UART
UART
Complex peripheral devices such as GPS modules, LCD displays, and XBee radios typically use Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter (UART) ports (often simply called serial ports) to communicate.
GPS模块, LCD模块 还有 xBee无线模块等这一系列的复杂外设, 一般会用 通用异步收发器 (UART, Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter) 端口 (通常进被叫做 串口 ) 来交互数据。
The UART is a generic interface for exchanging raw data with a peripheral device. It is universal because both the data transfer speed and data byte format are configurable. It is asynchronous in that there are no clock signals present to synchronize the data transfer between the two devices. The device hardware collects all incoming data in a first-in first-out (FIFO) buffer until read by your app.
UART 是外设用来交互原始数据的通用接口。 叫做 通用 是由于数据的格式以及数据传输速度都是可配置的。 异步 是由于在串口传输的两个设备之间,没有时钟信号用来同步数据。 设备硬件会把接收的所有数据存到先进先出 (FIFO) 缓冲区中,等待应用读取数据。
UART data transfer is full-duplex, meaning data can be sent and received at the same time. It is typically faster than I2C, but the lack of a shared clock means that both devices must agree on a common data transfer rate that each device can adhere to independently with minimal timing error.
UART 用 全双工 模式来传输数据,意味着同一时间能完成数据的收发操作。一般 UART 的数据传输速度比 I2C 还快, 由于没有共享的时钟信号,两个设备之间会以双方约定好的,通用的传输速率来传输数据,这种传输方式也可以使单个设备的时钟有些须误差时可以自动避免传输错误。
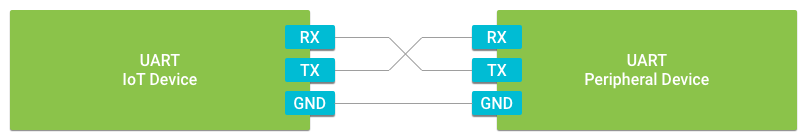
UART peripherals typically come in two flavors:
UART 外设一般以两种形式存在:
3-Wire ports include data receive (RX), data transmit (TX), and ground reference (GND) signals.
3线端口包括数据接收 (RX), 数据发送 (TX), 和地线 (GND) 信号。
5-Wire ports add request to send (RTS) and clear to send (CTS) signals used for hardware flow control. Flow control allows the receiving device to indicate that its FIFO buffer is temporarily full and the transmitting device should wait before sending any more data.
5线端口加入了请求发送 (RTS) 和 (CTS) 清除发送 (CTS) 信号这两种 硬件流控 信号。 流控保证当接收数据的设备的FIFO满时,发送数据的设备要等待,直到FIFO不为满时再发送数据。
Unlike SPI and I2C, UART only supports point-to-point communication between two devices.
与 SPI 和 I2C 不同的时, UART 只支持两个设备之间的点对点信号传输。
Managing the connection
管理连接
In order to open a connection to a particular UART, you need to know the unique port name. During the initial stages of development, or when porting an app to new hardware, it’s helpful to discover all the available device names from PeripheralManagerService using getUartDeviceList():
如果要为一个特定的 UART 设备建立连接,需要知道这个设备唯一的端口名称。 在开发的初始阶段,或者将新的硬件使用到应用中,最好用 PeripheralManagerService 中的 getUartDeviceList() 方法来显示当前可用的所有UART设备。
PeripheralManagerService manager = new PeripheralManagerService();List<String> deviceList = manager.getUartDeviceList();if (deviceList.isEmpty()) {Log.i(TAG, "No UART port available on this device.");}else {Log.i(TAG, "List of available devices: " + deviceList);}
Once you know the target name, use PeripheralManagerService to connect to that device. When you are done communicating with the peripheral device, close the connection to free up resources. Additionally, you cannot open a new connection to the device until the existing connection is closed. To close the connection, use the device’s close() method.
一旦知道当前 UART 的名称,可以使用 PeripheralManagerService 来连接外设。当您已经完成外设的数据传输时,记行关闭连接来释放资源。 直到正在使用的连接关闭之后,才可以打开一个新的连接。 用设备的 close() 方法可以关闭连接。
public class HomeActivity extends Activity {// UART Device Nameprivate static final String UART_DEVICE_NAME = ...;private UartDevice mDevice;@Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);// Attempt to access the UART devicetry {PeripheralManagerService manager = new PeripheralManagerService();mDevice = manager.openUartDevice(UART_DEVICE_NAME);}catch (IOException e) {Log.w(TAG, "Unable to access UART device", e);}}@Override protected void onDestroy() {super.onDestroy();if (mDevice != null) {try {mDevice.close();mDevice = null;}catch (IOException e) {Log.w(TAG, "Unable to close UART device", e);}}}}
Configuring port parameters
配置端口参数
After a connection is established, configure the data transfer rate and frame format to match the connected peripheral device.
