Sentinel 规则推送模式
Sentinel 规则的推送有三种模式:
| 推送模式 | 说明 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 原始模式 | api 将规则推送至客户端并直接更新到内存中,扩展写数据源(WritableDataSource) | 简单,无任何依赖 | 不保证一致性;规则保存在内存中,重启即消失;严重不建议用于生产环境 |
| Pull 模式 | 扩展写数据源(WritableDataSource),客户端主动向某个规则管理中心定期轮询拉取规则,这个规则中心可以是 RDBMS、文件等 | 简单,无任何依赖;规则持久化 | 不保证一致性;实时性不保证,拉取过于频繁也可能会有性能问题 |
| Push 模式 | 扩展读数据源(ReadableDataSource),规则中心统一推送,客户端通过注册监听器的方式时刻监听变化,es:使用 Nacos、zk 等配置中心;这种方式有更好的实时性和一致性保证;生产环境下一班采用 push 模式的数据源 | 规则持久化;一致性;快速 | 引入第三方依赖 |
原始模式
若不做任何修改,Dashboard 的推送规则方式是通过 api 将规则推送至客户端并直接更新到内存中: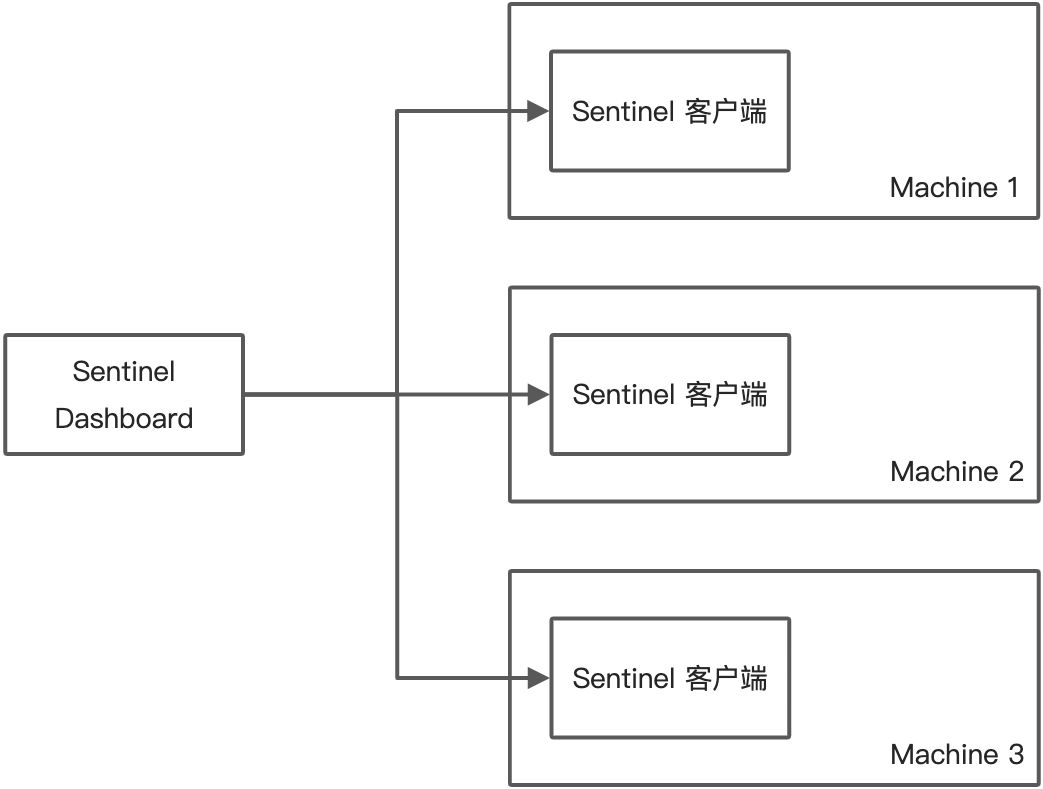
这种做法的好处是简单,无依赖;坏处是应用重启规则就会消失,仅用于简单测试,不能用于生产环境
拉模式
pull 模式的数据源(如本地文件、RDBMS 等)一般是可写入的;使用时需在客户端注册数据源:将对应的读数据源注册至对应的 RuleManager,将写数据源注册至 transport 的WritableDataSourceRegistry中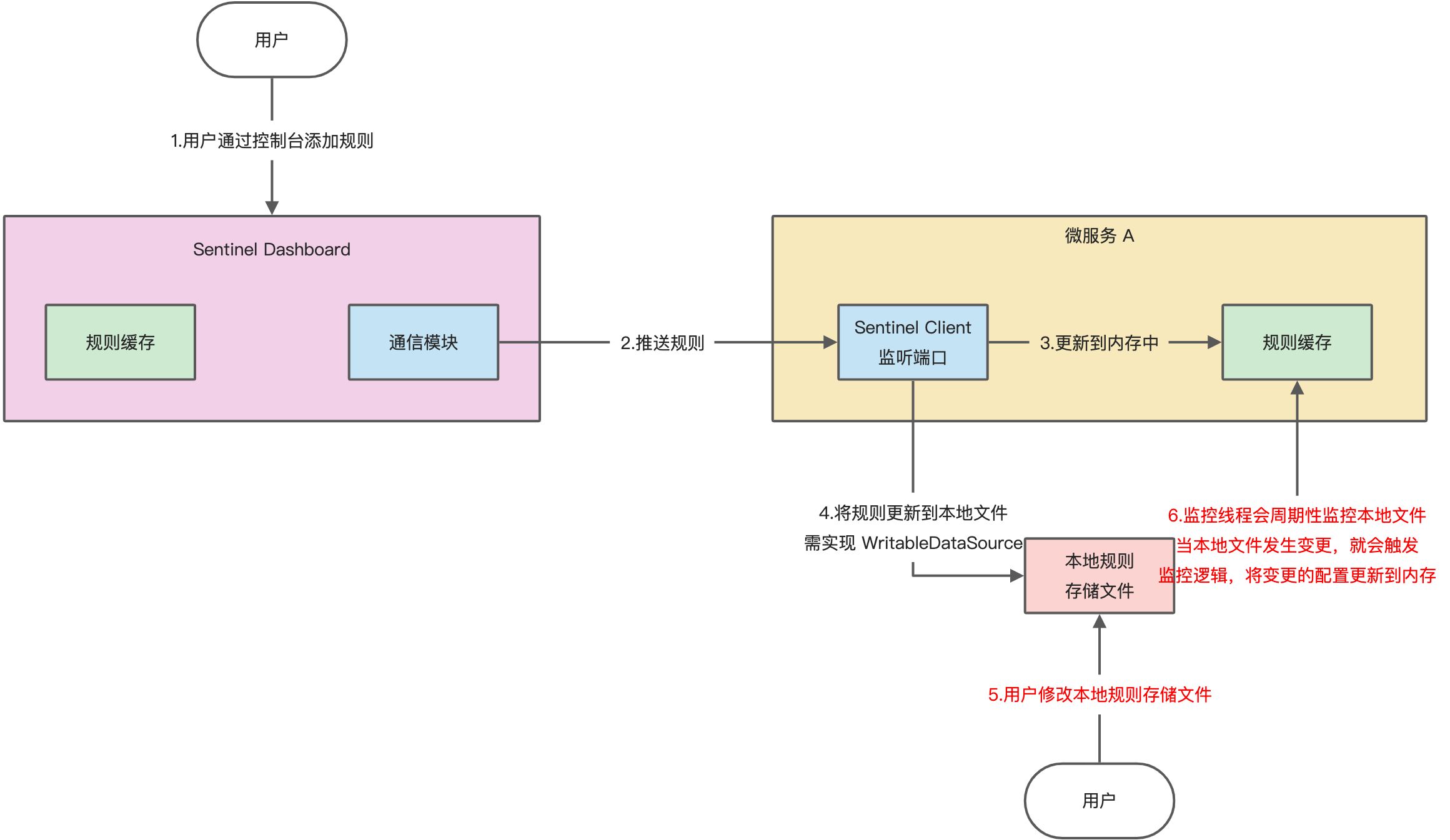
首先 Sentinel 控制台通过 api 将规则推送至客户端并更新到内存中,接着注册的写数据源会将新的规则保存到本地的文件中;使用 pull 模式的数据源时一般无需对 Sentinel 控制台进行改造;
官方 demo:sentinel-demo/sentinel-demo-dynamic-file-rule
引入依赖:
<dependency><groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId><artifactId>sentinel-datasource-extension</artifactId><version>1.8.0</version></dependency>
核心代码:
// FileRefreshableDataSource 会周期性的读取文件以获取规则,当文件有更新时会及时发现,并将规则更新到内存中。ReadableDataSource<String, List<FlowRule>> ds = new FileRefreshableDataSource<>(flowRulePath, source -> JSON.parseObject(source, new TypeReference<List<FlowRule>>() {}));// 将可读数据源注册至 FlowRuleManager.FlowRuleManager.register2Property(ds.getProperty());WritableDataSource<List<FlowRule>> wds = new FileWritableDataSource<>(flowRulePath, this::encodeJson);// 将可写数据源注册至 transport 模块的 WritableDataSourceRegistry 中.// 这样收到控制台推送的规则时,Sentinel 会先更新到内存,然后将规则写入到文件中.WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerFlowDataSource(wds);
拉模式改造
实现 InitFunc 接口,在 init 中处理 DataSource 初始化逻辑,并利用 SPI 机制实现加载
部分代码:
