HashSet
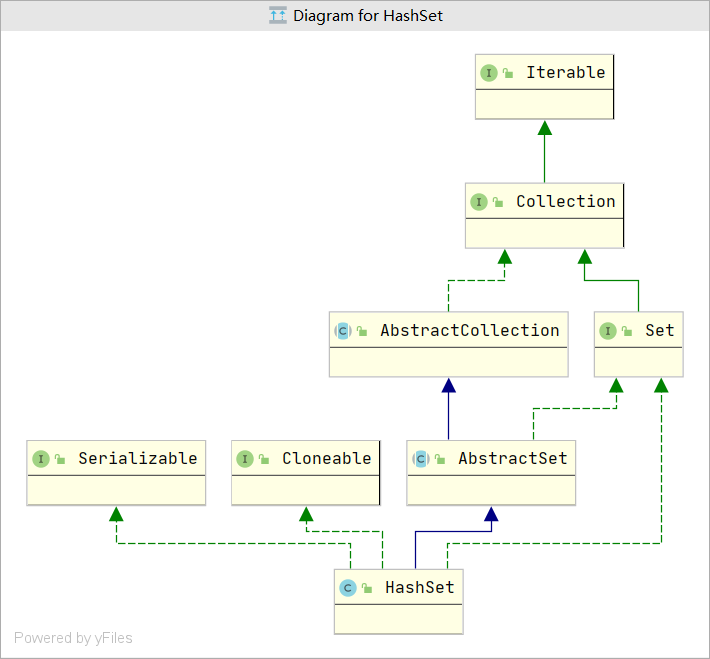
从类图中,可以看到, HashSet 继承了 AbstractSet 抽象类, 而 AbstractSet 又继承了 AbstractCollection 抽象类,此外,HashSet 还实现了 Set 接口等。
AbstractSet 抽象类主要实现了两个方法 equals 和 hashcode 方法,因为 HashSet 中没有重复元素,就是根据这两个方法来进行判断的:
public boolean equals(Object o) {if (o == this)return true;if (!(o instanceof Set))return false;Collection<?> c = (Collection<?>) o;if (c.size() != size())return false;try {return containsAll(c);} catch (ClassCastException unused) {return false;} catch (NullPointerException unused) {return false;}}public int hashCode() {int h = 0;Iterator<E> i = iterator();while (i.hasNext()) {E obj = i.next();if (obj != null)h += obj.hashCode();}return h;}
Set 接口,它是一个顶层接口,主要定义了一些公共的方法,如 add, isEmpty, size, remove, contains 等一些方法;HashSet, SortedSet,TreeSet 都实现了该接口。
public class HashSet<E> extends AbstractSet<E> implements Set<E>, Cloneable,java.io.Serializable{// 用来存放元素的 HashMapprivate transient HashMap<E,Object> map;// 因为 HashMap 是存放键值对的,而 HashSet 只会存放其中的key,即当做 HashMap 的key,// 而value 就是这个 Object 对象了,HashMap 中所有元素的 value 都是它private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();// 无参构造,创建 HashMap 对象,初始大小为 16public HashSet() {map = new HashMap<>();}public HashSet(Collection<? extends E> c) {map = new HashMap<>(Math.max((int) (c.size()/.75f) + 1, 16));addAll(c);}// 根据初始大小和加载因子创建 HashSetpublic HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {map = new HashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);}// 根据初始大小创建 HashSetpublic HashSet(int initialCapacity) {map = new HashMap<>(initialCapacity);}// 迭代器public Iterator<E> iterator() {return map.keySet().iterator();}.......}
从上面声明可看到,HashSet 底层是使用 HashMap 来存放元素的,且 HashMap 中所有元素的 value 都是同一个 Object 对象,且它被 final 修饰。
// 返回集合中元素的个数public int size() {return map.size();}// 判断集合是否为空public boolean isEmpty() {return map.isEmpty();}// 集合中是否包含某个值,即判断 HashMap 中是否包含该keypublic boolean contains(Object o) {return map.containsKey(o);}// 添加元素,在这里可以看到,添加元素的时候,会向 HashMap 中添加,//且 HashMap中的value都是同一个 Object对象public boolean add(E e) {return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;}// 删除元素public boolean remove(Object o) {return map.remove(o)==PRESENT;}// 清除集合public void clear() {map.clear();}
- HashSet 底层是使用 HashMap 来保存元素的
- 它不保证集合中存放元素的顺序,即是无序的,且这种顺序可能会随着时间的推移还会改变
- 允许 null 值,且只有一个
- HashSet底层的 HashMap 不是线程安全的,HashSet 自然也不是,可以使用
Collections.synchronizedSet(new HashSet())来创建线程安全的 HashSet - 集合中的元素不会重复
LinkedHashSet
HashSet是无序的,LinkedHashSet是有序的。
底层实现是linkedhashmap,通过双向链表实现遍历顺序就是添加顺序。TreeSet, SortedSet
