1. HDFS
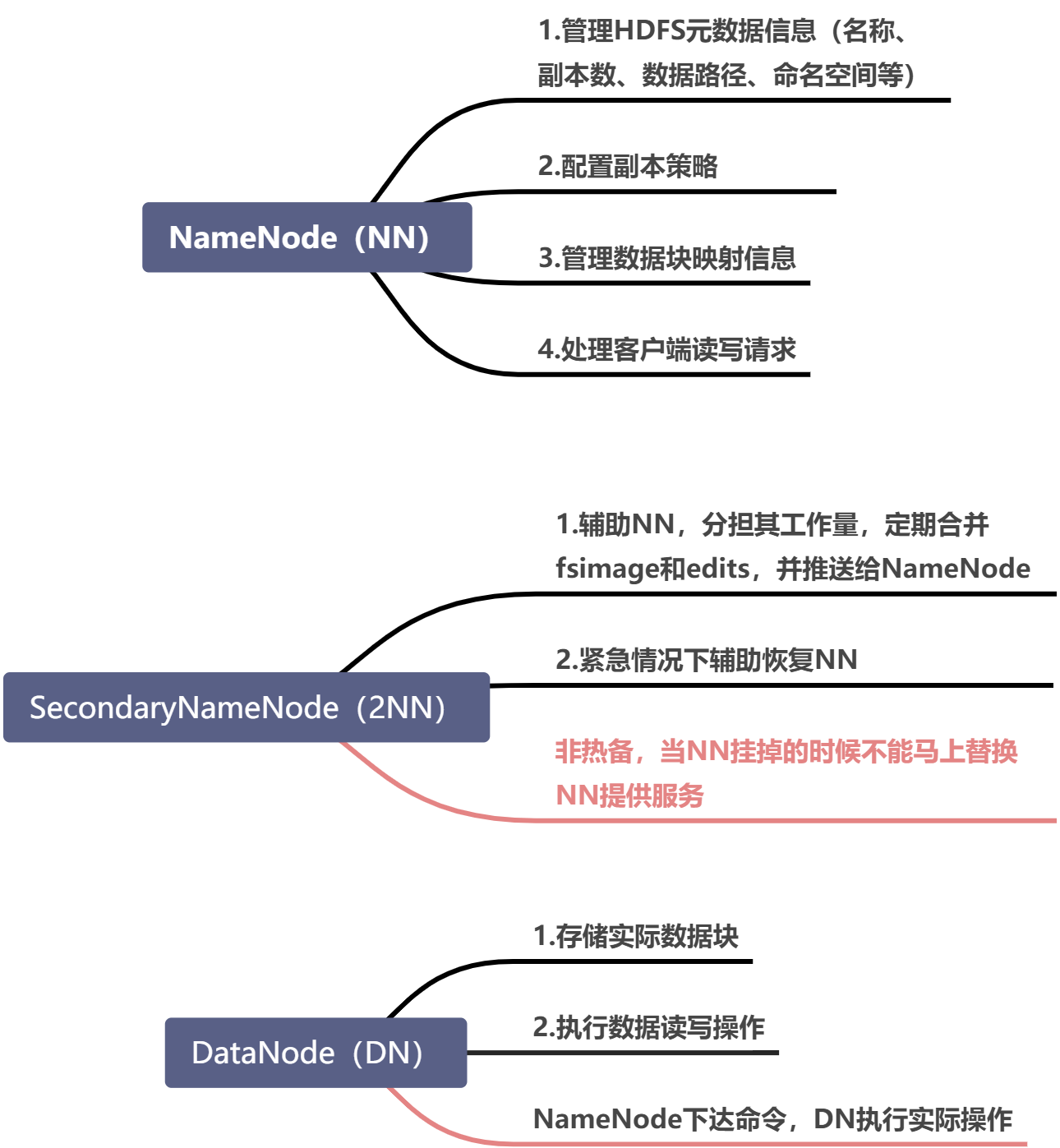
1.1. NameNode 与 SecondaryNameNode
- NameNode中存放edits_inprogress 和 fsimage 的位置:
{$HADOOP_HOME}/data/tmp/dfs/name/current
NameNode的安全模式:
该阶段不允许对HDFS进行访问外的操作,NameNode是只读的;
检查DN上面的块是否损坏
该阶段可以将fsimage和edits载入内存,进行合并。
- 为什么需要SecondaryNameNode?
