1 入门
作为构建软件组件和应用程序的编程语言,C#是更大、更复杂的执行平台——公共语言基础结构(Common Language Infrastructure,CLI)的一部分。
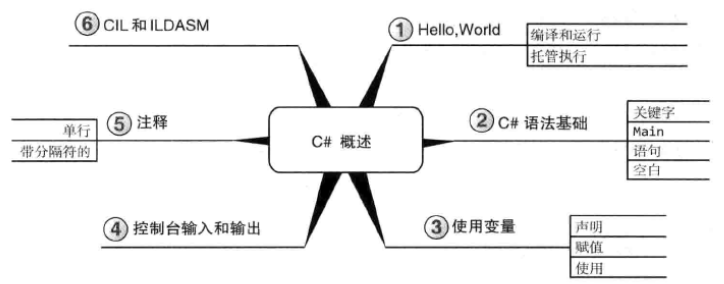
1.1 Hello,World
C#是区分大小写的语言。
class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Console.WriteLine("Hello World");}}
1.2 C#语法基础
1.2.1 C#关键字
1.2.2 标识符
C#用标识符编写代码的构造,应分配有意义的标识符。通常变量使用camelCase法,其他使用Pascal法。
规范要更注重标识符的清晰而不是简短、缩略。
1.2.3 类型定义
C#的所有代码都出现在一个类型定义的内部,最常见的类型定义是以关键字class开头的。类定义是class<标识符>{…}形式的一个代码块。
规范要用名词或名词短语命名类。
1.2.4 Main
将Main方法指定为static意味着这是静态方法,可用“类名.方法名”的形式调用它。如果不指定static,用于启动程序的命令控制台还要先对类进行实例化,然后才能调用方法。
1.2.5 语句和语句分隔符
1.2.6 空白
1.2.7 使用变量
class Program{static void Main(string[] args){string max;max = "Hello World";Console.WriteLine(max);}}
max为局部变量,变量一旦申明,数据类型就无法改变。声明变量=指定变量要包含的数据的类型+分配的标志符(变量名),局部变量名采用camel法命名。
1.2.8 数据类型
1.2.9 变量的赋值
局部变量声明后必须在引用之前为其赋值。
static void Main(string[] args){string valerie;string max = "Have fun storming the castle!";valerie = "Think it will work?";Console.WriteLine(max);Console.WriteLine(valerie);max = "It would take a miracle";Console.WriteLine(max);}
1.3 控制台输入和输出
1.3.1 从控制台获取输入
System.Console.ReadLine(),此方法的输出也称为返回值。
class Program{static void Main(string[] args){string firstName;string lastName;Console.WriteLine("Hey,Please input your firstname");firstName = Console.ReadLine();Console.WriteLine("Please input your lastname");lastName = Console.ReadLine();Console.WriteLine("Your name is {0}.{1}",firstName,lastName);}}
1.3.2 将输出写入控制台
System.Console.Write(),注意区别System.Console.WriteLine()之间的区别,前者不加换行符。
class Program{static void Main(string[] args){string firstName;string lastName;Console.Write("Hey,Please input your firstname:");firstName = Console.ReadLine();Console.Write("Please input your lastname:");lastName = Console.ReadLine();Console.WriteLine("Your name is {0}.{1}",firstName,lastName);}}
{0},{1}为索引占位符,索引值从零开始,每个要插入的参数,或者称为格式项(format item),按照与索引值对应的顺序排列在格式字符串之后。占位符可任意顺序出现也可以多次使用。每个占位符都必须对应一个参数,不能使用没有对应参数的占位符。占位符初次对应后,便无法更改对应项。
1.3.3 注释
规范不要使用注释,除非代码本身“一言难尽”;尽量编写清晰的代码
1.4 小结
2 数据类型
C#有几种非常简单的类型,被视为其他所有类型的基础。这些类型被称为预定义类型或基元类型。C#基元类型包含8种整数类型、2种二进制浮点类型、1种十进制浮点类型、1种布尔类型以及1种字符类型。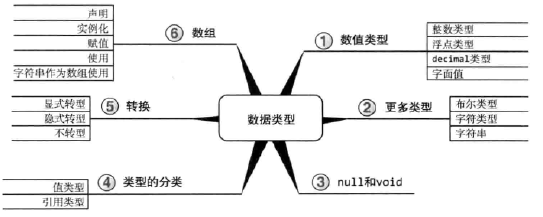
2.1 基本数值类型
2.1.1 整数类型

规范要在指定数据类型时使用C#关键字而不是BCL名称;保持一致性。
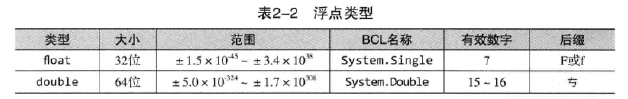
2.1.2 浮点类型
2.1.3 decimal类型

decimal类型保证了范围内所有十进制数都是精确的。注意,它表示的范围比浮点数小,转换时候要注意!
2.1.4 硬编码
字面值或字面量表示源代码中的固定值,直接将值放到源代码中称为硬解码。硬编码改变值,就需要重新编译代码。
默认情况,输入带小数点的字面值,编译器会自动把它解释为double类型,整数值(无小数点)通常默认为int/long。
每位十六进制数字都是4个位,所以一个字节可以表示两位十六进制数字。1Byte = 8bit = 两位16进制数字(十六进制四位一体)。
规范要使用大写的字面量后缀
class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Console.WriteLine(0x0064); //this display 100}}
将数格式化成十六进制:
方法1:使用x或X数值格式说明符,大小写决定了十六进制字母的大小写
class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Console.WriteLine("0x{0:X}",42);}}
方法2:使用convert类中Tostring方法转换
class Program{static void Main(string[] args){int x;x = 42;string y = Convert.ToString(x, 16);Console.WriteLine(y);}}
高级主题使用R格式说明符进行格式化
static void Main(string[] args){const double number = 1.618888888888887;double result;string text;text = string.Format("{0}", number);result = double.Parse(text);Console.WriteLine("{0}:result != number",result != number);text = string.Format("{0:R}", number); //Round-trip格式说明符返回的字符串//转换回数值肯定能获得原始值result = double.Parse(text);Console.WriteLine("{0}:result == number",result == number);}
2.2 更多基本类型
2.2.1 布尔类型
允许的值包括关键字true和false。
以不区分大小写的方式比较两个字符串:
class Program{static void Main(string[] args){string option;option = "/help";int comparison = string.Compare(option, "/help", true); //true表示不区分大小写Console.WriteLine(comparison);}}
2.2.2 字符类型
字符类型char 2个字节,16位,其取值范围对应于Unicode。Unicode是一个国际性标准,用来表示大多数语言中的字符,为不同的语言文化显示具有本地特色的字符。反斜杠和特殊字符代码统称为转义序列。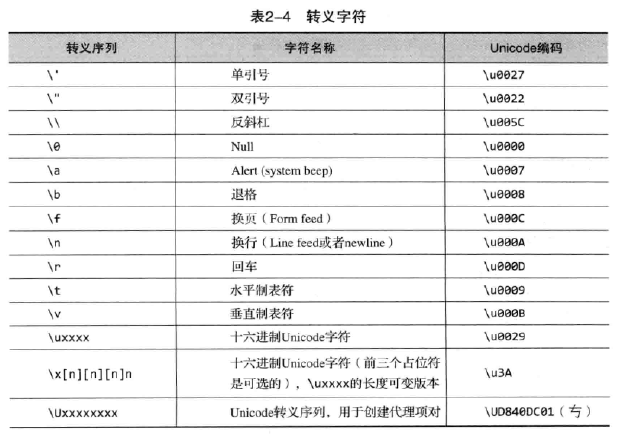
可以使用Unicode代码表示任何字符。前缀\u,可以使用十六进制计数法表示Unicode字符。
2.2.3 字符串
零或多个字符组成的有限序列称为字符串。
1.字面量
为了将字面量字符串输入代码,要将文本放入双引号”内。
class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Console.Write(" \"Truly,you have a dizzying intellect.\" ");\\ \"表示引号Console.Write("\n \"wait til r get going!\" \n"); \\ \n表示换行}}
