属性
原文: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/essential/environment/properties.html
属性是作为键/值对管理的配置值。在每对中,键和值都是 String 值。密钥标识并用于检索值,就像变量名用于检索变量的值一样。例如,能够下载文件的应用程序可能使用名为“download.lastDirectory”的属性来跟踪上次下载所使用的目录。
要管理属性,请创建 java.util.Properties 的实例。此类提供以下方法:
- 将键/值对从流中加载到
Properties对象中, - 从其键中检索值,
- 列出键及其值,
- 枚举键,和
- 将属性保存到流。
有关流的介绍,请参阅基本 I / O 课程中的 I / O 流部分。
Properties扩展 java.util.Hashtable 。从Hashtable继承的一些方法支持以下操作:
- 测试以查看特定键或值是否在
Properties对象中, - 获取当前键/值对的数量,
- 删除一个键及其值,
- 将键/值对添加到
Properties列表, - 枚举值或键,
- 通过其键检索值,和
- 找出
Properties对象是否为空。
Security Considerations: Access to properties is subject to approval by the current security manager. The example code segments in this section are assumed to be in standalone applications, which, by default, have no security manager. The same code in an applet may not work depending on the browser in which it is running. See What Applets Can and Cannot Do in the Java Applets lesson for information about security restrictions on applets.
System类维护一个Properties对象,该对象定义当前工作环境的配置。有关这些属性的更多信息,请参见系统属性。本节的其余部分介绍了如何使用属性来管理应用程序配置。
应用程序生命周期中的属性
下图说明了典型应用程序如何在执行过程中使用Properties对象管理其配置数据。
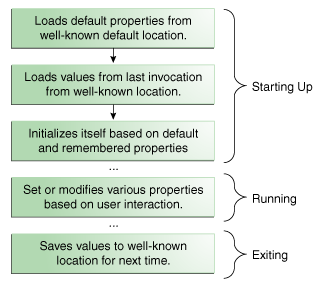
Starting Up前三个框中给出的操作在应用程序启动时发生。首先,应用程序将默认属性从一个众所周知的位置加载到Properties对象中。通常,默认属性与.class和应用程序的其他资源文件一起存储在磁盘上的文件中。 接下来,应用程序创建另一个Properties对象并加载上次运行应用程序时保存的属性。许多应用程序基于每个用户存储属性,因此在此步骤中加载的属性通常位于此应用程序在用户主目录中维护的特定目录中的特定文件中。最后,应用程序使用默认和记住的属性来初始化自身。 这里的关键是一致性。应用程序必须始终将属性加载并保存到同一位置,以便下次执行时可以找到它们。Running在执行应用程序期间,用户可能会在“首选项”窗口中更改某些设置,并更新Properties对象以反映这些更改。如果要在将来的会话中记住用户更改,则必须保存它们。Exiting退出时,应用程序将属性保存到其已知位置,以便在下次启动应用程序时再次加载。
设置属性对象
以下 Java 代码执行上一节中描述的前两个步骤:加载默认属性并加载记住的属性:
. . .// create and load default propertiesProperties defaultProps = new Properties();FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream("defaultProperties");defaultProps.load(in);in.close();// create application properties with defaultProperties applicationProps = new Properties(defaultProps);// now load properties// from last invocationin = new FileInputStream("appProperties");applicationProps.load(in);in.close();. . .
首先,应用程序设置默认的Properties对象。如果未在其他位置显式设置值,则此对象包含要使用的属性集。然后,load 方法从名为defaultProperties的磁盘上的文件中读取默认值。
接下来,应用程序使用不同的构造器来创建第二个Properties对象applicationProps,其默认值包含在defaultProps中。在检索属性时,默认值开始起作用。如果在applicationProps中找不到该属性,则搜索其默认列表。
最后,代码从名为appProperties的文件中将一组属性加载到applicationProps中。此文件中的属性是上次调用时从应用程序保存的属性,如下一节中所述。
保存属性
以下示例使用Properties.store从前一个示例中写出应用程序属性。每次都不需要保存默认属性,因为它们永远不会更改。
FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("appProperties");applicationProps.store(out, "---No Comment---");out.close();
store方法需要一个流写入,以及一个字符串,它用作输出顶部的注释。
获取房产信息
应用程序设置了Properties对象后,应用程序可以查询对象以获取有关其包含的各种键和值的信息。应用程序在启动后从Properties对象获取信息,以便它可以根据用户的选择进行初始化。 Properties类有几种获取属性信息的方法:
contains(Object value)和containsKey(Object key)如果值或键在Properties对象中,则返回true。Properties从Hashtable继承了这些方法。因此,他们接受Object参数,但只应使用String值。getProperty(String key)和getProperty(String key, String default)返回指定属性的值。第二个版本提供默认值。如果未找到密钥,则返回默认值。list(PrintStream s)和list(PrintWriter w)将所有属性写入指定的流或写入程序。这对调试很有用。elements(),keys()和propertyNames()返回包含Properties对象中包含的键或值(如方法名称所示)的Enumeration。keys方法仅返回对象本身的键;propertyNames方法也返回默认属性的键。stringPropertyNames()与propertyNames类似,但返回Set<String>,仅返回键和值均为字符串的属性名称。请注意,Set对象不支持Set对象,因此一个对象的更改不会影响另一个对象。size()返回当前键/值对的数量。
设置属性
用户在执行期间与应用程序的交互可能会影响属性设置。这些更改应反映在Properties对象中,以便在应用程序退出时保存它们(并调用store方法)。以下方法更改Properties对象中的属性:
setProperty(String key, String value)将键/值对放在Properties对象中。remove(Object key)删除与键关联的键/值对。
Note: Some of the methods described above are defined in Hashtable, and thus accept key and value argument types other than String. Always use Strings for keys and values, even if the method allows other types. Also do not invoke Hashtable.set or Hastable.setAll on Properties objects; always use Properties.setProperty.

