前面已经写过一篇很基础的文章了,这次会更全面!
定义:
所有php里面的值都可以使用函数serialize()来返回一个包含字节流的字符串来表示。unserialize()函数能够重新把字符串变回php原来的值。 序列化一个对象将会保存对象的所有变量,但是不会保存对象的方法,只会保存类的名字。
序列化:把对象转换为字节序列的过程称为对象的序列化。 反序列化:把字节序列恢复为对象的过程称为对象的反序列化。
看一下PHP序列化
<?phpclass Test{private $a;protected $b;public $c;var $d;static $f;function _construct(){$this->a=$this->b=$this->c=$this->d=$this->f=$this->e=1;}function _wakeup(){}function _desturt(){}}$t = new Test();$p = serialize($t);print($p);?>
输出结果:O:4:"Test":6:{s:7:"Testa";i:1;s:4:"*b";i:1;s:1:"c";i:1;s:1:"d";i:1;s:1:"e";i:1;s:1:"f";i:1;}
O代表对象 因为我们序列化的是一个对象 序列化数组则用A来表示
4代表类名占的字符数
Test代表类名
6代表类里有6个属性
s代表字符串 7代表属性长度 Testa属性名
i:1 整数 属性值
b、d、i、s 表示的是四种标量类型,目前其它语言所实现的 PHP 序列化程序基本上都实现了对这些类型的序列化和反序列化,不过有一些实现中对 s (字符串)的实现存在问题。
a - array b - boolean
d - double i - integer
o - common object r - reference
s - string C - custom object
O - class N - null
R - pointer reference U - unicode string
在这里有两个属性经过序列化格外的不同,需要说一下
protected(受保护)
private(私有的)
protected属性被序列化的时候属性值会变成%00*%00属性名
private属性被序列化的时候属性值会变成%00类名%00属性名
再看看
序列化得到的s:7:"Testa";i:1;s:4:"*b";i:1;
实际上: s:7:"%00Test%00a";i:1;s:4:"%00*%00b";i:1;
注意:在序列化之前会先调用__sleep返回的是一个需要序列化的成员名称数组,通过这样我们就可以控制需要序列化的数据。
PHP反序列化
反序列化函数unserialize(),将序列化的字符串,还原回去。
反序列化函数unserialize()会检查一个wakeup()魔术方法
如果存在,就会先调用wakeup()方法进行反序列化,可以在__wakeup()方法中对属性进行初始化 或者 改变值
wakeup得一个漏洞:
当序列化字符串表示对象属性个数的值大于真实个数的属性时就会跳过__wakeup的执行。
php常见的魔术方法
方法名 触发点
__construct 在创建对象时候初始化对象,一般用于对变量赋初值
__destruct 和构造函数相反,在对象不再被使用时(将所有该对象的引用设为null)或者程序退出时自动调用
__toString 当一个对象被当作一个字符串被调用,把类当作字符串使用时触发,返回值需要为字符串
__wakeup() 使用unserialize时触发,反序列化恢复对象之前调用该方法
__sleep() 使用serialize时触发 ,在对象被序列化前自动调用,该函数需要返回以类成员变量名作为元素的数组(该数组里的元素会影响类成员变量是否被序列化。只有出现在该数组元素里的类成员变量才会被序列化)
__destruct() 对象被销毁时触发
__call() 在对象上下文中调用不可访问的方法时触发,即当调用对象中不存在的方法会自动调用该方法
__callStatic() 在静态上下文中调用不可访问的方法时触发
__get() 用于从不可访问的属性读取数据,即在调用私有属性的时候会自动执行
__set() 用于将数据写入不可访问的属性
__isset() 在不可访问的属性上调用isset()或empty()触发
__unset() 在不可访问的属性上使用unset()时触发
__invoke() 当脚本尝试将对象调用为函数时触发
举个例子
<?php
class animal {
public $name = 'dahuang';//define a virable
public function sleep(){//define a simpe method
echo $this->name . " is sleeping...\n";
}
public function __construct(){
echo "the method:__construct is called\n";
}
public function __destruct(){
echo "the method:__destruct is called\n";
}
public function __toString(){
return "the method:__toString is called\n";
}
}
$dog = new animal();
$dog->sleep();
echo $dog;
?>
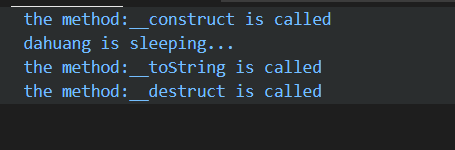
首先通过new对类进行实例化时,调用了construct构造函数,创建了dog对象
