);"><-timer.C</font>
- 目的:之前设置过时间,可能代码太多,忘了在哪,现在重置一下再执行
time.After(…)用法
- 语法:
<font style="color:rgb(0,0,0);"><- time.After(time.Second*n)</font>
函数返回值就是chan Time,优点是比NewTimer更直接,无需赋予变量,缺点是没它那么多功能 - 目的,实现一个等待,并返回时间
- 实例
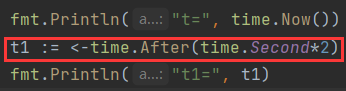
结果: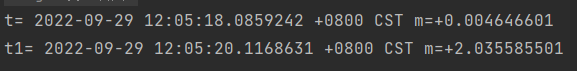
总结
- 实现延时功能
<font style="color:rgb(0,0,0);">timer := time.NewTimer(time.Second*n)</font>+<font style="color:rgb(0,0,0);"><-timer.C</font>可获得实时时间<font style="color:rgb(0,0,0);"><- time.After(time.Second*m)</font>可获得实时时间<font style="color:rgb(0,0,0);">time.Sleep(time.Second*3)</font>但不返回实时时间
- 功能性
1. 设置时间
<font style="color:rgb(0,0,0);">timer := time.NewTimer(time.Second*n)</font>,执行<font style="color:rgb(0,0,0);"><-timer.C</font>,在此基础上 1. 可停止计时器<font style="color:rgb(0,0,0);">timer.Stop()</font>2. 可重置计时器<font style="color:rgb(0,0,0);">timer.Reset(time.Second*m)</font>2.<font style="color:rgb(0,0,0);"><- time.After(time.Second*m)</font>只能延时+返回实时时间
Ticker
Timer只执行一次,而Ticker可周期执行语法
- 设置
<font style="color:rgb(0,0,0);">ticker := time.NewTicker(time.Second*n)</font> - 执行
<font style="color:rgb(0,0,0);"><- ticker.C</font> - 要是想停止,可
<font style="color:rgb(0,0,0);">ticker.Stop()</font>
应用
- 实例1
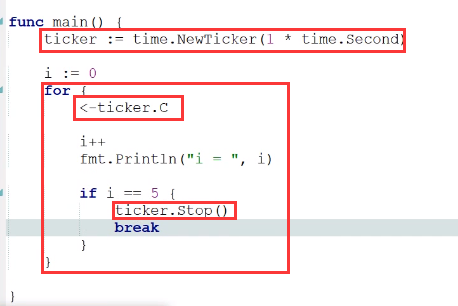
结果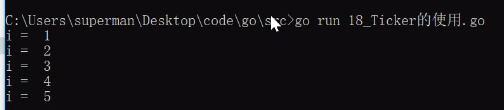
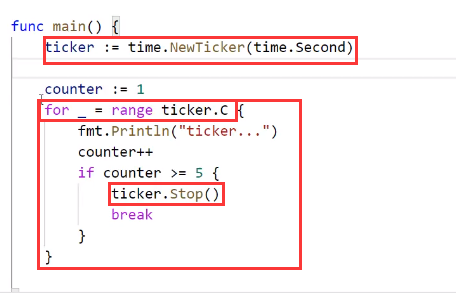
- 实例2——遍历
- for..range 是一个有周期的无限循环,记得必须有中断条件(或者这个中断条件是主线程结束)
- 可获得实时时间
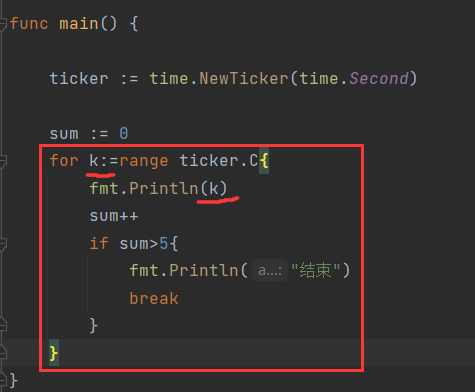
- 不获得时间就这么写,注意不是
:=
结果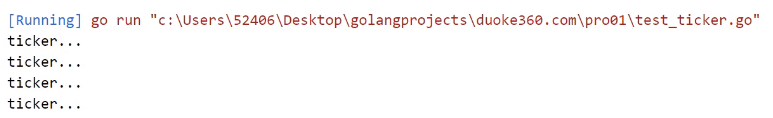
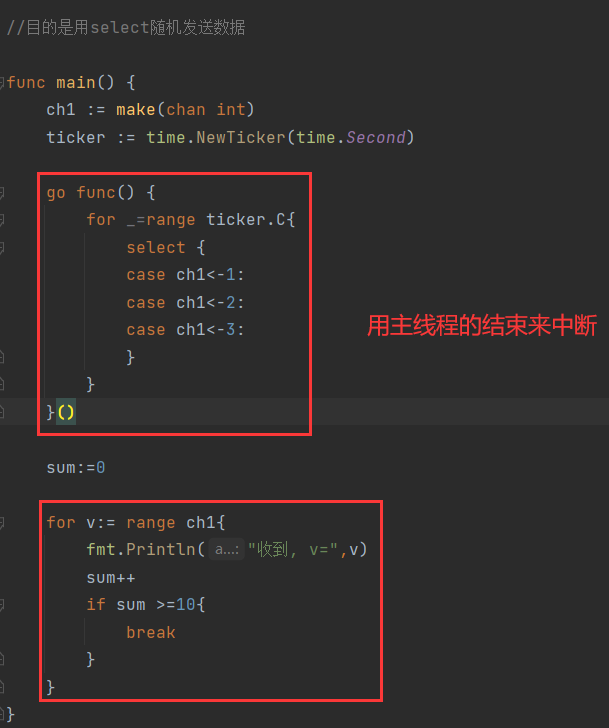
- 实例3,与select的结合,目的是用select随机发送数据,比如不间断随机发一些抽奖数字啊
package mainimport ("fmt""time")//目的是用select批量发送数据func main() {ch1 := make(chan int)ticker := time.NewTicker(time.Second)go func() {for _=range ticker.C{select {case ch1<-1:case ch1<-2:case ch1<-3:}}}()sum:=0for v:= range ch1{fmt.Println("收到, v=",v)sum++if sum >=10{break}}}