public class FileDataSourceInit implements InitFunc {@Overridepublic void init() throws Exception {//创建文件存储目录RuleFileUtils.mkdirIfNotExits(PersistenceRuleConstant.storePath);//创建规则文件RuleFileUtils.createFileIfNotExits(PersistenceRuleConstant.rulesMap);//处理流控规则逻辑dealFlowRules();// 处理降级规则dealDegradeRules();// 处理系统规则dealSystemRules();// 处理热点参数规则dealParamFlowRules();// 处理授权规则dealAuthRules();}private void dealFlowRules() throws FileNotFoundException {String ruleFilePath = PersistenceRuleConstant.rulesMap.get(PersistenceRuleConstant.FLOW_RULE_PATH).toString();//创建流控规则的可读数据源ReadableDataSource<String, List<FlowRule>> flowRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource(ruleFilePath, RuleListConverterUtils.flowRuleListParser);// 将可读数据源注册至FlowRuleManager 这样当规则文件发生变化时,就会更新规则到内存FlowRuleManager.register2Property(flowRuleRDS.getProperty());WritableDataSource<List<FlowRule>> flowRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<List<FlowRule>>(ruleFilePath, RuleListConverterUtils.flowFuleEnCoding);// 将可写数据源注册至 transport 模块的 WritableDataSourceRegistry 中.// 这样收到控制台推送的规则时,Sentinel 会先更新到内存,然后将规则写入到文件中.WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerFlowDataSource(flowRuleWDS);}private void dealDegradeRules() throws FileNotFoundException {//讲解规则文件路径String degradeRuleFilePath = PersistenceRuleConstant.rulesMap.get(PersistenceRuleConstant.DEGRAGE_RULE_PATH).toString();//创建流控规则的可读数据源ReadableDataSource<String, List<DegradeRule>> degradeRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource(degradeRuleFilePath, RuleListConverterUtils.degradeRuleListParse);// 将可读数据源注册至FlowRuleManager 这样当规则文件发生变化时,就会更新规则到内存DegradeRuleManager.register2Property(degradeRuleRDS.getProperty());WritableDataSource<List<DegradeRule>> degradeRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>(degradeRuleFilePath, RuleListConverterUtils.degradeRuleEnCoding);// 将可写数据源注册至 transport 模块的 WritableDataSourceRegistry 中.