辅助合并edits和fsimage
- edits文件记录每次操作,fsimage相当于内存状态的镜像。
- 当NN挂掉了,需要将fsimage和edits合并,恢复挂之前的内存状态;
- 如果edits太大了,则恢复需要很长时间;
- 如果在NN中对fsimage和edits进行定期合并,会占用大量内存和CPU;
- 所以借助SecondaryNameNode,在运行过程中辅助NameNode合并edits和fsimage,控制edits大小。
辅助恢复NameNode
- 由于fsimage都是由2NN合并edits产生的,所以2NN中的fsimage一定会比NN中的fsimage新(或相同);
- 当NN挂了以后,将2NN中的fsimage拷贝到NN中;
- 重启NN,将拷贝的fsimage与edits进行合并,恢复之前的内存状态。
- CheckPoint设置:查看hadoop-hdfs-2.7.2.jar中的 hdfs-default.xml,有如下几个设置(标红可改):
- SecondaryNameNode每隔一个小时执行一次checkpoint。
- SecondaryNameNode每分钟检查一次事务操作次数,如果操作次数达到100万次,则执行checkpoint。
```xml
执行checkpoint的时间间隔为3600秒,即1一个小时执行一次
dfs.namenode.checkpoint.period 3600 The number of seconds between two periodic checkpoints.
每分钟检查一次操作次数,如果操作次数达到100万次,则执行checkpoint
每隔多少秒检查一次操作次数,这里默认是一分钟。
<a name="pfxnE"></a>## 1.2. HDFS常用命令> hadoop fs -mkdir /tez> hadoop fs -put /opt/module/tez-0.9.1 /tez> hadoop fs -ls /tez/tez-0.9.1<a name="6OLN3"></a>## 1.3. 将文件从本地上传到HDFS的方法1. 命令:hadoop fs -put /localfile /hdfsfile1. 使用Flume上传1. 使用Hive load local inpath上传<a name="ndNxy"></a># 2. MapReduceMapReduce运行时有三类实例进程:1. **MRAppMaster**:负责整个程序的过程调度及状态协调1. **MapTask**:负责Map阶段的整个数据处理流程1. **ReduceTask**:负责Reduce阶段的整个数据流程处理一个MapReduce任务对应一个Job,Job在执行的不同阶段启动若干了Task其中MapTask分为 mapPhase 和 sortPhase<br />ReduceTask分为 copyPhase 、 sortPhase 和 reducePhase<a name="EWEbf"></a>## 2.0. MapReduce流程[语雀内容](https://www.yuque.com/lashuishulaoda/ez5etc/xxf4rs?view=doc_embed)1. 客户端调用**InputFormat**对文件进行切片1. 执行**MapTask**1. **MapTask**类中重写了**run()**方法1. 划分阶段:1. 如果没有reduce任务,则Map阶段只有map阶段1. 如果有reduce任务,则将Map阶段分为map阶段和sort阶段,其中mapPhase占66.7%,sortPhase占33.3%。**------见 code1**2. 判断新旧API2. 初始化:outputFormat、outputPath、committer等2. 根据API启动相应的**Mapper**:旧API:org.apache.hadoop.mapred.Mapper——**runNewMapper()**<br />新API:org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper——**runOldMapper()**1. 启动对应的Mapper **------见 code2**1. 创建当前MapTask的**Mapper**对象1. 创建当前MapTask的输入格式**InputFormat**对象1. 重建当前MapTask的**切片信息**对象split1. 创建当前MapTask的**RecordReader**输入对象input1. 创建输出收集器NewOutputCollector对象collector1. 创建当前MapTask的**MapOutputCollector**输出对象collector,根据**numReduceTasks**选择类型:1. **numReduceTasks>0 **选择**MapOutputBuffer**,(map结束后进入到**Shuffle**环节)1. 对collector进行初始化(缓冲区的初始化)**------见 code3**1. 获取溢写的百分比(默认0.8)1. 设置缓冲区的初始大小(默认100m)1. 设置排序方式(默认使用快排)1. 确定key的比较器1. 获取mapper输出的kv类型1. 根据key的类型指定序列化器 **------见 code4**1. 设置mapper的输出端使用压缩1. 设置combiner1. 新开一条SpillThread线程2. **numReduceTasks<=0 **选择 **DirectMapOutputCollector**,(map结束后跳过**shuffle**和**reduce**,直接输出)2. 根据numReduceTasks创建分区器partitioner(默认采用HashPartitioner)6. 创建当前MapTask的context对象6. 切片文件初始化6. 运行mapper.run(),执行业务逻辑。**------见 code5**1. 调用setup()方法1. 循环调用map()方法1. 最终调用cleanup()方法9. 完成mapPhase9. 设置Phase为SORT9. 设置状态为umbilical(中央的,脐带的) statusUpdate(umbilical)9. 刷出缓冲区中的数据9. mergeParts()1. 判断是否进行combinercode1:阶段划分```javaif (isMapTask()) {// If there are no reducers then there won't be any sort. Hence the map// phase will govern the entire attempt's progress.if (conf.getNumReduceTasks() == 0) {mapPhase = getProgress().addPhase("map", 1.0f);} else {// If there are reducers then the entire attempt's progress will be// split between the map phase (67%) and the sort phase (33%).mapPhase = getProgress().addPhase("map", 0.667f);sortPhase = getProgress().addPhase("sort", 0.333f);}}
