**第1章
**
1.Agent:Agent是一个JVM进程,它以事件(event)的形式将数据从源头送到目的。Agent包含了三个部分:Source、Channel、Sink。
2.Source:Source 是负责接收数据到 Flume Agent 的组件。Source 组件可以处理各种类型、各种格式的日志数据,包括 avro、thrift、exec、jms、spooling directory、netcat、sequence generator、syslog、http、legacy。
3.Channel:Channel 是位于 Source 和 Sink 之间的缓冲区。因此,Channel 允许 Source 和 Sink 运作在不同的速率上。Channel 是线程安全的,可以同时处理几个 Source 的写入操作和几个 Sink 的读取操作。
Flume 自带两种 Channel:Memory Channel 和 File Channel 以及 Kafka Channel。 Memory Channel 是内存中的队列。Memory Channel 在不需要关心数据丢失的情景下适用。如果需要关心数据丢失,那么 Memory Channel 就不应该使用,因为程序死亡、机器宕机或者重启都会导致数据丢失。File Channel 将所有事件写到磁盘。因此在程序关闭或机器宕机的情况下不会丢失数据。
4.Sink:Sink 不断地轮询 Channel 中的事件且批量地移除它们,并将这些事件批量写入到存储或索引系统、或者被发送到另一个 Flume Agent。Sink 组件目的地包括 hdfs、logger、avro、thrift、ipc、file、HBase、solr、自定义。
5.Event:传输单元,Flume 数据传输的基本单元,以 Event 的形式将数据从源头送至目的地。 Event 由 Header 和 Body 两部分组成,Header 用来存放该 event 的一些属性,为 K-V 结构, Body 用来存放该条数据,形式为字节数组。
1.2.
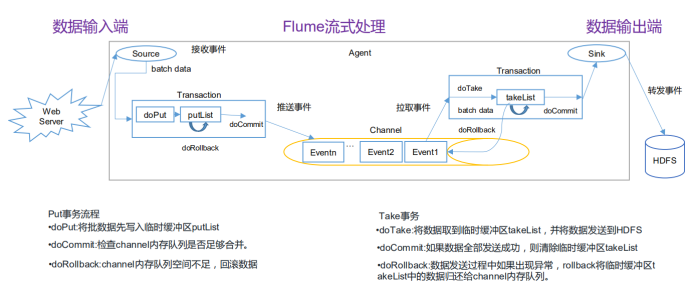
Source中的数据通过一个事务进入Channel。
Sink通过一个事务从Channel中拉取Event。
**
Channel中的数据由事件event构成,event由头信息(headers)和body构成:
headers 是一个Map构成的键值对
body 是一个byte[] 数组,存放数据的主体信息。
**
**
拦截器,判断event中的body信息,根据自定义的规则设置event的header。
定义一个类实现 Interceptor 接口,并重写接口方法;
在该类的内部定义一个静态内部类,该内部类实现Interceptor.Builder接口,重写接口方法(只要返回该类的一个对象return new 该类类名)。
**
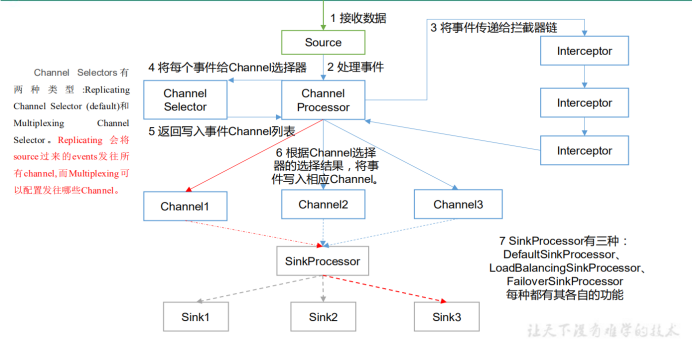
ChannelSelector 的作用就是选出 Event 将要被发往哪个 Channel。其共有两种类型,分别是 Replicating(复制)和 Multiplexing(多路复用)。ReplicatingSelector 会将同一个 Event 发往所有的 Channel,Multiplexing 会根据相应的原则,将不同的 Event 发往不同的 Channel。
**
SinkProcessor 共有三种类型 ,分别是 DefaultSinkProcessor(默认)、 LoadBalancingSinkProcessor(负载均衡) 和FailoverSinkProcessor(故障转移)
(1) DefaultSinkProcessor 对应的是单个的 Sink ;
LoadBalancingSinkProcessor 和 FailoverSinkProcessor 对应的是 Sink Group;
(2) LoadBalancingSinkProcessor 可以实现负载均衡的功能;有两种Selector供选择round_robin(轮询) 和 random(随机),默认为round_robin。
(3) FailoverSinkProcessor 可以实现故障转移的功能,一个高优先级的Sink可以优先使用,配置的优先级value 的值越大 优先级越高。如果没有定义优先级,那么优先级会按照配置文件中sink的定义顺序安排。
**第2章 Source & Channel
**
Source 是负责接收数据到 Flume Agent 的组件。Source 组件可以处理各种类型、各种格式的日志数据,常用Source如下:
netcat:监听本机的某个端口。
exec:监听某一条指令或某一个脚本的返回结果,适用于监控一个实时追加的文件,但不能保证数据不丢失。
Spooldir:监听某一个文件夹,
·如果这个文件夹里出现新的文件并且该文件没有指定后缀则会被扫描并最终传输到Sink端。
·扫描后该文件会被加上指定的后缀名。
·如果该文件已经有指定的后缀名则不会被扫描和传输。
·如果该文件夹已经存在x.suffix,再添加一个x文件,则该文件会被扫描但不会被改变后缀。
·可以用正则表达式指定不扫描的后缀。
·Spooldir能够保证数据不丢失,且能够实现断点续传,但延迟较高,不能实时监控。
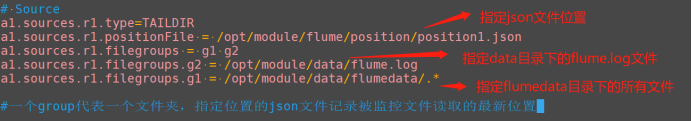
Taildir:对多个文件夹下的所有文件或指定文件实施监控,既能够实现断点续传,又可以保证数据不丢失,还能够进行实时监控。 Taildir Source 维护了一个 json 格式的 position File,其会定期的往 position File 中更新每个文件读取到的最新的位置,因此能够实现断点续传。
avro:监控本机端口,接受来自avro Sink的数据,用于客户端间传输。
自定义Source:继承AbstractSource类,实现Configurable, PollableSource接口,重写方法如下
configure(Context context):读取配置文件(XX.conf)中的配置信息
process():接收数据,将数据封装成一个个的Event,写入Channel。
getBackOffSleepIncrement():暂不用
getMaxBackOffSleepInterval():暂不用
**
Channel 是位于 Source 和 Sink 之间的缓冲区。因此,Channel 允许 Source 和 Sink 运作在不同的速率上。Channel 是线程安全的,可以同时处理几个 Source 的写入操作和几个 Sink 的读取操作。
Flume 自带两种 Channel:Memory Channel 和 File Channel 以及 Kafka Channel。
Memory Channel: 是内存中的队列。Memory Channel 在不需要关心数据丢失的情景下适用。如果需要关心数据丢失,那么 Memory Channel 就不应该使用,因为程序死亡、机器宕机或者重启都会导致数据丢失。
File Channel:将所有事件写到磁盘。因此在程序关闭或机器宕机的情况下不会丢失数据。
**
logger:打印INFO级别的日志,一般用于测试和debug。
hdfs:将数据内容输出到hdfs上
avro:和avro Source连接,用于flume之间的传输
file_roll:保存到本地文件
定义一个类继承AbstractSink,并实现Configurable接口,重写方法。
自定义Sink总会出现下述两个错误
java.lang.IllegalStateException: begin() called when transaction is OPEN! - you must either commit or rollback first
java.lang.IllegalStateException: begin() called when transaction is CLOSE! - you must either commit or rollback first
目前尚未解决
**
**
1. 案例描述:该案例在本机执行或跨机器执行,Flume监控本机xxxxx端口(自己设定),Flume的Source端读取数据,Sink端将读取内容输出到控制台。数据源来自netcat向客户端所在机器的指定端口发送数据。
Source :netcat
Channel:memory
Sink :logger
3. 创建Flume Agent配置文件**:netcat-memory-logger.conf
| # Name a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 a1.channels = c1 # Source a1.sources.r1.type = netcat a1.sources.r1.bind = localhost a1.sources.r1.port = 44444 # Sink a1.sinks.k1.type = logger # Channel a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 |
|---|

4. 启动Agent:
在 flumn目录下
bin/flume-ng agent -n a1 -c conf -f job/netcat-memory-logger.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
