Object构造函数的对象分为原型prototype和构造函数自身constructor方法: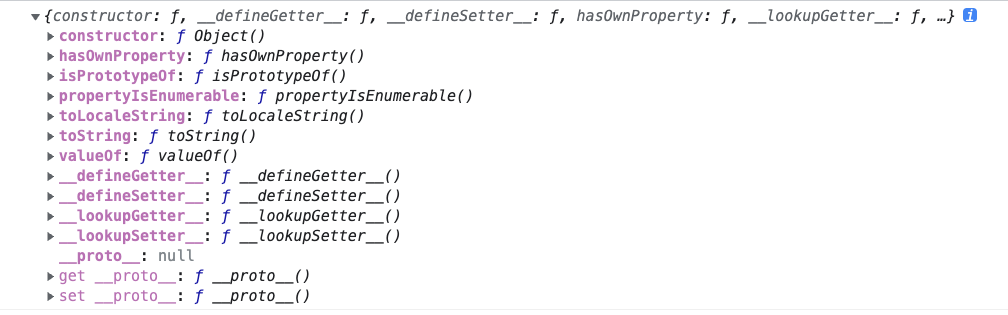
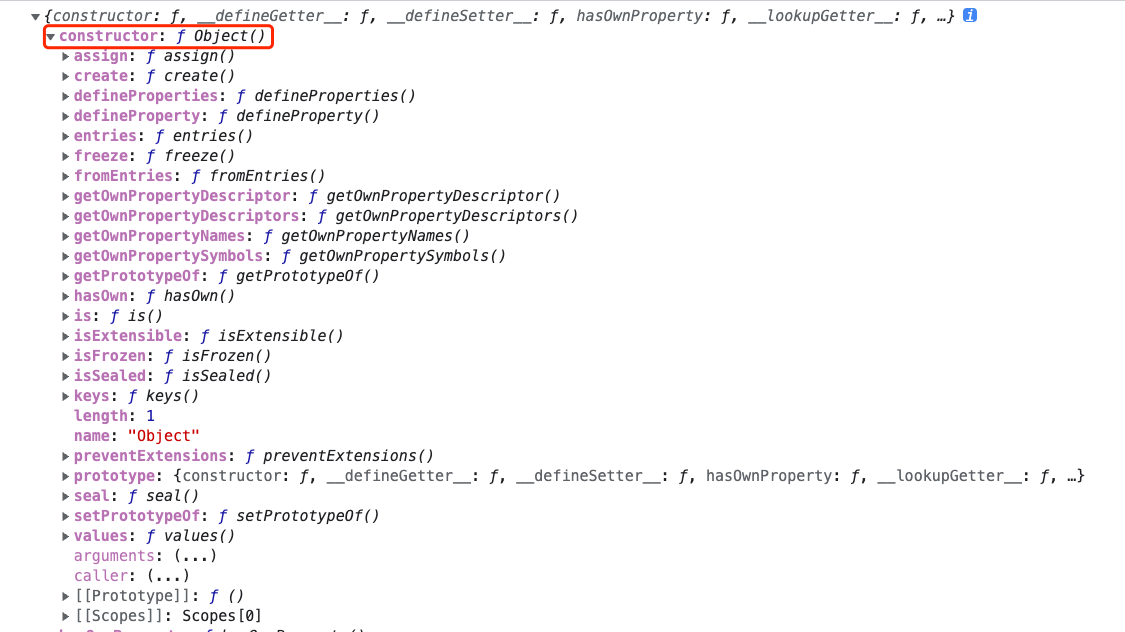
定义属性的特性
Object.defineProperty()
:::info 用于定义单个对象属性的特性 :::
var obj = Object.defineProperty({}, "test", {value: 1,writable: true,configurable: true,enumerable: true,});var value = 1;var obj2 = Object.defineProperty({}, "test", {configurable: true,enumerable: true,set: function () {return value;},get: function (newVal) {value = newVal;}});console.log(obj2.test);obj2.test = 2;
Object.defineProperties()
:::info 用于定义多个对象属性的特性 :::
var value = 1;var obj = Object.defineProperties({},{a: {configurable: true,enumerable: true,set: function () {return value;},get: function (newVal) {value = newVal;},},b: {value: 1,writable: true,configurable: true,enumerable: true,},});
更多细节请阅读:Object.defineProperty() / defineProperties()
读取属性的特性
Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor()
:::info
获取对象单个属性的特性。
参数1: 要获取的对象
参数2: 要获取的对象属性
:::
var obj = Object.defineProperty({}, "a", {value: 1,writable: true,configurable: true,enumerable: true,});console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj, "a"));// {value: 1, writable: true, enumerable: true, configurable: true}
Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors()
:::info
获取对象多个属性的特性。
参数1: 要获取的对象
:::
var obj = Object.defineProperties({},{a: {value: 1,writable: true,configurable: true,enumerable: true,},b: {value: 2,},});console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(obj));// {value: 1, writable: true, enumerable: true, configurable: true}// {value: 2, writable: false, enumerable: false, configurable: false}
操作对象的拓展性
Object.preventExtensions
:::info
用于禁止对象拓展,调用方法后对象不可新增属性,但是可以读取、更改、删除,返回原对象
参数1: 目标对象
:::
var obj = { a: 1, b: 2 };Object.preventExtensions(obj);console.log(Object.isExtensible(obj)); // false,不可拓展obj.c = 3; // 新增属性无效obj.a = 4; // 可以更改属性delete obj.b; // 可以删除属性console.log(obj.a); // 4,可以读取属性console.log(obj); // {a: 4}
Object.isExtensible()
:::info
用于获取对象是否可拓展,返回布尔值
参数1: 目标对象
:::
var obj = { a: 1, b: 2 };console.log(Object.isExtensible(obj));