package java.util;// TreeSet实现了NavigableSet接口,所以它是有序的public class TreeSet<E> extends AbstractSet<E>implements NavigableSet<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable{// 元素存储在NavigableMap中// 注意它不一定就是TreeMapprivate transient NavigableMap<E,Object> m;// 虚拟元素, 用来作为value存储在map中private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();// 直接使用传进来的NavigableMap存储元素// 这里不是深拷贝,如果外面的map有增删元素也会反映到这里// 而且, 这个方法不是public的, 说明只能给同包使用TreeSet(NavigableMap<E,Object> m) {this.m = m;}// 使用TreeMap初始化public TreeSet() {this(new TreeMap<E,Object>());}// 使用带comparator的TreeMap初始化public TreeSet(Comparator<? super E> comparator) {this(new TreeMap<>(comparator));}// 将集合c中的所有元素添加的TreeSet中public TreeSet(Collection<? extends E> c) {this();addAll(c);}// 将SortedSet中的所有元素添加到TreeSet中public TreeSet(SortedSet<E> s) {this(s.comparator());addAll(s);}// 迭代器public Iterator<E> iterator() {return m.navigableKeySet().iterator();}// 逆序迭代器public Iterator<E> descendingIterator() {return m.descendingKeySet().iterator();}// 以逆序返回一个新的TreeSetpublic NavigableSet<E> descendingSet() {return new TreeSet<>(m.descendingMap());}// 元素个数public int size() {return m.size();}// 判断是否为空public boolean isEmpty() {return m.isEmpty();}// 判断是否包含某元素public boolean contains(Object o) {return m.containsKey(o);}// 添加元素, 调用map的put()方法, value为PRESENTpublic boolean add(E e) {return m.put(e, PRESENT)==null;}// 删除元素public boolean remove(Object o) {return m.remove(o)==PRESENT;}// 清空所有元素public void clear() {m.clear();}// 添加集合c中的所有元素public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {// 满足一定条件时直接调用TreeMap的addAllForTreeSet()方法添加元素if (m.size()==0 && c.size() > 0 &&c instanceof SortedSet &&m instanceof TreeMap) {SortedSet<? extends E> set = (SortedSet<? extends E>) c;TreeMap<E,Object> map = (TreeMap<E, Object>) m;Comparator<?> cc = set.comparator();Comparator<? super E> mc = map.comparator();if (cc==mc || (cc != null && cc.equals(mc))) {map.addAllForTreeSet(set, PRESENT);return true;}}// 不满足上述条件, 调用父类的addAll()通过遍历的方式一个一个地添加元素return super.addAll(c);}// 子set(NavigableSet中的方法)public NavigableSet<E> subSet(E fromElement, boolean fromInclusive,E toElement, boolean toInclusive) {return new TreeSet<>(m.subMap(fromElement, fromInclusive,toElement, toInclusive));}// 头set(NavigableSet中的方法)public NavigableSet<E> headSet(E toElement, boolean inclusive) {return new TreeSet<>(m.headMap(toElement, inclusive));}// 尾set(NavigableSet中的方法)public NavigableSet<E> tailSet(E fromElement, boolean inclusive) {return new TreeSet<>(m.tailMap(fromElement, inclusive));}// 子set(SortedSet接口中的方法)public SortedSet<E> subSet(E fromElement, E toElement) {return