Topic 1
1.1 0.20 g MnO(s) is added to 1.0 g potassium chlorate (KClO) sample with inert impurities to catalyze its decomposition into potassium chloride and oxygen gas. After heating with a long time, the mass of the residual is stabilized to be 1.00 g. What is the KClO% (w/w) in the sample? __ (2 sig. fig.)
The synthesis and characterization of gold nanoparticles is currently an active research area. The Brust-Schiffrin method for the synthesis of gold nanoparticle (AuNP) allows the facile preparation of thermally stable and air-stable AuNPs of reduced polydispersity with a controlled size distribution ranging in diameter between 1.5 and 5.2 nm. The preparative procedure is briefly described as follows. An aqueous solution of HAuCl4 is mixed with a toluene solution of tetra-n-octylammonium bromide. The solution is mixed with dodecanethiol and is treated with an excess of NaBH4. Formation of the AuNPs is evidenced by the immediate, pronounced darkening of the toluene phase. After ca. 24 h, the toluene solvent is removed with a rotary evaporator and the resulting solid washed on a frit with ethanol and hexane to remove excess thiol. These AuNPs can be repeatedly isolated and re-dissolved in common organic solvents without irreversible aggregation or decomposition.
1.2 Is the methodology for
this fabrication referred to a top-down or a bottom-up approach? Select your
answer from the following choices.
A.
top-down approach, which entails reducing the size of the smallest structures
to the nanoscale
B.
bottom-up approach, which involves manipulating individual atoms and molecules
into nanostructures
1.3 The
trimethyl-n-octylammonium bromide can also be used as a phase-transfer reagent.
It can carry AlCl from an aqueous phase to an organic
phase. Which property does trimethyl-n-octylammonium bromide possess to
function as an efficient phase-transfer reagent? Select your answer from the
following choices.
A.
one side of the molecule is electropositive, the other side is electronegative.
B.
one side of the molecule is hydrophilic, the other side is hydrophobic.
C.
one side of the molecule is acidic, the other side is basic.
1.4 What is the function of
NaBH4 in this preparation? Select your answer from the following choices.
A.
reducing agent B. oxidizing
agent C. neutralization agent D. complexing agent
1.5 If the average diameter
of a gold nanoparticle is 3 nm, what is the estimated number of Au atoms in
each nanoparticle? (the atomic radius of Au is 0.144 nm). Select your answer
from the following choices.
A.
10 B. 10 C. 10 D. 10
1.6 What is the estimated
percentage of Au atoms on the surface of a nanoparticle? Select your answer
from the following choices.
A.
20 – 30 % B. 40 – 50 % C. 60 – 70 % D. 80 – 90 %
Topic 2
2.1 The water purification process using ion exchange is
shown in the figure below. What of the following statements is incorrect?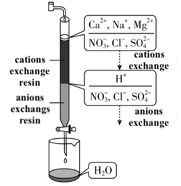
A.
After passing through the cations exchange resin, the total number of cations
in water does not change
B.
Anions such as NO, SO, and Cl
in water are removed after passing through the anions exchange resin
C.
After the purification treatment, the conductivity of water decreases
D.
Reaction H + OH = HO occurs in the anions
exchange resin section.
2.2 The atomic numbers of the main
group elements W, X, Y, and Z increase sequentially, and they are all not
greater than 20. The sum of the outermost electron numbers of W, X, and Z is
10; W and Y are in the same group; compounds formed by W and Z can react with
concentrated sulfuric acid, and the products can etch glass. Which of the
following statements is correct?
A. The elemental substance of X is
gaseous at normal temperature and pressure
B. The hydride of Z are ionic
compounds
C. Aqueous solutions of compound made
by Y and Z are alkaline
D. W and Y have the same highest oxidation
number
2.3 Considering 0.1 M aqueous solutions of each of
the following, which solution has the lowest pH ?
A. Na2CO3
B. Na2S
C. NaCl
D. CH3COONa
2.4 Which of the following is an n-type
semiconductor?