code2:启动Mapper
private <INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE>
void runNewMapper(final JobConf job,
final TaskSplitIndex splitIndex,
final TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical,
TaskReporter reporter
) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException,
InterruptedException {
// make a task context so we can get the classes
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.TaskAttemptContext taskContext =
new org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.task.TaskAttemptContextImpl(job,
getTaskID(),
reporter);
// make a mapper 一个MapTask只会创建一个Mapper对象
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE> mapper =
(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE>)
ReflectionUtils.newInstance(taskContext.getMapperClass(), job);
// make the input format 创建输入格式对象
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputFormat<INKEY,INVALUE> inputFormat =
(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputFormat<INKEY,INVALUE>)
ReflectionUtils.newInstance(taskContext.getInputFormatClass(), job);
// rebuild the input split 重建当前MapTask的切片
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputSplit split = null;
split = getSplitDetails(new Path(splitIndex.getSplitLocation()),
splitIndex.getStartOffset());
LOG.info("Processing split: " + split);
//构建MapTask的输入对象,负责整个MapTask的输入工作,RecordReader由input负责进行调用读取数据
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordReader<INKEY,INVALUE> input =
new NewTrackingRecordReader<INKEY,INVALUE>
(split, inputFormat, reporter, taskContext);
job.setBoolean(JobContext.SKIP_RECORDS, isSkipping());
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordWriter output = null;
//构建MapTask的输出对象
// get an output object
if (job.getNumReduceTasks() == 0) {
//如果没有reduce阶段,由Map收集输出的数据,直接输出
output =
new NewDirectOutputCollector(taskContext, job, umbilical, reporter);
} else {
// 创建记录收集器
output = new NewOutputCollector(taskContext, job, umbilical, reporter);
}
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.MapContext<INKEY, INVALUE, OUTKEY, OUTVALUE>
mapContext =
new MapContextImpl<INKEY, INVALUE, OUTKEY, OUTVALUE>(job, getTaskID(),
input, output,
committer,
reporter, split);
//构建Mapper中使用的context对象,代表MapTask的上下文(来龙去脉),
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE>.Context
mapperContext =
new WrappedMapper<INKEY, INVALUE, OUTKEY, OUTVALUE>().getMapContext(
mapContext);
try {
// 会执行输入过程中所需要组件的一系列初始化
// 调用RecordReader.initialize()
input.initialize(split, mapperContext);
// 调用自己编写的Mapper的run()
mapper.run(mapperContext);
mapPhase.complete();
setPhase(TaskStatus.Phase.SORT);
statusUpdate(umbilical);
input.close();
input = null;
output.close(mapperContext);
output = null;
} finally {
closeQuietly(input);
closeQuietly(output, mapperContext);
}
}
code3:收集器对象collector的初始化
public void init(MapOutputCollector.Context context
) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
job = context.getJobConf();
reporter = context.getReporter();
mapTask = context.getMapTask();
mapOutputFile = mapTask.getMapOutputFile();
sortPhase = mapTask.getSortPhase();
spilledRecordsCounter = reporter.getCounter(TaskCounter.SPILLED_RECORDS);
partitions = job.getNumReduceTasks();
rfs = ((LocalFileSystem)FileSystem.getLocal(job)).getRaw();