然后通过dog对象调用sleep()方法,触发sleep,在进行$dog->sleep();时,$dog初始化字符串,toString()被调用;
echo $dog使得脚本结束,调用__destruct函数
PHP的序列化与反序列化过程中sleep()、wakeup()的调用过程
<?php
class animal {
public $name = 'dahuang';//define a virable
public $age = '20';
public function eat(){//define a simpe method
echo $this->name . " is eatting...\n";
}
public function __construct(){
echo "the method:__construct is called\n";
}
public function __destruct(){
echo "the method:__destruct is called\n";
}
public function __toString(){
return "the method:__toString is called\n";
}
public function __wakeup(){
echo "the method:__wakeup is called\n";
}
public function __sleep(){
echo "the method:__sleep is called\n";
return array('name','age');
}
}
$dog = new animal();//对类进行实例化时,自动调用__construct()
$serializedDog = serialize($dog);//对dog对象进行序列化时,自动调用__sleep()
echo $serializedDog . "\n";//echo 序列化的dog对象
$dog->eat();//dog对象调用eat()方法
//程序结束,调用__destruct()
?>
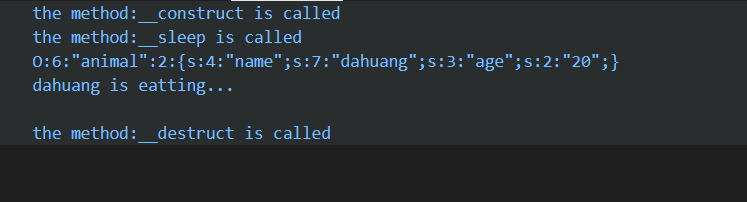
在进行序列化的过程中的调用:
1、当不进行序列化时: 在进行类的实例化时,自动调用construct();在输出对象时,自动调用
toString();在程序结束时,自动调用destruct();sleep()与wakeup()均与序列化与反序列化
有关,在此过程不被调用。
2、当进行序列化时: 在进行类的实例化时,自动调用construct();在对创建的dog对象进行序列化时,自动调用sleep();echo $serializedDog,输出序列化的dog对象,在此不再调用
_toString();dog兑现调用eat()方法,然后程序结束,调用destruct().
3、在整个过程中,construct()总是在程序的开始调用,destruct()总是在程序的结束调用,这很简单,因为,对所有的变量的初始化总是在程序的开始,释放变量总是在程序结束。
反序列化调用的过程
<?php
class animal {
public $name = 'dahuang';//define a virable
public $age = '20';
public function eat(){//define a simpe method
echo $this->name . " is eatting...\n";
}
public function __construct(){
echo "the method:__construct is called\n";
}
public function __destruct(){
echo "the method:__destruct is called\n";
}
public function __toString(){
return "the method:__toString is called\n";
}
public function __wakeup(){
echo "the method:__wakeup is called\n";
}
public function __sleep(){
echo "the method:__sleep is called\n";
return array('name','age');
}
}
$dog = new animal();//对类进行实例化时,自动调用__construct()
$serializedDog = serialize($dog);//对dog对象进行序列化时,自动调用__sleep()
echo $serializedDog . "\n";//echo 序列化的dog对象
$newDog = unserialize($serializedDog);//反序列化已经被序列化的dog对象,自动调用__wakeup()
var_dump($newDog);//输出反序列化的结果
$newDog->eat();//dog对象调用eat()方法
//程序结束,调用__destruct()
?>
看一下结果
the method:__construct is called
the method:__sleep is called
O:6:"animal":2:{s:4:"name";s:7:"dahuang";s:3:"age";s:2:"20";}
the method:__wakeup is called
object(animal)#2 (2) {
["name"]=>
string(7) "dahuang"
["age"]=>
string(2) "20"
}
dahuang is eatting...