// 这样收到控制台推送的规则时,Sentinel 会先更新到内存,然后将规则写入到文件中.WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerDegradeDataSource(degradeRuleWDS);}private void dealSystemRules() throws FileNotFoundException {//讲解规则文件路径String systemRuleFilePath = PersistenceRuleConstant.rulesMap.get(PersistenceRuleConstant.SYSTEM_RULE_PATH).toString();//创建流控规则的可读数据源ReadableDataSource<String, List<SystemRule>> systemRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource(systemRuleFilePath, RuleListConverterUtils.sysRuleListParse);// 将可读数据源注册至FlowRuleManager 这样当规则文件发生变化时,就会更新规则到内存SystemRuleManager.register2Property(systemRuleRDS.getProperty());WritableDataSource<List<SystemRule>> systemRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>(systemRuleFilePath, RuleListConverterUtils.sysRuleEnCoding);// 将可写数据源注册至 transport 模块的 WritableDataSourceRegistry 中.// 这样收到控制台推送的规则时,Sentinel 会先更新到内存,然后将规则写入到文件中.WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerSystemDataSource(systemRuleWDS);}private void dealParamFlowRules() throws FileNotFoundException {//讲解规则文件路径String paramFlowRuleFilePath = PersistenceRuleConstant.rulesMap.get(PersistenceRuleConstant.HOT_PARAM_RULE).toString();//创建流控规则的可读数据源ReadableDataSource<String, List<ParamFlowRule>> paramFlowRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource(paramFlowRuleFilePath, RuleListConverterUtils.paramFlowRuleListParse);// 将可读数据源注册至FlowRuleManager 这样当规则文件发生变化时,就会更新规则到内存ParamFlowRuleManager.register2Property(paramFlowRuleRDS.getProperty());WritableDataSource<List<ParamFlowRule>> paramFlowRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>(paramFlowRuleFilePath, RuleListConverterUtils.paramRuleEnCoding);// 将可写数据源注册至 transport 模块的 WritableDataSourceRegistry 中.