subSet(fromElement, true, toElement, false);}// 头set(SortedSet接口中的方法)public SortedSet<E> headSet(E toElement) {return headSet(toElement, false);}// 尾set(SortedSet接口中的方法)public SortedSet<E> tailSet(E fromElement) {return tailSet(fromElement, true);}// 比较器public Comparator<? super E> comparator() {return m.comparator();}// 返回最小的元素public E first() {return m.firstKey();}// 返回最大的元素public E last() {return m.lastKey();}// 返回小于e的最大的元素public E lower(E e) {return m.lowerKey(e);}// 返回小于等于e的最大的元素public E floor(E e) {return m.floorKey(e);}// 返回大于等于e的最小的元素public E ceiling(E e) {return m.ceilingKey(e);}// 返回大于e的最小的元素public E higher(E e) {return m.higherKey(e);}// 弹出最小的元素public E pollFirst() {Map.Entry<E,?> e = m.pollFirstEntry();return (e == null) ? null : e.getKey();}public E pollLast() {Map.Entry<E,?> e = m.pollLastEntry();return (e == null) ? null : e.getKey();}// 克隆方法@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public Object clone() {TreeSet<E> clone;try {clone = (TreeSet<E>) super.clone();} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {throw new InternalError(e);}clone.m = new TreeMap<>(m);return clone;}// 序列化写出方法private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)throws java.io.IOException {// Write out any hidden stuffs.defaultWriteObject();// Write out Comparators.writeObject(m.comparator());// Write out sizes.writeInt(m.size());// Write out all elements in the proper order.for (E e : m.keySet())s.writeObject(e);}// 序列化写入方法private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {// Read in any hidden stuffs.defaultReadObject();// Read in Comparator@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")Comparator<? super E> c = (Comparator<? super E>) s.readObject();// Create backing TreeMapTreeMap<E,Object> tm = new TreeMap<>(c);m = tm;// Read in sizeint size = s.readInt();tm.readTreeSet(size, s, PRESENT);}// 可分割的迭代器public Spliterator<E> spliterator() {return TreeMap.keySpliteratorFor(m);}// 序列化idprivate static final long serialVersionUID = -2479143000061671589L;}
- TreeSet底层使用NavigableMap存储元素;
- TreeSet是有序的;
- TreeSet是非线程安全的;
- TreeSet实现了NavigableSet接口,而NavigableSet继承自SortedSet接口;
LinkedHashSet并没有实现SortedSet接口,它的有序性主要依赖于LinkedHashMap的有序性,所以它的有序性是指按照插入顺序保证的有序性;
而TreeSet实现了SortedSet接口,它的有序性主要依赖于NavigableMap的有序性,而NavigableMap又继承自SortedMap,这个接口的有序性是指按照key的自然排序保证的有序性,而key的自然排序又有两种实现方式,一种是key实现Comparable接口,一种是构造方法传入Comparator比较器。
CopyOnWriteArraySet
CopyOnWriteArraySet底层是使用CopyOnWriteArrayList存储元素的,所以它并不是使用Map来存储元素的。
但是,我们知道CopyOnWriteArrayList底层其实是一个数组,它是允许元素重复的,那么用它来实现CopyOnWriteArraySet怎么保证元素不重复呢?
