- Topic 1 - Stoichiometry
- Topic 2 - Descriptive Chemistry/Laboratory
- Topic 3 - Solids, Liquids, Gases, & Phase Changes
- Topic 4 - Thermodynamics
- Topic 5 - Kinetics
- Topic 6 - Equilibrium
- Topic 7 - Redox/Electrochemistry
- Topic 8 - Atomic Structures/Periodicity
- Topic 9 - Molecular Structures/Bonding
- Topic 10 - Organic Chemistry/Biochemistry
The top two questions with the percentage of correction answers lower than 40% in each topic are listed here for further analysis.
Data for the percentage of correction answers in 2017 is not officially provided, so hard questions of this year listed here are based on Dr. Chen’s analysis.
Topic 1 - Stoichiometry
2016
2017
2018
[25%] 5. After mixing 30.0 mL of 0.30 M Ca(NO) solution and 15.0 mL of 0.60 M NaF solution, which ions are present in solution at concentrations of at least 0.10 M?
I. Ca
II. F
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) Both I and II
(D) Neither I nor II
[34%] 6. A salt whose formula is NaSx_O_y is 47.5% sulfur by mass. What is the value of x in the formula?
(A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4
2019
Topic 2 - Descriptive Chemistry/Laboratory
2016
[31%] 9. When 6 M sodium hydroxide is added to an unknown white solid, the solid dissolves. What is a possible identity for this solid?
(A) Mg(OH) (B) Al(SO) (C) BaCO3 (D) AgBr
[18%] 10. A student standardizes a solution of aqueous NaOH against a measured mass of solid potassium hydrogen phthalate. She then uses this NaOH solution to titrate a measured mass of an unknown monocarboxylic acid to its phenolphthalein endpoint to determine its molar mass. Which errors will lead to a value of the molar mass that is too high?
I. The potassium hydrogen phthalate is partially hydrated.
II. The NaOH solution is allowed to stand after being standardized and absorbs some carbon dioxide from the air.
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) Both I and II
(D) Neither I nor II
2017
2018
[31%] 7. Which salt is diamagnetic?
(A) K[NO(SO)]
(C) Ce(SO)
(B) K[Fe(CN)]
(D) Hg[Co(SCN)]
[40%] 10. A copper-nickel alloy is analyzed by dissolving it in 8 M nitric acid, diluting the solution with water, and then adding 1 mL of this diluted solution to an excess of aqueous potassium iodide. What are the principal forms of copper and nickel in this final mixture?
(A) Cu(aq), Ni(aq)
(B) CuI2(s), NiI2(s)
(C) CuI(s), Ni(aq)
(D) Cu(aq), Ni(s)
2019
[34%] 8. A 0.1 M solution of which compound is most acidic?
(A) KNO (B) NHNO (C) Ba(NO) (D) Fe(NO)
[19%] 11. A chemist has isolated a solid carboxylic acid of unknown formula from a medicinal herb. Which experiment will be most useful in assessing the purity of the isolated material?
(A) Melting point
(B) Titration with NaOH
(C) Combustion analysis
(D) UV-visible spectrophotometry
Topic 3 - Solids, Liquids, Gases, & Phase Changes
2016
[40%] 16. Which statement about the properties of barium chloride and mercury(II) chloride is correct?
(A) BaCl has a higher melting point than HgCl.
(B) BaCl has a higher solubility in nonpolar solvents than HgCl.
(C) BaCl has a higher vapor pressure than HgCl.
(D) Molten BaCl has a lower electrical conductivity than molten HgCl.
2017
2018
2019
[20%] 16. An adjustable-volume container holds 10.0 g pentane (M = 72.15, normal boiling point = 36.1 C). The pressure in the container is measured as a function of volume while maintaining the temperature at 30 C. Which graph shows the results of this experiment?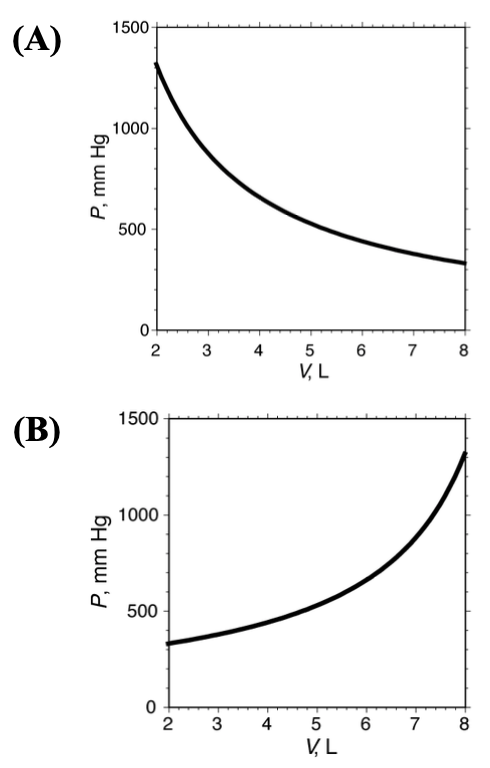
Topic 4 - Thermodynamics
2016
[33%] 22. What is ∆G of CH(g) at 298 K?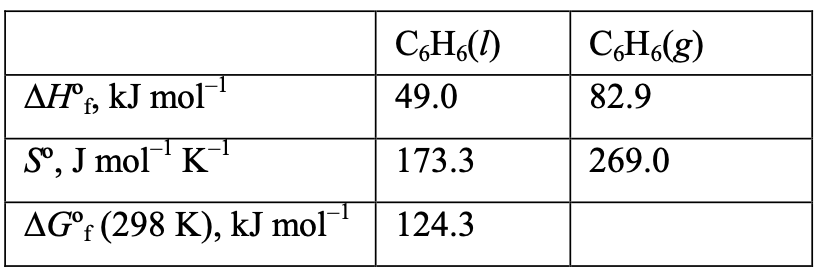
(A) 2.7 kJ mol
(B) 121.6 kJ mol–1
(C) 127.0 kJ mol
(D) 129.7 kJ mol
[36%] 23. Assuming that ∆H and ∆S do not vary significantly with temperature, at what temperature will graphite and diamond be in equilibrium at 1 atm pressure?