在以@开头的字符串中,唯一支持的转义序列是””,它代表一个双引号,这个双引号不会终止字符串。
2.字符串方法
3.字符串长度
class Program{static void Main(string[] args){string palindRome;Console.WriteLine("Enter a palindrom:");palindRome = Console.ReadLine();Console.WriteLine("The palindrome,\"{0}\" is {1} characters.",palindRome,palindRome.Length);}}
4.大小写转换
字符串是不可变的(immutable),无法修改字符串内容,只能新建。
class Program{static void Main(string[] args){string okay,upper;okay = Console.ReadLine();upper = okay.ToUpper(); //返回大写字体 ToLower返回小写字体Console.WriteLine(upper);}}
2.3 null和void
与类型有关的两个额外关键字是null和void。null值表明变量不引用任何有效的对象。void表示没有类型或没有任何值。
null表示将变量设为“无”。null值只能赋值给引用类型、指针类型、和可空值类型。将变量设为null,会显式地设置引用,使他不指向任何位置。
区分null和“”的区别
2.4 类型的分类
所有类型都可以划分为值类型和引用类型。两者区别在于复制方式:值类型的数据总是进行值复制,而引用类型的数据总是进行引用复制。
2.4.1 值类型
2.4.3 引用类型
小孩牵气球,引用类型的变量存储的是对数据存储位置的引用,指向的内存区域是堆heap。
不同使用场景如果对象在逻辑上是固定大小的不可变值,考虑定义为值类型;逻辑上可引用可变的对象,定义为引用类型。
2.5 可空修饰符
单个?是可空,使用方法int? count = null;将null赋给值类型,这在数据库编程中尤为有用。
2.6 数据类型之间的转换
会造成转换的最常见操作就说转型或者强制类型转换casting。有可能造成大小变小或者引发异常(因为转换失败)的任何转换都需要执行显示转型explicit cast。相反,不会变小,而且不会引发异常(无论操作数的类型是什么)的任何转换都属于隐式转型implicit cast。
2.6.1 显示转型
在C#中,可以使用转型操作符执行转型。这操作有时候只是程序员的“一厢情愿”,执行显示转换时,如果数据未转换成功,“运行时”可能引发异常。
高级主题checked和unchecked转换
溢出检测:
static void Main(string[] args){checked{int elegant = int.MaxValue;int okay = elegant + 1;Console.WriteLine(okay);}}
2.6.2 隐式转型
2.6.3 不使用转型操作符的类型转换
由于没有定义从字符串到数值类型的转换。
解决办法1:使用Parse()方法将一个string转换为数值数据类型高级主题TryParse()方法,在转换失败不会引发异常,而是返回false。
解决办法2:使用convert类进行转换(局限性: 只支持预定义类型,而且是不可扩展的。优点:允许从任何基元类型转换到其他基元类型)。
Parse()
class Program{static void Main(string[] args){string elegant = "235654";int okay = int.Parse(elegant);Console.WriteLine(okay);}}
TryParse()代替无效转型异常,无效会返回false,有效返回true
class Program{static void Main(string[] args){string elegant = "235654";int okay;Console.WriteLine(int.TryParse(elegant, out okay));Console.WriteLine(okay);}}
Convert使用(数值转字符串,不同进制显示)
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int elegant = 200;
string okay = Convert.ToString(elegant, 2);
Console.WriteLine("100 Bin is {0}",okay);
string okayTwo = Convert.ToString(elegant, 16);
Console.WriteLine("100 hex is {0}",okayTwo);
Console.WriteLine("100 hex is 0x{0:X}",elegant);
}
}
2.7 数组
利用数组声明,可以在单个变量中存储同一种类型的多个数据项,而且可以利用索引来单独访问这些数据项。C#中的数组是基于零的。目前,在存储数据集合时,大多数程序使用的都是泛型集合类型而不是数组。
2.7.1 数组的声明
C#中,方括号声明数组变量。 类型[] 变量名;[,]二维数组
2.7.2 数组的实例化和赋值
几种赋值情况:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//firt method
string[] elegant = { "C#", "LabVIEW", };
//second method
string[] okay;
okay = new string[]{"C#","LabVIEW",};
string[] elegantTwo = new string[3] { "C#", "LabVIEW", "Matlab" }; //创建实例这里是数组长度!!!
Console.WriteLine(elegantTwo[2]);
string[] okayTwo = new string[2];
}
}
2.7.3 数组的使用
Example1:交换数组中不同位置的数据:打印数组所有元素目前只会用遍历法打印。
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//firt method
string[] elegant = { "C#", "LabVIEW", };
string okay = elegant[0];
elegant[0] = elegant[1];
elegant[1] = okay;
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(elegant[i]);
}
}
}
Notes访问超过数组的边界会引发异常
小技巧比较好的做法是使用Length-1代替硬编码的数组大小
Example2L:More Method to operate array
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string[] elegant = new string[] { "LabVIEW","C#", "Matlab", };
Array.Sort(elegant); //数组排序
for (int i = 0; i < elegant.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(elegant[i]);
}
string searchString = "C#";
int index = Array.BinarySearch(elegant, searchString); //根据元素名搜索数组索引值
Console.WriteLine("The wave of the future,{0} ,is at index {1}.",searchString,index);
Console.WriteLine("========================");
Array.Reverse(elegant); //数组反转
for (int i = 0; i < elegant.Length; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(elegant[i]);
}
Console.WriteLine("========================");
Console.WriteLine("this is the last array {0}",elegant[elegant.Length-1]);
}
}
2.7.4 字符串作为数组使用