public class CopyOnWriteArraySet<E> extends AbstractSet<E>implements java.io.Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = 5457747651344034263L;// 内部使用CopyOnWriteArrayList存储元素private final CopyOnWriteArrayList<E> al;// 构造方法public CopyOnWriteArraySet() {al = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<E>();}// 将集合c中的元素初始化到CopyOnWriteArraySet中public CopyOnWriteArraySet(Collection<? extends E> c) {if (c.getClass() == CopyOnWriteArraySet.class) {// 如果c是CopyOnWriteArraySet类型,说明没有重复元素,// 直接调用CopyOnWriteArrayList的构造方法初始化@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") CopyOnWriteArraySet<E> cc =(CopyOnWriteArraySet<E>)c;al = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<E>(cc.al);}else {// 如果c不是CopyOnWriteArraySet类型,说明有重复元素// 调用CopyOnWriteArrayList的addAllAbsent()方法初始化// 它会把重复元素排除掉al = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<E>();al.addAllAbsent(c);}}// 获取元素个数public int size() {return al.size();}// 检查集合是否为空public boolean isEmpty() {return al.isEmpty();}// 检查是否包含某个元素public boolean contains(Object o) {return al.contains(o);}// 集合转数组public Object[] toArray() {return al.toArray();}// 集合转数组public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {return al.toArray(a);}// 清空所有元素public void clear() {al.clear();}// 删除元素public boolean remove(Object o) {return al.remove(o);}// 添加元素// 这里是调用CopyOnWriteArrayList的addIfAbsent()方法// 它会检测元素不存在的时候才添加public boolean add(E e) {return al.addIfAbsent(e);}// 是否包含c中的所有元素public boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) {return al.containsAll(c);}// 并集public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {return al.addAllAbsent(c) > 0;}// 单方向差集public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {return al.removeAll(c);}// 交集public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {return al.retainAll(c);}// 迭代器public Iterator<E> iterator() {return al.iterator();}// equals()方法public boolean equals(Object o) {// 如果两者是同一个对象,返回trueif (o == this)return true;// 如果o不是Set对象,返回falseif (!(o instanceof Set))return false;Set<?> set = (Set<?>)(o);Iterator<?> it = set.iterator();// 集合元素数组的快照Object[] elements = al.getArray();int len = elements.length;boolean[] matched = new boolean[len];int k = 0;// 从o这个集合开始遍历outer: while (it.hasNext()) {// 如果k>len了,说明o中元素多了if (++k > len)return false;// 取值Object x = it.next();// 遍历检查是否在当前集合中for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {if (!matched[i] && eq(x, elements[i])) {matched[i] = true;continue outer;}}// 如果不在当前集合中,返回falsereturn false;}return k == len;}// 移除满足过滤条件的元素public boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) {return al.removeIf(filter);}// 遍历元素public void forEach(Consumer<? super E> action) {al.forEach(action);}// 分割的迭代器public Spliterator<E> spliterator() {return Spliterators.spliterator(al.getArray(), Spliterator.IMMUTABLE | Spliterator.DISTINCT);}// 比较两个元素是否相等private static boolean eq(Object o1, Object o2) {return (o1 == null) ? o2 == null : o1.equals(o2);}}
(1)CopyOnWriteArraySet是用CopyOnWriteArrayList实现的;
(2)CopyOnWriteArraySet是有序的,因为底层其实是数组;
(3)CopyOnWriteArraySet是并发安全的,而且实现了读写分离;