(A) 0.62 K
(B) 620 K
(C) 2400 K
(D) Graphite is more stable than diamond at all temperatures.
2017
Upon which factors can the Gibbs free energy change for a reaction (∆G) depend?
I. Temperature
II. Concentration of species in solution
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) Both I and II
(D) Neither I nor IIWhat is ∆G of CH(g) at 298 K? (All data are given at 298 K.)
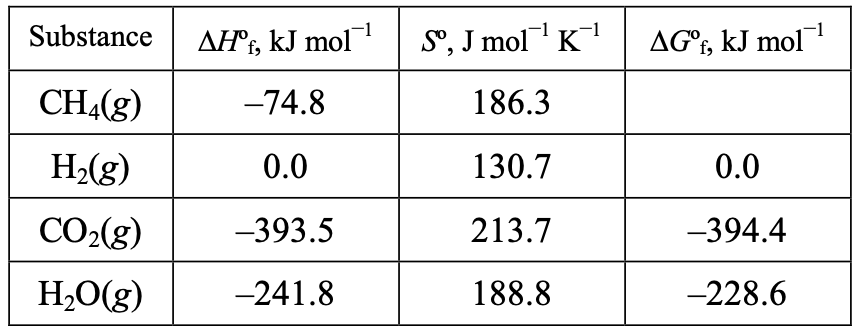
(A) –50.7 kJ mol
(B) –75.7 kJ mol–1
(C) –98.0 kJ mol
(D) –130.3 kJ mol
2018
[31%] 21. The K of AgBr is 5.0×10 at 25.0 C and 6.5×10 at 50.0 C. What is ∆H for the precipitation of AgBr shown?
Ag(aq) + Br(aq) ⇌ AgBr(s)
(A) –82 kJ mol (B) –1.1 kJ mol (C) 1.1 kJ mol (D) 82 kJ mol
[15%] 23. The natural logarithm of the K of NH is plotted below as a function of the reciprocal of the absolute temperature.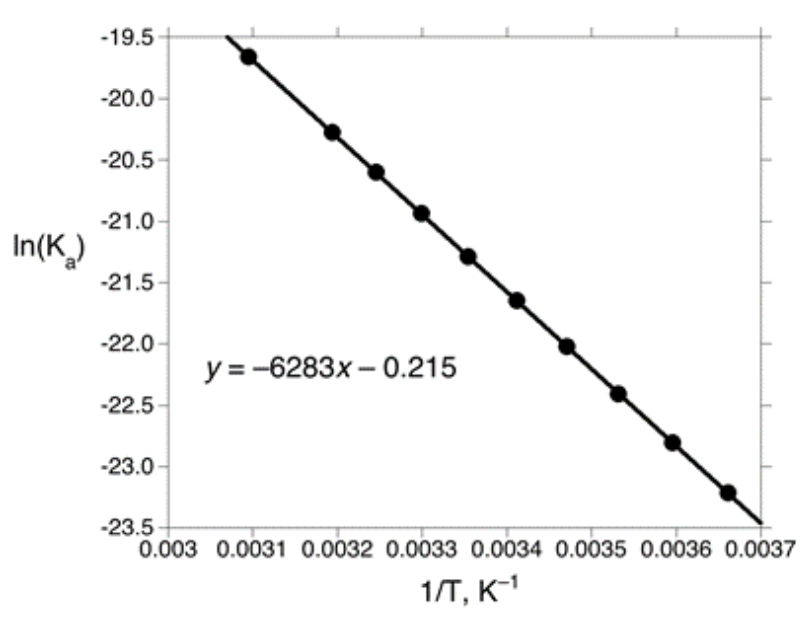
Which statements are correct?
I. The pH of a 0.100 M solution of NHNO increases as the temperature is raised.
II. ∆S for the acid dissociation of ammonium ion is positive.
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) Both I and II
(D) Neither I nor II
2019
[23%] 22. A system confined in a rigid, well-insulated container undergoes a spontaneous change. What statement about the system must be true?
