ArrayList
LinkedList
构造方法
//集合元素数量transient int size = 0;//链表头节点transient Node<E> first;//链表尾节点transient Node<E> last;//啥都不干public LinkedList() {}//调用public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) 将集合c所有元素插入链表中public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {this();addAll(c);}
节点Node结构
private static class Node<E> {E item;//元素值Node<E> next;//后置节点Node<E> prev;//前置节点Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {this.item = element;this.next = next;this.prev = prev;}}
addAll()
//addAll ,在尾部批量增加public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {return addAll(size, c);//以size为插入下标,插入集合c中所有元素}//以index为插入下标,插入集合c中所有元素public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {checkPositionIndex(index);//检查越界 [0,size] 闭区间Object[] a = c.toArray();//拿到目标集合数组int numNew = a.length;//新增元素的数量if (numNew == 0)//如果新增元素数量为0,则不增加,并返回falsereturn false;Node<E> pred, succ; //index节点的前置节点,后置节点if (index == size) { //在链表尾部追加数据succ = null; //size节点(队尾)的后置节点一定是nullpred = last;//前置节点是队尾} else {succ = node(index);//取出index节点,作为后置节点pred = succ.prev; //前置节点是,index节点的前一个节点}//链表批量增加,是靠for循环遍历原数组,依次执行插入节点操作。//对比ArrayList是通过System.arraycopy完成批量增加的for (Object o : a) {//遍历要添加的节点@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o;Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null);//以前置节点 和 元素值e,构建new一个新节点,if (pred == null) //如果前置节点是空,说明是头结点first = newNode;else//否则 前置节点的后置节点设置为新节点pred.next = newNode;pred = newNode;//步进,当前的节点为前置节点了,为下次添加节点做准备}if (succ == null) {//循环结束后,判断,如果后置节点是null。 说明此时是在队尾append的。last = pred; //则设置尾节点} else {pred.next = succ; // 否则是在队中插入的节点 ,更新前置节点 后置节点succ.prev = pred; //更新后置节点的前置节点}size += numNew; // 修改数量sizemodCount++; //修改modCountreturn true;}//根据index 查询出Node,Node<E> node(int index) {// assert isElementIndex(index);//通过下标获取某个node 的时候,(增、查 ),会根据index处于前半段还是后半段//进行一个折半,以提升查询效率if (index < (size >> 1)) {Node<E> x = first;for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)x = x.next;return x;} else {Node<E> x = last;for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)x = x.prev;return x;}}private void checkPositionIndex(int index) {if (!isPositionIndex(index))throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));}private boolean isPositionIndex(int index) {return index >= 0 && index <= size; //插入时的检查,下标可以是size [0,size]}
add()
//在尾部插入一个节点: addpublic boolean add(E e) {linkLast(e);return true;}//生成新节点 并插入到 链表尾部, 更新 last/first 节点。void linkLast(E e) {final Node<E> l = last; //记录原尾部节点final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);//以原尾部节点为新节点的前置节点last = newNode;//更新尾部节点if (l == null)//若原链表为空链表,需要额外更新头结点first = newNode;else//否则更新原尾节点的后置节点为现在的尾节点(新节点)l.next = newNode;size++;//修改sizemodCount++;//修改modCount}
add(int index,E element)
//在指定下标,index处,插入一个节点public void add(int index, E element) {checkPositionIndex(index);//检查下标是否越界[0,size]if (index == size)//在尾节点后插入linkLast(element);else//在中间插入linkBefore(element, node(index));}//在succ节点前,插入一个新节点evoid linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {// assert succ != null;//保存后置节点的前置节点final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;//以前置和后置节点和元素值e 构建一个新节点final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);//新节点new是原节点succ的前置节点succ.prev = newNode;if (pred == null)//如果之前的前置节点是空,说明succ是原头结点。所以新节点是现在的头结点first = newNode;else//否则构建前置节点的后置节点为newpred.next = newNode;size++;//修改数量modCount++;//修改modCount}
remove(int index)
unlink(Node x)
//将节点x,从链表中删除E unlink(Node<E> x) {// assert x != null;final E element = x.item;//记录元素值,供返回final Node<E> next = x.next;//保存当前节点的后置节点final Node<E> prev = x.prev;//前置节点if (prev == null) {//前置节点为null,first = next;//则首节点为next} else {//否则 更新前置节点的后置节点prev.next = next;x.prev = null;//记得将要删除节点的前置节点置null}//如果后置节点为null,说明是尾节点if (next == null) {last = prev;} else {//否则更新 后置节点的前置节点next.prev = prev;x.next = null;//记得删除节点的后置节点为null}//将删除节点的元素值置null,以便GCx.item = null;size--;//修改sizemodCount++;//修改modCountreturn element;//返回删除的元素值}