// 这样收到控制台推送的规则时,Sentinel 会先更新到内存,然后将规则写入到文件中.ModifyParamFlowRulesCommandHandler.setWritableDataSource(paramFlowRuleWDS);}private void dealAuthRules() throws FileNotFoundException {//讲解规则文件路径String authFilePath = PersistenceRuleConstant.rulesMap.get(PersistenceRuleConstant.AUTH_RULE_PATH).toString();//创建流控规则的可读数据源ReadableDataSource<String, List<AuthorityRule>> authRuleRDS = new FileRefreshableDataSource(authFilePath, RuleListConverterUtils.authorityRuleParse);// 将可读数据源注册至FlowRuleManager 这样当规则文件发生变化时,就会更新规则到内存AuthorityRuleManager.register2Property(authRuleRDS.getProperty());WritableDataSource<List<AuthorityRule>> authRuleWDS = new FileWritableDataSource<>(authFilePath, RuleListConverterUtils.authorityEncoding);// 将可写数据源注册至 transport 模块的 WritableDataSourceRegistry 中.// 这样收到控制台推送的规则时,Sentinel 会先更新到内存,然后将规则写入到文件中.WritableDataSourceRegistry.registerAuthorityDataSource(authRuleWDS);}}
推模式
对于 push 模式的数据源,es:远程配置中心(zk、Nacos 等),推送的操作不应由 Sentinel 客户端进行,而应该经控制台统一进行管理,直接进行推送,数据源仅负责获取配置中心推送的配置并更新到本地;因此推送规则正确的做法应该是配置中心控制台/Sentinel 控制台 --> 配置中心 --> Sentinel 数据源 --> Sentinel
基于 Nacos 配置中心实现推送
官方 demo:sentinel-demo-nacos-datasource
引入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-datasource-nacos</artifactId>
<version>1.8.0</version>
</dependency>
核心代码:
// nacos server ip
private static final String remoteAddress = "localhost:8848";
// nacos group
private static final String groupId = "Sentinel:Demo";
// nacos dataId
private static final String dataId = "com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.demo.flow.rule";
ReadableDataSource<String, List<FlowRule>> flowRuleDataSource = new NacosDataSource<>(remoteAddress, groupId, dataId,source -> JSON.parseObject(source, new TypeReference<List<FlowRule>>() {}));
FlowRuleManager.register2Property(flowRuleDataSource.getProperty());
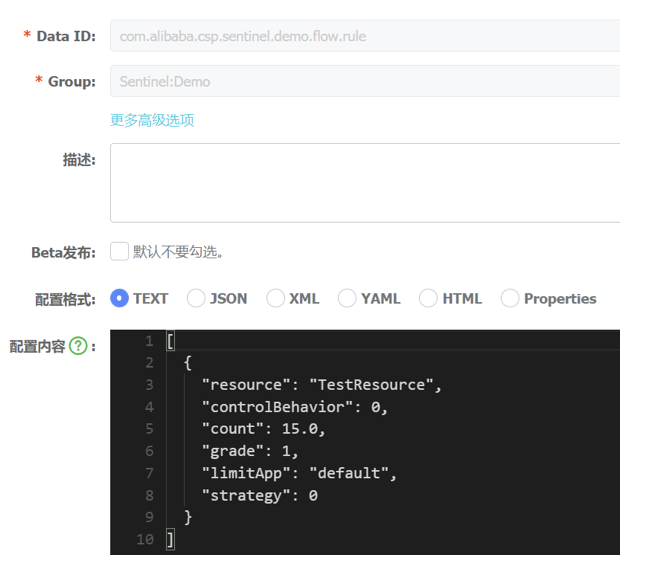
