简介
Java8中有两大最为重要的改变,第一个是Lambda表达式,另一个则是Stream API(java.util.stream.*)
Stream是Java8中处理集合的关键抽象概念,他可以指定你希望对集合进行的操作,,可以执行非常复杂的查找,过滤和映射数据等操作
使用Stream API 对集合数据进行操作,就类似于使用SQL执行的数据库查询,也可以使用Stream API 来并行执行操作,简而言之Stream API提供了一种高效且易于使用的处理数据的方式
什么是Stream
流(Stream)到底是什么呢?
是数据渠道,用于操作数据源(集合,数组等)所生成的元素序列,”集合讲的是数据,流讲的是计算!”
注意:
- Stream自己不会存储元素
- Stream不会改变源对象,相反,他们会返回一个持有结果的新Stream
- Stream操作是延迟执行的,这意味着他们会等到需要的时候才执行
Stream的操作三个步骤
创建Stream
一个数据源(如:集合,数组),获取一个流通过Collection系列集合提供的Stream()或parallelStream()创建流
@Testpublic void createStream(){// 1:通过Collection系列集合提供的stream() 或 parallelStream()List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();Stream<String> stream = list.stream();Stream<String> stringStream = list.parallelStream();}
通过Arrays中的静态方法Stream()获取数组流
@Testpublic void createStream(){// 2:通过Arrays中的静态方法Stream()获取数组流String[] strings = new String[10];Stream<String> stream1 = Arrays.stream(strings);}
通过Stream类中的静态方法of()创建流
@Testpublic void createStream(){// 3:通过Stream类中的静态方法of()Stream<String> stringStream1 = Stream.of("1", "2", "3");}
创建无线流
为什么叫无线流呢,是应为他是由一个执行开始,却没有结尾的语句返回的流,可以一直循环,所以叫无线流迭代
@Testpublic void createStream(){// 4:创建无限流// 迭代Stream<Integer> iterate = Stream.iterate(0, x -> x + 2);// 产生10个数值iterate.limit(10).forEach(System.out::println);}
生成
@Testpublic void createStream(){// 4:创建无限流// 生成Stream<Double> generate = Stream.generate(Math::random);generate.forEach(System.out::println);}
中间操作
一个中间操作链,对数据源的数据进行处理
创建数据源
Person实体类增加两个注解
创建数据源@AllArgsConstructor@NoArgsConstructor
多个中间操作可以链接起来形成一条流水线,除非流水线上触发终止操作,否则中间操作不会执行任何处理,而在终止操作时一次性全部处理,称为”惰性求值”List<Person> personList = Arrays.asList(new Person("张三",18),new Person("李四",22),new Person("王五",27),new Person("赵六",31),new Person("天启",50));
筛选与切片
filter
filter(Predicate p) - 接收Lambda,从流中排除某些元素@Test public void test2(){ // 过滤年龄大于30的人员 personList.stream().filter(x -> x.getAge() > 30).forEach(System.out::println); }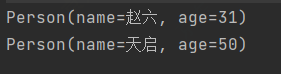
limit
limit(long maxSize) - 截断流,使其元素不超过给定数量@Test public void test3(){ // 获取两个人员 personList.stream().limit(2).forEach(System.out::println); }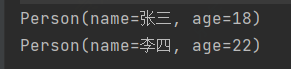
skip
skip(n) - 跳过元素,返回一个扔掉前N个元素的流,若流中元素不足N个,则返回一个空流,与limit(n)互补@Test public void test4(){ // 获取年龄大于18的后两位 personList.stream().filter(x -> x.getAge() > 18).skip(2).forEach(System.out::println); }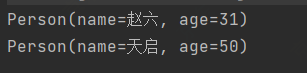
distinct
distinct() - 筛选,通过流所产生元素的hashcode()和equals()去除重复元素
修改数据源添加重复数据List<Person> personList = Arrays.asList( new Person("张三",18), new Person("张三",18), new Person("张三",18), new Person("李四",22), new Person("王五",27), new Person("赵六",31), new Person("天启",50) );@Test public void test5(){ // 去重 // 如果没有去除重复的,可以重写Equals和HashCode personList.stream().distinct().forEach(System.out::println); }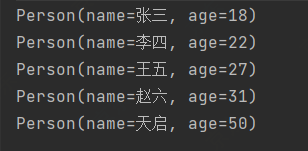
映射
map
map - 接收 Lambda,将元素转换成其他形式或提取信息,接收一个函数作为参数,该函数会被应用到每个元素上,并将其映射成一个新的元素@Test public void test6(){ List<String> list = Arrays.asList("a", "b", "c", "d"); // 全部转大写 list.stream().map(String::toUpperCase).forEach(System.out::println); }
flatmap