A. Silicon
B. Silicon carbide
C. Arsenic-doped silicon
D. Gallium-doped silicon
- 2.5 NH(aq) is added to the small amount of Cu powder, which changes into a colorless solution after shaking. The colorless solution becomes blue after standing. What is the solute in the colorless solution?
A. Cu B. Cu(NH) C. Cu D. Cu(NH)
- 2.6 Na[Fe(CN)(NO)] is diamagnetic, what is the oxidation number of Fe in the compound?
A. 0 B. +1 C. +2 C. +3
Topic 3/4
- 3.1 Among the 4 substances involved in the low-pressure synthesis of methanol (CO + H = CHOH + HO), the order of the boiling point from high to low is
A. CHOH > HO > CO > H
B. HO > CHOH > H > CO
C. HO > CHOH > CO > H
D. HO > CO > CHOH > H
3.2 MgO has a NaCl structure, in which the anion adopts the face-centered cubic closest packing. X-ray diffraction experiments have determined that the unit cell parameter of MgO is a = 0.420 nm, so r(O) is __ nm if adjacent cations and anions are tangent to each other.
3.3 LiO is an ionic crystal, and its lattice energy can be calculated by the Born-Haber cycle in figure (a).
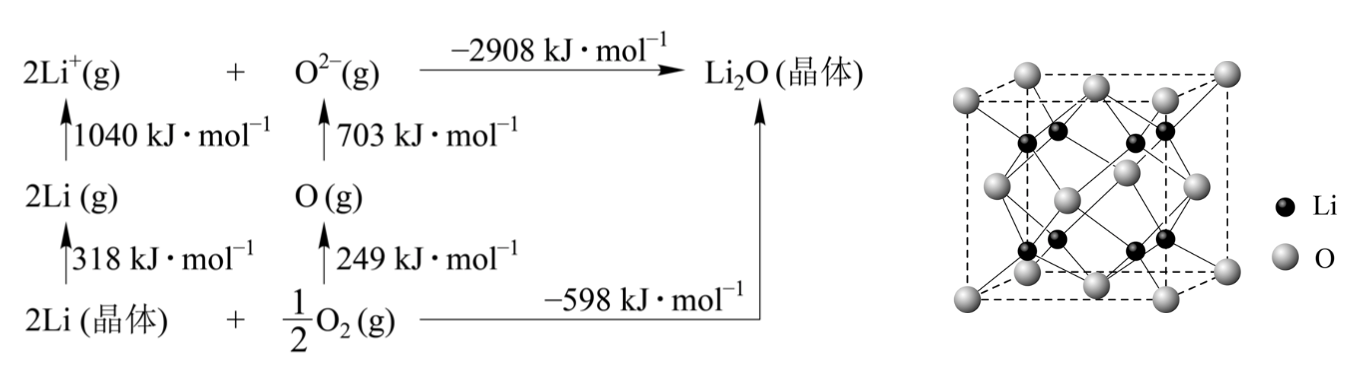
Figure (a) Figure (b)
The lattice energy of LiO is _ _ kJ mol.3.4 LiO has an anti-fluorite structure. The unit cell is shown in Figure (b). The known unit cell parameter is 0.4665 nm. So the density of LiO is __ g cm.
3.5
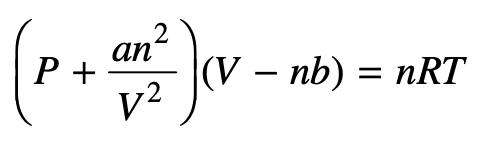
Of the following substances, which is likely to have the largest value of the coefficient _a _in the van der Waals equation of state for real gases shown above?
A. H2 B. N2 C. NH3 D. CO2
Topic 5
5.1
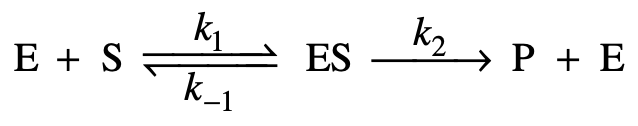
The mechanism shown above has been proposed for the enzyme-catalyzed hydrolysis of certain biochemical compounds (substrates), where ES is an enzyme-substrate complex. Given a fixed amount of enzyme, E, which of the following could be the plot of the initial rate of the production of product, P, when using varying initial concentrations of substrate, [S]0?