(A) Its Gibbs free energy increases during the change.
(B) Its Gibbs free energy decreases during the change.
(C) Its entropy increases during the change.
(D) Its entropy decreases during the change.
[27%] 23. What is ∆G for the decomposition of CaCO at 298 K and a partial pressure of CO of 4.00×10 bar?
CaCO(s) → CaO(s) + CO(g)
∆G (298 K, P(CO) = 0.400 mbar) = ???
Compound ∆G° (kJ mol)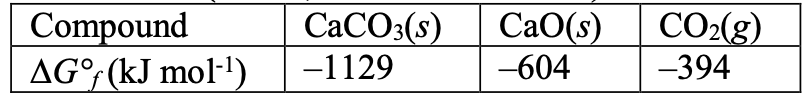
(A) –131 kJ mol
(B) 112 kJ mol–1
(C) 131 kJ mol
(D) 150 kJ mol
Topic 5 - Kinetics
2016
[33%] 25. Cyclopropane isomerizes to propene in an irreversible, first-order reaction. At 700 K, a sample of 22.0 mm Hg of cyclopropane is introduced into a reaction vessel. After 1.0 min, the partial pressure of the product, propene, was found to be 17.5 mm Hg. What is the rate constant for the isomerization at this temperature?
(A) 3.8×10 s (B) 2.6×10 s (C) 0.23 s (D) 1.6 s
2017
A sample containing only the isotope 99Mo undergoes radioactive decay as shown:
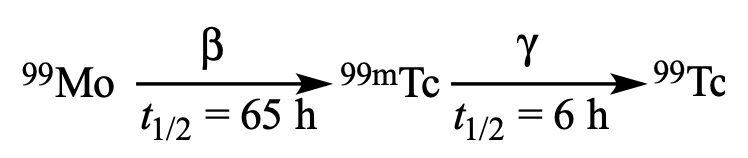
Which of the following statements about the relative activity of Mo and Tc in the sample is correct?
(A) The activity of Tc exceeds that of the Mo after about 20 h.
(B) The activity of Tc exceeds that of the Mo after about 120 h.
(C) The activity of Tc becomes roughly equal to that of the Mo after about 20 h.
(D) The activity of Tc becomes roughly equal to that of the Mo after about 120 h.Hydrogen peroxide disproportionates to water and molecular oxygen in the presence of iodide in neutral solution according to a mechanism consisting of two elementary steps:
HO(aq) + I(aq) → IO(aq) + HO(l) reaction 1
HO(aq) + IO(aq) → I(aq) + O(g) + HO(l) reaction 2
The rate constant for reaction 1 is much larger than the rate constant for reaction 2. Which statement is correct?
(A) As the reaction proceeds, the predominant form of iodine in solution is IO(aq).
(B) Adding more iodide to the reaction will not increase the rate of production of O.
(C) The reaction is zeroth-order in HO.
(D) The reaction will go more slowly at higher O pressures.Which of the following are true about the overall reaction A + B → D illustrated in the diagram?
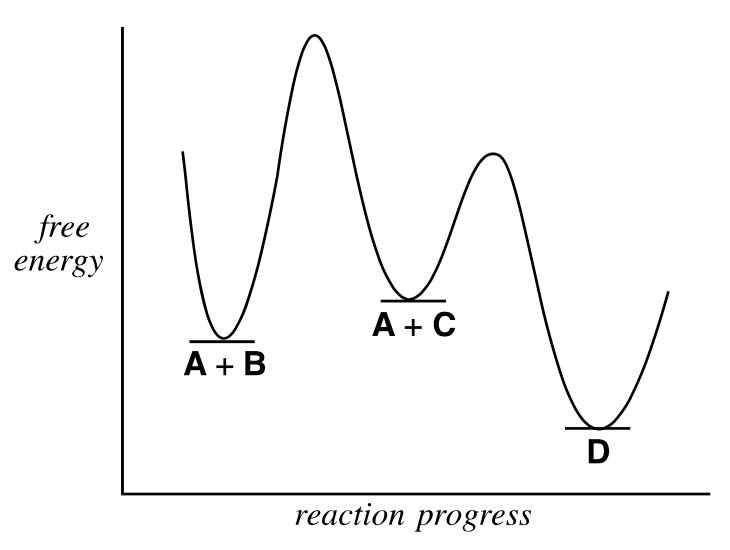
I. The reaction displays second-order kinetics.
II. The reaction has two intermediates.
(A) I only (B) II only
(C) Both I and II (D) Neither I nor II
2018
- An irreversible reaction A + B → products is studied under conditions where the initial concentrations of A and B are equal. Under these circumstances, a graph of ln([A]) as a function of time is linear. What is the order in A?
(A) Zeroth order
(B) First order
(C) Second order
(D) The order in A cannot be determined based on the information given.
2019
[34%] 27. At 650 K, β-pinene isomerizes to form either 4-isopropenyl-1-methylcyclohexene or myrcene. The former reaction has a rate constant of 0.22 s and the latter a rate constant of 0.13 s. What is the overall rate law for the isomerization of β-pinene?