(4)CopyOnWriteArraySet通过调用CopyOnWriteArrayList的addIfAbsent()方法来保证元素不重复;
ConcurrentSkipListSet
把前面偷工减料的skiplist补了一遍。
ConcurrentSkipListSet是一个有序的线程安全的集合,基本上都是使用ConcurrentSkipListMap实现的。
ConcurrentSkipListMap
内部节点Node
static final class Node<K, V>{final K key; // key 是 final 的, 说明节点一旦定下来, 除了删除, 不然不会改动 key 了volatile Object value; // 对应的 valuevolatile Node<K, V> next; // 下一个节点// 构造函数public Node(K key, Object value, Node<K, V> next) {this.key = key;this.value = value;this.next = next;}/*** 创建一个标记节点(通过 this.value = this 来标记)* 这个标记节点非常重要: 有了它, 就能对链表中间节点进行同时删除和插入* ps: ConcurrentLinkedQueue 只能在头上, 尾端进行插入, 中间进行删除*/public Node(Node<K, V> next) {this.key = null;this.value = this;this.next = next;}/*** CAS 操作设置 Value*/boolean casValue(Object cmp, Object val){return unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(this, valueOffset, cmp, val);}/*** CAS 操作设置 next*/boolean casNext(Node<K, V> cmp, Node<K, V> val){return unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(this, nextOffset, cmp, val);}/*** 检测是否为标记节点*/boolean isMarker(){return value == this;}/*** 检测是否为 链表最左下角的 BASE_HEADER 节点*/boolean isBaseHeader(){return value == BASE_HEADER;}/*** 对节点追加一个标记节点, 为最终的删除做准备*/boolean appendMarker(Node<K, V> f){return casNext(f, new Node<K, V>(f));}/*** Help out a deletion by appending marker or unlinking from* predecessor. This called during traversals when value* field seen to be null** helpDelete 方法, 这个方法要么追加一个标记节点, 要么进行删除操作*/void helpDelete(Node<K, V> b, Node<K, V> f){/*** Rechecking links and then doing only one of the* help-out stages per call tends to minimize CAS* interference among helping threads*/if(f == next && this == b.next){if(f == null || f.value != f){ // 还没有对删除的节点进行节点 markercasNext(f, new Node<K, V>(f));}else{b.casNext(this, f.next); // 删除 节点 b 与 f.next 之间的节点}}}/*** 校验数据*/V getValidValue(){Object v = value;if(v == this || v == BASE_HEADER){return null;}V vv = (V)v;return vv;}/*** Creates and returns a new SimpleImmutableEntry holding current* mapping if this node holds a valid value, else null.** @return new entry or null*/AbstractMap.SimpleImmutableEntry<K, V> createSnapshot(){Object v = value;if(v == null || v == this || v == BASE_HEADER){return null;}V vv = (V) v;return new AbstractMap.SimpleImmutableEntry<K, V>(key, vv);}// UNSAFE mechanicsprivate static final Unsafe unsafe;private static final long valueOffset;private static final long nextOffset;static {try {unsafe = UnSafeClass.getInstance();Class<?> k = Node.class;valueOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset(k.getDeclaredField("value"));nextOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset(k.getDeclaredField("next"));}catch (Exception e){throw new Error(e);}}}
index