-n:agent名
-c:配置文件目录,目录下存放有flume-env.sh(保存jdk路径)以及log4j.properties
-f:Agent配置文件
-Dflume… :表示 flume 运行时动态修改 flume.root.logger 参数属性值,并将控制台日志打印级别设置为 INFO 级别。日志级别包括:log、info、warn、error。
5. 启动netcat:向本机的某个端口发送数据
nc localhost 44444
此时向阻塞进程的控制台输入内容,Agent端会接收到输入的内容并打印到控制台。
注意:
1) 在配置文件中a1.sources.r1.bind=localhost如果替换成 a1.sources.r1.bind=192.168.220.102那么启动netcat时也必须将localhost替换成192.168.220.102。
2) 如果配置文件中a1.sources.r1.bind=localhost那么启动netcat时输入192.168.220.102是无效的。
3) 可以在虚拟机103上启动netcat,向102的44444端口发送数据。
**
1. 案例描述:该案例在对某一条监控指令或某一个脚本做监控,将指令或脚本的返回结果打印在控制台。
Source :exec
Channel:memory
Sink :logger
3. 创建Flume Agent配置文件**:exec-memory-logger.conf
| # Name a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 a1.channels = c1 # Source a1.sources.r1.type = exec a1.sources.r1.command = tail -f /opt/module/hive/logs/hive.log # Sink a1.sinks.k1.type = logger # Channel a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 |
|---|
bin/flume-ng agent -n a1 -c conf -f job/exec-memory-logger.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
**
1. 案例描述:该案例在对某一条监控指令或某一个脚本做监控,将指令或脚本的返回结果以文件的形式保存在hdfs上。
2. 组件设置:
Source :exec
Channel:memory
Sink :hdfs
3. 创建Flume Agent配置文件:exec-memory-hdfs.conf
| # Name a2.sources = r2 a2.sinks = k2 a2.channels = c2 # Source a2.sources.r2.type = exec a2.sources.r2.command = tail -F /opt/module/hive/logs/hive.log # Sink a2.sinks.k2.type = hdfs a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.path = hdfs://hadoopstudy102:9000/flume/%Y%m%d/%H #上传文件的前缀 a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.filePrefix = logs- #是否按照时间滚动文件夹 a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.round = true #多少时间单位创建一个新的文件夹 a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.roundValue = 1 #重新定义时间单位 a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.roundUnit = hour #是否使用本地时间戳 a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true #积攒多少个 Event 才 flush 到 HDFS 一次 a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.batchSize = 1000 #设置文件类型,可支持压缩 a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.fileType = DataStream #多久生成一个新的文件 a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.rollInterval = 30 #设置每个文件的滚动大小(接近128m) a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.rollSize = 134217700 #文件的滚动与 Event 数量无关 a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.rollCount = 0 # Channel a2.channels.c2.type = memory a2.channels.c2.capacity = 1000 a2.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind a2.sources.r2.channels = c2 a2.sinks.k2.channel = c2 |
|---|
bin/flume-ng agent -n a2 -c conf -f job/exec-memory-logger.conf
**
**
1. 案例描述:该案例监控某个文件夹,返回结果以文件的形式保存在hdfs上。
2. 组件设置:
Source :spooldir
Channel:memory
Sink :hdfs
3. 创建Flume Agent配置文件:spooldir-memory-hdfs.conf
| # Name a2.sources = r2 a2.sinks = k2 a2.channels = c2 # Source a2.sources.r2.type = spooldir a2.sources.r2.spoolDir = /opt/module/flume/upload a2.sources.r2.fileSuffix = .COMPLETED a2.sources.r2.fileHeader = true #忽略所有以.tmp 结尾的文件,不上传 a2.sources.r2.ignorePattern = ([^ ]*\.tmp) # Sink a2.sinks.k2.type = hdfs a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.path = hdfs://hadoopstudy102:9000/flume/%Y%m%d/%H #上传文件的前缀 a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.filePrefix = logs- #是否按照时间滚动文件夹 a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.round = true #多少时间单位创建一个新的文件夹 a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.roundValue = 1 #重新定义时间单位 a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.roundUnit = hour #是否使用本地时间戳 a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true #积攒多少个 Event 才 flush 到 HDFS 一次 a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.batchSize = 1000 #设置文件类型,可支持压缩 a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.fileType = DataStream #多久生成一个新的文件 a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.rollInterval = 30 #设置每个文件的滚动大小(接近128m) a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.rollSize = 134217700 #文件的滚动与 Event 数量无关 a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.rollCount = 0 # Channel a2.channels.c2.type = memory a2.channels.c2.capacity = 1000 a2.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind a2.sources.r2.channels = c2 a2.sinks.k2.channel = c2 |