flatmap - 接收一个函数作为参数,将流中的每个值都换成另一个流,然后把所有流链接成一个流@Test public void test7(){ List<String> list = Arrays.asList("aaa","bbb","ccc","ddd"); // Stream<Stream<Character>> streamStream = list.stream().map(TestStreamApi::stringToCharacter); // 应为返回的是流,所以会造成嵌套流结构 // streamStream.forEach(s -> { // s.forEach(System.out::println); // }); // 这个时候就可以使用flatmap,将所有的流整合成一个流 list.stream().flatMap(TestStreamApi::stringToCharacter).forEach(System.out::println); }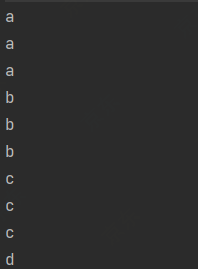
排序
sorted - 自然排序
sorted() - 自然排序@Test public void test8(){ List<String> list = Arrays.asList("c", "f", "a", "d", "b"); // 自然排序 list.stream().sorted().forEach(System.out::println); }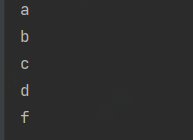
sorted - 定制排序
sorted(Comparator c) - 定制排序@Test public void test9(){ personList.stream().sorted(((o1, o2) -> { if(o1.getAge().equals(o2.getAge())){ return o1.getName().compareTo(o2.getName()); } return o1.getAge().compareTo(o2.getAge()); })).forEach(System.out::println); }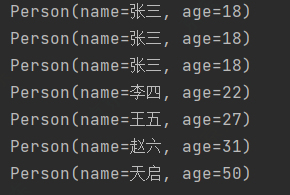
终止操作(终端操作)
一个终止操作,执行中间操作链,并产生结果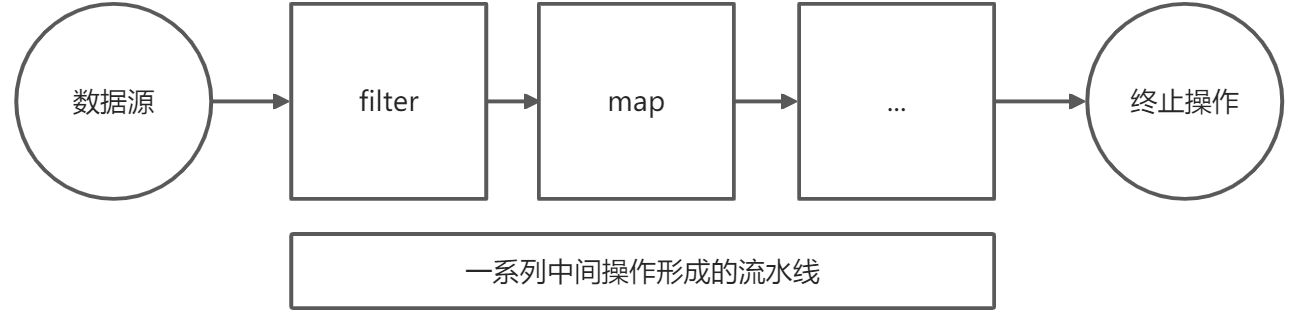
查找与匹配
allMatch - 检查是否匹配所有元素
anyMatch - 检查是否至少匹配一个元素
noneMatch - 检查是否没有匹配所有元素
findFirst - 返回第一个元素
findAny - 返回当前流中的任意元素
count - 返回流中元素的总个数
max - 返回流中的最大值
min - 返回流中的最小值
@Test
public void test10() {
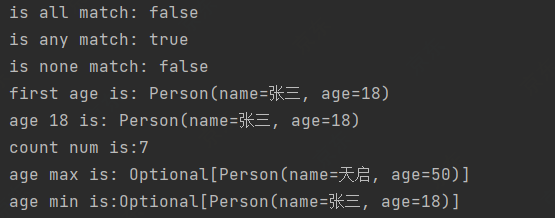
// 是否全部为18岁
boolean b = personList.stream().allMatch(e -> e.getAge().equals(18));
System.out.println("is all match: " + b);
// 是否有人为18岁
boolean b1 = personList.stream().anyMatch(e -> e.getAge().equals(18));
System.out.println("is any match: " + b1);
// 是否没有人为18岁
boolean b2 = personList.stream().noneMatch(e -> e.getAge().equals(18));
System.out.println("is none match: " + b2);
// 获取年龄最小的人
Optional<Person> first = personList.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparingInt(Person::getAge)).findFirst();
System.out.println("first age is: " + first.get());
// 从年龄为18岁的人群中随便找一个人
Optional<Person> any = personList.stream().filter(s -> s.getAge().equals(18)).findAny();
System.out.println("age 18 is: " + any.get());
// 获取总数
long count = personList.stream().count();
System.out.println("count num is:" + count);
// 获取年龄最大的人
Optional<Person> max = personList.stream().max(Comparator.comparingInt(Person::getAge));
System.out.println("age max is: " + max);
// 获取年龄最小的人
Optional<Person> min = personList.stream().min(Comparator.comparingInt(Person::getAge));
System.out.println("age min is:" + min);
}
归约
reduce(T identity,BinaryOperator) / reduce(BinaryOperator) - 可以从流中元素反复结合起来,得到一个值
@Test
public void test11(){
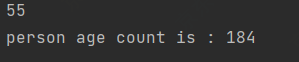
// 计算数组总和
List<Integer> integers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10);
Integer reduce = integers.stream().reduce(0, Integer::sum);
System.out.println(reduce);
// 计算人员年龄总和
Optional<Integer> reduce1 = personList.stream().map(Person::getAge).reduce(Integer::sum);
System.out.println("person age count is : "+reduce1.get());
}
收集
collect - 将流转化为其他形式,接收一个Collector接口的实现,用于Stream中元素做汇总的方法
@Test
public void test12(){
// 收集所有人员的名字并转换为List<String>
List<String> collect = personList.stream().map(Person::getName).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(" name list is : "+collect);
// 收集所有人员的名字并转换为Set<String>
Set<String> collect1 = personList.stream().map(Person::getName).collect(Collectors.toSet());
// 收集所有人员的名字并转换为HashSet<String>
HashSet<String> collect2 = personList.stream().map(Person::getName).collect(Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new));