nacos 配置中心中配置流控规则:
[
{
"resource": "TestResource",
"controlBehavior": 0,
"count": 10.0,
"grade": 1,
"limitApp": "default",
"strategy": 0
}
]
微服务中通过 yml 配置实现
SentinelProperties内部提供了TreeMap类型的datasource属性用于配置数据源信息
引入依赖:
<!--sentinel持久化 采用 Nacos 作为规则配置数据源-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-datasource-nacos</artifactId>
</dependency>
yml 配置:
spring:
application:
name: mall-user-sentinel-demo
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
sentinel:
transport:
# 添加sentinel的控制台地址
dashboard: 127.0.0.1:8080
# 指定应用与Sentinel控制台交互的端口,应用本地会起一个该端口占用的HttpServer
port: 8719
datasource:
ds1:
nacos:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
dataId: ${spring.application.name}
groupId: DEFAULT_GROUP
data-type: json
rule-type: flow
nacos 配置中心添加:
[
{
"resource": "userinfo",
"limitApp": "default",
"grade": 1,
"count": 1,
"strategy": 0,
"controlBehavior": 0,
"clusterMode": false
}
]
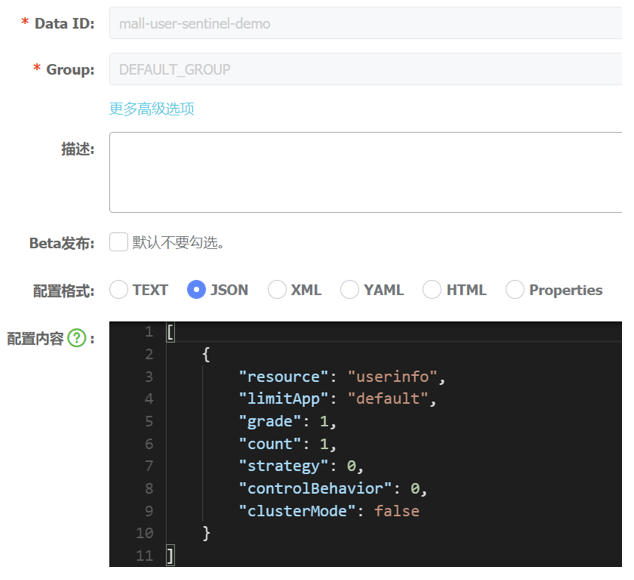
缺点:直接在 Sentinel Dashboard 中修改规则配置,配置中心的配置不会发生变化
基于 Sentinel 控制台实现推送
从 Sentinel 1.4.0 开始,Sentinel 控制台提供
DynamicRulePublisher和DynamicRuleProvider接口用于实现应用维度的规则推送和拉取
Sentinel Dashboard 改造
在 com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.dashboard.rule 包下创建 nacos 包,然后把各种场景的配置规则拉取和推送的实现类写到此包下: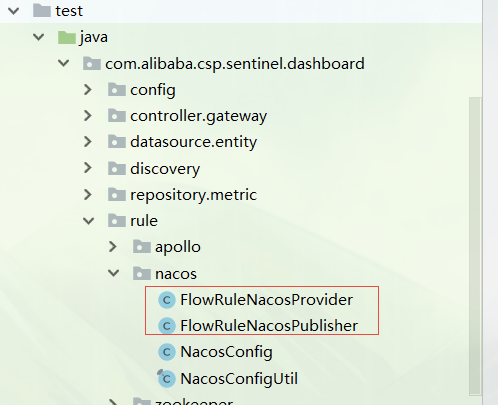
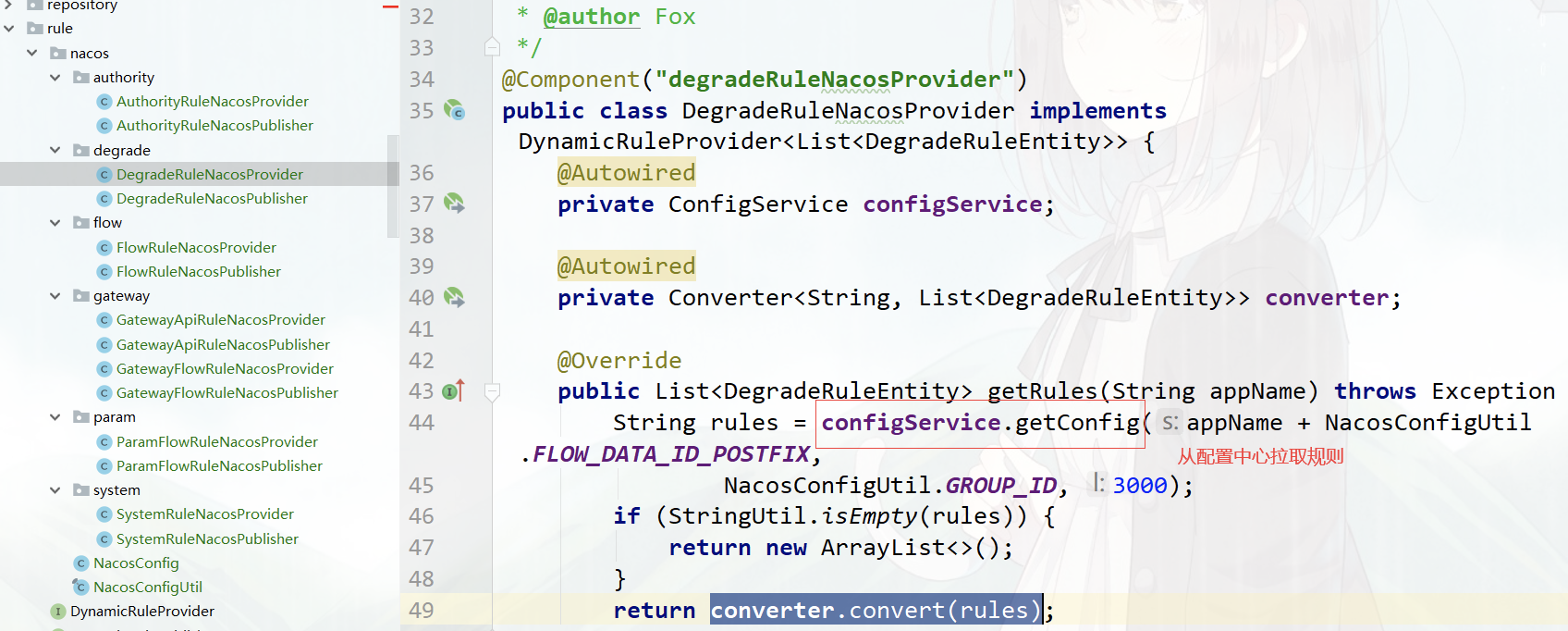
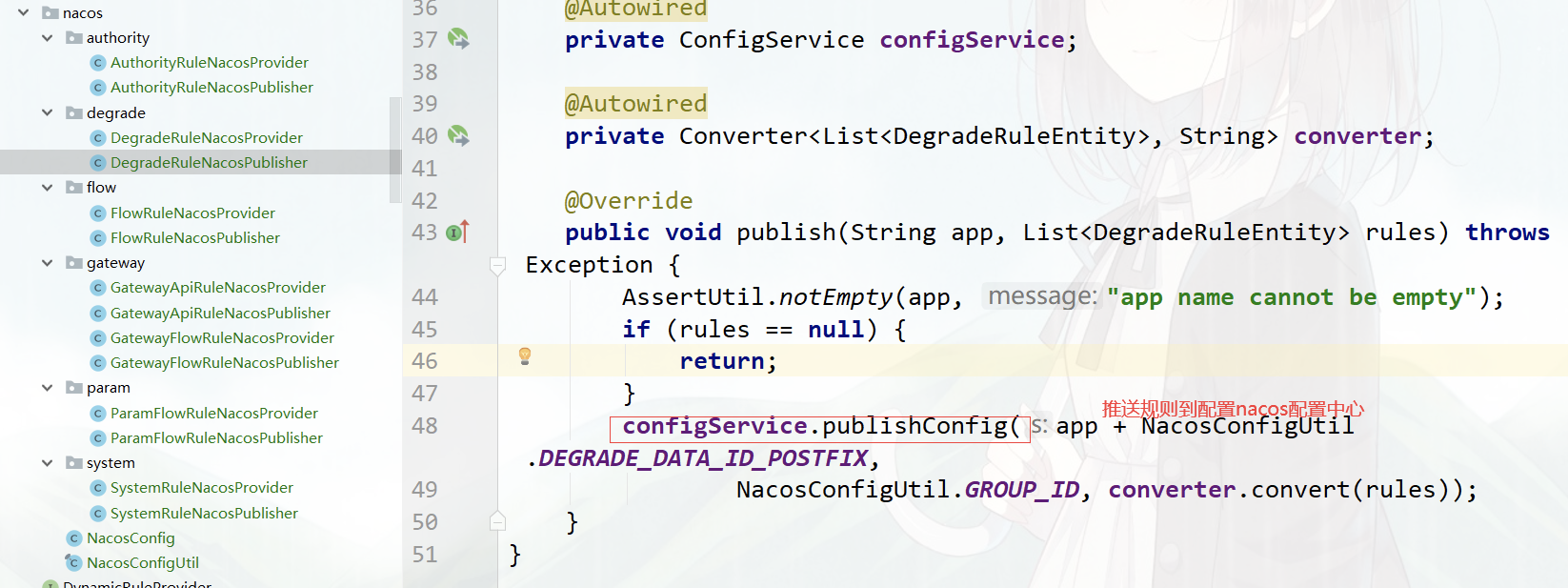
注:微服务接入 Sentinel client,yml 配置需匹配对应的规则后缀
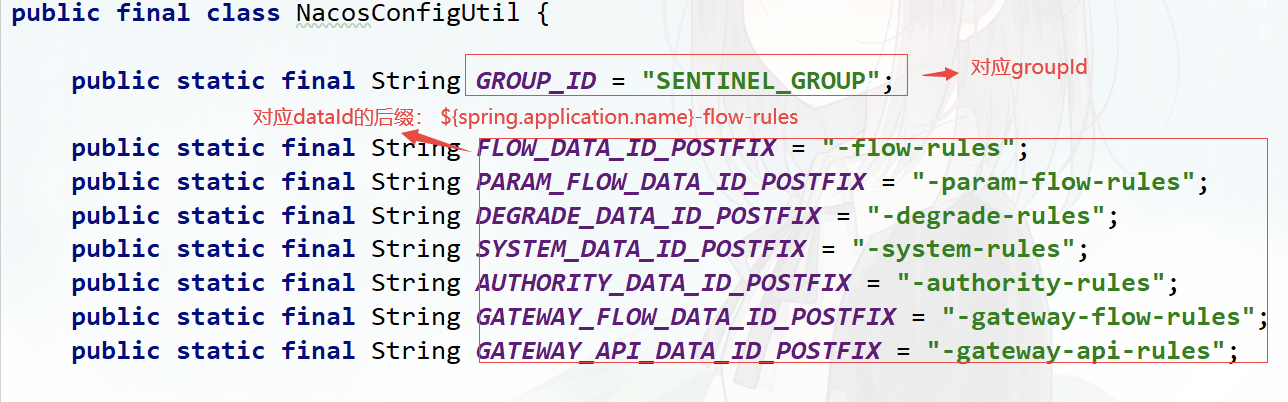
进入 com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.dashboard.controller 包下修改对应的规则 controller 实现类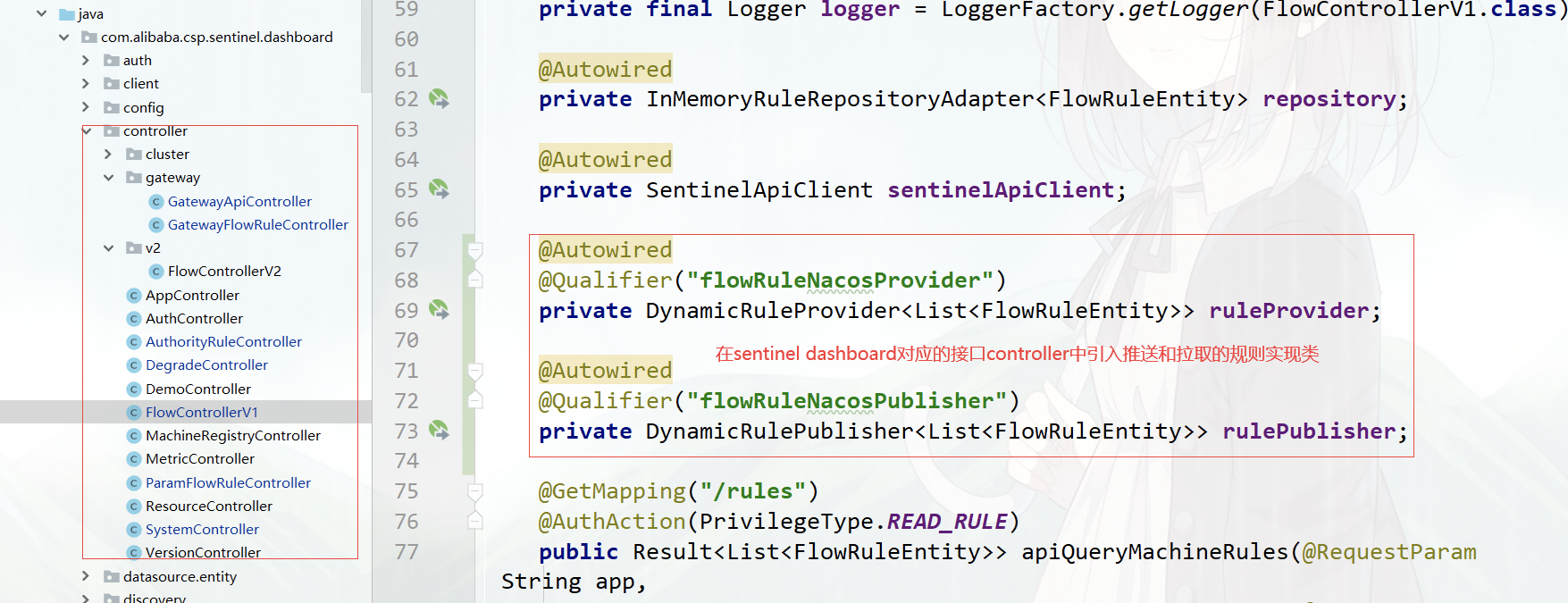
以流控规则为例,从 Nacos 配置中心获取所有的流控规则
@GetMapping("/rules")
@AuthAction(PrivilegeType.READ_RULE)
public Result<List<FlowRuleEntity>> apiQueryMachineRules(@RequestParam String app,
@RequestParam String ip,
@RequestParam Integer port) {