|---|

bin/flume-ng agent -n a2 -c conf -f job/spooldir-memory-hdfs.conf
**
1. 案例描述:该案例监控多个文件夹下的所有文件或指定文件,实现断点续传,返回结果以文件的形式保存在hdfs上。
2. 组件设置:
Source :taildir
Channel:memory
Sink :hdfs
3. 创建Flume Agent配置文件:taildir-memory-hdfs.conf
| # Name a1.sources=r1 a1.channels=c1 a1.sinks=k1 # Source a1.sources.r1.type=TAILDIR a1.sources.r1.positionFile = /opt/module/flume/position/position1.json a1.sources.r1.filegroups = g1 g2 a1.sources.r1.filegroups.g2 = /opt/module/data/flume.log a1.sources.r1.filegroups.g1 = /opt/module/data/flumedata/.* #Channel a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 #Sink a1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = hdfs://hadoopstudy102:9000/flume/%Y%m%d/%H #上传文件的前缀 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = logs- #是否按照时间滚动文件夹 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.round = true #多少时间单位创建一个新的文件夹 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue = 1 #重新定义时间单位 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit = hour #是否使用本地时间戳 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true #积攒多少个 Event 才 flush 到 HDFS 一次 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.batchSize = 1000 #设置文件类型,可支持压缩 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType = DataStream #多久生成一个新的文件 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval = 30 #设置每个文件的滚动大小(接近128m) a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize = 134217700 #文件的滚动与 Event 数量无关 a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount = 0 #Bind a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 |
|---|
bin/flume-ng agent -n a1 -c conf -f job/taildir-memory-hdfs
**
**
创建Flume Agent配置文件:kafka.conf
| # define a1.sources = r1 a1.sinks = k1 a1.channels = c1 # source a1.sources.r1.type = netcat a1.sources.r1.bind = localhost a1.sources.r1.port = 44444 # channel a1.channels.c1.type = memory a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # sink a1.sinks.k1.type = org.apache.flume.sink.kafka.KafkaSink a1.sinks.k1.kafka.bootstrap.servers = hadoopstudy102:9092,hadoopstudy103:9092,hadoopstudy104:9092 a1.sinks.k1.kafka.topic = first a1.sinks.k1.kafka.flumeBatchSize = 20 a1.sinks.k1.kafka.producer.acks = 1 a1.sinks.k1.kafka.producer.linger.ms = 1 # bind a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 |
|---|
启动kafka消费者:bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh —zookeeper hadoopstudy102:2181 —topic first
开启agent:bin/flume-ng agent -c conf -f job/kafka.conf -n a1
开启netcat发送数据:nc localhost 44444
**
**
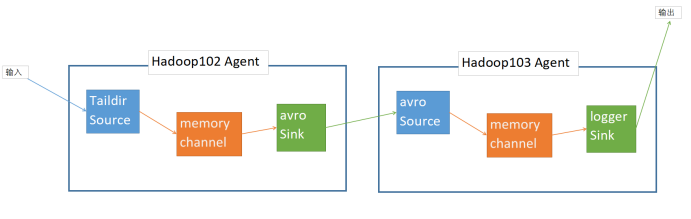
1. 案例描述:
如图所示,102的客户端采用Taildir Source监控文件,通过avro Sink将数据发送到Hadoop103的4142端口,Hadoop103的客户端监控本机4142端口,将接收到的数据打印到控制台。
hadoop102:Taildir -> memory -> avro
hadoop103:avro -> memory -> logger
分别在hadoop102和hadoop103上创建102.conf和103.conf,在102上开启客户端依赖于102.conf,在103上开启客户端依赖于103.conf。
| # Name a2.sources=r2 a2.channels=c2 a2.sinks=k2 # Source a2.sources.r2.type=TAILDIR a2.sources.r2.positionFile = /opt/module/flume/position/position3.json a2.sources.r2.filegroups = g1 a2.sources.r2.filegroups.g1 = /opt/module/data/hive.log # Channel a2.channels.c2.type=memory a2.channels.c2.capacity=1000 a2.channels.c2.transactionCapacity=100 # Sink a2.sinks.k2.type = avro a2.sinks.k2.hostname = hadoopstudy103 a2.sinks.k2.port = 4142 # Bind a2.sources.r2.channels = c2 a2.sinks.k2.channel = c2 |
|---|
| # Name a3.sources=r3 a3.channels=c3 a3.sinks=k3 # Source a3.sources.r3.type = avro a3.sources.r3.bind = hadoopstudy103 a3.sources.r3.port = 4142 # Channel a3.channels.c3.type=memory a3.channels.c3.capacity=1000 a3.channels.c3.transactionCapacity=100 # Sink a3.sinks.k3.type = logger # Bind a3.sources.r3.channels = c3 a3.sinks.k3.channel = c3 |
|---|
[flume] bin/flume-ng agent -n a3 -c conf -f job/jianDanChuanLian/103.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
102服务器作为数据的发送端,如果始终没有接收端,那么putList缓冲区和Channel可能因为堆积过多的数据而无法工作。所以要先打开数据的接收端,再打开数据的发送端。
**
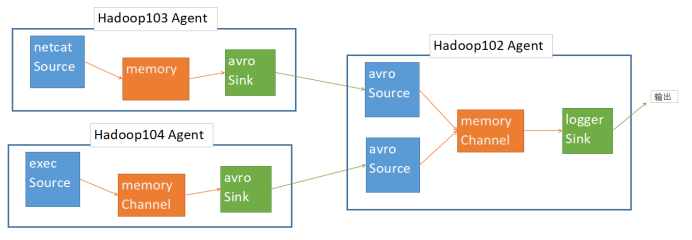
如图所示