CopyOnWriteArrayList
CopyOnWriteArrayList是ArrayList的线程安全版本,从他的名字可以推测,CopyOnWriteArrayList是在有写操作的时候会copy一份数据,然后写完再设置成新的数据。CopyOnWriteArrayList适用于读多写少的并发场景,CopyOnWriteArraySet是线程安全版本的Set实现,它的内部通过一个CopyOnWriteArrayList来代理读写等操作,使得CopyOnWriteArraySet表现出了和CopyOnWriteArrayList一致的并发行为,他们的区别在于数据结构模型的不同,set不允许多个相同的元素插入容器中。
成员属性
/** The lock protecting all mutators */final transient ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();/** The array, accessed only via getArray/setArray. */private transient volatile Object[] array;
add()
public boolean add(E e) {final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;lock.lock(); //上锁,只允许一个线程进入try {Object[] elements = getArray(); // 获得当前数组对象int len = elements.length;Object[] newElements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, len + 1);//拷贝到一个新的数组中newElements[len] = e;//插入数据元素setArray(newElements);//将新的数组对象设置回去return true;} finally {lock.unlock();//释放锁}}
add(int index, E element)
public void add(int index, E element) {final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;lock.lock();try {Object[] elements = getArray();int len = elements.length;if (index > len || index < 0)throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index+", Size: "+len);Object[] newElements;int numMoved = len - index;if (numMoved == 0)newElements = Arrays.copyOf(elements, len + 1);else {newElements = new Object[len + 1];System.arraycopy(elements, 0, newElements, 0, index);System.arraycopy(elements, index, newElements, index + 1,numMoved);}newElements[index] = element;setArray(newElements);} finally {lock.unlock();}}
ConcurrentSkipList
多线程并发存取
ConcurrentSkipListMap的数据结构: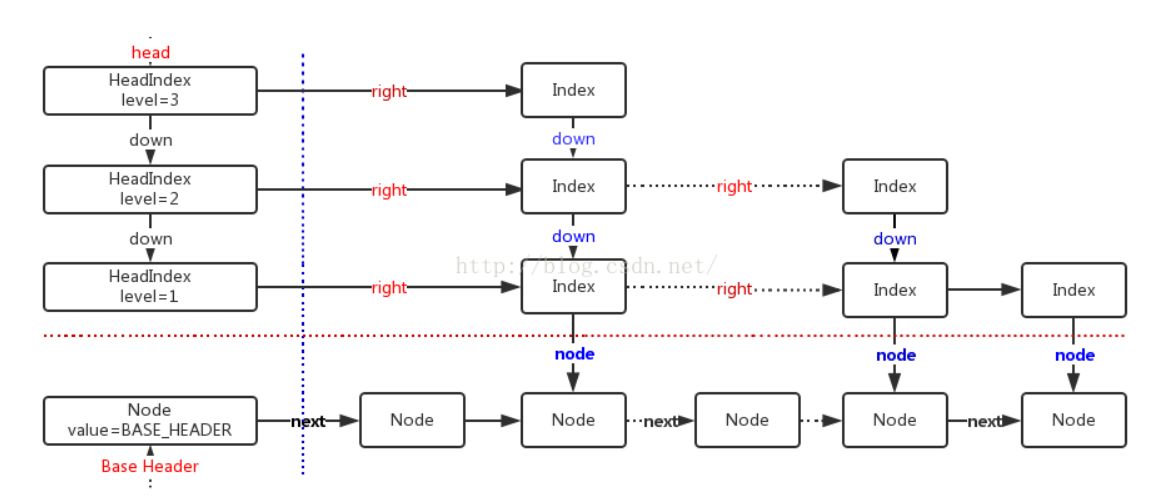
图示
public class ConcurrentSkipListMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V> implementsConcurrentNavigableMap<K,V>,Cloneable,java.io.Serializable {/** Special value used to identify base-level header*/private static final Object BASE_HEADER = new Object();//该值用于标记数据节点的头结点/** The topmost head index of the skiplist.*/private transient volatile HeadIndex<K,V> head;//最高级别索引的索引头....../** Nodes hold keys and values, and are singly linked in sorted order, possibly with some intervening marker nodes.The list is headed by a dummy node accessible as head.node. The value field is declared only as Object because ittakes special non-V values for marker and header nodes. */static final class Node<K,V> {//保存键值对的数据节点,并且是有序的单链表。final K key;volatile Object value;volatile Node<K,V> next;//后继数据节点......}/** Index nodes represent the levels of the skip list.Note that even though both Nodes and Indexes have forward-pointing fields, they have different types and are handledin different ways, that can't nicely be captured by placing field in a shared abstract class.*/static class Index<K,V> {//索引节点final Node<K,V> node;//索引节点关联的数据节点final Index<K,V> down;//下一级别索引节点(关联的数据节点相同)volatile Index<K,V> right;//当前索引级别中,后继索引节点......}/** Nodes heading each level keep track of their level.*/static final class HeadIndex<K,V> extends Index<K,V> {//索引头final int level;//索引级别HeadIndex(Node<K,V> node, Index<K,V> down, Index<K,V> right, int level) {super(node, down, right);this.level = level;}}......}
doGet()
private V doGet(Object okey) {Comparable<? super K> key = comparable(okey);// Loop needed here and elsewhere in case value field goes null just as it is about to be returned, in which case we// lost a race with a deletion, so must retry.// 这里采用循环的方式来查找数据节点,是为了防止返回刚好被删除的数据节点,一旦出现这样的情况,需要重试。for (;;) {Node<K,V> n = findNode(key);//根据key查找数据节点if (n == null)return null;Object v = n.value;if (v != null)return (V)v;}}private Node<K,V> findNode(Comparable<? super K> key) {for (;;) {Node<K,V> b = findPredecessor(key);//根据key查找前驱数据节点Node<K,V> n = b.next;for (;;) {if (n == null)return null;Node<K,V> f = n.next;//1、b的后继节点两次读取不一致,重试if (n != b.next) // inconsistent readbreak;Object v = n.value;//2、数据节点的值为null,表示该数据节点标记为已删除,移除该数据节点并重试。