if (StringUtil.isEmpty(app)) {
return Result.ofFail(-1, "app can't be null or empty");
}
if (StringUtil.isEmpty(ip)) {
return Result.ofFail(-1, "ip can't be null or empty");
}
if (port == null) {
return Result.ofFail(-1, "port can't be null");
}
try {
// List<FlowRuleEntity> rules = sentinelApiClient.fetchFlowRuleOfMachine(app, ip, port);
//从配置中心获取规则配置
List<FlowRuleEntity> rules = ruleProvider.getRules(app, ip, port);
rules = repository.saveAll(rules);
return Result.ofSuccess(rules);
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
logger.error("Error when querying flow rules", throwable);
return Result.ofThrowable(-1, throwable);
}
}
新增流控规则,会推送到 nacos 配置中心:
@PostMapping("/rule")
@AuthAction(PrivilegeType.WRITE_RULE)
public Result<FlowRuleEntity> apiAddFlowRule(@RequestBody FlowRuleEntity entity) {
Result<FlowRuleEntity> checkResult = checkEntityInternal(entity);
if (checkResult != null) {
return checkResult;
}
entity.setId(null);
Date date = new Date();
entity.setGmtCreate(date);
entity.setGmtModified(date);
entity.setLimitApp(entity.getLimitApp().trim());
entity.setResource(entity.getResource().trim());
try {
entity = repository.save(entity);
//publishRules(entity.getApp(), entity.getIp(), entity.getPort()).get(5000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
//发布规则到配置中心
publishRules(entity.getApp());
return Result.ofSuccess(entity);
} catch (Throwable t) {
Throwable e = t instanceof ExecutionException ? t.getCause() : t;
logger.error("Failed to add new flow rule, app={}, ip={}", entity.getApp(), entity.getIp(), e);
return Result.ofFail(-1, e.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* 发布到配置中心
* @param app
* @throws Exception
*/
private void publishRules(/*@NonNull*/ String app) throws Exception {
List<FlowRuleEntity> rules = repository.findAllByApp(app);
rulePublisher.publish(app, rules);