| # Name a2.sources=r1 a2.channels=c1 a2.sinks=k1 # Source a2.sources.r1.type = avro a2.sources.r1.bind = hadoopstudy102 a2.sources.r1.port = 4141 # Channel a2.channels.c1.type=memory a2.channels.c1.capacity=1000 a2.channels.c1.transactionCapacity=100 # Sink a2.sinks.k1.type = logger # Bind a2.sources.r1.channels = c1 a2.sinks.k1.channel = c1 |
|---|
| # Name a3.sources = r1 a3.sinks = k1 a3.channels = c1 # Source a3.sources.r1.type = netcat a3.sources.r1.bind = localhost a3.sources.r1.port = 44444 # Channel a3.channels.c1.type = memory a3.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a3.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Sink a3.sinks.k1.type = avro a3.sinks.k1.hostname = hadoopstudy102 a3.sinks.k1.port = 4141 # Bind a3.sources.r1.channels =c1 a3.sinks.k1.channel = c1 |
|---|
| # Name a4.sources = r1 a4.sinks = k1 a4.channels = c1 # Source a4.sources.r1.type = exec a4.sources.r1.command = tail -F /opt/module/data/hive.log # Channel a4.channels.c1.type = memory a4.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a4.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Sink a4.sinks.k1.type = avro a4.sinks.k1.hostname = hadoopstudy102 a4.sinks.k1.port = 4141 # Bind a4.sources.r1.channels =c1 |
|---|
依次开启103、104、102客户端
bin/flume-ng agent -n a3 -c conf -f job/juhe/103.conf
bin/flume-ng agent -n a4 -c conf -f job/juhe/104.conf
bin/flume-ng agent -n a2 -c conf -f job/juhe/102.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
在103中 nc localhost 44444 ,输入内容
在104中 echo hahah >> /opt/module/data/hive.log
在102客户端查看控制台打印的结果。
**
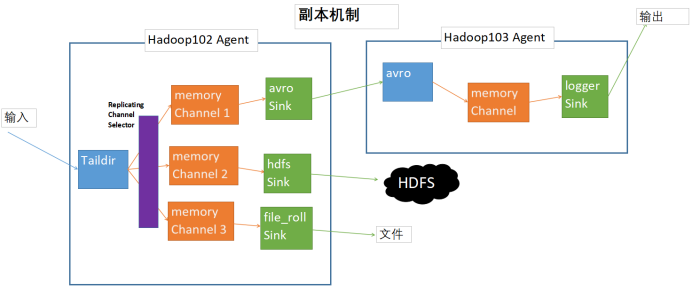
1. 案例描述:
如图所示,102的客户端采用Taildir Source监控文件,通过三个Channel将数据分别发送到Hadoop103Agent,HDFS,和本机文件输出。应用Replicating Channel Selector,在开启多路的客户端中进行replicating,replicating为默认配置,也可不进行设置。
hadoop102:Taildir -> memory -> avro
-> memory -> HDFS
-> memory -> file_roll
hadoop103:avro -> memory -> logger
分别在hadoop102和hadoop103上创建102.conf和103.conf,在102上开启客户端依赖于102.conf,在103上开启客户端依赖于103.conf。
| # Taildir -> memory -> avro -> memory -> HDFS -> memory -> logger # Name a2.sources=r1 a2.channels=c1 c2 c3 a2.sinks=k1 k2 k3 # Source a2.sources.r1.type=TAILDIR a2.sources.r1.positionFile = /opt/module/flume/position/position3.json a2.sources.r1.filegroups = g1 a2.sources.r1.filegroups.g1 = /opt/module/data/hive.log #将数据流赋值给所有channel (开启了副本机制,默认为副本机制,可添加) a2.sources.r1.selector.type = replicating # Channel a2.channels.c1.type=memory a2.channels.c1.capacity=1000 a2.channels.c1.transactionCapacity=100 a2.channels.c2.type=memory a2.channels.c2.capacity=1000 a2.channels.c2.transactionCapacity=100 a2.channels.c3.type=memory a2.channels.c3.capacity=1000 a2.channels.c3.transactionCapacity=100 # Sink a2.sinks.k1.type = avro a2.sinks.k1.hostname = hadoopstudy103 a2.sinks.k1.port = 4142 a2.sinks.k2.type = hdfs a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.path = hdfs://hadoopstudy102:9000/flume/%Y%m%d/%H a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.filePrefix = logs- a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.round = true a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.roundValue = 1 a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.roundUnit = hour a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.batchSize = 1000 a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.fileType = DataStream a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.rollInterval = 30 a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.rollSize = 134217700 a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.rollCount = 0 a2.sinks.k3.type = file_roll a2.sinks.k3.sink.directory = /opt/module/datas/fubenjizhi # Bind a2.sources.r1.channels = c1 c2 c3 a2.sinks.k1.channel = c1 a2.sinks.k2.channel = c2 a2.sinks.k3.channel = c3 |
|---|
103.conf
| # avro -> memory -> logger # Name a3.sources=r3 a3.channels=c3 a3.sinks=k3 # Source a3.sources.r3.type = avro a3.sources.r3.bind = hadoopstudy103 a3.sources.r3.port = 4142 # Channel a3.channels.c3.type=memory a3.channels.c3.capacity=1000 a3.channels.c3.transactionCapacity=100 # Sink a3.sinks.k3.type = logger # Bind a3.sources.r3.channels = c3 a3.sinks.k3.channel = c3 |
|---|
该方法不能自动创建文件夹,必须手动创建。
**
**
**

1. 案例描述:
