概述
相信大家在在各自的项目中都使用过@Value和@ConfigurationProperties两个注解,他们可以自动从我们的配置文件中获取配置信息,那他们之间有什么区别呢,我们该优先选择哪种方式来读取配置呢?
区别
两个注解的使用方式和源码解析可以参考下面的两个文章,本篇我们重点关注在他们的区别上。**@Value**的使用: 一文深入了解Spring中的@Value注解**@ConfigurationProperties**的使用: 一文深入了解ConfigurationProperties注解
| 比较项 | @Value | @ConfigurationProperties |
|---|---|---|
| 使用方式 | 需要一个个指定 | 能够批量地注入配置文件中的属性 |
| 所属框架 | Spring | Spring Boot |
| SPEL | 支持 | 不支持 |
| JSR303数据校验 | 不支持 | 支持 |
| 松散绑定 | 不支持 | 支持 |
| 复杂类型绑定 | 不支持 | 支持 |
使用方式
@Value需要在Bean的成员属性或者set方法上,逐个设置,和配置文件进行映射。@Value("${user.username}")@ConfigurationProperties可以在类上直接配置,属性会自动映射绑定。@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "bsfit.user")@Componentpublic class User {private String userName;private Integer age;
小结: 如果一个bean下的配置比较多的话,使用
@ConfigurationProperties比较方便。所属框架
@Value是spring框架的注解,在spring-beans这个工程中。@ConfigurationProperties注解是Spring Boot实现的一个注解,用于配置文件对对象属性的配置。SPEL
@Value是支持SPEL表达式的,如下:@Value("#{ T(java.lang.Math).random() * 100.0 }")private double randomNumber;
@ConfigurationProperties不支持SPEL表达式,验证方式如下:bsfit.user:user-name: ${person.last-name}age: #{5*2}
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "bsfit.user")@Componentpublic class User {private String userName;private Integer age;
输出结果如下,
@ConfigurationProperties无法执行SPEL表达式。
小结:@Value在取值方面更加强大,支持SPEL, 同时还能注入URL、文件等资源数据校验