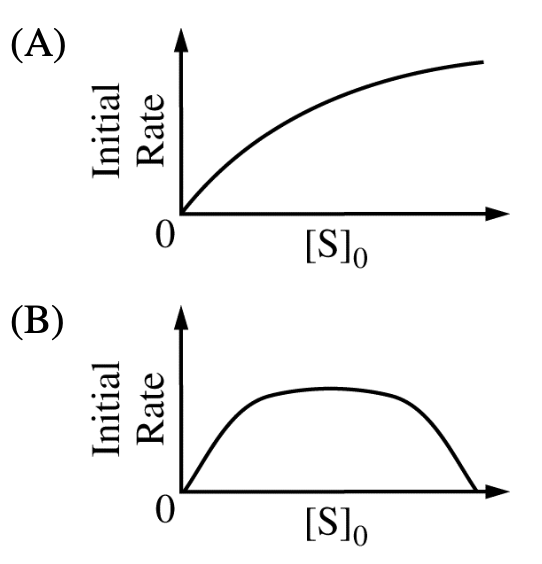
5.2 The reaction of propane with halogen radicals and their standard enthalpy changes are as follows:

When the
reaction temperature increases, the rate of the above reactions will
A. Both
are lowered;
B. Both
rise;
C. The
reactions (1) and (2) decrease, and the reaction (3) increases;
D. None
of the above
- 5.3 25 C, the proportion of the two products in the following reaction has been given.
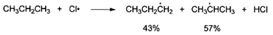
Combined
the information given in (a), the proportion of the primary substituted product
will be __ when the temperature is increased while other conditions are
remained.
A.
lower; B.
higher; C. unchanged; D. unable to judge
Topic 6
- 6.1 The application of colorful inorganic pigments has created the splendor of ancient paintings and painted pottery. Cadmium sulfide (CdS) is a yellow pigment that is hard to dissolve in water. Its precipitation and dissolution equilibrium curve in water is shown in the figure below. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
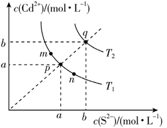
A. In the figure, a and b
shows the molar solubility of CdS in water at temperature T and T.
B. The relationship between K
at different points in the figure is: K(m) = K(n)
< K(p) < K(q)
C. Add a small amount of NaS
solid to the solution at point m, and the composition of the solution
moves from m along the mpn line to the p direction
D. When the temperature decreases,
the composition of the saturated solution of CdS at point q moves from q
along the qp line to the p direction
- 6.2 In two identical solutions of Ba(OH), the HSO and NaHSO solutions with the same molarity are added into the solution dropwise. The curve of the conductivity of the solution with the volume of the solution added is shown in figure below. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
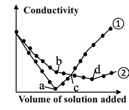
A.
① represents the curve of the addition
of HSO solution
B.
At point b, the predominant ions in the solution are
Na, OH
C.
At point c, the two solutions contain the same amount of OH
D.
The solutions at point a and d are neutral
6.3 0.100 mol·LAgNO is used to titrate 50.0 mL 0.0500 mol·LCl solution. The titration curve is shown in the figure below. Which of the following descriptions is incorrect?