(A) Rate = (0.029 s)[β-pinene]
(B) Rate = (0.082 s)[β-pinene]
(C) Rate = (0.17 s)[β-pinene]
(D) Rate = (0.35 s)[β-pinene]
[35%] 30. Methyl iodide reacts irreversibly with azide ion with rate = k[CHI][N].
CHI(aq) + N(aq) → CHN(aq) + I(aq)
The reaction is carried out with an initial concentration of CHI of 0.01 M. Which statement about the reaction is correct?
(A) The time it takes for [CHI] to decrease to 0.005 M is independent of [N], as long as [N] >> [CHI].
(B) If the initial concentrations of azide and CHI are equal, then it takes half as long for [CHI] to decrease to 0.005 M as it does for it to decrease from 0.005 M to 0.0025 M.
(C) The reaction rate is significantly smaller if excess I is added to the solution.
(D) The reaction cannot take place in a single elementary step.
Topic 6 - Equilibrium
2016
[30%] 35. A sample of a washing powder that contains a mixture of NaCO and NaHCO is titrated with aqueous HCl and the following result is obtained: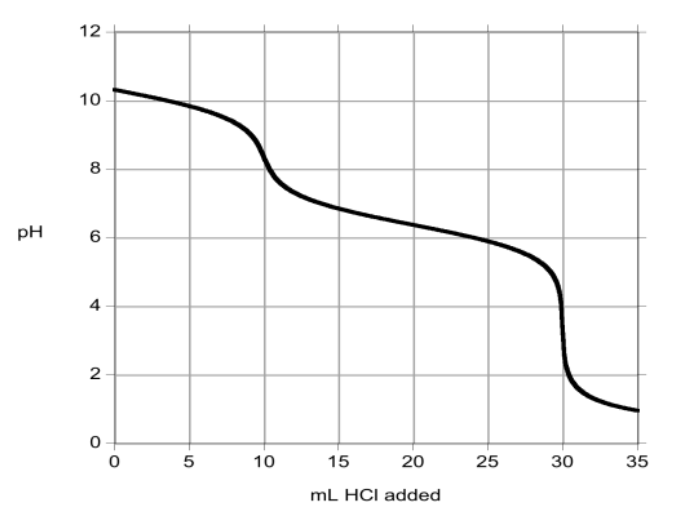
What is the mole ratio of CO to HCO in the washing powder?
(A) 2 mol CO : 1 mol HCO
(B) 1 mol CO : 1 mol HCO
(C) 1 mol CO : 2 mol HCO
(D) 1 mol CO : 3 mol HCO
[33%] 36. Hydrocyanic acid, HCN, is a weak acid with K = 4.9×10. Nickel(II) ion complexes strongly with cyanide ion to form Ni(CN), K = 1.0×10 . What is the pH of 1.00 L of a 0.100 M solution of HCN to which 0.025 mol NiCl has been added?
(A) 1.00 (B) 4.05 (C) 5.15 (D) 8.92
2017
The autoionization constant of water at 60 C is K = 1.0×10. Which of the following statements are
I. Autoionization of water is exothermic.
II. A sample of pure water at 60 C is slightly acidic.
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) Both I and II
(D) Neither I nor IIThe ionization of ammonium ion is endothermic:
NH(aq) + HO(l) ⇌ NH(aq) + HO(aq) ∆H> 0
Which changes will result in the increase in [HO] of a 0.100 M solution of NHCl?
I. Diluting the solution from 1.00 L to 2.00 L
II. Raising the temperature from 25 C to 35 C
(A) Ionly
(B) IIonly
(C) Both I and II
(D) Neither I nor II
2018
[24%] 33. Silver ion forms a complex ion with thiosulfate ion, Ag(SO), with K = 2.8×10. How much AgBr (K= 5.4×10) will dissolve in 1.00 L of 0.200 M NaSO solution?
(A) 0.089 mol (B) 0.10 mol (C) 0.16 mol (D) 0.78 mol
2019
[28%] 35. A metal M forms a sparingly soluble sulfate salt. The logarithm of the concentration of the dissolved metal ion in a solution saturated in the metal sulfate is plotted below as a function of the logarithm of the concentration of sulfate ion in solution. What is the formula of the metal sulfate?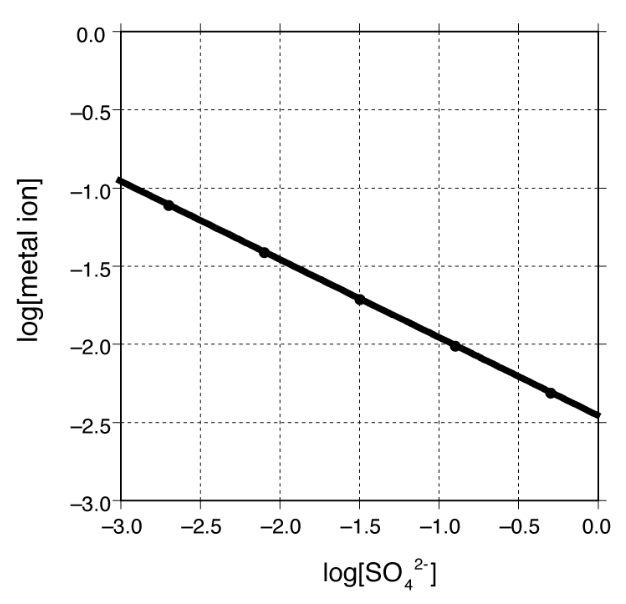
(A) MSO (B) MSO (C) M(SO) (D) M(SO)
[27%] 36. A 1.00 g pill contains morphine (M = 285.34), a monobasic compound whose conjugate acid has pK = 8.21, in addition to an unknown amount of inert material. To analyze the morphine content of the pill, it is dissolved in 50.0 mL 0.1000 M aqueous HCl and the unreacted acid in the resulting solution back-titrated with 0.1000 M NaOH. Which of the following statements about this experiment are correct?
