Given the root of an n-ary tree, return the preorder traversal of its nodes’ values.
Nary-Tree input serialization is represented in their level order traversal. Each group of children is separated by the null value (See examples)
Example 1: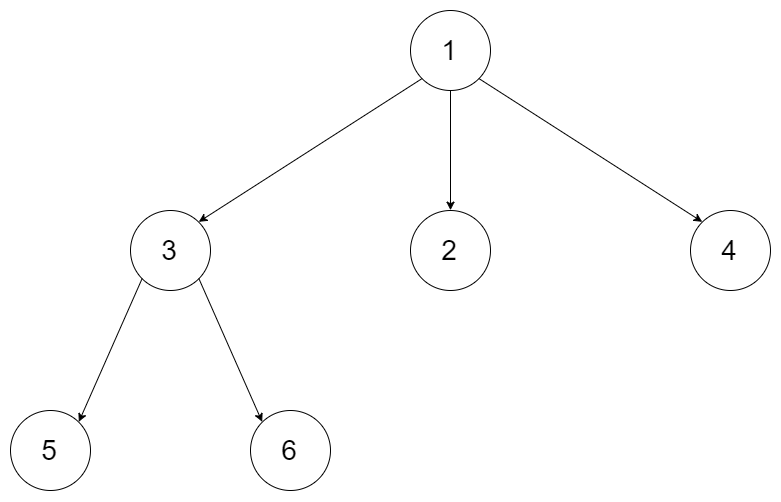
Input: root = [1,null,3,2,4,null,5,6] Output: [1,3,5,6,2,4]
Example 2: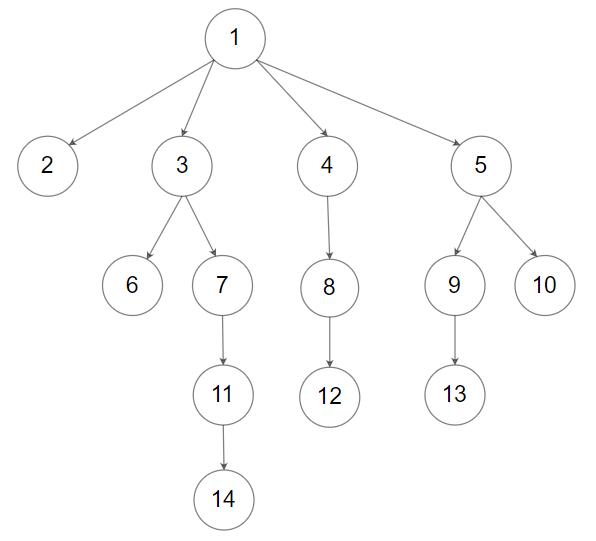
Input: root = [1,null,2,3,4,5,null,null,6,7,null,8,null,9,10,null,null,11,null,12,null,13,null,null,14] Output: [1,2,3,6,7,11,14,4,8,12,5,9,13,10]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 104].
- 0 <= Node.val <= 104
- The height of the n-ary tree is less than or equal to 1000.
Follow up: Recursive solution is trivial, could you do it iteratively?
Runtime: 96 ms, faster than 75.51% of JavaScript online submissions for N-ary Tree Preorder Traversal.
Memory Usage: 42 MB, less than 76.89% of JavaScript online submissions for N-ary Tree Preorder Traversal.
/*** // Definition for a Node.* function Node(val, children) {* this.val = val;* this.children = children;* };*//*** @param {Node|null} root* @return {number[]}*/var preorder = function(root) {const stack = [];const result = [];let node = root;let children = [];while(stack.length > 0 || node) {if (node) {result.push(node.val);children = node.children || [];node = children[0];for (let i = children.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {stack.push(children[i]);}} else {node = stack.pop();}}return result;};