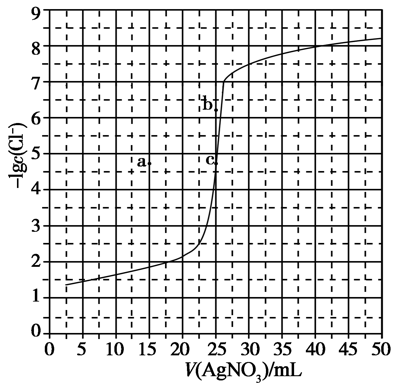
A. Based on the curve, it can be known that the magnitude of K (AgCl) is 10.
B. The solution at each point on the curve satisfies the relationship c(Ag)·c(Cl) = K(AgCl)
C. Under the same experimental conditions, if it is changed to 0.0400 mol·L Cl, the end point c moves to a
D. Under the same experimental conditions, if it is changed to 0.0500 mol·L Br, the end point c moves to b6.4 NaOH solution is added to adipic acid (HX) solution at room temperature, the relationship between the pH of the mixed solution and the ratio of ion concentrations is shown in the figure below. Which of the following statements is wrong?

A. K(HX)
is on the order of 10
B. Curve N shows the relationship
between pH and lg[c(HX)/c(HX)]
C. c(H)> c(OH)
in NaHX solution
D. When the mixed solution is neutral,
c(Na) > c(HX) > c(X)
c(OH) > c(H)
6.5. In the electrolytic solution used for wet zinc smelting, higher concentration of Cl will corrode the anode plate and increase the energy consumption. Cu and CuSO can be added to the solution at the same time, resulting in a CuCl precipitation and the removal of Cl. According to the relationship diagram of the relevant ion concentration at equilibrium in the solution, which of the following statements is wrong?
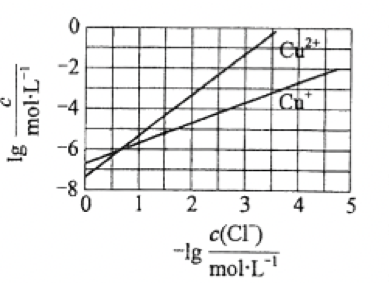
A. K(CuCl) has a magnitude of 10
B. The removal reaction of Cl is Cu + Cu + 2Cl = 2CuCl
C. The more Cu is added, the higher the Cu concentration, the better effect of removing Cl
D. The equilibrium constant of 2Cu ⇌ Cu + Cu is large, and the reaction tends to be complete
- 6.6 At a given temperature, the forward rate constant, _k_1, for the one-step reaction below
<br /> 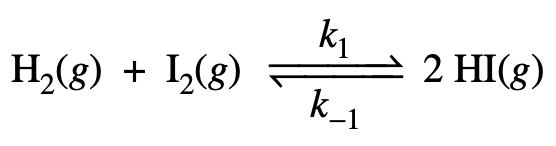<br />above is 4×10-7 M s .Given that the equilibrium constant is 1 × 10-2, what is the reverse rate constant, _k_−1 ?<br />(A) 8×10-5 M-1s-1 (B) 4×10-5 M-1s-1 (C) 4×10-7 M-1s-1 (D) 8×10−9 M−1s−1
(E) 4 × 10−9 M−1 s−1
- 6.7 p_K_1 = 2.95 p_K_2 = 6.79
Phthalic acid, (COOH)C6H4(COOH), is a weak,
diprotic acid with dissociation constants above.
The pH of an aqueous solution of potassium acid phthalate, (COOH)C6H4(COO−K+), is
closest to
(A) 9.74
(B) 7.00
(C) 6.79
(D) 4.87
(E) 2.95
Interconversion of NO and NO, NO(g) ⇌ 2NO(g) is a commonly used system for discussing chemical equilibrium. It is known that the equilibrium constants K of the reaction at temperatures of 295 K and 315 K is 0.100 and 0.400, respectively. A certain amount of gas is put into a special container with a piston, and the total pressure of the system is kept into 1 bar (1 bar = 100 kPa) by the movement of the piston.
- 6.8 The above system is raised from 295 K to 315 K under constant external pressure. Which of the following statements is correct?
A.
Equilibrium shifts to the left side
B.
Equilibrium does not shift
C.
Equilibrium shifts to the right side
D.
None of the above
- 6.9 Compared to the change of the system when temperature increases from 295 K to 315 K under constant volume, how is the change of the system under constant pressure with the same temperature in easement?
A.
There is more shift of the equilibrium under constant pressure
B.