static class Index<K, V>{final Node<K, V> node; // 索引指向的节点, 纵向上所有索引指向链表最下面的节点final Index<K, V> down; // 下边level层的 Indexvolatile Index<K, V> right; // 右边的 Index/*** Creates index node with given values* @param node* @param down* @param right*/public Index(Node<K, V> node, Index<K, V> down, Index<K, V> right) {this.node = node;this.down = down;this.right = right;}/*** compareAndSet right field* @param cmp* @param val* @return*/final boolean casRight(Index<K, V> cmp, Index<K, V> val){return unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(this, rightOffset, cmp, val);}/*** Returns true if the node this indexes has been deleted.* @return true if indexed node is known to be deleted*/final boolean indexesDeletedNode(){return node.value == null;}/*** Tries to CAS newSucc as successor. To minimize races with* unlink that may lose this index node, if the node being* indexed is known to be deleted, it doesn't try to link in** @param succ the expecteccurrent successor* @param newSucc the new successor* @return true if successful*//*** 在 index 本身 和 succ 之间插入一个新的节点 newSucc* @param succ* @param newSucc* @return*/final boolean link(Index<K, V> succ, Index<K, V> newSucc){Node<K, V> n = node;newSucc.right = succ;return n.value != null && casRight(succ, newSucc);}/*** Tries to CAS field to skip over apparent successor* succ. Fails (forcing a retravesal by caller) if this node* is known to be deleted* @param succ the expected current successor* @return true if successful*//*** 将当前的节点 index 设置其的 right 为 succ.right 等于删除 succ 节点* @param succ* @return*/final boolean unlink(Index<K, V> succ){return node.value != null && casRight(succ, succ.right);}// Unsafe mechanicsprivate static final Unsafe unsafe;private static final long rightOffset;static {try{unsafe = UnSafeClass.getInstance();Class<?> k = Index.class;rightOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset(k.getDeclaredField("right"));}catch (Exception e){throw new Error(e);}
doPut()
1.初始状态:只存在 HeadIndex 和 Base_Header 节点
2.节点添加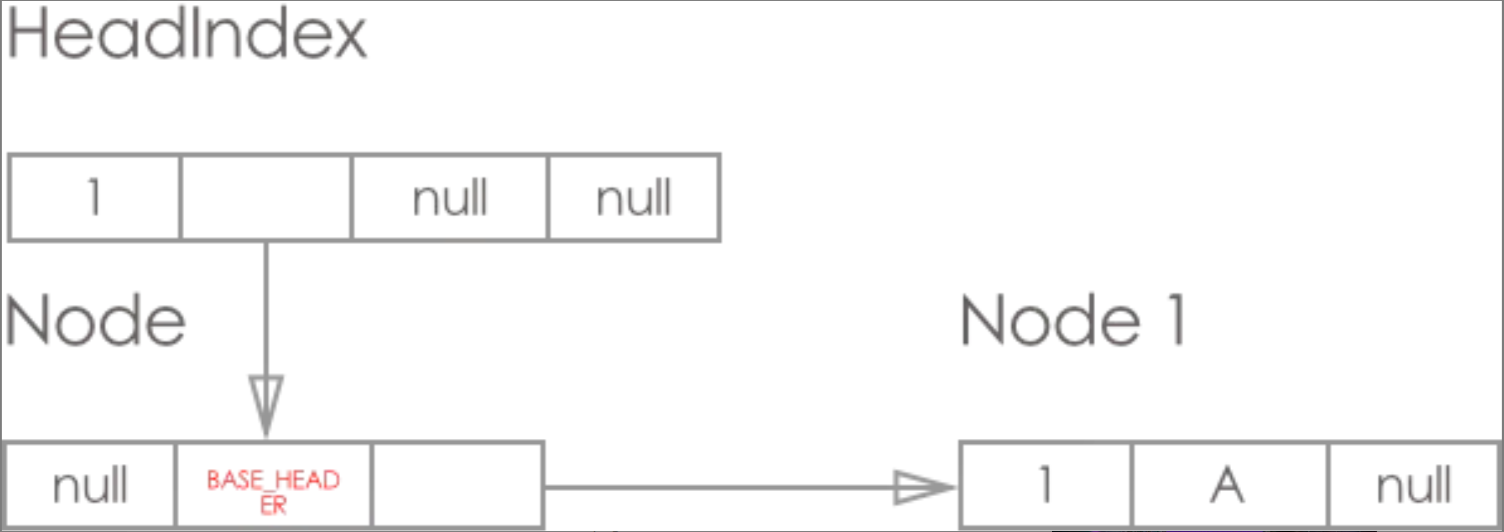
/*** Main insetion method. Adds element if not present, or* replaces value if present and onlyIfAbsent is false.** @param key the key* @param value the values that must be associated with key* @param onlyIfAbstsent if should not insert if already present* @return the old value, or null if newly inserted*/private V doPut(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbstsent){Node<K, V> z; // adde nodeif(key == null){throw new NullPointerException();}Comparator<? super K> cmp = comparator;outer:for(;;){// 0.for(Node<K, V> b = findPredecessor(key, cmp), n = b.next;;){ // 1. 将 key 对应的前继节点找到, b 为前继节点, n是前继节点的next, 若没发生 条件竞争, 最终 key在 b 与 n 之间 (找到的b在 base_level 上)if(n != null){ // 2. n = null时 b 是链表的最后一个节点, key 直接插到 b 之后 (调用 b.casNext(n, z))Object v; int c;Node<K, V> f = n.next; // 3 获取 n 的右节点if(n != b.next){ // 4. 条件竞争(另外一个线程在b之后插入节点, 或直接删除节点n), 则 break 到位置 0, 重新break ;}if((v = n.value) == null){ // 4. 若 节点n已经删除, 则 调用 helpDelete 进行帮助删除 (详情见 helpDelete), 则 break 到位置 0, 重新来n.helpDelete(b, f);break ;}if(b.value == null || v == n){ // 5. 节点b被删除中 ,则 break 到位置 0, 调用 findPredecessor 帮助删除 index 层的数据, 至于 node 层的数据 会通过 helpDelete 方法进行删除break ;}if((c = cpr(cmp, key, n.key)) > 0){ // 6. 若 key 真的 > n.key (在调用 findPredecessor 时是成立的), 则进行 向后走b = n;n = f;continue ;}if(c == 0){ // 7. 直接进行赋值if(onlyIfAbstsent || n.casValue(v, value)){V vv = (V) v;return vv;}break ; // 8. cas 竞争条件失败 重来}// else c < 0; fall through}// 9. 