the method:__destruct is called
the method:__destruct is called
首先,在对animal类进行实例化时,自动调用construct()对变量进行初始化;然后通过serialize()方法对dog对象进行序列化,自动调用sleep();输出序列化的dog对象;之后,通过unserialize()方法对序列化的dog对象进行反序列化,自动调用wakeup()方法;输出反序列化的结果,可以看到被序列化的dog对象得到了还原;然后通过新的newDog对象调用eat()方法,程序结束,自动调用destruct()方法,注意这里的__construct()被调用了两次,这是因为在整个过程中产生了两个对象dog和newDog,在程序结束需要分写释放。
本地搭的一个环境:
一个类用于临时将日志存储在某个文件,当__destruct()被调用时,删除日志文件。
saveLog.php:
<?php
class logFile{
public $logname = "error.log";//定义日志文件的名字
public function saveLog($text){//定义将内容写入日志文件的方法
echo "Log same data: " . $text . "<br>";
file_put_contents($this->logname, $text . PHP_EOL, FILE_APPEND);
}
public function __destruct(){//调用__destruct时删除日志文件
echo "the method:__destruct is called<br>";
unlink(dirname(__FILE__) . DIRECTORY_SEPARATOR . $this->logname);//删除日志文件
if(!file_exists(dirname(__FILE__) . DIRECTORY_SEPARATOR . $this->logname)){//如果文件已被删除,则回显日志
echo "the method:__destruct is called and " . $this->logname ." has been deleted<br>";
}
}
}
deleteLog.php
<?php
include 'saveLog.php'; //包含文件
$obj = new logFile(); //初始化logFile函数
$obj->logname = 'somefile.log';//给变量赋值
$obj->saveLog('this is a test file');//调用方法保存一些内容
首先,注释掉saveLog.php中的unlink()方法看,保存文件,访问deletLog.php:
可以看到由于unlink()被注释掉了,保存的日志文件并没有被删除;但是输出“the method:destruct is called”,destruct()方法已经调用