Object.seal()
:::info
用于封闭对象,封闭后的对象不可新增、删除,可以修改、读取,返回原对象
参数1: 目标对象
:::
var obj = { a: 1, b: 2 };Object.seal(obj);console.log(Object.isExtensible(obj)); // false,不可拓展obj.a = 4; // 可以修改obj.c = 3; // 新增属性无效delete obj.b; // 删除属性无效console.log(obj.a); // 4,可以读取属性console.log(obj); // {a: 4, b: 2}
Object.isSealed()
:::info 用来判断对象是否被封闭,返回布尔值 :::
let obj = { name: "李四" };let res = Object.seal(obj);console.log(Object.isSealed(obj)); // trueconsole.log(obj === res); // true
Object.freeze()
:::info
用于冻结对象,冻结后的对象不可新增、修改、删除,可以读取,返回原对象
参数1: 目标对象
:::
var obj = { a: 1, b: 2 };Object.freeze(obj);console.log(Object.isExtensible(obj)); // false,不可拓展obj.a = 4; // 修改属性无效obj.c = 3; // 新增属性无效delete obj.b; // 删除属性无效console.log(obj.a); // 1,可以读取属性console.log(obj); // {a: 1, b: 2}
Object.isFrozen()
:::info 用来判断对象是否被冻结,返回布尔值 :::
let obj = { name: "李四" };let res = Object.freeze(obj);console.log(Object.isFrozen(obj)); // trueconsole.log(obj === res); // true
创建对象
Object.create()
:::info
用于创建对象且给该对象指定一个原型
返回:一个对象
:::
var obj = Object.create({a: 3,b: 4,});console.log(obj);

操作原型
Object.setPrototypeOf()
:::info
用于给对象设置原型
参数1:要设置原型的对象
参数2: 要设置的原型
:::
var obj = { a: 1, b: 2 };Object.setPrototypeOf(obj, { c: 3, d: 4 });console.log(obj);// 还可以直接设置对象的原型obj.__proto__ = { c: 3, d: 4 };
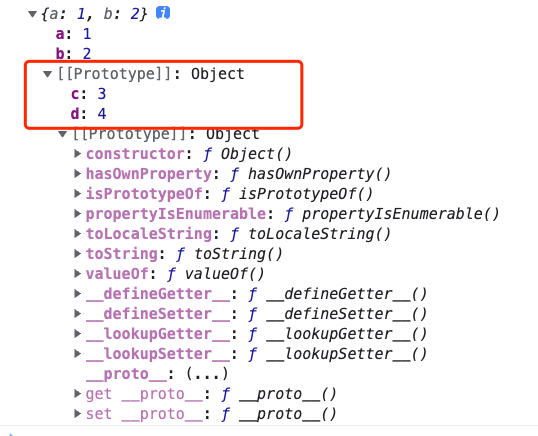
Object.getPrototypeOf()
:::info
用于获取对象的原型
参数1: 要获取原型的对象
:::
var obj = { a: 1, b: 2 };var proto = Object.getPrototypeOf(obj);console.log(proto);// 还可以通过属性直接获取console.log(obj.__proto__);
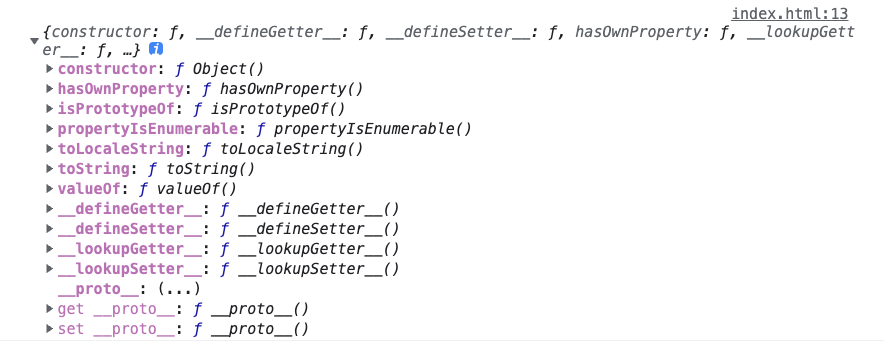
获取对象本身属性
Object.getOwnPropertyNames()
:::info
用于获取对象非原型属性
参数1: 目标对象
返回:属性名组合的数组
:::
var obj = { a: 1, b: 2 };Object.setPrototypeOf(obj, { c: 3, d: 4 });console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyNames(obj)); // ['a', 'b']
Object.hasOwnProperty()
:::info
用于获取对象非原型属性
返回:true/false
:::
var obj = { a: 1, b: 2 };Object.setPrototypeOf(obj, { c: 3, d: 4 });console.log(Object.hasOwnProperty.call(obj, "a")); // trueconsole.log(Object.hasOwnProperty.call(obj, "c")); // false