到这边时 n.key > key > b.keyz = new Node<K, V> (key, value, n);if(!b.casNext(n, z)){break ; // 10. cas竞争条件失败 重来}break outer; // 11. 注意 这里 break outer 后, 上面的 for循环不会再执行, 而后执行下面的代码, 这里是break 不是 continue outer, 这两者的效果是不一样的}}int rnd = KThreadLocalRandom.nextSecondarySeed();if((rnd & 0x80000001) == 0){ // 12. 判断是否需要添加levelint level = 1, max;while(((rnd >>>= 1) & 1) != 0){++level;}// 13. 上面这段代码是获取 level 的, 我们这里只需要知道获取 level 就可以 (50%的几率返回0,25%的几率返回1,12.5%的几率返回2...最大返回31。)Index<K, V> idx = null;HeadIndex<K, V> h = head;if(level <= (max = h.level)){ // 14. 初始化 max 的值, 若 level 小于 max , 则进入这段代码 (level 是 1-31 之间的随机数)for(int i = 1; i <= level; ++i){idx = new Index<K, V>(z, idx, null); // 15 添加 z 对应的 index 数据, 并将它们组成一个上下的链表(index层是上下左右都是链表)}}else{ // 16. 若 level > max 则只增加一层 index 索引层level = max + 1; // 17. 跳表新的 level 产生Index<K, V>[] idxs = (Index<K, V>[])new Index<?, ?>[level + 1];for(int i = 1; i <= level; ++i){idxs[i] = idx = new Index<K, V>(z, idx, null);}for(;;){h = head;int oldLevel = h.level; // 18. 获取老的 level 层if(level <= oldLevel){ // 19. 另外的线程进行了index 层增加操作, 所以 不需要增加 HeadIndex 层数break;}HeadIndex<K, V> newh = h;Node<K, V> oldbase = h.node; // 20. 这里的 oldbase 就是BASE_HEADERfor(int j = oldLevel+1; j <= level; ++j){ // 21. 这里其实就是增加一层的 HeadIndex (level = max + 1)newh = new HeadIndex<K, V>(oldbase, newh, idxs[j], j); // 22. idxs[j] 就是上面的 idxs中的最高层的索引}if(casHead(h, newh)){ // 23. 这只新的 headIndexh = newh; // 24. 这里的 h 变成了 new HeadIndexidx = idxs[level = oldLevel]; // 25. 这里的 idx 上从上往下第二层的 index 节点 level 也变成的 第二break;}}}// find insertion points and splice insplice:for(int insertionLevel = level;;){ // 26. 这时的 level 已经是 第二高的 level(若上面 步骤19 条件竞争失败, 则多出的 index 层其实是无用的, 因为 那是 调用 Index.right 是找不到它的)int j = h.level;for(Index<K, V> q = h, r = q.right, t = idx;;){ // 27. 初始化对应的数据if(q == null || t == null){ // 28. 节点都被删除 直接 break出去break splice;}if(r != null){Node<K, V> n = r.node;// compare before deletion check avoids needing recheckint c = cpr(cmp, key, n.key);if(n.value == null){ // 29. 老步骤, 帮助index 的删除if(!q.unlink(r)){break ;}r = q.right; // 30. 向右进行遍历continue ;}if(c > 0){ // 31. 向右进行遍历q = r;r = r.right;continue ;}}// 32.// 代码运行到这里, 说明 key < n.key// 第一次运行到这边时, j 是最新的 HeadIndex 的level j > insertionLevel 非常用可能, 而下面又有 --j, 所以终会到 j == insertionLevelif(j == insertionLevel){if(!q.link(r, t)){ // 33. 将 index t 加到 q 与 r 中间, 若条件竞争失败的话就重试break ; // restrt}if(t.node.value == null){ // 34. 若这时 node 被删除, 则开始通过 findPredecessor 清理 index 层, findNode 清理 node 层, 之后直接 break 出去, doPut调用结束findNode(key);break splice;}if(--insertionLevel == 0){ // 35. index 层添加OK, --1 为下层插入 index 做准备break splice;}}/*** 下面这行代码其实是最重要的, 理解这行代码, 那 doPut 就差不多了* 1). --j 要知道 j 是 newhead 的level, 一开始一定 > insertionLevel的, 通过 --1 来为下层操作做准备 (j 是 headIndex 的level)* 2). 通过 19. 21, 22 步骤, 个人认为 --j >= insertionLevel 是横成立, 而 --j 是必须要做的* 3) j 经过几次--1, 当出现 j < level 时说明 (j+1) 层的 index已经添加成功, 所以处理下层的 index*/if(--j >= insertionLevel && j < level){t = t.down;}/** 到这里时, 其实有两种情况* 1) 还没有一次index 层的数据插入* 2) 已经进行 index 层的数据插入, 现在为下一层的插入做准备*/q = q.down; // 从 index 层向下进行查找r = q.right;}}}return null;}