访问string类型的变量类似于访问字符数组。例如,可调用elegant[3]获取名为elegant的string的第四个字符。但不允许给特定字符赋值,基元类型不可更改。
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string elegant = "Mr.elegant";
Console.WriteLine(elegant[1]); //showdialog 1
}
}
反转字符串:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string elegant, okay;
char[] temp;
Console.Write("Enter string:");
okay = Console.ReadLine();
elegant = okay.Replace(" ", ""); //字符串替代
elegant = elegant.ToLower(); //转换成小写
temp = elegant.ToCharArray(); //字符串变成字符数组
Array.Reverse(temp); //反转字符
Console.WriteLine(temp);
Array.Reverse(temp);
if (elegant == new string(temp))
{
Console.WriteLine("ok");
}
else
Console.WriteLine("NO");
}
2.7.5 常见数组错误
2.8 小结
C#与众不同的是使用@作为字符串逐字前缀字符,它强迫字符串忽略转义字符。C#中的string数据类型是不可以变的。
3 操作符和控制流
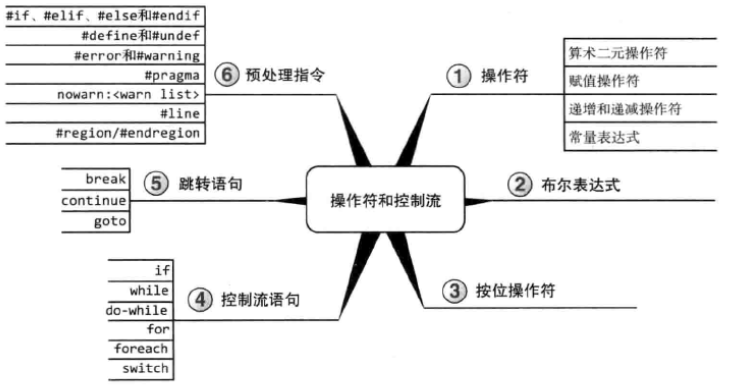
3.1 操作符
操作符对一系列称为操作数operand的值(或变量)执行数学或逻辑运算/操作来生成新值(称为结果)。
3.1.1 一元操作符 + -
3.1.2 二元算术操作符

Example1 加法操作符用于字符串拼接:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string elegant;
elegant = "Mr.Elegant";
Console.WriteLine("{0}"+" is elegant",elegant);
}
}
Example2 将加法操作符应用于char数据类型
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int elegant = '3' + '4'; //字符有Unicode值,
//ASCII码和Unicode以及UTF-8编码原理查阅计算机基础篇
char okay = (char)elegant;
Console.WriteLine(elegant);
Console.WriteLine(okay);
}
}
Example3 判断两个字符之间的“距离”
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int distance = 'z' - 'a';
Console.WriteLine(distance);
}
}
3.1.3 复合赋值操作符
+= ++ —(自增自减,直接看谁离等号近就先进行什么操作)
Example1 降序显示每个字母的ASCII值
static void Main(string[] args)
{
char current;
int unicodeValue;
current = 'z';
do
{
unicodeValue = current;
Console.WriteLine("\"{0}\"",unicodeValue);
current--;
} while (current>='a');
}
高级主题线程安全的递增和递减:两者执行的都不是原子级别的运算,在操作符执行期间,可能发生线程上下文切换,可能造成竞争条件,可以用lock语句来防止出现竞争条件。System.Threading.Interlocked类提供的线程安全方法Increment()和Decrement()。
3.1.4 常量表达式和常量符号
const关键字的作用就是声明常量符号。
规范不要使用常量表示将来可能改变的任何值。
3.2 控制流程序概述
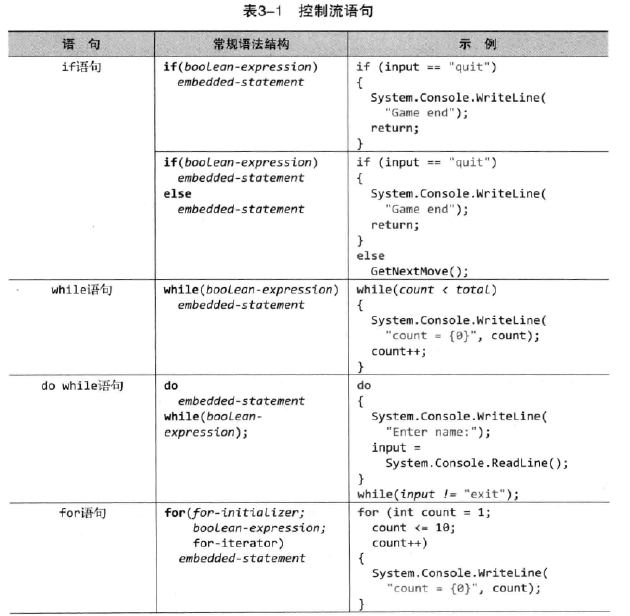
3.2.1 If语句
if/else连贯格式化,多用此种格式来书写代码。
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int input;
Console.Write("What is the maximum number" + "of turns in tic-tac-toe?" + "(Enter 0 to exit.):");
input = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
if(input == 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("Exit....");
}
else if(input<9)
{
Console.WriteLine("Maximum number has more than {0}",input);
}
else if(input>9)
{
Console.WriteLine("Maximum number has less than {0}",input);
}
else
Console.WriteLine("Congrutulations! You are right");
}
}
3.3 代码块
规范避免在If语句中省略大括号,除非只有一行语句.
高级主题数学常量 System.Math.PI或者System.Math.E
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
double raduis;
double areas;
Console.Write("Please input a raduis to calculate circle areas,your input raduis:");
raduis = double.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
if(raduis>=0)
{
areas = Math.PI * raduis * raduis;
Console.WriteLine(areas);
}
else
Console.WriteLine("Your input is invalid.");
}
}
3.4 代码块、作用域和声明空间
代码块经常被称为作用域。
代码块不仅定义了作用域,还定义了局部变量声明空间。C#编译器禁止一个代码块中声明(或作为参数声明)的局部变量在其子代码块中重复声明。
3.5 布尔表达式
if语句中包含在圆括号内的部分是布尔表达式boolean expression,称为条件。
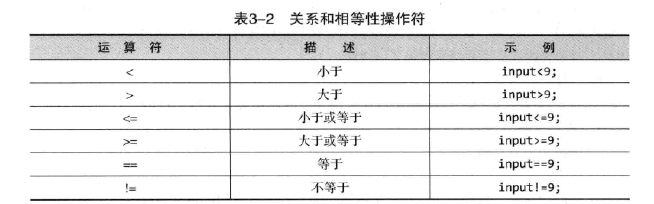
3.5.1 关系操作符和相等操作符
3.5.2 逻辑布尔操作符
可用逻辑操作符合并多个布尔表达式来构成更复杂的布尔表达式。
|、||、&、&&和^,C#操作符是从左向右求值的
OR操作符(||)其中任何一个为True,就返回true
ADN操作符(&&) 都T才为T,任何为F则为F
XOR操作符(^) 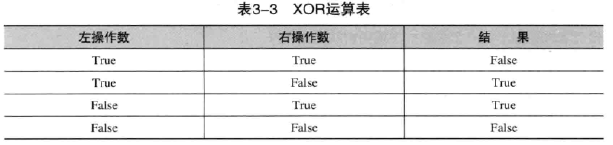
3.5.3 逻辑求反操作符
3.5.4 条件操作符
可用条件操作符取代if-else语句来选择两个值中的一个。
格式 condition?consequence:alternative C#中唯一的三元操作符。和If语句不同,条件操作符的结果必须赋给某个变量(或者作为参数传递),它不能单独作为一个语句使用。条件操作符consequence和alternative表达式类型需要一致。
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int elegant;
elegant = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
int okay;
okay = (elegant == 1) ? 1 : 2;
Console.WriteLine(okay);
}
规范考虑使用if/else语句,而不是使用过于复杂的条件表达式。
3.5.5 空结合操作符
Null coalescing operator ??如果这个值为空,就使用另一个值。形式:expression1 ?? expression2;,此操作符支持短路求值,如果expression1不为null则返回表达式1的值。
3.6 按位操作符
3.6.1 移位操作符(算术移位)
移位操作符的优先级低于算术操作符!