There is more shift of the equilibrium under constant volume
C.
They have the same shifting degree of equilibrium
D.
All of the above are possible
6.10 1.0 g CaCO(s) is added to 0.3 L water and obtained a saturated solution with a molarity of xxx, what is the pH of the solution?
6.11 If 0.03 M HSO is added to adjust the pH of the above saturated solution with remaining solid by 1 unit, what is the volume of HSO used?
- AgCl(s)
is soluble in 0.10 M NH(aq), when HCl(g) is bubbled into the
solution until pH = 2, how many times does the solubility of AgCl decrease?
_ constants
needed
2. 0.20 mmol BaSO(s) is washed with 1.0 mL saturated NaCO(aq) with a molarity of 1.6 M for several times. In order to dissolve all of the precipitate, how many times of washing is needed at least? __. constants needed
3. What is the molarity of NH(aq) must be maintained to prevent the precipitation of Mg(OH)(s) from a solution mixed by 0.010 M MgCl and 0.10 M NH? _ K = 1.8×10, K = 1.8×10
Titration curve analysis
Topic 8/9
- For the alkali metals Li, Na, K, Rb and Cs, which of the following properties is NOT monotonic as the atomic number increases?
A. melting point B. atomic radius C. crystal density D. first ionization energy
- The flame color of element K is purplish red, which of the radiation wavelengthes corresponding to purple?
(A) 404.4 nm (B) 553.5 nm (C) 589.2 nm (D) 670.8 nm
- X-ray diffraction measurement found that I ions were present in IAsF. The geometry of the I ion is _, and the hybrid type of the central atom is __.
A.
B.
C.
D.
LiAlH4 is a reducing agent commonly used in organic synthesis. The geometry of the anion in LiAlH4 is _, and the hybrid form of the central atom in the anion is _. _ exist(s) in LiAlH4.A. Ionic bond B. s bond C. p bond D. Hydrogen bonding
Of the magnesium in the following states, which one has the largest first ioniztion energy?

Which of the following lists the hydrides of group-14 elements in order of thermal stability, from lowest to highest?
(A)PbH4
- The length of O-O bond is 121 pm, which is the following the post possible O-O bond length in O[AsF]?
A. 112 pm B. 121 pm C. 128 pm D. 149 pm
It was
predicted in March 2006 that element 126, an unknown element of heavy weight,
is likely to form a stable compound with fluorine. According to the known law
of the element period, the element should be in the 7 period, and
its energy level that is not filled with electrons should be _.
A.
7s B. 7p C. 6d D. 5f
Condensation of a carboxylic
acid with an amine gives an amide product. For example, condensation of formic
acid with dimethylamine forms N, N-dimethylformamide (DMF), which can be
described as the following resonance structures.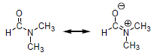
Predict the order of melting points among N, N-dimethylformamide
(compound A), N-methylacetamide (CHCONHCH,
compound B), and propionamide (compound C, CHCHCONH,).
Express your answer from high to low melting point as follows: >
__ (Insert compound codes A, B, C)
Carbonyl groups are
usually identified by their characteristic strong absorptions in the infrared
spectra. The position of the absorption is dependent on the strength of the C=O
bond, which in turn is reflected in their bond lengths. In amides, the strength
of the carbonyl groups can be shown by the resonance structure noted above. For
example, cyclohexanone shows an absorption at 1715 cm for the
carbonyl group (C=O). In comparison with cyclohexanone, predict the absorption
band for the carbonyl group in propionamide. Select your answer from the
following choices.
A.
1660 cm because of the shorter carbonyl bond length.
B.
1660 cm because of the longer carbonyl bond length.
C.
1740 cm because of the shorter carbonyl bond length.
D.
1740 cm because of the longer carbonyl bond length.
more questions
Topic 10
L has a molecular formula of C7H8O2, which can react with FeCl3 solution. 1 mol of L can react with 2 mol of Na2CO3, how many isomers does L have to satisfy the above description?
How many above isomers have NMR spectrum with four peaks (ratio = 3:2:2:1)?