}
测试:微服务接入改造后的 Sentinel Dashboard
引入依赖:
<!--sentinel持久化 采用 Nacos 作为规则配置数据源-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.csp</groupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-datasource-nacos</artifactId>
</dependency>
增加 yml 配置:
server:
port: 8806
spring:
application:
name: mall-user-sentinel-rule-push-demo #微服务名称
#配置nacos注册中心地址
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
sentinel:
transport:
# 添加sentinel的控制台地址
dashboard: 127.0.0.1:8080
# 指定应用与Sentinel控制台交互的端口,应用本地会起一个该端口占用的HttpServer
#port: 8719
datasource:
# ds1: #名称自定义,唯一
# nacos:
# server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
# dataId: ${spring.application.name}
# groupId: DEFAULT_GROUP
# data-type: json
# rule-type: flow
flow-rules:
nacos:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
dataId: ${spring.application.name}-flow-rules
groupId: SENTINEL_GROUP # 注意groupId对应Sentinel Dashboard中的定义
data-type: json
rule-type: flow
degrade-rules:
nacos:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
dataId: ${spring.application.name}-degrade-rules
groupId: SENTINEL_GROUP
data-type: json
rule-type: degrade
param-flow-rules:
nacos:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
dataId: ${spring.application.name}-param-flow-rules
groupId: SENTINEL_GROUP
data-type: json
rule-type: param-flow
authority-rules:
nacos:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
dataId: ${spring.application.name}-authority-rules
groupId: SENTINEL_GROUP
data-type: json
rule-type: authority
system-rules:
nacos:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848
dataId: ${spring.application.name}-system-rules
groupId: SENTINEL_GROUP
data-type: json
rule-type: system
在 Sentinel Dashboard 配置了流控规则,会在nacos 配置中心生成对应的配置
热点参数规则失效和解决思路
注:控制台改造后有可能出现规则不生效的情况,es:热点参数规则因为 Converter 解析 json 错误的原因会导致不生效