然后再去掉注释看一下,真正的效果:在deleteLog.php中的__destruct()添加了判断函数,所以当文件被unlink()函数删除后弹出日志;文件被删除。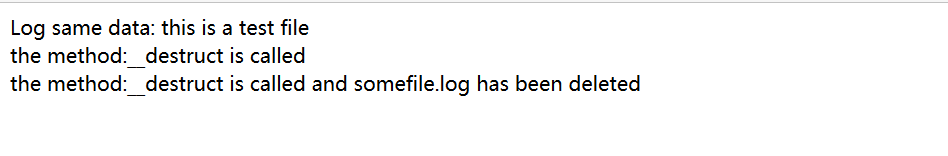
加入序列化和反序列化之后的操作
saveLog.php:
<?php
class logFile{
public $logname = "error.log";//define the name of log
public function saveLog($text){//define the method to write the contents to a logfile
echo "Log same data: " . $text . "<br>";
file_put_contents($this->logname, $text . PHP_EOL, FILE_APPEND);
}
public function __destruct(){//delete the logfile when __destruct is called
echo "the method:__destruct is called<br>";
if(!file_exists(dirname(__FILE__) . DIRECTORY_SEPARATOR . $this->logname)){//if the file has been deleted ,echo the log
echo "the method:__destruct is called and " . $this->logname ." has been deleted<br>";
}else{
unlink(dirname(__FILE__) . DIRECTORY_SEPARATOR . $this->logname);//delete the logfile
}
}
}
创建测试的文件
<?php
echo "this is a test file";
?>
序列化脚本serialize.php
<?php
include 'saveLog.php';
$obj = new logFile();
$obj->logname = "testPHP.php";
echo serialize($obj)."<br>";
反序列化脚本unrialize.php
<?php
include 'saveLog.php';
$obj = new logFile();
$obj->logname = "testPHP.php";
echo serialize($obj)."<br>";
 测试文件已经就位
测试文件已经就位
访问serialize.php
O:7:"logFile":1:{s:7:"logname";s:11:"testPHP.php";}
the method:__destruct is called
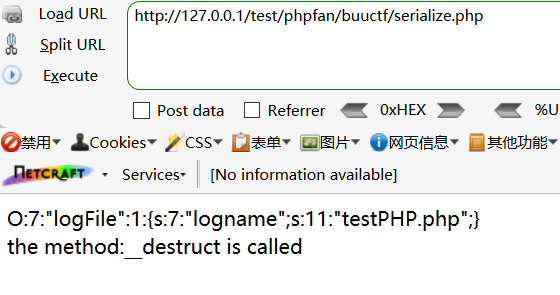
输出了序列化之后的字符,然后调用了destruct()方法,testPHP.php文件已经被删除了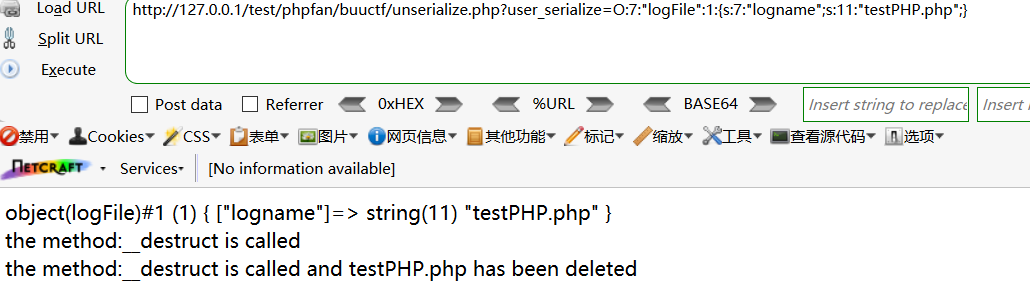