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int x;
x = (-7>>2);
Console.WriteLine(x);
}
向左移位两位calculate演示: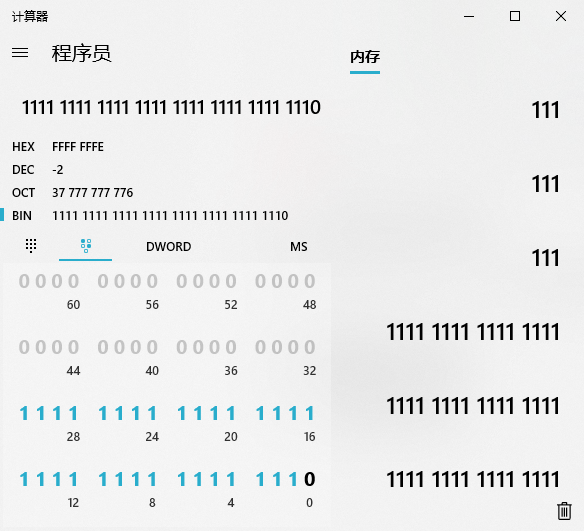
3.6.2 按位操作符(逻辑移位)
3.6.3 按位赋值操作符 &= |= ^=
3.6.4 按位取反操作符 ~
3.7 控制流语句(续)
3.7.1 while和do/while
do/while与while非常相似,只是它最适合需要循环1-n次情况。最典型的应用就是反复提示用户输入。
do
statement
while(condition);
3.7.2 For
3.7.3 foreach
foreach,遍历数据项集合。设置循环变量来依次表示其中每一项。特点:每一项只被遍历依次,不会像其他循环那样出现计数错误,也不可能越过集合边界。
形式:foreach(type variable in collection)
statement
解释:type 代表collection中每一项的variable声明数据类型,建议写为var;
variable是只读变量,foreach循环自动将collection中的下一项赋给它,作用域限于循环主体;
collection是代表多个数据项的表达式,如数组;
statement循环主体。
static void Main(string[] args)
{
char[] cells = new char[9] { '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9' };
Console.Write("The available moves are as follow:");
foreach (var value in cells)
{
if(value !='0'&&value!='X')
{
Console.WriteLine(value);
}
}
}
foreach循环期间禁止修改循环变量(上述程序value)
3.7.4 switch
switch(expression)
{
case constant;
statement
default:
statements
}
3.8 跳转语句
3.8.1 break
3.8.2 continue
通常可以用if语句替代
Example 判断电子邮件地址的域名部分
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string email;
bool insideDomain = false;
Console.WriteLine("Enter an email address:");
email = Console.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine("The email domain is: ");
foreach(var letter in email)
{
if(insideDomain)
{
Console.Write(letter);
Console.WriteLine("=======");
}
else
{
if(letter == '@')
{
insideDomain = true;
}
}
}
}
3.8.3 goto语句
3.9 C#预处理指令
3.9.1 排除和包含代码
处理不同平台、不同版本的CLI、调试(用#if DEBUG指令将调试代码包围起来,大部分IDE都能在发布版中移除这些代码)
#if CSHAP2
xxxx
#endif
3.9.2 生成错误和警告
warning 定义警告,提醒开发者任务尚未完结的好帮手。
关闭警告消息 # pragma warning disable 1030
还原警告 #pragma warning restore 1020
3.10 小结
独立编写井字棋程序来巩固1-3章所学内容。
#define CSHAP2
#pragma warning disable 1030
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Elegant
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] playerPositions = { 0, 0 }; //store player location
int currentPlayer = 1;
int winner = 0;
string input = null;
for (int turn = 1; turn < 11; ++turn)
{
DisplayBoard(playerPositions);
if (EndGame(winner, turn, input))
{
break;
}
input = NextMove(playerPositions, currentPlayer);
winner = DetermineWinner(playerPositions);
currentPlayer = (currentPlayer == 2) ? 1 : 2;
}
}
private static string NextMove(int[] playerPositions, int currentPlayer)
{
string input;
bool validMove;
do
{
Console.Write("\nPlayer {0} - Enter move:", currentPlayer);
input = Console.ReadLine();
validMove = ValidateAndMove(playerPositions, currentPlayer, input);
} while (!validMove);
return input;
}
static bool EndGame(int winner, int turn, string input)
{
bool endGame = false;
if (winner > 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("\nPlayer {0} has won!!!!!", winner);
endGame = true;
}
else if (turn == 10)
{
Console.WriteLine("\nThe game was a tie!");
endGame = true;
}
else if (input == "" || input == "quit")
{
Console.WriteLine("The last player quit");
endGame = true;
}
return endGame;
}
static int DetermineWinner(int[] playerPositions)
{
int winner = 0;
int[] winningMasks = { 7, 56, 448, 73, 146, 292, 84, 273 };
foreach (int mask in winningMasks)
{
if ((mask & playerPositions[0]) == mask)
{
winner = 1;
break;
}
else if ((mask & playerPositions[1]) == mask)
{
winner = 2;
break;
}
}
return winner;
}
static bool ValidateAndMove(int[] playerPositions, int currentPlayer, string input)
{
bool valid = false;
switch (input)
{
case "1":
case "2":
case "3":
case "4":
case "5":
case "6":
case "7":
case "8":
case "9":
#warning "Same move allowed multiple times."
int shifter;
int position;
shifter = int.Parse(input) - 1;
position = 1 << shifter;
playerPositions[currentPlayer - 1] |= position;
valid = true;
break;
case "":
case "quit":
valid = true;
break;
default:
Console.WriteLine("\nError: Enter a value from 1-9." + "Push Enter to quit");
break;
}
return valid;
}
static void DisplayBoard(int[] playerPositions)
{
string[] borders = { "|", "|", "\n---+---+---\n", "|", "|", "\n---+---+---\n", "|","|" ,"" };
int border = 0;
#if CSHARP2
System.Console.Clear();
#endif
for (int position = 1; position <= 256; position <<= 1, border++)
{
char token = CalculateToken(playerPositions, position);
Console.Write("{0} {1}", token, borders[border]);
}
}
static char CalculateToken(int[] playerPositions, int position)
{
char[] players = { 'X', 'O' };
char token;
if ((position & playerPositions[0]) == position)
{
token = players[0];
}
else if ((position & playerPositions[1]) == position)
{
token = players[1];
}
else
{
token = ' ';
}
return token;
}
#line 113 "TicTacToe.cs"
#line default
}
}
namespace MrElegant
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] playPositions = { 0, 0 }; //
DisplayBoard(playPositions);
}
static void DisplayBoard(int[] playPositions)
{
string[] boards = { "|", "|","\n-+-+-\n","|","|","\n-+-+-\n","|","|","\n"}; //棋盘初始构造
int board = 0;
for (int position = 1;position <=256; position<<=1, board++)
{
char token = CalculateToken(playPositions,position);
Console.Write("{0}{1}",token,boards[board]);
}
}
static char CalculateToken(int[] playPositions,int position)
{
char[] players = { 'X', 'O' }; //选手与符号进行绑定 选手1 X 选手2 O
char token;
if ((position & playPositions[0]) == position)
{
token = players[0];
}
else if ((position & playPositions[1]) == position)
{
token = players[1];
}
else
token = ' ';
return token;
}
}
}
4 方法和参数
单元化、结构化、模块化。
方法的定义、调用,递归、方法的重载、可选参数和命名参数。特殊的C#语法(ref和out)让参数向方法传递变量而不是值。
4.1 方法的调用
方法Method组合一系列语句以执行特定操作或计算特定结果。它能够为构成程序的语句提供更好的结构和组织。
方法总是和类型(通常是类)相关联。类型将相关的方法分为一组。
方法通过实参接收数据,实参由方法的参数或形参定义。参数是调用者用于向被调用的方法传递数据的变量。下面代码中files和lineCount为传递给CoutLines和DisplayLineCount的实参。
规范要为方法名使用动词或动词短语。
class LineCount
{
static void main()
{
int lineCount;
string files;
DisplayHelpText();
files = GetFiles();
lineCount = Countline(files);
DisplayLineCount(lineCount);
}
}
一个简单的主法调用
class Elegant
{
static void main()
{
string firstName;
string lastName;
System.Console.Writeline("Hey you");
// System是名称空间 Console是类型名称 Writeline是方法名 “Hey you”是实参。
}
}
4.1.1 命名空间
命名空间主要用于按照功能领域组织类型。命名空间有助于防止类型名称发生冲突。
规范要为命名空间使用Pascal大小写风格;考虑将源代码的文件目录结构组织成与命名空间的层次结构相匹配的形式。
4.1.2 类型名称
4.1.3 作用域
4.1.4 方法名称
方法名称可以用、也可以不用命名空间和类型名称加以限定。在方法名称之后是圆括号中的实参列表,每个实参以逗号分隔,对于声明方法时指定的形参。
4.1.5 形参和实参
方法可接收任意数量的形参,每个形参都具有特定的数据类型。调用者为形参提供的值称为实参;每一个实参都要和一个形参对应。
4.1.6 方法的返回值
可以将方法的返回值作为另一个方法的实参使用。
class Program
{
static void main()
{
System.Console.Write("Enter your first name:");
System.Console.WriteLine("Hello {0}!",System.Console.ReadLine());
}
}
4.1.7 语句与方法调用的比较
语句通常包含一个或多个表达式,每个表达式都是方法调用。所以,方法调用构成了语句的不同部分。
虽然一个语句中包含多个方法调用能减少代码量,但不一定能增强可读性,而且很少能带来性能上的优势。
4.2 方法的声明
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string firstName;
string lastName;
string fullName;
Console.WriteLine("Hey you!");
firstName = GetUserInput("Enter your first name:");
lastName = GetUserInput("Enter your last name:");
fullName = GetFullName(firstName, lastName);
DisplayGreeting(fullName);
}
static string GetUserInput(string prompt)
{
System.Console.Write(prompt);
return System.Console.ReadLine();
}
static string GetFullName(string firstName,string lastName)
{
return firstName + "." + lastName;
}
static void DisplayGreeting(string name)
{
Console.WriteLine("Your full name is {0}.",name);
return;
}
}
用方法进行重构,将一组相关语句转移到一个方法中,而不是把他们留在一个较大的方法中,这是重构的一种形式。重构有助于减少代码重复,有助于增强可读性。
4.2.1 形式参数声明
参数名采用的是camel大小写风格。不能在方法中声明与参数同名的局部变量。
4.2.4 方法返回类型声明
虽然方法可以指定多个参数,但返回类型只能有一个。具有返回类型的方法几乎总是包含一个或多个return语句。
4.3 Using指令
在程序头写using指令,避免完全限定名。
高级主题嵌套的using指令,可以在命名空间的顶部添加using指令。
namespace EssentialCSharp
{
using System;
class HelloWorld
{
.......