如图所示,102的客户端采用Taildir Source监控文件,memory Channel 中的事务经过 LoadBalancing Sink Processor 由Sink Group1中的两个avro Sink 随机拉取。两个avro Sink 会将事务传递给103或104。
hadoop102:Taildir -> memory -> avro 1
-> avro 2
hadoop103:avro -> memory -> logger
hadoop104:avro -> memory -> logger
分别在hadoop102、hadoop103、hadoop104上创建102.conf、103.conf、104.conf,在102上开启客户端依赖于102.conf,在103上开启客户端依赖于103.conf,在104上开启客户端依赖于104.conf
| # Name a2.sources = r1 a2.channels = c1 a2.sinks = k1 k2 a2.sinkgroups = g1 # Source a2.sources.r1.type=TAILDIR a2.sources.r1.positionFile = /opt/module/flume/position/position4.json a2.sources.r1.filegroups = g1 a2.sources.r1.filegroups.g1 = /opt/module/data/hive.log # Channel a2.channels.c1.type = memory a2.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a2.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 #Sink Group a2.sinkgroups.g1.sinks = k1 k2 a2.sinkgroups.g1.processor.type = load_balance a2.sinkgroups.g1.processor.backoff = true a2.sinkgroups.g1.processor.selector = random # Sink a2.sinks.k1.type = avro a2.sinks.k1.hostname = hadoopstudy103 a2.sinks.k1.port = 4141 a2.sinks.k2.type = avro a2.sinks.k2.hostname = hadoopstudy104 a2.sinks.k2.port = 4142 # Bind a2.sources.r1.channels = c1 a2.sinks.k1.channel = c1 a2.sinks.k2.channel = c1 |
|---|
| # avro -> memory -> logger # Name a3.sources=r1 a3.channels=c1 a3.sinks=k1 # Source a3.sources.r1.type = avro a3.sources.r1.bind = hadoopstudy103 a3.sources.r1.port = 4141 # Channel a3.channels.c1.type=memory a3.channels.c1.capacity=1000 a3.channels.c1.transactionCapacity=100 # Sink a3.sinks.k1.type = logger # Bind a3.sources.r1.channels = c1 a3.sinks.k1.channel = c1 |
|---|
| # Name a4.sources=r1 a4.channels=c1 a4.sinks=k1 # Source a4.sources.r1.type = avro a4.sources.r1.bind = hadoopstudy104 a4.sources.r1.port = 4142 # Channel a4.channels.c1.type=memory a4.channels.c1.capacity=1000 a4.channels.c1.transactionCapacity=100 # Sink a4.sinks.k1.type = logger # Bind a4.sources.r1.channels = c1 a4.sinks.k1.channel = c1 |
|---|
103:bin/flume-ng agent -n a3 -c conf -f job/fuzaijunheng/103.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
104:bin/flume-ng agent -n a4 -c conf -f job/fuzaijunheng/104.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
102:bin/flume-ng agent -n a2 -c conf -f job/fuzaijunheng/102.conf
多添加几次内容,会发现被组合成事务的内容会随机发送到三个客户端。
**
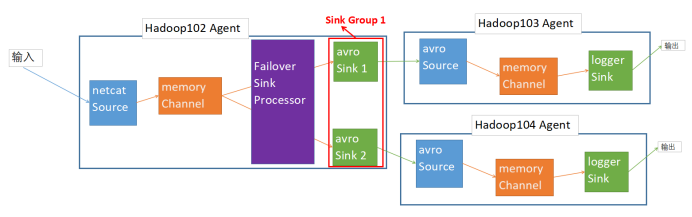
1. 案例描述:
如图所示,102的客户端采用netcat 监控44444端口,memory Channel 中的事务经过 Failover Sink Processor 由Sink Group1中优先级高的Sink先拉取,当优先级高的Sink的输出Agent挂掉了,则按照优先级继承。
hadoop102:netcat -> memory -> avro 1
-> avro 2
hadoop103:avro -> memory -> logger
hadoop104:avro -> memory -> logger
分别在hadoop102、hadoop103、hadoop104上创建102.conf、103.conf、104.conf,在102上开启客户端依赖于102.conf,在103上开启客户端依赖于103.conf,在104上开启客户端依赖于104.conf
| # Name a2.sources = r1 a2.channels = c1 a2.sinks = k1 k2 a2.sinkgroups = g1 # Source a2.sources.r1.type = netcat a2.sources.r1.bind = localhost a2.sources.r1.port = 44444 # Channel a2.channels.c1.type = memory a2.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a2.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Sink a2.sinks.k1.type = avro a2.sinks.k1.hostname = hadoopstudy103 a2.sinks.k1.port = 4141 a2.sinks.k2.type = avro a2.sinks.k2.hostname = hadoopstudy104 a2.sinks.k2.port = 4142 #Sink Group a2.sinkgroups.g1.sinks = k1 k2 a2.sinkgroups.g1.processor.type = failover a2.sinkgroups.g1.processor.priority.k1 = 5 a2.sinkgroups.g1.processor.priority.k2 = 10 a2.sinkgroups.g1.processor.maxpenalty = 10000 #Bind a2.sources.r1.channels = c1 a2.sinks.k1.channel = c1 a2.sinks.k2.channel = c1 |
|---|
| # avro -> memory -> logger # Name a3.sources=r1 a3.channels=c1 a3.sinks=k1 # Source a3.sources.r1.type = avro a3.sources.r1.bind = hadoopstudy103 a3.sources.r1.port = 4141 # Channel a3.channels.c1.type=memory a3.channels.c1.capacity=1000 a3.channels.c1.transactionCapacity=100 # Sink a3.sinks.k1.type = logger # Bind a3.sources.r1.channels = c1 a3.sinks.k1.channel = c1 |
|---|
| # Name a4.sources=r1 a4.channels=c1 a4.sinks=k1 # Source a4.sources.r1.type = avro a4.sources.r1.bind = hadoopstudy104 a4.sources.r1.port = 4142 # Channel a4.channels.c1.type=memory a4.channels.c1.capacity=1000 a4.channels.c1.transactionCapacity=100 # Sink a4.sinks.k1.type = logger # Bind a4.sources.r1.channels = c1 a4.sinks.k1.channel = c1 |