该方法也存在于Object的原型上,所以继承于Object原型的势力对象也可以直接调用该方法。
var obj = { a: 1, b: 2 };Object.setPrototypeOf(obj, { c: 3, d: 4 });console.log(obj.hasOwnProperty("a")); // trueconsole.log(obj.hasOwnProperty("c")); // falseconsole.log(Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(obj, "b")); // true
对象遍历
in
:::info
in关键字用于判断一个属性是否存在于一个对象上(包括对象的原型)
返回:true/false
:::
var obj = { a: 1, b: 2 };Object.setPrototypeOf(obj, { c: 3, d: 4 });console.log("a" in obj); // trueconsole.log("c" in obj); // true
for…in…
:::info
for...in..语句字用于遍历对象上的属性(包括对象的原型属性)
:::
var obj = { a: 1, b: 2 };Object.setPrototypeOf(obj, { c: 3, d: 4 });for (const key in obj) {console.log(key, obj[key]);}// a 1// b 2// c 3// d 4
Object.keys()
:::info
用于获取对象属性的key值(不包括对象的原型属性)
返回key组成的数组
:::
var obj = { a: 1, b: 2 };Object.setPrototypeOf(obj, { c: 3, d: 4 });console.log(Object.keys(obj)); // ["a", "b"]
Object.values()
:::info
用于获取对象属性的value值(不包括对象的原型属性)
返回value组成的数组
:::
var obj = { a: 1, b: 2 };Object.setPrototypeOf(obj, { c: 3, d: 4 });console.log(Object.values(obj)); // [1, 2]
Object.entries()
:::info
用于获取对象属性的key和value值(不包括对象的原型属性)
返回key和value组成的二维数组
:::
var obj = { a: 1, b: 2 };Object.setPrototypeOf(obj, { c: 3, d: 4 });console.log(Object.entries(obj)); // [["a", 1], ["b", 2]]
其他
instanceof
:::info
该关键字是用来判断一个实例对象是否是一个构造函数的实例
返回:true/false
:::
function Person() {}var p1 = new Person();console.log(p1 instanceof Person); // trueconsole.log([] instanceof Person); // false
不过instanceof也存在着问题,当我们去检查array等数据的时候,返回的结果不是那么的准确。
console.log({} instanceof Object); // trueconsole.log([] instanceof Array); // trueconsole.log([] instanceof Object); // trueconsole.log(function () {} instanceof Function); // trueconsole.log(function () {} instanceof Object); // true
这是因为所有的数据类型原型顶端都是Object,所以我们可以使用Object.toString()来更准确的判断数据。
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call({})); // [object Object]console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call([])); // [object Array]console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(function(){})); // [object Function]
待补充。。。