if (v == null) { // n is deletedn.helpDelete(b, f);break;}//3、b节点被标记为删除,重试if (v == n || b.value == null) // b is deletedbreak;int c = key.compareTo(n.key);if (c == 0)//找到返回return n;if (c < 0)//给定key小于当前可以,不存在return null;b = n;//否则继续查找n = f;}}}private Node<K,V> findPredecessor(Object key, Comparator<? super K> cmp) {if (key == null)throw new NullPointerException(); // don't postpone errorsfor (;;) {for (Index<K,V> q = head, r = q.right, d;;) {if (r != null) {Node<K,V> n = r.node;K k = n.key;if (n.value == null) {if (!q.unlink(r))break; // restartr = q.right; // reread rcontinue;}if (cpr(cmp, key, k) > 0) {q = r;r = r.right;continue;}}//执行到这里有两种情况://1、当前级别的索引查找结束//2、给定key小于等于当前keyif ((d = q.down) == null)return q.node;q = d;r = d.right;}}}
doPut()
private V doPut(K kkey, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {Comparable<? super K> key = comparable(kkey);for (;;) {// 找到key的前继节点Node<K,V> b = findPredecessor(key);// 设置n为“key的前继节点的后继节点”,即n应该是“插入节点”的“后继节点”Node<K,V> n = b.next;for (;;) {if (n != null) {Node<K,V> f = n.next;// 如果两次获得的b.next不是相同的Node,就跳转到”外层for循环“,重新获得b和n后再遍历。if (n != b.next)break;// v是“n的值”Object v = n.value;// 当n的值为null(意味着其它线程删除了n);此时删除b的下一个节点,然后跳转到”外层for循环“,重新获得b和n后再遍历。if (v == null) { // n is deletedn.helpDelete(b, f);break;}// 如果其它线程删除了b;则跳转到”外层for循环“,重新获得b和n后再遍历。if (v == n || b.value == null) // b is deletedbreak;// 比较key和n.keyint c = key.compareTo(n.key);if (c > 0) {b = n;n = f;continue;}if (c == 0) {if (onlyIfAbsent || n.casValue(v, value))return (V)v;elsebreak; // restart if lost race to replace value}// else c < 0; fall through}// 新建节点(对应是“要插入的键值对”)Node<K,V> z = new Node<K,V>(kkey, value, n);// 设置“b的后继节点”为zif (!b.casNext(n, z))break; // 多线程情况下,break才可能发生(其它线程对b进行了操作)// 随机获取一个level// 然后在“第1层”到“第level层”的链表中都插入新建节点int level = randomLevel();if (level > 0)insertIndex(z, level);return null;}}}
https://www.cnblogs.com/java-zzl/p/9767255.html
https://blog.csdn.net/sunxianghuang/article/details/52221913
……….
Vector
线程安全的(synchronized)
成员变量
protected Object[] elementData;protected int elementCount;protected int capacityIncrement;
构造方法
public Vector() {this(10);}public Vector(int initialCapacity) {this(initialCapacity, 0);}public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) {super();if (initialCapacity < 0)throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+initialCapacity);this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];this.capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement;}public Vector(Collection<? extends E> c) {Object[] a = c.toArray();elementCount = a.length;if (c.getClass() == ArrayList.class) {elementData = a;} else {elementData = Arrays.copyOf(a, elementCount, Object[].class);}}
add()
public synchronized boolean add(E e) {modCount++;ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);elementData[elementCount++] = e;return true;}private void ensureCapacityHelper(int minCapacity) {// overflow-conscious codeif (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)grow(minCapacity);}private void grow(int minCapacity) {// overflow-conscious codeint oldCapacity = elementData.length;int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)newCapacity = minCapacity;if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);}private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {if (minCapacity < 0) // overflowthrow new OutOfMemoryError();return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?Integer.MAX_VALUE :MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;}public void add(int index, E element) {insertElementAt(element, index);}public synchronized void insertElementAt(E obj, int index) {modCount++;if (index > elementCount) {throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index+ " > " + elementCount);}ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, elementCount - index);elementData[index] = obj;elementCount++;}
Stack
封装vector的方法完成stack的peek,pop,push方法。
https://www.jianshu.com/p/62a989e7448c