|---|
103:bin/flume-ng agent -n a3 -c conf -f job/guzhangzhuanyi/103.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
104:bin/flume-ng agent -n a4 -c conf -f job/guzhangzhuanyi/104.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
102:bin/flume-ng agent -n a2 -c conf -f job/guzhangzhuanyi/102.conf
104的优先级高于103,事务先由对应104的Sink拉取,当hadoop104的客户端挂掉,103的Sink才开始拉取事务。
**
**5.1. 案例1多路复用和拦截器(Multiplexing
根据Flume Agent 原理,事务在进入Channel 之前会经过拦截器(Interceptor)和 Channel选择器(Channel Selector)分配到Channel中,使用Multiplexing Channel Selectory,根据 event 中 Header 的某个 key 的值,将不同的 event 发送到不同的 Channel中。而拦截器(Interceptor)可以为不同类型的 event 的 Headers 中的 key 赋予不同的值。 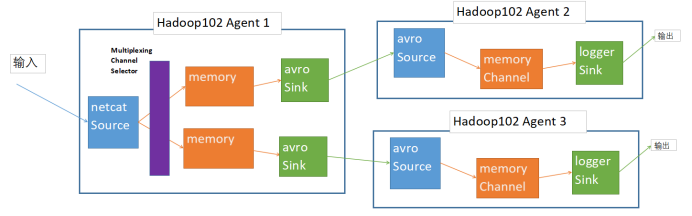
1. 案例描述:
自定义一个拦截器,判断event的body的长度,
如果长度≥10则将headers设置为
如果长度<10则将headers设置为
2. 定义拦截器:
根据1.4.1的方法定义拦截器,打成Jar包,放在/opt/module/flume/lib目录下
package com.mhj.interceptor;import org.apache.flume.Context;import org.apache.flume.Event;import org.apache.flume.interceptor.Interceptor;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;import java.util.Map;public class DIYInterceptor implements Interceptor {//声明一个存放事件的集合private List<Event> addHeaderEvents;@Overridepublic void initialize() {//初始化addHeaderEvents = new ArrayList<>();}@Overridepublic Event intercept(Event event) {//1.获取事件中的头信息Map<String, String> headers = event.getHeaders();//2.如果内容长度大于10则添加headers 设置为long,不大于则设置为shortif (event.getBody().length >= 10) {headers.put("type" , "long");} else {headers.put("type" , "short");}return event;}@Overridepublic List<Event> intercept(List<Event> events) {//1.清空集合addHeaderEvents.clear();//2.遍历events,for (Event event : events) {// 3.给每一个事件添加头信息,然后添加到List中addHeaderEvents.add(intercept(event));}//4.返回结果return addHeaderEvents;}@Overridepublic void close() {}//定义内部类public static class fk implements Interceptor.Builder {@Overridepublic Interceptor build() {return new DIYInterceptor();}@Overridepublic void configure(Context context) {}}}
3. 创建配置文件:
102-1.conf
| # Name a21.sources = r1 a21.channels= c1 c2 a21.sinks = k1 k2 # Source a21.sources.r1.type = netcat a21.sources.r1.bind = localhost a21.sources.r1.port = 44444 #Interceptor type为全类名$静态内部类名 a2.sources.r1.interceptors = i1 a2.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.type = com.mhj.interceptor.DIYInterceptor$fk #Channel Selector header和mapping后面的内容根据编程中定义的写 a2.sources.r1.selector.type = multiplexing a2.sources.r1.selector.header = type a2.sources.r1.selector.mapping.long = c1 a2.sources.r1.selector.mapping.short = c2 # Channel a21.channels.c1.type = memory a21.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a21.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 a21.channels.c2.type = memory a21.channels.c2.capacity = 1000 a21.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100 # Sink a21.sinks.k1.type = avro a21.sinks.k1.hostname = hadoopstudy102 a21.sinks.k1.port = 4141 a21.sinks.k2.type = avro a21.sinks.k2.hostname = hadoopstudy102 a21.sinks.k2.port = 4142 # Bind a21.sources.r1.channels = c1 c2 a21.sinks.k1.channel = c1 a21.sinks.k2.channel = c2 |
|---|
102-2.conf
| # Name a22.sources=r1 a22.channels=c1 a22.sinks=k1 # Source a22.sources.r1.type = avro a22.sources.r1.bind = hadoopstudy102 a22.sources.r1.port = 4141 # Channel a22.channels.c1.type=memory a22.channels.c1.capacity=1000 a22.channels.c1.transactionCapacity=100 # Sink a22.sinks.k1.type = logger # Bind a22.sources.r1.channels = c1 a22.sinks.k1.channel = c1 |
|---|
102-3.conf
| # Name a23.sources=r1 a23.channels=c1 a23.sinks=k1 # Source a23.sources.r1.type = avro a23.sources.r1.bind = hadoopstudy102 a23.sources.r1.port = 4142 # Channel a23.channels.c1.type=memory a23.channels.c1.capacity=1000 a23.channels.c1.transactionCapacity=100 # Sink a23.sinks.k1.type = logger # Bind a23.sources.r1.channels = c1 a23.sinks.k1.channel = c1 |
|---|
102:bin/flume-ng agent -n a3 -c conf -f job/duolufuyong/102-2.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
102:bin/flume-ng agent -n a4 -c conf -f job/duolufuyong/102-3.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