再反序列化出原始字符串
此时,testPHP.php文件已经被删除,因为在脚本运行结束时,destruct()方法,然而我们可以通过给定不同的字符串控制logFile类的变量。这就是PHP反序列化漏洞的名称由来,PHP反序列化漏洞的
条件:
1.unserialize函数的变量可控(本例中:unserialize($_GET[‘USER_serialized’])是用户设定);
2.php文件中存在可利用的类,类中有魔术方法(本例中:__destruct());
看到了大师傅提了__tostring的具体触发场景:
(1) echo($obj) / print($obj) 打印时会触发 (2) 反序列化对象与字符串连接时 (3) 反序列化对象参与格式化字符串时 (4) 反序列化对象与字符串进行==比较时(PHP进行==比较的时候会转换参数类型) (5) 反序列化对象参与格式化SQL语句,绑定参数时 (6) 反序列化对象在经过php字符串函数,如 strlen()、addslashes()时 (7) 在in_array()方法中,第一个参数是反序列化对象,第二个参数的数组中有toString返回的字符串的时候toString会被调用 (8) 反序列化的对象作为 class_exists() 的参数的时候
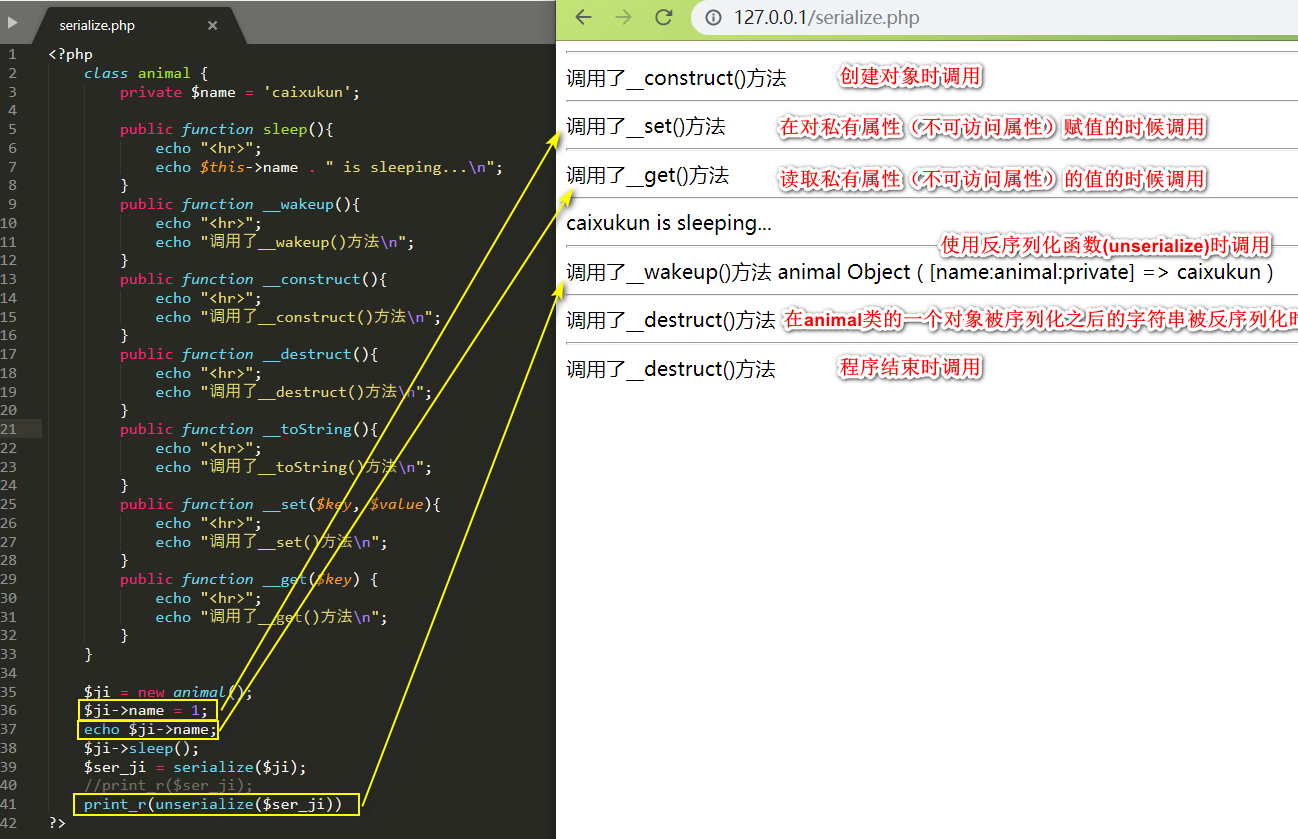
<?php
class animal {
private $name = 'caixukun';
public function sleep(){
echo "<hr>";
echo $this->name . " is sleeping...\n";
}
public function __wakeup(){
echo "<hr>";
echo "调用了__wakeup()方法\n";
}
public function __construct(){
echo "<hr>";
echo "调用了__construct()方法\n";
}
public function __destruct(){
echo "<hr>";
echo "调用了__destruct()方法\n";
}
public function __toString(){
echo "<hr>";
echo "调用了__toString()方法\n";
}
public function __set($key, $value){
echo "<hr>";
echo "调用了__set()方法\n";
}
public function __get($key) {
echo "<hr>";
echo "调用了__get()方法\n";
}
}
$ji = new animal();
$ji->name = 1;
echo $ji->name;
$ji->sleep();
$ser_ji = serialize($ji);
//print_r($ser_ji);
print_r(unserialize($ser_ji))
?>
后续会抓紧由浅入深的学习php反序列化!!!