}
}
可以使用别名 using CountDownTimer = System.Timers.Timer;
4.4 Main()方法的返回值和参数
4.5 方法的参数
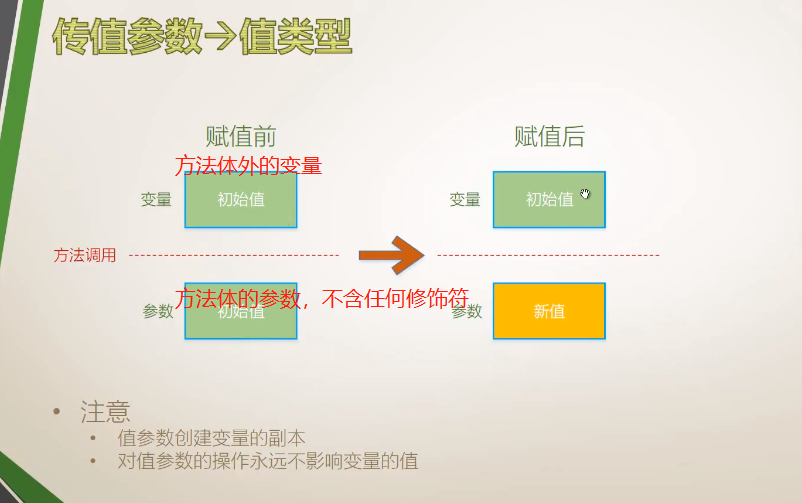
4.5.1 值参数
传值参数—值类型
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu = new Student();
int y = 100;
stu.AddOne(y); //不会影响方法体外的参数,操作的只是副本,x为传值参数
Console.WriteLine(y);
}
}
class Student
{
public void AddOne(int x) //值类型的传值参数 //实例方法
{
x = x + 1;
Console.WriteLine(x);
}
}
传值参数—引用类型
值类型—引用类型:值类型和引用类型详解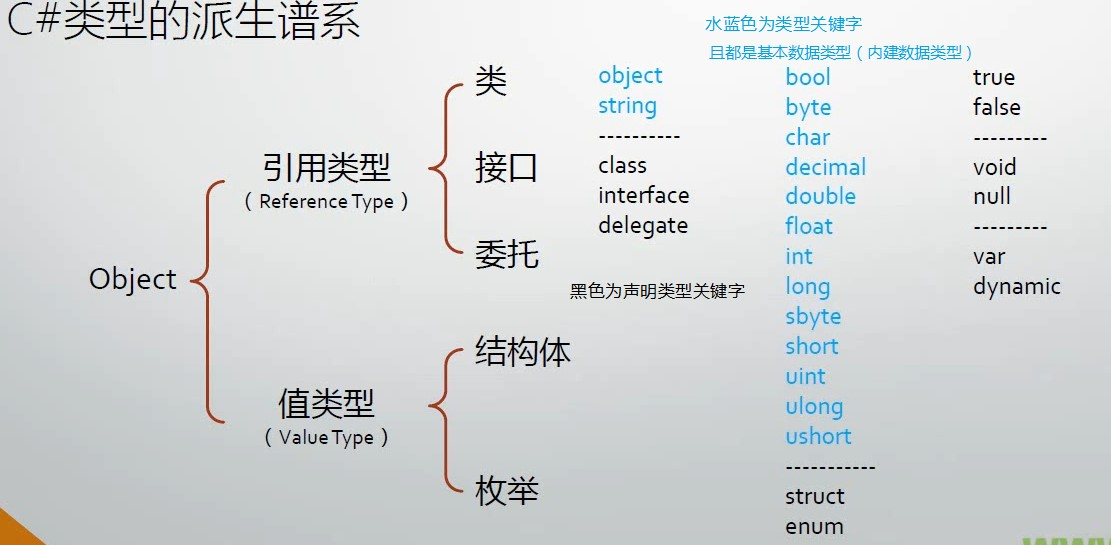

创建对象的情况:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student oldStu = new Student() { Name = "Mr.Elegant" };
Console.WriteLine("{0},{1}", oldStu.GetHashCode(), oldStu.Name);
SomeMethod(oldStu);//传递mr.elegant值给stu,但在方法中值又被新建的值给替换了
}
static void SomeMethod(Student stu) //静态方法(引用类型 传值参数)
{
stu = new Student() { Name = "Tom" };//新建了一个链接,链接到了Tom;//实际工作当作没有太大意义,相当于传递进来的oldStu值没有被它链接
Console.WriteLine("{0},{1}",stu.GetHashCode(),stu.Name);
}
}
class Student
{
public string Name { get; set; } //实例属性,无static,隶属于实例
}
不创建新实例,直接修改原始引用地址中的值,调用此方法后,引用地址的值会进行变更。
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student oldStu = new Student();
oldStu.Name = "Mr.elegant";
Console.WriteLine("HashCode = {0},Name={1}", oldStu.GetHashCode(), oldStu.Name);
SomeMethod(oldStu);
Console.WriteLine("HashCode = {0},Name={1}", oldStu.GetHashCode(), oldStu.Name);
}
static void SomeMethod(Student stu) //静态方法(引用类型 传值参数)
{
stu.Name = "Tom";//副作用,side-effect
Console.WriteLine("HashCode = {0},Name={1}",stu.GetHashCode(),stu.Name);
}
}
class Student
{
public string Name { get; set; } //实例属性,无static,隶属于实例
}
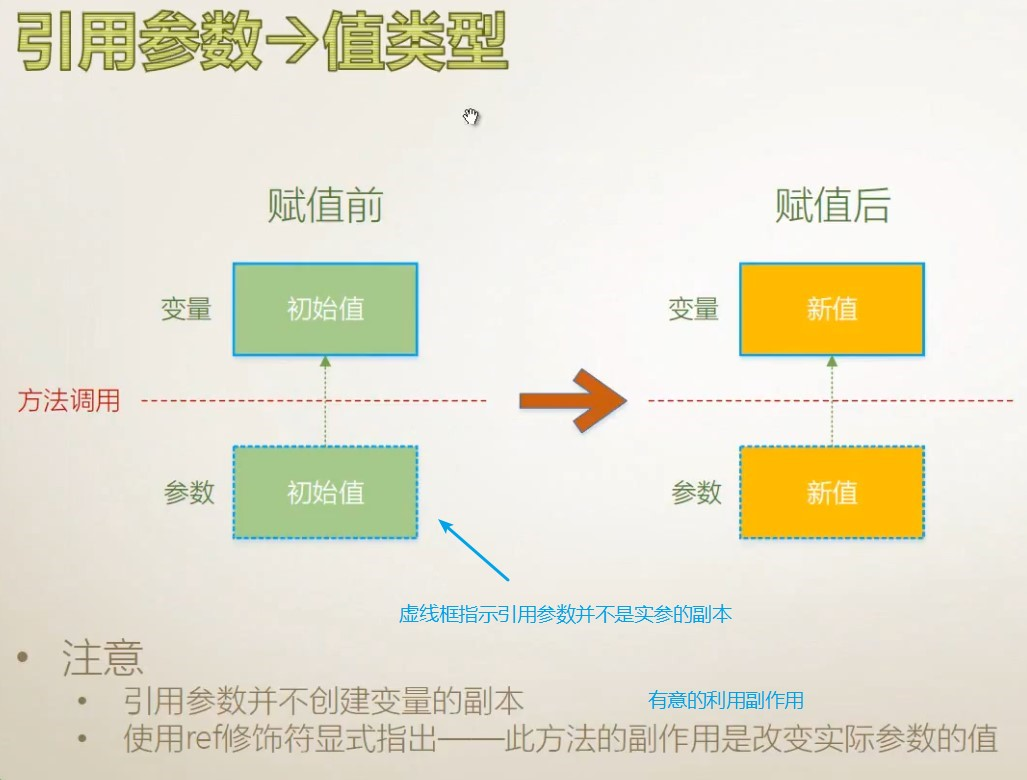
4.5.2 引用参数ref
引用参数—值类型 直接指向传进来的存储位置
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int y = 1;
IWantSideEffect(ref y);//引用参数直接修改原数据的内存地址的值
Console.WriteLine(y);
}
static void IWantSideEffect(ref int x) //值类型的引用参数
{
x = x + 100;
}
}
class Student
{
public string Name { get; set; } //实例属性,无static,隶属于实例
}
引用参数—引用类型,创建新对象

未调用则不生效,在方法调用之前,都new了一个新的实例,变量指向class student的引用地址,地址里面存放的是mr.elegant。方法也new了一个新的实例,引用参数也指向class student的引用地址,地址里面存放的是mr.elegant.