//sanity checks
//从配置中读取溢写的百分比,默认读取mapreduce.map.sort.spill.percent
//如果没有配置,使用0.8作为百分比
final float spillper =
job.getFloat(JobContext.MAP_SORT_SPILL_PERCENT, (float)0.8);
//缓冲区的初始大小,默认读取mapreduce.task.io.sort.mb,如果没有配置,默认使用100(m)
final int sortmb = job.getInt(JobContext.IO_SORT_MB, 100);
indexCacheMemoryLimit = job.getInt(JobContext.INDEX_CACHE_MEMORY_LIMIT,
INDEX_CACHE_MEMORY_LIMIT_DEFAULT);
if (spillper > (float)1.0 || spillper <= (float)0.0) {
throw new IOException("Invalid \"" + JobContext.MAP_SORT_SPILL_PERCENT +
"\": " + spillper);
}
if ((sortmb & 0x7FF) != sortmb) {
throw new IOException(
"Invalid \"" + JobContext.IO_SORT_MB + "\": " + sortmb);
}
//排序默认使用快排
sorter = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(job.getClass("map.sort.class",
QuickSort.class, IndexedSorter.class), job);
// buffers and accounting
int maxMemUsage = sortmb << 20;
maxMemUsage -= maxMemUsage % METASIZE;
kvbuffer = new byte[maxMemUsage];
bufvoid = kvbuffer.length;
kvmeta = ByteBuffer.wrap(kvbuffer)
.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder())
.asIntBuffer();
setEquator(0);
bufstart = bufend = bufindex = equator;
kvstart = kvend = kvindex;
maxRec = kvmeta.capacity() / NMETA;
softLimit = (int)(kvbuffer.length * spillper);
bufferRemaining = softLimit;
...
// k/v serialization
//获取key的比较器
comparator = job.getOutputKeyComparator();
//获取mapper输出的key-value的类型
keyClass = (Class<K>)job.getMapOutputKeyClass();
valClass = (Class<V>)job.getMapOutputValueClass();
serializationFactory = new SerializationFactory(job);
//根据key的类型返回序列化器
keySerializer = serializationFactory.getSerializer(keyClass);
keySerializer.open(bb);
valSerializer = serializationFactory.getSerializer(valClass);
valSerializer.open(bb);
// output counters
mapOutputByteCounter = reporter.getCounter(TaskCounter.MAP_OUTPUT_BYTES);
mapOutputRecordCounter =
reporter.getCounter(TaskCounter.MAP_OUTPUT_RECORDS);
fileOutputByteCounter = reporter
.getCounter(TaskCounter.MAP_OUTPUT_MATERIALIZED_BYTES);
// compression
//在mapper的输出阶段使用压缩
if (job.getCompressMapOutput()) {
Class<? extends CompressionCodec> codecClass =
job.getMapOutputCompressorClass(DefaultCodec.class);
codec = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(codecClass, job);
} else {
codec = null;
}
// combiner
//设置combiner
final Counters.Counter combineInputCounter =
reporter.getCounter(TaskCounter.COMBINE_INPUT_RECORDS);
combinerRunner = CombinerRunner.create(job, getTaskID(),
combineInputCounter,
reporter, null);
if (combinerRunner != null) {
final Counters.Counter combineOutputCounter =
reporter.getCounter(TaskCounter.COMBINE_OUTPUT_RECORDS);
combineCollector= new CombineOutputCollector<K,V>(combineOutputCounter, reporter, job);
} else {
combineCollector = null;
}
spillInProgress = false;
minSpillsForCombine = job.getInt(JobContext.MAP_COMBINE_MIN_SPILLS, 3);
spillThread.setDaemon(true);
spillThread.setName("SpillThread");
spillLock.lock();
try {
//启动spillThread线程
spillThread.start();
while (!spillThreadRunning) {
spillDone.await();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new IOException("Spill thread failed to initialize", e);
} finally {
spillLock.unlock();
}
if (sortSpillException != null) {
throw new IOException("Spill thread failed to initialize",
sortSpillException);