// 获取总数
Long collect3 = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.counting());
System.out.println("counting is : "+collect3);
// 获取人员年龄平均自
Double collect4 = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.averagingInt(Person::getAge));
System.out.println("avg is :" + collect4);
// 获取所有人员的年龄总和
Integer collect5 = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.summingInt(Person::getAge));
System.out.println("sum is : " + collect5);
// 获取年龄最大的
Optional<Person> collect6 = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.maxBy((x, y) -> Integer.compare(x.getAge(), y.getAge())));
System.out.println("max by is : "+collect6);
// 获取年龄最小值
Optional<Integer> collect7 = personList.stream().map(Person::getAge).collect(Collectors.minBy(Integer::compare));
System.out.println("age min is:" + collect7);
// 按照年龄分组
Map<Integer, List<Person>> collect8 = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getAge));
System.out.println("grouping by is:"+collect8);
// 多级分组
Map<String, Map<String, List<Person>>> collect9 = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getName, Collectors.groupingBy(Person::getName)));
System.out.println("多级分组:"+collect9);
// 条件分区
Map<Boolean, List<Person>> collect10 = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(x -> x.getAge() > 25));
System.out.println("partitioningBy is:"+collect10);
// 多级分区
Map<Boolean, Map<Boolean, List<Person>>> collect11 = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(x -> x.getAge() > 25, Collectors.partitioningBy(y -> y.getName().equals("张三"))));
System.out.println("多级分区:"+collect11);
// 获取数值计算容器类
IntSummaryStatistics collect12 = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.summarizingInt(Person::getAge));
System.out.println(collect12.getMax());
System.out.println(collect12.getSum());
System.out.println(collect12.getAverage());
System.out.println(collect12.getMin());
System.out.println(collect12.getCount());
// 通过中划线链接所有人的名称
String collect13 = personList.stream().map(Person::getName).collect(Collectors.joining("-"));
System.out.println("names is :" + collect13);
}
name list is : [张三, 张三, 张三, 李四, 王五, 赵六, 天启]
counting is : 7
avg is :26.285714285714285
sum is : 184
max by is : Optional[Person(name=天启, age=50)]
age min is:Optional[18]
grouping by is:{50=[Person(name=天启, age=50)], 18=[Person(name=张三, age=18), Person(name=张三, age=18), Person(name=张三, age=18)], 22=[Person(name=李四, age=22)], 27=[Person(name=王五, age=27)], 31=[Person(name=赵六, age=31)]}
多级分组:{李四={李四=[Person(name=李四, age=22)]}, 张三={张三=[Person(name=张三, age=18), Person(name=张三, age=18), Person(name=张三, age=18)]}, 王五={王五=[Person(name=王五, age=27)]}, 赵六={赵六=[Person(name=赵六, age=31)]}, 天启={天启=[Person(name=天启, age=50)]}}
partitioningBy is:{false=[Person(name=张三, age=18), Person(name=张三, age=18), Person(name=张三, age=18), Person(name=李四, age=22)], true=[Person(name=王五, age=27), Person(name=赵六, age=31), Person(name=天启, age=50)]}
多级分区:{false={false=[Person(name=李四, age=22)], true=[Person(name=张三, age=18), Person(name=张三, age=18), Person(name=张三, age=18)]}, true={false=[Person(name=王五, age=27), Person(name=赵六, age=31), Person(name=天启, age=50)], true=[]}}
50
184
26.285714285714285
18
7
names is :张三-张三-张三-李四-王五-赵六-天启
并行流与顺序流
并行流就是把一个内容分成多个数据块,并用不同的线程分别处理每个数据块的流.