How many ester isomers does the following compound E have (exclude this structure)? (H-NMR spectrum shows two groups of peaks, and the peak area ratio is 1: 1).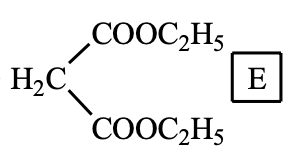
- How many isomers does the molecular CHBrCl have without considering the stereoisomers?
A. 8 B. 10 C. 12 D. 14
Povidone-iodine, also known as iodopovidone, is an antiseptic
used for skin disinfection before and after surgery. Povidone forms
povidone-iodine through hydrogen bonding with HI. The structure is
as follows: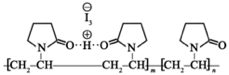
(The dotted line in the figure
indicates the hydrogen bond)
Which of the following statements is incorrect?A. The monomer of povidone is 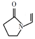
B. The povidone is polymerized from (m+n) monomersC. Povidone-iodine is water solubleD. Povidone can undergo hydrolysis under certain conditions
- A compound that shares a carbon atom between the rings is called a spiro compound, and spiro[2.2]pentane (structure shown as below) is the simplest one. Which of the following statements about the compound is incorrect?

A. It is the isomer of cyclopentene
B. It has more than two dichlorides
C. All carbon atoms are on the same
plane
D. At least 2 mol H is
required to produce 1 mol CH from it.
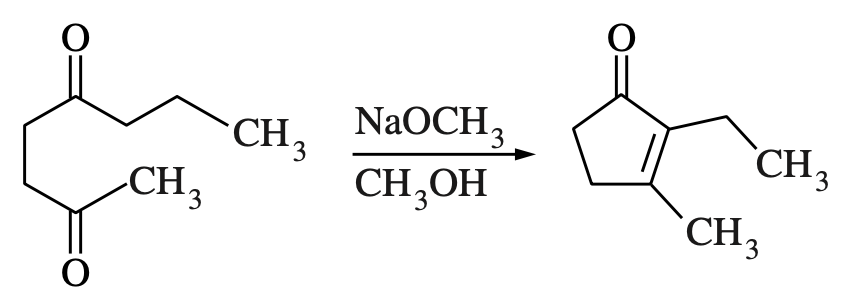
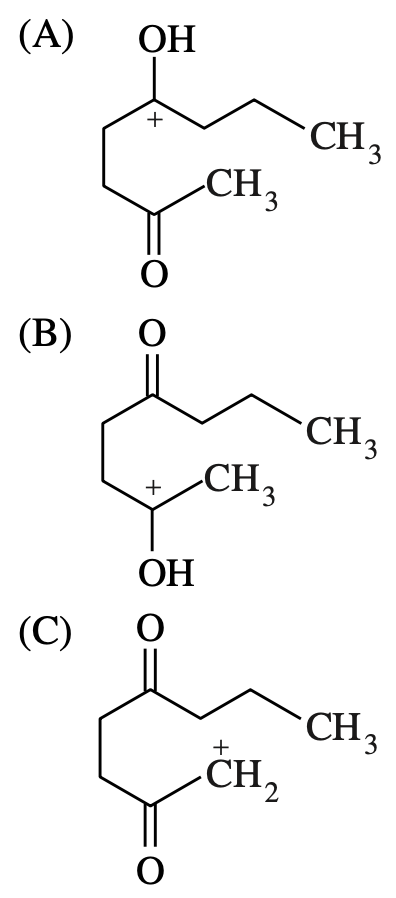
60. The product of the reaction shown above is produced via
which of the following intermediates?
~~
 ~~
~~
- Of the following fatty acids, which has the lowest melting point?