I. If the pill contains only morphine, the titration will require 35.0 mL NaOH solution to reach the endpoint.
II. Methyl red, which changes color from red to yellow between pH = 4.4 and pH = 6.2, would be a suitable indicator for this titration.
(A) I only
(B) II only
(C) Both I and II
(D) Neither I nor II
Topic 7 - Redox/Electrochemistry
2016
[10%] 40. What is the standard reduction potential for Cr(aq) to Cr(s)?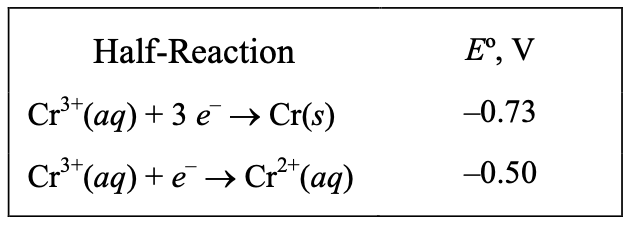
(A) –0.23 V (B) –0.85 V (C) –1.23 V (D) –1.69 V
[36%] 42. If water is electrolyzed for 2.0 hr with a current of 10.0 A, what volume of dry oxygen gas is collected at STP?
(A) 4.2L (B) 4.6L (C) 8.4L (D) 17L
2017
- Which graph represents the reduction potential of O (at 1 bar pressure and 25 C) as a function of pH?
O(g) + 4H(aq) + 4e → 2HO(l) E = 1.23 V
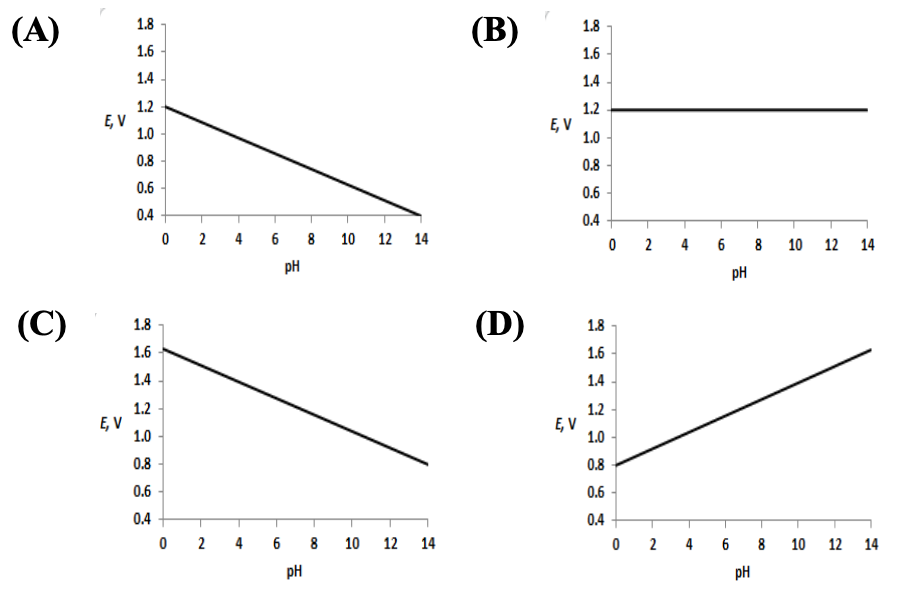
2018
[35%] 38. In the carbon monoxide complex Na[V(CO)], what is the oxidation number of vanadium?
(A) -1 (B) +3 (C) +5 (D) +6
[37%] 40. A 0.100-g sample of an alloy of copper and silver is dissolved in nitric acid to give a solution containing Cu and Ag ions. This mixture is electrolyzed exhaustively to redeposit all the metal ions as the elemental metals, requiring a current of 0.150 A for 1429 s. What is the mass percent of copper in the alloy?
(A) 20.0% (B) 58.3% (C) 70.6% (D) 77.2%
2019
[29%] 40. What is the standard reduction potential for the reduction of V(aq) to V(s)?