原因:改造 Dashboard,提交到 nacos 配置中心的数据是 ParamFlowRuleEntity 类型,微服务拉取配置要解析的是 ParamFlowRule 类型,会导致规则解析丢失数据,造成热点规则不生效;其他的规则原理也一样,存在失效的风险
提供两种解决思路:
自定义一个解析热点规则配置的解析器 FlowParamJsonConverter,继承 JsonConverter,重写 convert 方法;然后利用后置处理器替换 beanName 为”param-flow-rules-sentinel-nacos-datasource”的 converter 属性,注入 FlowParamJsonConverter ```java @Configuration public class ConverterConfig {
@Bean(“sentinel-json-param-flow-converter2”) @Primary public JsonConverter jsonParamFlowConverter() {
return new FlowParamJsonConverter(new ObjectMapper(), ParamFlowRule.class);} }
@Component public class FlowParamConverterBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Autowired
private JsonConverter jsonParamFlowConverter;
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (beanName.equals("param-flow-rules-sentinel-nacos-datasource")) {
NacosDataSourceFactoryBean nacosDataSourceFactoryBean = (NacosDataSourceFactoryBean) bean;
nacosDataSourceFactoryBean.setConverter(jsonParamFlowConverter);
return bean;
}
return bean;
}
}
public class FlowParamJsonConverter extends JsonConverter { Class ruleClass;
public FlowParamJsonConverter(ObjectMapper objectMapper, Class ruleClass) {
super(objectMapper, ruleClass);
this.ruleClass = ruleClass;
}
@Override
public Collection<Object> convert(String source) {
List<Object> list = new ArrayList<>();
JSONArray jsonArray = JSON.parseArray(source);
for (int i = 0; i < jsonArray.size(); i++) {
//解析rule属性
JSONObject jsonObject = (JSONObject) jsonArray.getJSONObject(i).get("rule");
Object object = JSON.toJavaObject(jsonObject, ruleClass);
list.add(object);
}
return list;
}
} ```
- 改造 Sentinel Dashboard 控制台,发布配置时将 ParamFlowRuleEntity 转成 ParamFlowRule 类型,再发布到 Nacos 配置中心;从配置中心拉取配置后将 ParamFlowRule 转成 ParamFlowRuleEntity


Sentinel 规则持久化源码解析
https://www.processon.com/view/link/607fef267d9c08283ddc2f8d