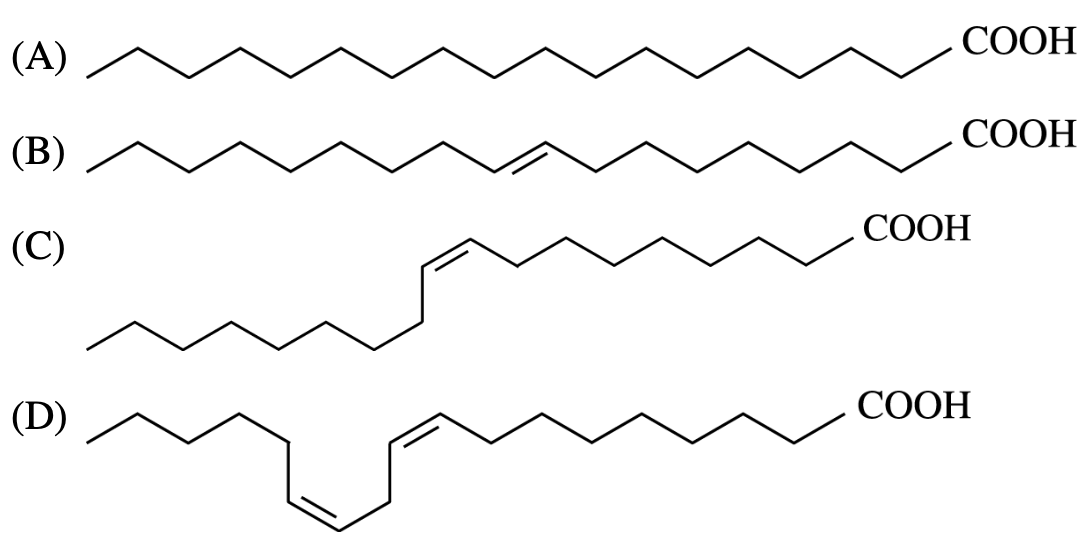<br />
Theoretical calculations show that there are some energy differences between the Z and E-type isomers of formic acid.
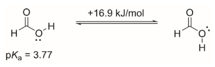
It
is known that the Z-type isomer has a
pK = 3.77, what is the pK of the E-isomer?
A.
3.77 B. < 3.77 C. – 3.77 D. The information listed here is not enough to tell
- What is the product of esterification of CHC(=O)OH and CHCHOH?
A.
CHC(=O)OCHCH
B. CHC(=O)OCHCH
C.
CHC(=O)OCHCH
D.
CHC(=O)OCHCHAND CHC(=O)OCHCH
Which of
the following is aromatic?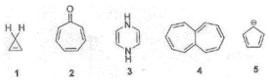
A.
1, 2, 5 B. 2, 5 C. 2, 4, 5 D. all of them
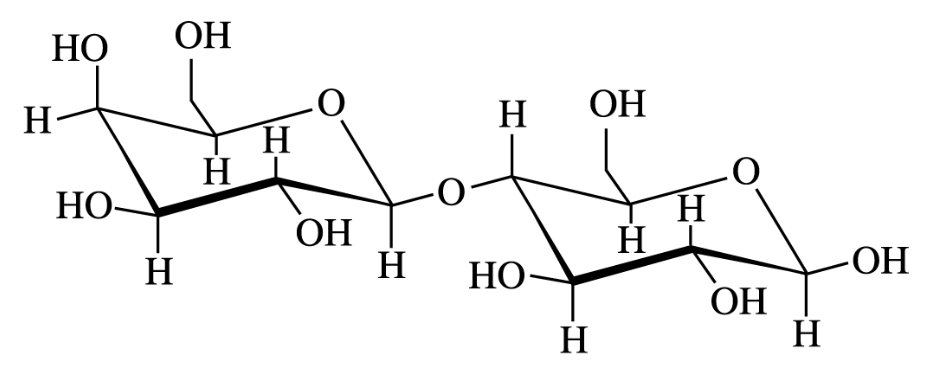
- Which of the following is NOT true about the disaccharide lactose shown above?
A. Lactose is a reducing sugar.
B. Lactose is optically active.
C. Lactose can be hydrolyzed to monosaccharides with HO/HSO.
D. Lactose has a 1,1’-alpha-glycosidic linkage.