V(aq) + 3 e → V(s)
E = ???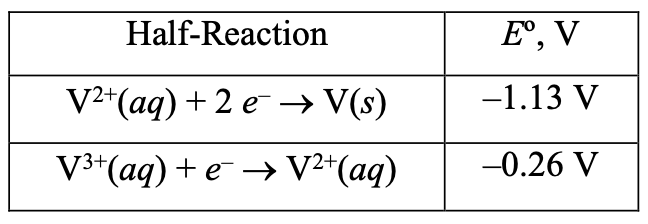
(A) –0.70 V (B) –0.84 V (C) –1.39 V (D) –1.65 V
[35%] 41. For the cell,
Ag(s) | Ag(NH)(aq, 0.010 M) | NH(aq, 0.40 M) || Ag(aq, 0.010 M) | Ag(s)
What is the cell potential? The K of Ag(NH) is 1.6×10.
(A) 0.12V (B) 0.38V (C) 0.40V (D) 0.44V
Topic 8 - Atomic Structures/Periodicity
2016
[27%] 43. Which graph best describes the radial wavefunction of a 2p orbital?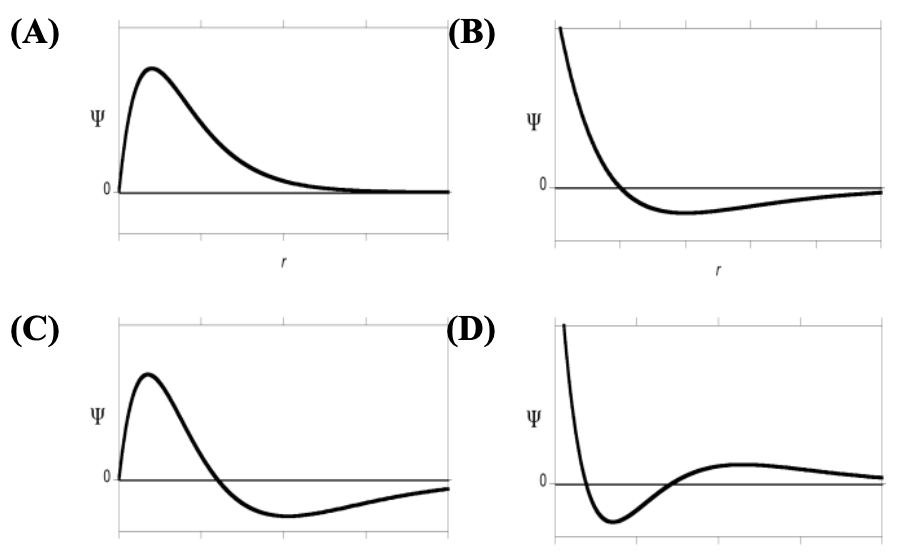
[30%] 46. Which elements are most similar in atomic size?
(A) H (Z = 1) and Li (Z = 3)
(B) C (Z = 6) and Si (Z = 14)
(C) Mn (Z = 25) and Tc (Z = 43)
(D) Zr (Z = 40) and Hf (Z = 72)
2017
- Rank the elements Si, P, Ge, and As in increasing order of their first ionization energies.
(A) Si < P < Ge < As
(B) As < Ge < P < Si
(C) Ge < Si < As < P
(D) Ge < As < Si < P
2018
[12%] 46. Atoms of which element release the most energy when an electron is added to them in the gas phase?
(A)C (B)O (C)Si (D)S
2019
[17%] 44. In which list are the ions ranked in order of increasing ionic radius?
(A) K
[28%] 48. Aluminum has a smaller first ionization energy than magnesium. Which is the best explanation for this observation?
(A) Al has an odd number of electrons, while Mg has an even number of electrons.
(B) Al has more valence electrons than Mg.
(C) The highest-energy electron in Al has less electron
density near the nucleus than the highest-energy electron in Mg.
(D) The highest-energy electron in Al is on average farther from the nucleus than the highest-energy electron in Mg.
Topic 9 - Molecular Structures/Bonding
2016
[24%] 53. How many stereoisomers of octahedral CoCl(NH)(CN) are possible?
(A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6
[18%] 54. What is the best description of the geometry of the nitrogen atoms in dimethylnitrosamine, (CH)NNO?
N bonded to CH groups N bonded to O Linear
(A) Trigonal planar linear
(B) Trigonal planar bent
(C) Trigonal pyramidal linear
(D) Trigonal pyramidal bent
2017
Which statement about the molecular orbitals in a molecule is correct?
(A) No molecular orbital may have a net overlap with any other molecular orbital.
(B) Each molecular orbital must have a different number of nodes than every other molecular orbital.
(C) The number of molecular orbitals is equal to half the number of atomic orbitals of the atoms that make up the molecule.
(D) The lowest-energy molecular orbitals are the most antibonding in character and the highest-energy molecular orbitals are the most bonding in character.Allene has the structure HC=C=CH. What is the best description of the geometry of allene?
Geometry at central carbon Positions of hydrogen atoms
(A) linear All in the same plane
(B) linear In two perpendicular planes
(C) bent All in the same plane
(D) bent In two perpendicular planes
2018
[27%] 53. What is the coordination geometry of cobalt in the complex ion [Co(HNCHCHNH)Br]?