建立连接之后,需要配置数据传输的速率和数据传输的帧格式来匹配已经连接的外设。
The Data Frame
数据帧
Every character sent across the UART is wrapped in a data frame, which contains the following components:
数据帧 包含了经过 UART 端口传输的第一个字符, 数据帧一般包括以下内容:

Start Bit - Before sending data, the line is held active for a fixed time interval of 1 bit duration to indicate the start of a new character.
起始位 - 数据发送之前,在一段固定时间之内,用 1 位的数据保持持续的激活状态,用来表示开始新的字符需要发送。
Data Bits - Individual bits representing the data character. The UART may be configured to send between 5-9 data bits to represent the character. Fewer bits reduces the range of data, but can increase the effective data transfer rate.
数据位 - 代表数据字符的各个位。UART可以配置发送 5-9 个数据位来表示字符。更少的位虽然减少了数据传输的范围,但是能够增大有效的数据传输率。
Parity Bit - Optional error checking value. If the UART is configured for even or odd parity, an extra bit will be added to the frame to indicate if the contents of the data bits sum to an even or odd value. Setting this to none removes the bit from the frame.
校验位 - 可选的错误检查值。 如果 UART 配置了 奇 或者 偶 校验,增加的这个位用来表示数据位的每一位相加的和,是奇数,还是偶数, 如果将校验位设置为 none 可以在帧中间移掉这一位。
Stop Bits - After all data is transmitted, the line is reset for a configurable time interval to indicate the end of that character. This can be configured to remain idle for 1- or 2-bit durations.
停止位 - 当数据传输完成之后,可以配置一个时间间隔来保证数据传输完成,一般可配置成保持空闲一到两位的持续时间。
Note: The default configuration for most UART devices is 8 data bits, no parity, and 1 stop bit (8N1).
注意: 大多数的UART设备会配成 8 个数据位,无校验位,1个停止位(8N1)。
The data transfer rate across the UART is called the baud rate. It represents the speed, in bits per second, for both receive and transmit. Since there is no shared clock between two devices connected over UART, both must be configured ahead of time to use the same baud rate for the data to be decoded correctly.
UART 上的数据传输速度一般被叫做 波特率 。 通常表示发送端和接收端每一秒传输多少比特的数据。由于 UART 没有共享的时钟信号,所以发送端和接收端要设置成相同的波特率,来保证正确的数据解码。
Common baud rates include 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200, and 921600. This rate includes the overhead of the data frame (start, stop, and parity bits), so the effective data transfer rate will be slightly lower and vary based on the number of frame bits you have configured.
通常的波特率包括9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200和 921600。这个速率包括了数据帧以及数据帧之外的所有内容(起始位,停止位,校验位),所以说真实的数据传输速度会低于数据帧上的所有位的传输速度。
The following code configures the UART connection to operate at 115200 baud, 8 data bits, no parity, and 1 stop bit (8N1):
下面的代码用来配置 UART 连接的波特率为 115200 ,8 个数据位,无校验位,1个 停止位(8N1):
public void configureUartFrame(UartDevice uart) throws IOException {// Configure the UART portuart.setBaudrate(115200);uart.setDataSize(8);uart.setParity(UartDevice.PARITY_NONE);uart.setStopBits(1);}
Note: Choosing uncommon baud rates can lead to high error rates in data transmission. You should always verify whether your chosen baud rate is well supported by your device hardware.
注意: 如果配置的波特率不是设备支持的波特率,会带来数据传输中的大量的错误。在开发之前,要先确认您的设备支持哪几种波特率。
Hardware Flow Control
硬件流控
If your device supports 5-wire UART ports, enabling hardware flow control can increase the reliability of the data transfer. Often this also means you can safely use faster baud rates with a much lower chance of missing incoming data.
如果您的设备支持5线的端口,使能硬件流控能够提高数据传输的稳定性。通常来说,硬件流控也保证在一个很高的波特率时,不怎么会丢失接收数据。
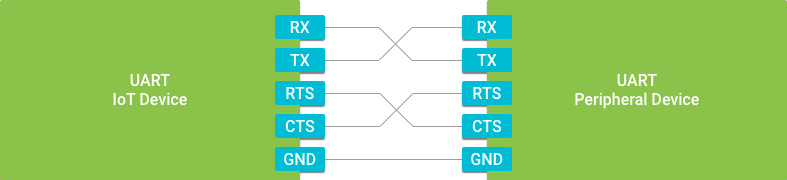
With hardware flow control enabled, the UART asserts the Request to Send (RTS) signal when the receive buffer on the device is full and cannot accept any more data. The signal will be cleared once the buffer has been drained. Similarly, the UART monitors the Clear to Send (CTS) signal, and will pause transmitting data if it sees that line asserted by the peripheral device.