}
}
code4:获取key的比较器
public RawComparator getOutputKeyComparator() {
//尝试获取参数中配置的mapreduce.job.output.key.comparator.class,作为比较器
//如果没有定义,默认为null,定义的话必须是RawComparator类型
Class<? extends RawComparator> theClass = getClass(
JobContext.KEY_COMPARATOR, null, RawComparator.class);
//如果用户有配置,就实例化此类型的一个对象
if (theClass != null)
return ReflectionUtils.newInstance(theClass, this);
// 判断Mapper输出的key是否是writableComparable类型的子类,
// 如果是,就默认由系统提供比较器,如果不是就抛出异常
return WritableComparator.get(getMapOutputKeyClass().asSubclass(WritableComparable.class), this);
}
code5:运行Mapper.run(),执行业务逻辑
public void run(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
setup(context);
try {
while (context.nextKeyValue()) {
map(context.getCurrentKey(), context.getCurrentValue(), context);
}
} finally {
cleanup(context);
}
}
2.1. 文件切片
- Client对文件进行切片,并将切片信息提交给 Yarn ResourseManager。
- 文件的切片是对文件进行的逻辑划分,真实的大文件是分块保存在HDFS中的。
- 默认的切片机制是TextInputFormat,按照单个文件为一片;
- TextInputFormat、CombineTextInputFormat、KeyValueTextInputFormat等都是FileInputFormat的实现类;
- 自定义InputFormat,继承FileInputFormat类;(FileInputFormat继承InputFormat类)。
InputFormat类通过createRecordReader()方法创建一个RecordReader实例对象,将数据读取为KV形式;
2.1.1. FileInputFormat切片机制
- 按照文件内容进行切片;
- 切片大小默等于Block大小;
- 切片时不考虑数据集整体,而是针对每个文件单独切片,如下图所示,如果切片时考虑数据集整体应该是切出3个100m的切片文件。
2.1.2. TextInputFormat切片机制
框架默认的TextInputFormat切片机制是对任务按文件规划切片,不管文件大小,都会是一个单独的切片,都会交给一个MapTask。
按行读取每条记录:
- 键是存储该行在整个文件中的起始字节偏移量,LongWritable类型。
- 值是这行的内容,不包括任何终止符(换行符和回车符)。
如果有大量小文件,就会产生大量的MapTask;
如果有个别特别大的文件,就会产生数据倾斜,有几个MapTask特别慢,且占用内存特别高。
2.1.3. CombineTextInputFormat切片机制
应对小文件过多的情况。
虚拟存储过程:
将输入目录下所有文件的大小依次和设置的setMaxInputSplitSize值比较:
- 如果不大于设置的最大值,逻辑上划分为一个块;
- 如果输入文件大于设置的最大值的两倍,那么以最大值切一块;
- 如果输入文件大于设置的最大值,但不大于其两倍,将该文件均分为两个虚拟存储块(对半分);
- 当剩余数据超过设置的最大值且不大于最大值的两倍,
切片过程:
判断虚拟存储的文件大小是否大于setMaxInputSplitSize值,
- 大于等于则单独形成一个切片;
- 如果不大于则跟下一个虚拟存储文件进行合并,共同形成一个切片。
2.1.4. KeyValueTextInputFormat
每一行为一条记录,被分隔符分割为key,value;
默认分隔符为tab(\t)。
可以在驱动类中设置分隔符。
2.1.5. NLineInputFormat
按照行数划分切片。
2.2. 自定义类
| 自定义 | 继承/实现 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| InputFormat | extends FileInputFormat | 定义输入文件的路径、读取方式(RecordReader) |
| RecordReader | extends RecordReader | 定义输入的KV,开流读取,实现读取的具体过程 |
| Partitioner | extends Partitioner | 定义分区规则,分区数需和ReduceTask数量一致 |
| 对象 | implements Writable | 实现序列化,使对象可以提交给框架 |
| key对象 | implements WritableComparable | 实现序列化与比较器,用于key的传输与比较 |
| Comparator | implements RawComparator | 定义一个比较器,用于key的比较 |
2.3. 分区
- 在写入环形缓冲区的时候按照分区规则在kvmeta中写入PARTITION。
- 分区表示该数据去往哪个ReduceTask,分区数需要和ReduceTask数量一致
- 分区数不能大于ReduceTask的数量
- 分区数可以小于ReduceTask的数量,但会产生闲置的Rducer,浪费空间
- 在SpillThread中会进行sortAndSpill(),对索引进行排序,遍历每个分区依次写入spill文件。
2.4. 比较key
提供一个key的比较器实现RawComparator
或key对象实现WritableComparable
2.5. Combiner
一个可选的中间函数,发生在Map阶段
- sortAndSpill()方法中 Sorter.sort()之后循环遍历partitions,每次都判断是否需要进行combiner
- mergeParts()方法中 遍历spills文件,判断时都需要进行combiner
用来减少发送到Reducer的数据量,提高网络效率以及Reduce端处理效率。
计算平均值时不能用Combiner
参考文献
https://blog.csdn.net/elpsyco/article/details/100597959
MR全流程** https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39261894/article/details/104630148
环形缓冲区:https://blog.csdn.net/lw305080/article/details/56479170?utm_source=blogxgwz4
Map输出跟踪:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39261894/article/details/104630148