@Value不支持数据校验@ConfigurationProperties支持数据校验,验证如下:bsfit.user:user-name: ${person.last-name}age: 500userId: E000001sex: boy
```java @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “bsfit.user”) @Component @ToString @Validated public class User {
private String userName;
@Max(value = 150, message = “最大值不能超过100岁”) @Min(value = 10, message = “最大值不能超过10岁”) private Integer age;
}
``
**启动报错如下:**<br />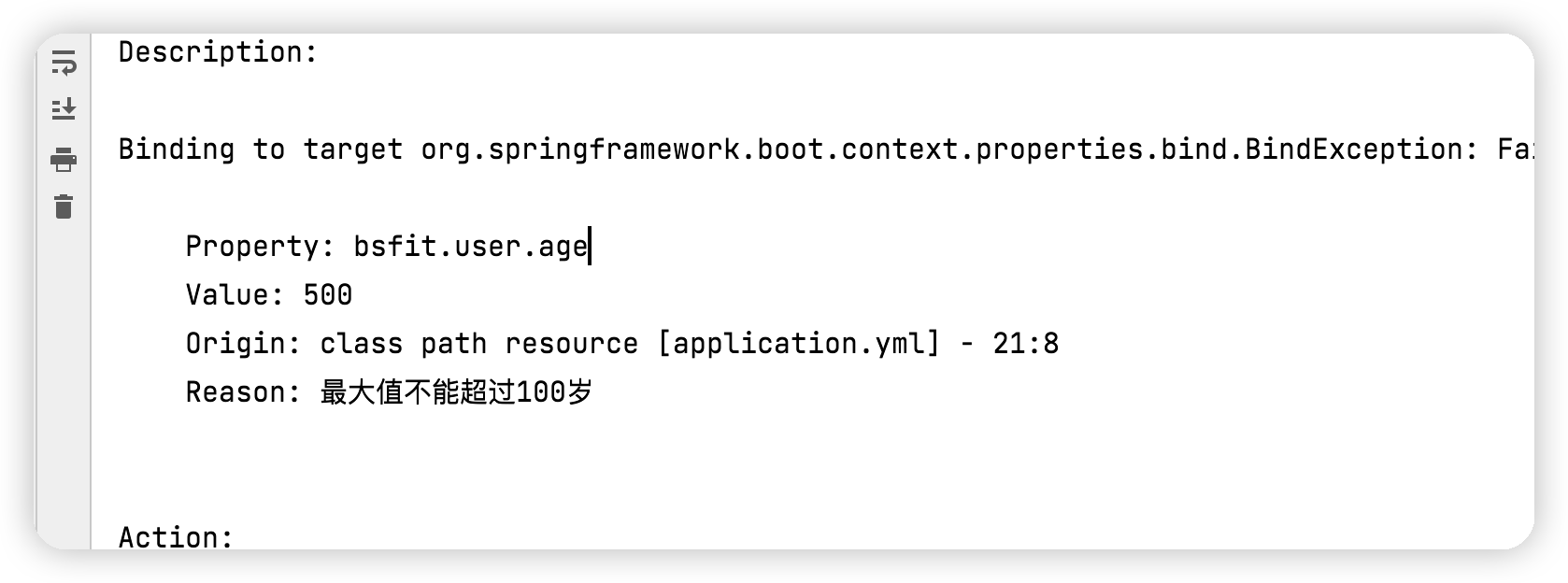<br />**小结:**数据校验可以用来校验注入的属性是否正确、符合规范。而@ConfigurationProperties`具备这样的能力。
松散绑定
松散绑定的意思就是一个属性在配置文件中可以有多个属性名,比如学生类当中的 firstName 属性,在配置文件中可以叫 firstName、first-name、first_name 以及 FIRST_NAME。
@Value不支持松散绑定

执行结果如下,未绑定配置中的值。
@ConfigurationProperties支持松散绑定
执行结果如下,绑定了配置中的值。
小结:@ConfigurationProperties在这方便宽泛,支持松散绑定,这样会导致有多个配置都满足情况,那么程序会取匹配到的第一个绑定到bean的属性上。
复杂类型绑定
复杂类型绑定是指绑定复杂的数据结果,比如List, Map, List对象等。
@Value不支持复杂类型的绑定
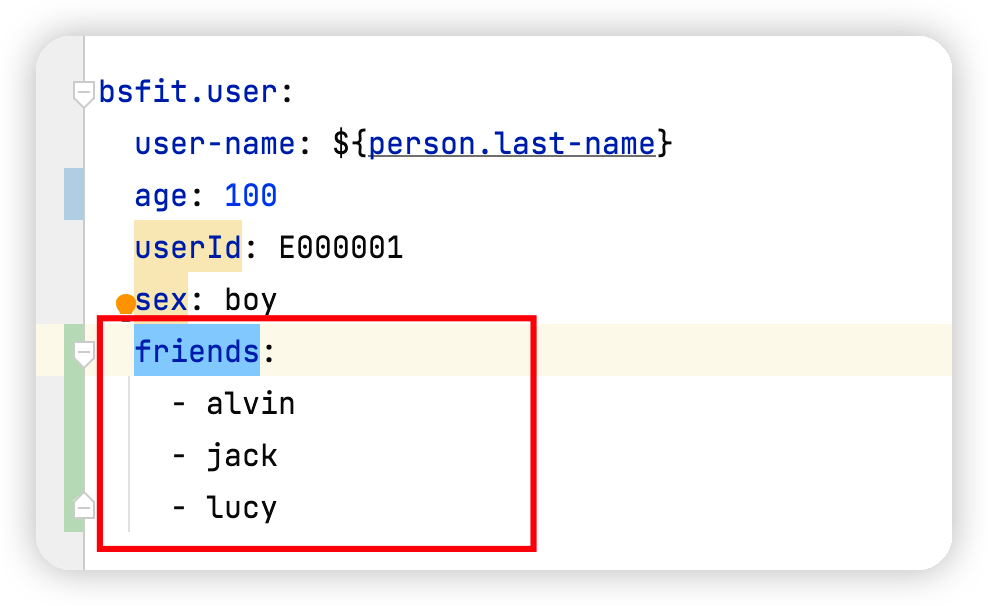

执行结果如下显示不支持复杂类型。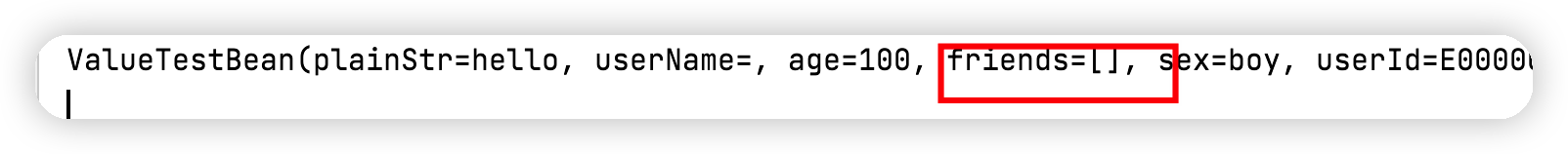
@ConfigurationProperties支持复杂类型
执行结果如下显示支持复杂类型。
小结:@ConfigurationProperties在对复杂类型的支持上比较强大,可以绑定List,Map等,而@Value不行。
总结
上面阐述了两者的区别,那我们该如何选择呢,什么情况下适用@Value,什么情况下用@ConfigurationProperties?
我的原则是尽量使用@ConfigurationProperties,特别是下面的情况:
- 如果Bean的属性超过2个,并且有可能被多个Bean注入使用,用
@ConfigurationProperties更加方便。 - 在微服务项目适用配置中心的情况下,尽量使用
@ConfigurationProperties,它可以直接动态更新配置。而@Value需要加上@RefreshScope注解。
当然,如果你只有一个配置注入或者需要用到SPEL,那么也可以用@Value注解。