调用后方法创建新的实例,存放的数据变更为tom,变量再次通过引用地址获取到的数据则是tom,即变更后的实例的地址的数据。
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student oldStu = new Student() { Name = "Mr.elegant" };
// IWantSideEffect(ref oldStu);
Console.WriteLine(oldStu.Name);
}
static void IWantSideEffect(ref Student stu) //引用类型的引用参数
{
stu = new Student() { Name = "tom" };
Console.WriteLine("HasCode is {0},{1}",stu.GetHashCode(),stu.Name);
}
}
class Student
{
public string Name { get; set; } //实例属性,无static,隶属于实例
}
操作同一个对象:
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu1 = new Student() { Name = "Mr.elegant" };
Console.WriteLine("HasCode is {0},{1}", stu1.GetHashCode(), stu1.Name);
SomeSideEffect(ref stu1);
Console.WriteLine("HasCode is {0},{1}", stu1.GetHashCode(), stu1.Name);
}
static void SomeSideEffect(ref Student stu) //引用类型的引用参数
{
stu.Name = "Tom";
Console.WriteLine("HasCode is {0},{1}",stu.GetHashCode(),stu.Name);
}
}
class Student
{
public string Name { get; set; } //实例属性,无static,隶属于实例
}
4.5.3 输出参数 out(可替代)
输出参数—值类型
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Please input first number:");
string arg1 = Console.ReadLine();
double x = 0;
bool b1 = double.TryParse(arg1, out x); //tryparse方法将字符串转换成等效的双精度浮点数
if (b1==false)
{
Console.WriteLine("input error!");
return;
}
Console.WriteLine("Please input second number:");
string arg2 = Console.ReadLine();
double y = 0;
bool b2 = double.TryParse(arg2, out y);
if (b2==false)
{
Console.WriteLine("input error!");
return;
}
Console.WriteLine(x+y);
}
自写tryparse方法
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
double x = 0;
DoubleParser.Tryparse("789",out x);
Console.WriteLine(x+1);
}
}
class DoubleParser
{
public static bool Tryparse(string arg, out double result)
{
try
{
result = double.Parse(arg);
return true;
}
catch //抓住所有异常
{
result = 0;
return false;
}
}
输出参数—引用类型
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu = new Student();
string inputName = "Mr.elegant";
int inputAge = 40;
bool b1= Factory.Create(inputName, inputAge, out stu);
Console.WriteLine(stu.Name);
Console.WriteLine(stu.Age);
Console.WriteLine(stu);
}
}
class Student
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
}
class Factory
{
public static bool Create(string stuName, int stuAge, out Student result)
{
result = null;
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(stuName))
{
return false;
}
if (stuAge < 29 || stuAge > 80)
{
return false;
}
result = new Student() { Name = stuName, Age = stuAge }; //创建实例,实例的地址数据等于传进来的数据
return true;
}
}
4.5.4 数组参数params
Combine()方法可接受数量可变的参数,这些参数要么是以逗号分隔的字符串参数,要么是单个字符串数组。前者的语法称为方法调用的“展开”Expanded,后者称为“正常形式”Normal。
Combine()方法需要:(1)在方法声明的最后一个参数之前添加params关键字(2)将最后一个参数声明为数组。
使用params后无需单独声明数组,必须是形参列表中的最后一个,才能使用params修饰
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int sum = Calculate(1, 3, 4);
Console.WriteLine(sum);
}
static public int Calculate(params int[] intArray) //无需在上面方法调用时再创建新的数组了
{
int sum = 0;
foreach (var item in intArray)
{
sum+=item;
}
return sum;
}
}
string.split方法可以进行分割号的判定
string str = "tim,tom.jack;lucy";
string[] result = str.Split(',', '.',';'); //注意这里是单引号,一个字符
foreach (var item in result)
{
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
4.5.5 具名参数
具名参数的优点:
- 提高代码可读性
参数的位置不在受参数列表约束
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { PrintInfo(name: "jack", age: 23); //具名参数,是一种方法的使用 } static void PrintInfo(string name, int age) { Console.WriteLine("hello,{0},your name is {1}",name,age); } }4.5.6 可选参数
参数因为具有默认值而变得“可选”
- 不推荐使用可选参数
static int DirectoryCountLines(string directory,string extension = “*.cs”)
4.5.7 参数选择总结
4.6 递归
4.7 方法的重载
5 类
定义类型是任何C#程序的核心构造,正是由于C#支持类以及根据类来创建对象,所以我们说C#是一种面向对象语言。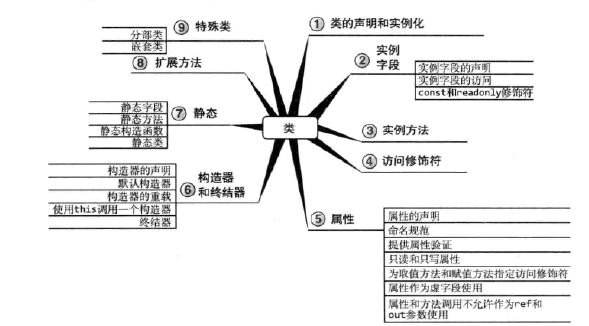
面向对象编程的关键技术优势之一是不需要完全从头创建新的程序。
面向对象编程最基本的构造是类。一组类构成了编程抽象、模型或者模板,通常对应于一个现实世界的概念。
类是面向对象编程的3个主要特征(封装、继承、多态)的基础。
封装:封装的目的是隐藏细节。在必要的时候,细节仍然可以访问,但通过巧妙地封装细节,大的程序变得更容易理解,数据不会因为不慎而被修改,代码也变得更容易维护。方法就是封装的一个例子。
继承:面向对象编程中的继承允许在这些相似但又不同的物件之间建立“属于”(isa)关系。