(A) Tetrahedral
(B) Square planar
(C) Octahedral
(D) Trigonal prismatic
[11%] 54. Sulfur tetrafluoride adopts a see-saw geometry with two axial F atoms with a F–S–F angle of about 180 and two equatorial F atoms at about 90 from the axial fluorines. Which statement most accurately describes the axial and equatorial S–F bonds?
(A) The axial S–F bonds are longer because the two fluorines must share bonding to the same orbital on sulfur.
(B) The axial S–F bonds are longer because they experience greater repulsion from the other fluorine atoms in the molecule.
(C) The equatorial S–F bonds are longer because the equatorial F–S–F bond angle is the smallest in the molecule.
(D) The equatorial S–F bonds are longer because they experience greater repulsion from the lone pair on sulfur.
2019
[24%] 53. Which is the best depiction of the three-dimensional arrangement of the atoms in nitric acid, HNO?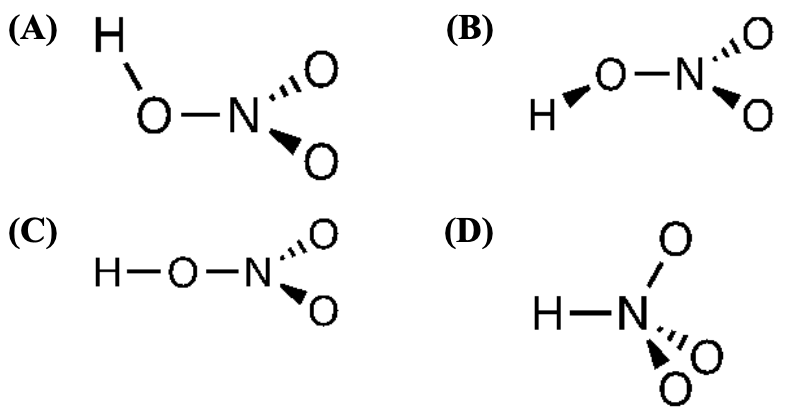
[25%] 54. Which of these is NOT a correct statement about the ferrioxalate ion, Fe(CO)?
(A) It is chiral.
(B) There are two different carbon-oxygen bond distances in the ion.
(C) There are two different iron-oxygen bond distances in the ion.
(D) There are six iron-oxygen bonds in the ion.