102:bin/flume-ng agent -n a2 -c conf -f job/duolufuyong/102-1.conf
字符个数大于等于10的将被打印在102-2的控制台;
字符个数小于10的将被打印在102-3的控制台
**
根据2.1中自定义Source的方法定义Source,最终将内容打印到本机控制台。
定义source 从配置文件中读取 name、money、delay,将读取的name按照空格切分成一个个独立的name,将name和money组合在一起生成“name:money”输出,每过delay个毫秒重复一次上述动作。
package com.mhj.source;import org.apache.flume.Context;import org.apache.flume.EventDeliveryException;import org.apache.flume.PollableSource;import org.apache.flume.conf.Configurable;import org.apache.flume.event.SimpleEvent;import org.apache.flume.source.AbstractSource;public class DIYSource extends AbstractSource implements Configurable , PollableSource {private int money;private String names;private String[] names_arr;private int delay;@Overridepublic void configure(Context context) {money = context.getInteger("money",888);names = context.getString("name" , "nobody");//每隔多少毫秒source产生一次数据delay = context.getInteger("delay",2000);names_arr = names.split(" ");}@Overridepublic Status process() throws EventDeliveryException {Status status = null;try {for (String name : names_arr) {//构建事件对象SimpleEvent event = new SimpleEvent();//设置body为 name:moneyevent.setBody((name+":"+money).getBytes());//将事件传给channel,经过拦截器,经过channel选择器getChannelProcessor().processEvent(event);status = Status.READY;}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();//如果事务执行出错则设置状态为回滚status = Status.BACKOFF;}//睡delay秒try {Thread.sleep(delay);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return status;}@Overridepublic long getBackOffSleepIncrement() {return 0;}@Overridepublic long getMaxBackOffSleepInterval() {return 0;}}
**
| # Name a2.sources = r1 a2.sinks = k1 a2.channels = c1 # Source a2.sources.r1.type = com.mhj.source.DIYSource a2.sources.r1.delay = 3000 a2.sources.r1.name = mhj lmf zk nzy a2.sources.r1.money = 200 # Sink a2.sinks.k1.type = logger # Channel a2.channels.c1.type = memory a2.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a2.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind a2.sources.r1.channels = c1 |
|---|
**
bin/flume-ng agent -n a2 -c conf -f job/DIYSource/102.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
**
1. 案例描述:通过netcat Source和memory Channel 以及自定义Sink构成一个Flume。自定义一个Sink实现对event中的body值进行提取,然后减去配置文件中的midValue,将处理后的信息打印到控制台。(定义的这个案例看上去没问题,但执行会出现2.3中所述错误,目前尚未解决)
2. 定义Sink:
根据2.3 Sink定义,案例定义如下所示
package com.mhj.sink;
import org.apache.flume.*;
import org.apache.flume.conf.Configurable;
import org.apache.flume.sink.AbstractSink;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class DIYSink extends AbstractSink implements Configurable {
Logger logger;
int midValue;
@Override
public void configure(Context context) {
logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DIYSink.class);
//读取配置文件里的字段
midValue = context.getInteger("midValue");
}
@Override
public Status process() throws EventDeliveryException {
//1.定义返回值,事件
Status status;
Event event;
//2.获取Channel
Channel channel = getChannel();
//3.从Channel获取事务
Transaction transaction = channel.getTransaction();
//4.开启事务
transaction.begin();
while(true) {
//5.从Channel获取数据
event = channel.take();
if (event !=null) {
break;
}
}
try {
//6.处理事件
int body = Integer.parseInt(String.valueOf(event.getBody()));
String res = String.valueOf((body-midValue));
logger.info(res);//这里调用INFO方法,将来日志输出为INFO级别
//7.提交事务
transaction.commit();
//8.成功提交,修改状态信息
status = Status.READY;
} catch (ChannelException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
//9.提交事务失败,回滚
transaction.rollback();
//10.修改状态
status = Status.BACKOFF;
} finally {
//11.关闭当前事务
transaction.close();
}
//12.返回状态信息
return status;
}
}
**
| # Name a2.sources = r1 a2.sinks = k1 a2.channels = c1 # Source a2.sources.r1.type = netcat a2.sources.r1.bind = localhost a2.sources.r1.port = 44444 # Channel a2.channels.c1.type = memory a2.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 a2.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Sink a2.sinks.k1.type = com.mhj.sink.DIYSink a2.sinks.k1.midValue = 320 # Bind a2.sources.r1.channels = c1 a2.sinks.k1.channel = c1 |
|---|
**
bin/flume-ng agent -n a2 -c conf -f job/DIYSink/102.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
**
过程参考5.1