多态性:不同的类型能自己照料一个方法的实现细节,因为共享同一个公共基类型(或接口)的多个派生类型也包含了相同的方法签名。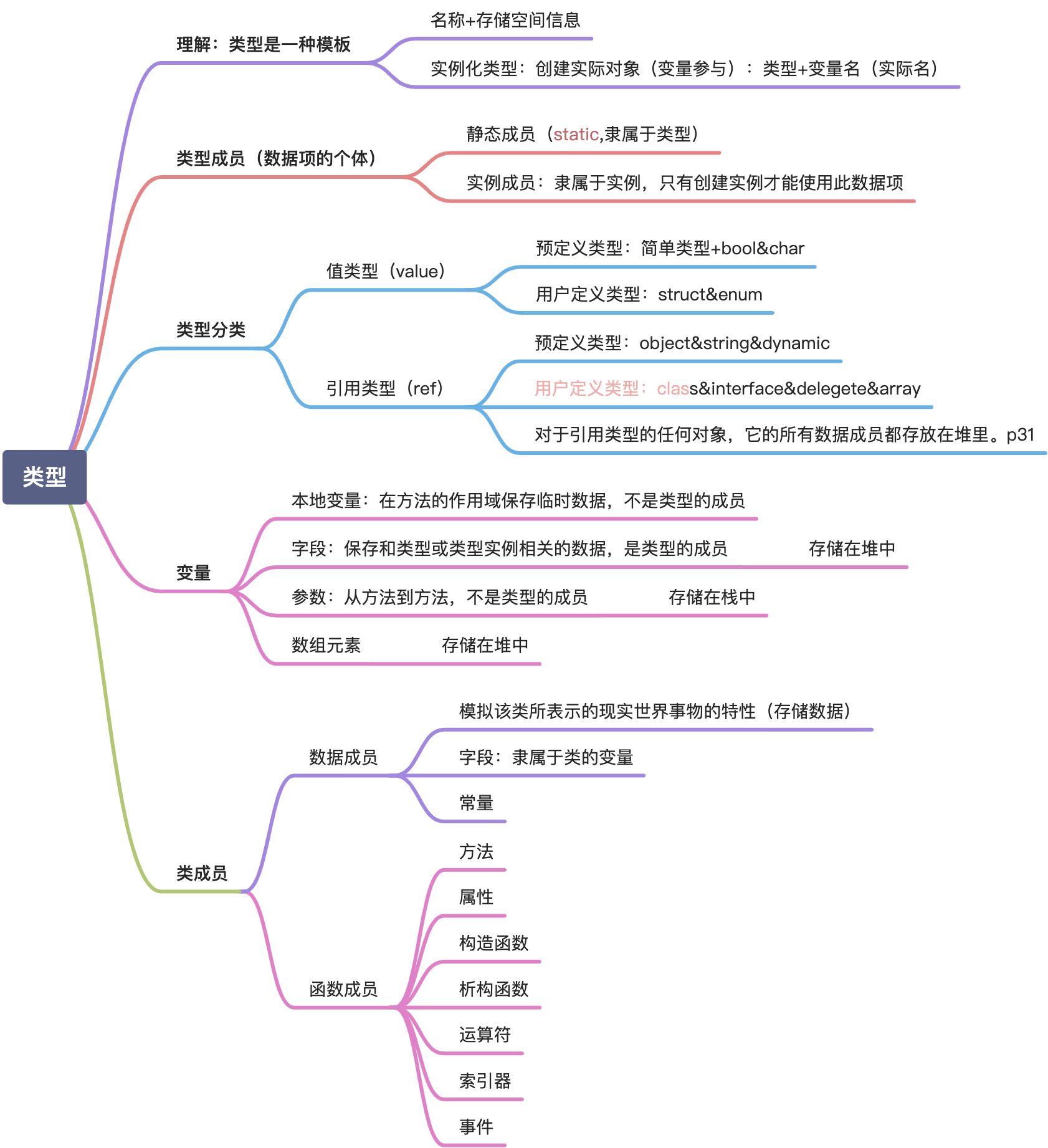
5.1 类的定义和实例化
一般将每个类放在自己的文件中,用类名对文件进行命名。
规范不要在一个源代码文件中放置多个类。要用所含公共类型的名称来命名源代码。
从类创建对象的过程成为实例化,对象是类的实例。
5.2 实例字段
面向对象设计的核心部分是对数据进行分组,以提供一个特定的结构。在类中存储数据的变量称为成员变量(字段)。创建实例才能进行访问。
字段实际上是一种变量,用于存储数据。字段是一种类型的成员,声明字段必须要写在类体里面。写在函数体里面的是局部变量,不是字段。语句只可能出现在函数体里面。
字段的声明必须是名词!
字段:实例字段,类型字段(需要用static修饰)
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu1 = new Student();
stu1.Age = 40;
stu1.Score = 90;
Student.ReporAmount(); //创建一个实例amount加1
Student stu2 = new Student();
stu2.Age = 24;
stu2.Score = 100;
Student.ReporAmount(); //创建第二个实例amount变为2
}
}
class Student
{
public int Age; //实例字段
public int Score;
public static int AverAge; //类型字段,需要用static来修饰
public static int AverScore;
public static int Amount;
public Student() //构造器
{
Student.Amount++;
}
public static void ReporAmount() //静态方法
{
Console.WriteLine(Student.Amount);
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<Student> stuList = new List<Student>(); //泛型类,
//List<T>类是ArrayList类型的泛型等效类。该类使用大小可按需动态增加的数组实现IList<T>泛型接口
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
Student stu = new Student();
stu.Age = 24; //用于修饰stu(i)
stu.Score = i; //用于修饰stu(i)
stuList.Add(stu); //增加元素 List<T>.Add(增加的元素,此处为一个实例变量)
}
int totalAge = 0;
int totalScore = 0;
foreach (var stu in stuList)
{
totalAge += stu.Age;
totalScore += stu.Score;
}
Student.AverAge = totalAge / Student.Amount; //计算平均年龄
Student.AverScore = totalScore / Student.Amount; //计算平均分数
Student.ReportAverage();
Student.ReportAverScore();
Student.ReporAmount(); //创建第二个实例amount变为2
}
}
class Student
{
public int Age; //实例字段
public int Score;
public static int AverAge;
public static int AverScore;
public static int Amount; //数据类型被运行环境第一次加载的时候执行静态构造器 statci Student(),永远只执行一次
public Student() //实例构造器,每次创建实例都进行加载
{
Student.Amount++;
}
public static void ReporAmount() //静态方法
{
Console.WriteLine(Student.Amount);
}
public static void ReportAverage()
{
Console.WriteLine(Student.AverAge);
}
public static void ReportAverScore()
{
Console.WriteLine(Student.AverScore);
}
}
字段声明:字段在类体里面,而不是函数体中
访问级别+数据类型+变量名
访问级别+static+数据类型+变量名(静态字段)
若不赋初始值,则表示字段类型的默认初始值,尽量创建的时候就赋初始值。
对于只读字段,只有一次机会进行赋值,初始化构造器进行赋值。
class 1{
Student testID = new Student(2);//初始化只读实例字段
Console.WriteLine(testID.ID);
}
class 2{
Student testID = new Student(2);//初始化只读实例字段
Console.WriteLine(testID.ID);
public Student (int id)
{
this.ID = id; //初始化
}
}
5.3 实例方法
创建实例才能进行访问。对于实例方法和静态方法的理解:实例方法和静态方法的理解。使用了static 修饰符的方法为静态方法,反之则是非静态方法。 静态方法是一种特殊的成员方法,它不属于类的某一个具体的实例,而是属于类本身。所以对静态方法不需要首先创建一个类的实例,而是采用类名.静态方法的格式 。
5.3.1 静态方法和实例方法的区别
1. static方法是类中的一个成员方法,属于整个类,即不用创建任何对象也可以直接调用!
static内部只能出现static变量和其他static方法!而且static方法中还不能使用this….等关键字..因为它是 属于整个类!
2. 静态方法效率上要比实例化高,静态方法的缺点是不自动进行销毁,而实例化的则可以做销毁。
3. 静态方法和静态变量创建后始终使用同一块内存,而使用实例的方式会创建多个内存.
4. C#中的方法有两种:实例方法,静态方法. 类的方法代码只有一份,它们的生命周期和类是一致的.实例方法是通过对象名调用的,静态方法与类关联而不是 与对象名关联.
5. 那么在程序中什么地方可以利用静态字段和静态构造方法,通常适用于于一些不会经常变化而又频繁使用的数据,比如连接字符串,配置信息等,当满足上面所 说的两点时,进行一次读取,以后就可以方便的使用了,同时也节约了托管资源,因为对于静态成员,一个静态字段只标识一个存储位置。
5.4 使用this关键字
在类的实例成员内部,可以获取对这个类的引用。调用任何实例成员时this都是隐式的,它返回对象本身的实例。可以用this来避免歧义,对比下列程序。
代码1:
class Employee
{
public string firstName;
public string lastName;
public string salary;
public string GetName()
{
return firstName + " " +lastName;
}
public void SetName(string newFirstName,string newLastName)
{
this.firstName = newFirstName;
this.lastName = newLastName;
}
}
代码2:
class Employee
{
public string firstName;
public string lastName;
public string salary;
public string GetName()
{
return firstName + " " +lastName;
}
public void SetName(string firstName,string lastName)
{
this.firstName = newFirstName;
this.lastName = newlastName;
}
}
在方法调用中传递this
class Employee
{
public string firstName;
public string lastName;
public string salary;
public void Save()
{
DataStorage.Store(this);
}
}
class DataStorage
{
public static void Store(Employee employee)
{
//...