如果使能硬件流控的话,UART会对请求发送 (RTS) 信号产生断言,如时接数数据的缓冲区满了的话,就停止接收数据,一直到接收缓冲区的数据被清除,这个信号才被清除。同样的,UART也会监视清除发送(CTS)信号,如果外围设备对这个信号已经断言,则暂停发送数据。
To enable hardware flow control, use the setHardwareFlowControl() method with HW_FLOW_CONTROL_AUTO_RTSCTS. The default value is HW_FLOW_CONTROL_NONE, which indicates that flow control is disabled.
使能硬件流控,使用 setHardwareFlowControl() 方法,并且输入 HW_FLOW_CONTROL_AUTO_RTSCTS 参数, 如果禁用硬件流控, 则在 setHardwareFlowControl() 中输入 HW_FLOW_CONTROL_NONE 参数。默认参数状态是禁止硬件流控状态。
public void setFlowControlEnabled(UartDevice uart, boolean enable) throws IOException {if (enable) {// Enable hardware flow controluart.setHardwareFlowControl(UartDevice.HW_FLOW_CONTROL_AUTO_RTSCTS);} else {// Disable flow controluart.setHardwareFlowControl(UartDevice.HW_FLOW_CONTROL_NONE);}}
Transmitting outgoing data
发送数据
To transmit a buffer of data over the UART to a peripheral, use the write() method:
使用 write() 方法将缓冲区数据通过 UART 传输到外设:
public void writeUartData(UartDevice uart) throws IOException {byte[] buffer = {...};int count = uart.write(buffer, buffer.length);Log.d(TAG, "Wrote " + count + " bytes to peripheral");}
Note: A Java byte is an 8-bit value. If you configure a smaller data width using setDataSize(), the upper bits of each byte will be truncated.
注意: JAVA的 byte 一般是 8 位。如果用 setDataSize() 来定义大于 8 位的数据,那么byte的高位会被截断。
Listening for incoming data
监听接收数据
Use the read() method to pull incoming data from the UART FIFO buffer into your application. This method accepts an empty buffer to fill with the incoming data and a maximum number of bytes to read. UART reads are non-blocking, and will return immediately if there is no data available in the FIFO.
使用 read() 方法可以从 UART 的 FIFO 中连续的读取数据到您的应用程序。这种方法可以使一个空的缓冲区接收最大的字节数的数据用于读取。UART 的读取操作是非阻塞式的,如果 FIFO 中没有数据的话,就立刻返回。
UartDevice will return the number of available bytes in the FIFO at the time of the read, up to the requested count. To ensure that all data was recovered, loop over the UART until it reports that no more data is present:
UartDevice 会在读取到数据的第一时间返回在 FIFO 中的可用字节数,最大值为请求的可用字节数。在 UART 上循环读取直到没有数据,确保所有的数据能够完成传输。
public void readUartBuffer(UartDevice uart) throws IOException {// Maximum amount of data to read at one timefinal int maxCount = ...;byte[] buffer = new byte[maxCount];int count;while ((count = uart.read(buffer, buffer.length)) > 0) {Log.d(TAG, "Read " + count + " bytes from peripheral");}}
To avoid polling the UART unnecessarily when the buffer is empty, register a UartDeviceCallback with the UartDevice. This callback invokes the onUartDeviceDataAvailable() method when there is data available to read. You should unregister the callback when your application is no longer listening for incoming data.
如果要避免缓冲区为空时,我们还在读取缓冲区。可以通过 UartDevice注册回调函数UartDeviceCallback。这个回调函数会在有可用数据时,调用onUartDeviceDataAvailable()` 这个方法。 如果您的应用不再监听输入数据,应该注销这个回调函数。
public class HomeActivity extends Activity {private UartDevice mDevice;...@Override protected void onStart() {super.onStart();// Begin listening for interrupt eventsmDevice.registerUartDeviceCallback(mUartCallback);}@Override protected void onStop() {super.onStop();// Interrupt events no longer necessarymDevice.unregisterUartDeviceCallback(mUartCallback);}private UartDeviceCallback mUartCallback = new UartDeviceCallback() {@Override public boolean onUartDeviceDataAvailable(UartDevice uart) {// Read available data from the UART devicetry {readUartBuffer(uart);}catch (IOException e) {Log.w(TAG, "Unable to access UART device", e);}// Continue listening for more interruptsreturn true;}@Override public void onUartDeviceError(UartDevice uart, int error) {Log.w(TAG, uart + ": Error event " + error);}};}
The onUartDeviceDataAvailable() callback returns a boolean value, indicating whether the callback should be automatically unregistered from receiving future interrupt events. Return true here to continue receiving events each time data appears in the UART FIFO.
回调函数 onUartDeviceDataAvailable() 一般返回为一个 boolean 类型的值,用来判断回调函数是否应该从接收未来中断的事件中注销。如果返回 true 则表示,每当 UART FIFO 中有数据存在时,继续调用接收事件。