Topic 10 - Organic Chemistry/Biochemistry
2016
[24%] 56. Which alkyl halide reacts most rapidly with aqueous sodium hydroxide solution?
(A) CHCl
(B) CH3I
(C) (CH)CCHCl
(D) (CH)CCHI
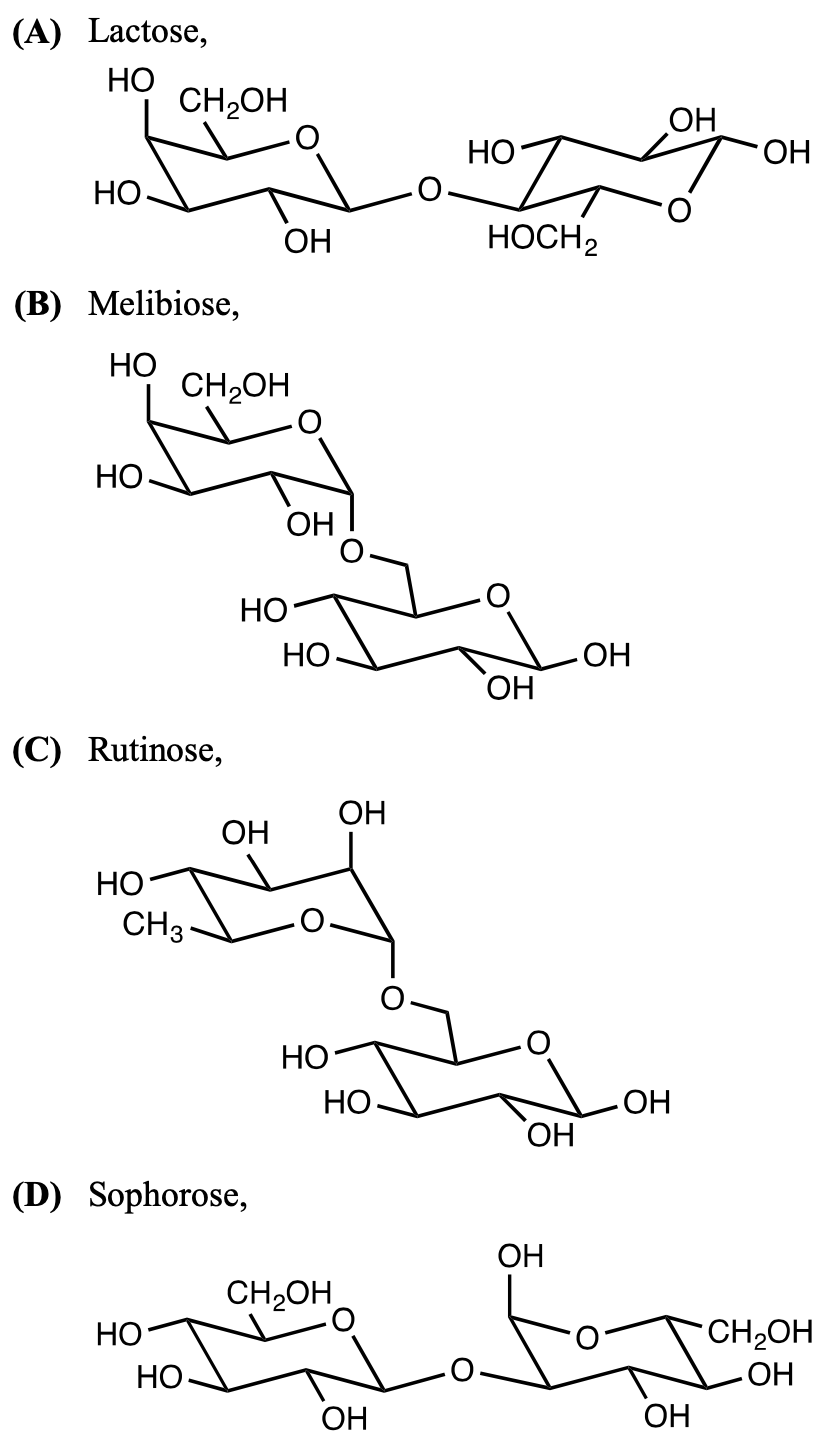
[21%] 60. Tollens’ reagent, basic diamminesilver(I) solution, gives a positive test (in the form of a silver mirror) in the presence of aldehydes. Which sugars give a positive Tollens’ test?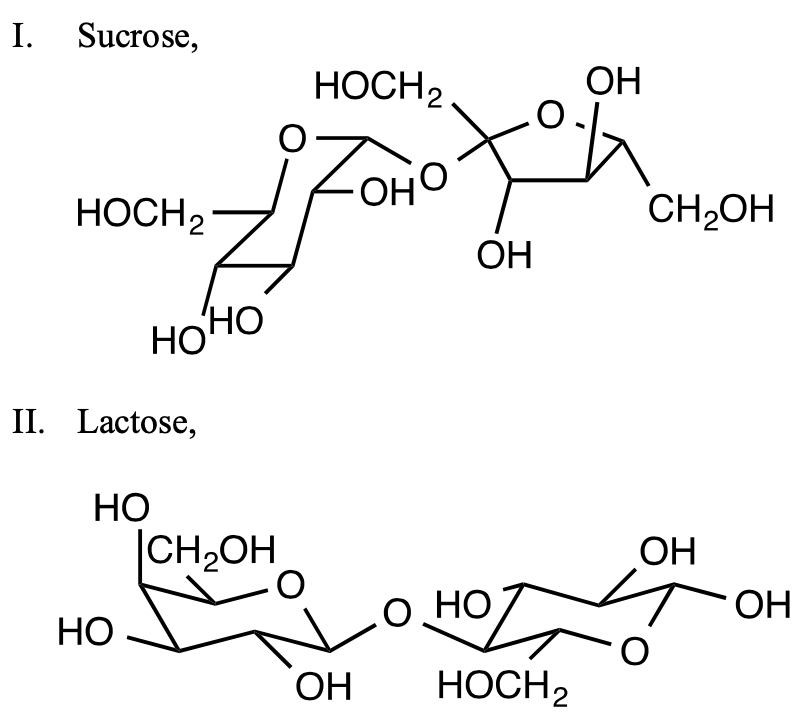
(A) I only (B) II only (C) Both I and II (D) Neither I nor II
2017
- Hydrolysis of which disaccharide with dilute acid gives only a single type of monosaccharide as a product
2018
[18%] 57. How many distinct acyclic compounds have the formula CH?
(A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 5 (D) 6
[26%] 58. When acetaldehyde (CHCHO) reacts in methanol (CHOH) solution under basic conditions, which compound is NOT formed?
(A) CHCH(OH)(OCH) (B) CHCH(OCH) (C) CHCH(OH)CHCHO (D) CHCH=CHCHO
2019
[33%] 56. How many distinct compounds of the formula CHCl can be formed by free radical chlorination of 2-methylbutane?
(A) 2 (B) 4 (C) 6 (D) 8
[14%] 58. Which C–H bond has the smallest bond dissociation enthalpy?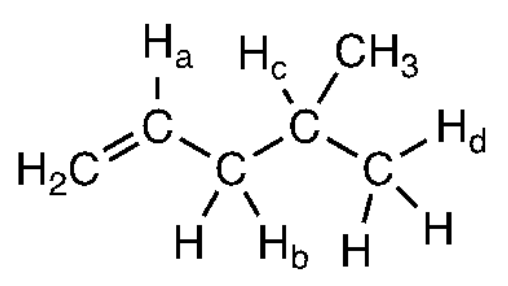
(A) C–H (B) C–H (C) C–H (D) C–H