}
}
需要向Store()方法传递准备进行持久化存储的Employee对象,这是使用关键字this来完成的,它传递了正在其上调用Save()方法的那个Employee对象实例。
5.6 属性
字段的包装器,永远使用属性而不是字段向外暴露数据。用方法的Get/Set来保护字段不被污染,添加限定条件。
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu1 = new Student();
stu1.SetAge(30);
Student stu2 = new Student();
stu2.SetAge(40);
Console.WriteLine((stu1.GetAge()+stu2.GetAge())/Student.Amount);
}
}
class Student
{
private int age; //设置为私有的时候变为小写
public static int Amount;
public Student()
{
Amount++;
}
public static void ReportAmount()
{
Console.WriteLine(Student.Amount);
}
public int GetAge() //用方法来获取字段
{
return this.age;
}
public void SetAge(int value)//设置字段,防止让非法值污染字段
{
if (value >= 0 && value <= 120)
{
this.age = value;
}
else
{
throw new Exception("Age value is valid");//抛出异常
}
}
}
属性,public int Age{}将字段包装起来 set get。propfull+tab*2 即可直接创建出属性的样子。prop+tab2 简略声明,用来*传递数据。
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu1 = new Student();
stu1.Age = 20;
Student stu2 = new Student();
stu2.Age = 40;
Console.WriteLine((stu1.Age+stu2.Age)/Student.Amount);
}
}
class Student
{
private int age; //设置为私有的时候变为小写 ,私有字段
public static int Amount;
public Student()
{
Amount++;
}
public static void ReportAmount()
{
Console.WriteLine(Student.Amount);
}
public int Age //公有属性
{
get
{
return this.age;
}
set
{
if (value >= 0 && value <= 120) //上下文关键字
{
this.age = value;
}
else
{
throw new Exception("this age value is valid");
}
}
}
}
静态字段—属性 两边都要加static(归属于类型)。
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student stu1 = new Student();
stu1.Age = 20;
Student stu2 = new Student();
stu2.Age = 30;
Student.Amount = 2;
Console.WriteLine((stu1.Age+stu2.Age)/Student.Amount);
}
}
class Student
{
private int age;
public int Age
{
get { return age; }
set
{
if (value >= 0 && value <= 200)
{ age = value; }
else
{
throw new Exception("this Age value is valid");
}
}
}
private static int amount;
public static int Amount
{
get { return amount; }
set
{
if (value <= 3) { amount = value; }
else
{
throw new Exception("this Amount is more than regular number");
}
}
}
}
5.7 构造器
5.8 索引器
索引器(Indexer)允许一个对象可以像数组一样使用下标的方式来访问。
当您为类定义一个索引器时,该类的行为就会像一个虚拟数组(virtual array)一样。可以使用数组访问运算符 [ ] 来访问该类的的成员。
using System;
namespace IndexerApplication
{
class IndexedNames
{
private string[] namelist = new string[size];
static public int size = 10;
public IndexedNames()
{
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
namelist[i] = "N. A.";
}
public string this[int index]
{
get
{
string tmp;
if( index >= 0 && index <= size-1 )
{
tmp = namelist[index];
}
else
{
tmp = "";
}
return ( tmp );
}
set
{
if( index >= 0 && index <= size-1 )
{
namelist[index] = value;
}
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
IndexedNames names = new IndexedNames();
names[0] = "Zara";
names[1] = "Riz";
names[2] = "Nuha";
names[3] = "Asif";
names[4] = "Davinder";
names[5] = "Sunil";
names[6] = "Rubic";
for ( int i = 0; i < IndexedNames.size; i++ )
{
Console.WriteLine(names[i]);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
5.9 静态成员
5.10 扩展方法
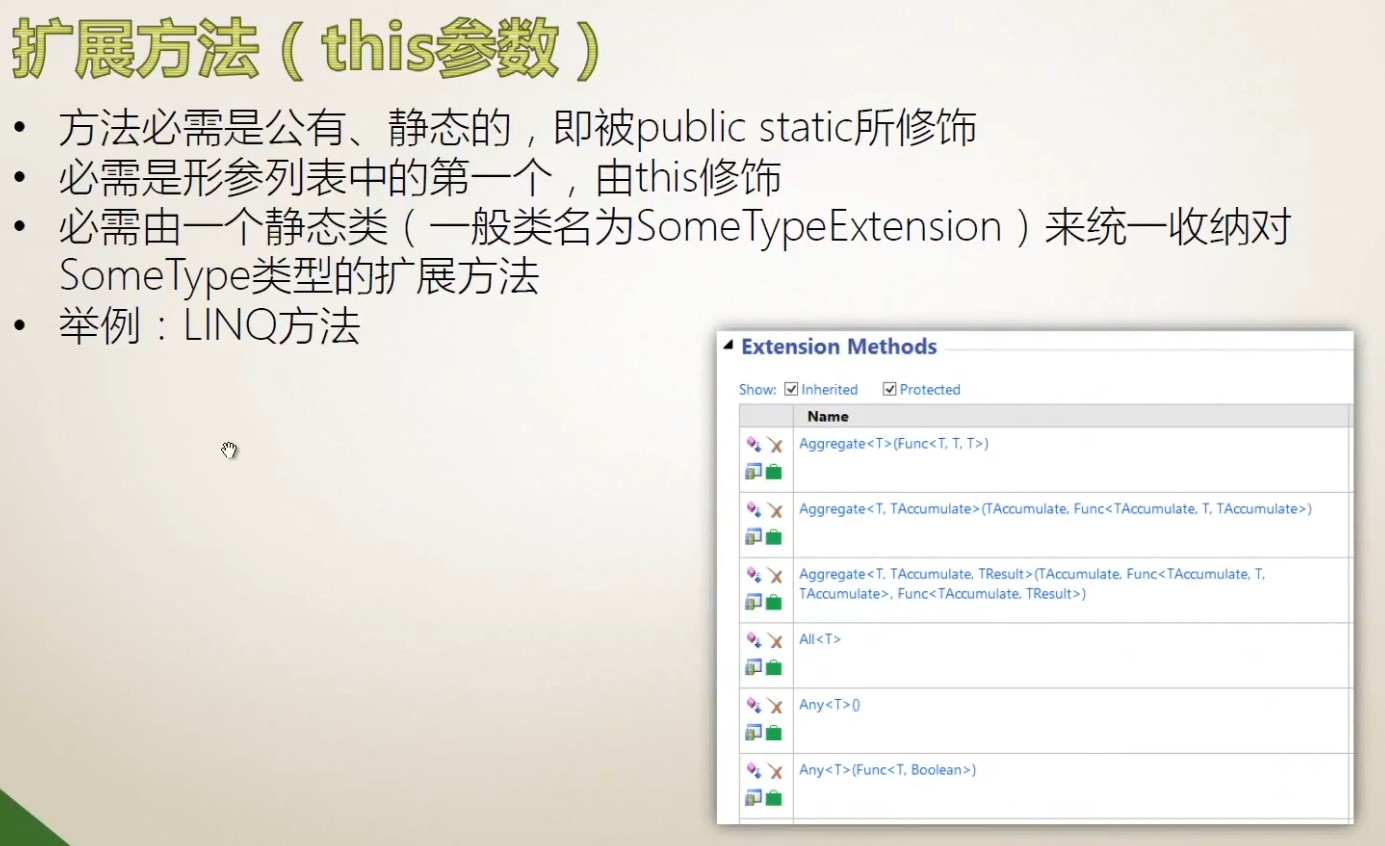
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
double x = 3.14159;
double y = x.result(4); //扩展方法图标不同
Console.WriteLine(y);
}
}
public static class DoubleExtension //静态类,需要用static修饰 ,类名默认为TypeExtension
{
public static double result(this double input, int digits) //this 扩展方法 //必须是public static修饰的方法
{
return Math.Round(input, digits);
}
}