Java8中将并行进行了优化,我们可以很容易的对数据进行并行操作,Stream API 可以声明性的通过parallel()与sequential()在并行流与顺序流之间进行切换
顺序流计算1000亿的和
@Test
public void test13(){
Instant now = Instant.now();
long reduce = LongStream.rangeClosed(0, 100000000000L)
.reduce(0, Long::sum);
System.out.println(reduce);
Instant end = Instant.now();
System.out.println("耗时:"+Duration.between(now,end).toMillis());
}
CPU利用率
执行时间 ms
932356074711512064
耗时:50036
并行流计算1000亿的和
@Test
public void test14(){
Instant now = Instant.now();
long reduce = LongStream.rangeClosed(0, 100000000000L)
.parallel()
.reduce(0, Long::sum);
System.out.println(reduce);
Instant end = Instant.now();
System.out.println("耗时:"+Duration.between(now,end).toMillis());
}
CPU利用率
执行时间 ms
932356074711512064
耗时:20068
切换方法
sequential() 切换为顺序流
parallel() 切换为并行流
Optional类
简介
Optional
常用方法
of
Optional.of(T t) - 创建一个Optional的实例
@Test
public void test1(){
// 创建一个人员
Optional<Person> person = Optional.of(new Person());
// 获取其中的值
Person person1 = person.get();
System.out.println("get method : " + person1);
}
get method : Person(name=null, age=null)
empty
Optional.empty() - 创建一个空的Optional实例
@Test
public void test2(){
Optional<Object> empty = Optional.empty();
System.out.println(empty);
}
Optional.empty
ofNullable
Optional.ofNullable(T t) - 若t不为null 创建Optional实例,否则创建空实例
@Test
public void test3(){
Optional<Object> empty = Optional.ofNullable(null);
System.out.println(empty);
Optional<Object> empty1 = Optional.ofNullable(new Person());
System.out.println(empty1);
}
Optional.empty
Optional[Person(name=null, age=null)]
isPresent
isPresent() - 判断是否包含值
@Test
public void test4(){
Optional<Object> empty = Optional.ofNullable(null);
System.out.println(empty.isPresent());
Optional<Object> empty1 = Optional.ofNullable(new Person());
System.out.println(empty1.isPresent());
}
false
true
orElse
orElse(T t) - 如果调用对象包含值,返回该值,否则返回t
@Test
public void test5(){
Optional<Object> empty = Optional.ofNullable(null);
System.out.println(empty.orElse("this is null"));
Optional<Object> empty1 = Optional.ofNullable(new Person());
System.out.println(empty1.orElse("this is null"));
}
this is null
Person(name=null, age=null)
orElseGet
orElseGet(Supplier s) - 如果调用对象包含值,返回该值,否则返回s获取的值
@Test
public void test6(){
Optional<Object> empty = Optional.ofNullable(null);
System.out.println(empty.orElseGet(Person::new));
}
Person(name=null, age=null)
map
map(Function f) - 如果有值对其处理,并返回处理后的Optional,否则返回Optional.empty
@Test
public void test7(){
Optional<Person> empty = Optional.of(new Person("lisa", 18));
Optional<String> s = empty.map(Person::getName);
System.out.println(s.get());
}
lisa
flatMap
flatMap(Function mapper) - 与Map类似,要求返回值必须是Optional
@Test
public void test8(){
Optional<Person> empty = Optional.of(new Person("lisa", 18));
Optional<String> s = empty.flatMap(e -> Optional.of(e.getName()));
System.out.println(s.get());
}
lisa