1. 案例描述:通过定义拦截器,让指定的内容进入相应的topic,根据kafka的特性,无需添加channel即可让消息进入不同的目标。
2. 定义拦截器:
package com.mhj.interceptor;
import org.apache.flume.Context;
import org.apache.flume.Event;
import org.apache.flume.interceptor.Interceptor;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class TypeInterceptor implements Interceptor{
//声明一个存放事件的集合
private List<Event> addHeaderEvents;
@Override
public void initialize() {
//初始化
addHeaderEvents = new ArrayList<>();
}
//单个事件拦截
//传输的数据如果含有hello则头信息设置为 mhj ,如果不含有hello 则头信息设置为 others
@Override
public Event intercept(Event event) {
//1.获取事件中的头信息
Map<String, String> headers = event.getHeaders();
//2.根据事件中的body信息
String body = new String(event.getBody());
//3.根据body中是否有"hello"来决定添加怎样的头信息
if (body.contains("hello")) {
//4.添加头信息
// headers.put("type","mhj");
headers.put("topic","first");
} else {
//添加头信息
// headers.put("type","others");
headers.put("topic","second");
}
return event;
}
//批量事件拦截
@Override
public List<Event> intercept(List<Event> events) {
//1.清空集合
addHeaderEvents.clear();
//2.遍历events,
for (Event event : events) {
// 3.给每一个事件添加头信息,然后添加到List中
addHeaderEvents.add(intercept(event));
}
//4.返回结果
return addHeaderEvents;
}
@Override
public void close() {
}
public static class Builder implements Interceptor.Builder {
@Override
public Interceptor build() {
return new TypeInterceptor();
}
@Override
public void configure(Context context) {
}
}
}
3. 创建配置文件
# define
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# source
a1.sources.r1.type = netcat
a1.sources.r1.bind = localhost
a1.sources.r1.port = 44444
# interceptor
a1.sources.r1.interceptors = i1
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.type = com.mhj.interceptor.TypeInterceptor$Builder
# channel
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = org.apache.flume.sink.kafka.KafkaSink
a1.sinks.k1.kafka.bootstrap.servers = hadoopstudy102:9092,hadoopstudy103:9092,hadoopstudy104:9092
a1.sinks.k1.kafka.topic = first
a1.sinks.k1.kafka.flumeBatchSize = 20
a1.sinks.k1.kafka.producer.acks = 1
a1.sinks.k1.kafka.producer.linger.ms = 1
# bind
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
- 启动客户端
启动kafka消费者1:bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh —zookeeper hadoopstudy102:2181 —topic first
启动kafka消费者2:bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh —zookeeper hadoopstudy102:2181 —topic second
开启agent:bin/flume-ng agent -c conf -f job/kafka.conf -n a1
开启netcat发送数据:nc localhost 44444
**
Ganglia 由 gmond、gmetad 和 gweb 三部分组成。
gmond(Ganglia Monitoring Daemon)是一种轻量级服务,安装在每台需要收集指标数据的节点主机上。使用 gmond,你可以很容易收集很多系统指标数据,如 CPU、内存、 磁盘、网络和活跃进程的数据等。
gmetad(Ganglia Meta Daemon)整合所有信息,并将其以 RRD 格式存储至磁盘的服务。
gweb(Ganglia Web)Ganglia 可视化工具,gweb 是一种利用浏览器显示 gmetad 所存储数据的 PHP 前端。在 Web 界面中以图表方式展现集群的运行状态下收集的多种不同指标数据。
配置下载等见笔记
**
**7.1. 你是如何实现
**7.2. Flume 的 Source,Sink,
作用
(1)Source 组件是专门用来收集数据的,可以处理各种类型、各种格式的日志数据,
包括 avro、thrift、exec、jms、spooling directory、netcat、sequence generator、syslog、http、legacy
(2)Channel 组件对采集到的数据进行缓存,可以存放在 Memory 或 File 中。
(3)Sink 组件是用于把数据发送到目的地的组件,目的地包括 HDFS、Logger、avro、thrift、ipc、file、Hbase、solr、自定义。
**7.3. 你们
我公司采用的 Source 类型为
(1)监控后台日志:exec
(2)监控后台产生日志的端口:netcat
**
Channel Selectors,可以让不同的项目日志通过不同的Channel到不同的Sink中去。 官方文档上Channel Selectors 有两种类型:Replicating Channel Selector (default)和 Multiplexing Channel Selector 这两种Selector的区别是:
Replicating 会将Source过来的events发往所有channel;
Multiplexing可以选择该发往哪些Channel。
**
·增加 Source 个(使用 Tair Dir Source 时可增加 FileGroups 个数)可以增大 Source 的读取数据的能力。例如:当某一个目录产生的文件过多时需要将这个文件目录拆分成多个文件目录,同时配置好多个 Source 以保证 Source 有足够的能力获取到新产生的数据。
·batchSize 参数决定 Source 一次批量运输到 Channel 的 event 条数,适当调大这个参数可以提高 Source 搬运 Event 到 Channel 时的性能。
·type 选择 memory 时 Channel 的性能最好,但是如果 Flume 进程意外挂掉可能会丢失数据。type 选择 file 时 Channel 的容错性更好,但是性能上会比 memory channel 差。使用 file Channel 时 dataDirs 配置多个不同盘下的目录可以提高性能。
·capacity 参数决定 Channel 可容纳最大的 event 条数。
·transactionCapacity 参数决定每次 Source 往 channel里面写的最大event 条数和每次 Sink 从 channel 里面读的最大event条数。transactionCapacity 需要大于 Source 和 Sink 的 batchSize 参数。
·增加 Sink 的个数可以增加 Sink 消费 event 的能力。Sink 也不是越多越好够用就行,过多的 Sink 会占用系统资源,造成系统资源不必要的浪费。
·batchSize 参数决定 Sink 一次批量从 Channel 读取的 event 条数,适当调大这个参数可以提高 Sink 从 Channel 搬出 event 的性能。