v-if 和 v-show 的认识
在Vue框架中,我们可以通过v-if/v-else-if/v-else和v-show来控制元素或组件的渲染,当v-if和v-show的指令表达式条件返回true的时候就会渲染元素或组件。
<h1 v-if="awesome">Vue is awesome!</h1>
v-if指令是利用了注释节点<-- if -->对文档进行了占位,当v-if指令的值为真的时候,Vue会把相应的注释节点替换为真实的元素,反之就是把真实的元素替换为注释节点。
:::warning
⚠️ 注意v-if在切换渲染的时候,条件区块内的事件监听器和子组件都会被销毁与重建。
:::

而v-show则不同,v-show里利用CSS给给元素新增dispaly: none;来实现视觉上的隐藏,并没有真正的从文档中被移除。
:::info
因为v-if频繁的切换显示隐藏会提高性能的开销,所以,我们在开发的时候如果需要频繁的切换显示和隐藏就要使用v-show,因为v-show的性能开销会比较低。
:::
模拟实现 v-if 和 v-show
我们如何模拟实现一个v-if和v-show这样的操作呢?
首先我们需要一个Vue.js文件用于创建Vue实例,再创建一个index.js文件作为实例化入口。
首先,我们用熟悉的Vue2配方进行实例化Vue对象:
<!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="UTF-8" /><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" /><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" /><title>Document</title></head><body><div id="app"></div><script type="module" src="./index.js"></script></body></html>
import VueTest from "./Vue.js";const vm = new VueTest({el: "#app",// 页面模版template: `<div><img v-if="isShowImg1" src="https://cdn.pixabay.com/photo/2022/11/15/04/54/automotive-7593064__340.jpg" /><img v-show="isShowImg2" src="https://cdn.pixabay.com/photo/2022/12/15/18/15/christmas-7658297__340.jpg" /></div><button @click="showImg1">显示图片1</button><button @click="showImg2">显示图片2</button>`,// 数据响应劫持data() {return {isShowImg1: true,isShowImg2: false,};},// 事件处理methods: {showImg1() {this.isShowImg1 = !this.isShowImg1;},showImg2() {this.isShowImg2 = !this.isShowImg2;},},});console.log(vm);
这样我们就把一个最基本的实例化配置写好了,下面重点要放在Vue.js文件上面。
Vue文件我们利用一个立即执行函数来实现模块化,立即执行函数执行后返回一个Vue的构造函数,所以我们可以在index.js中进行实例化。
var VueTest = (function () {function Vue(options){}return Vue;})();export default VueTest;
接着,我们要把options里面的相关属性暴露在实例化对象上:
var VueTest = (function () {function Vue(options){this.$el = document.querySelector(options.el);this.$data = options.data();}return Vue;})();export default VueTest;
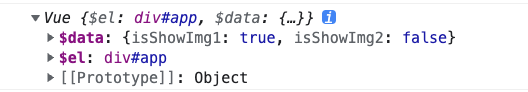
我们还需要一个函数用于初始化数据:
var VueTest = (function () {function Vue(options) {this.$el = document.querySelector(options.el);this.$data = options.data();this._init();}Vue.prototype._init = function () {var showPool = new Map(); // 存储dom和数据的对应关系var eventPool = new Map(); // 存储dom和事件处理的对应关系initData();initPool();bindEvent();render();};// 初始化数据,对 data 数据进行拦截function initData() {}// 初始化数据池function initPool() {}// 绑定事件处理function bindEvent() {}// 对 template 进行渲染function render() {}// 更改 data 数据后更新视图function update() {}return Vue;})();export default VueTest;
initPool方法主要有两个作用:
1、存储dom和指令+数据的对应关系
2、存储dom和事件处理函数的对应关系
我们利用的是Map数据结构进行存储,因为Map的Key可以是任意的数据类型,这样我们在后续处理的时候就能根据对应关系去处理数据啦。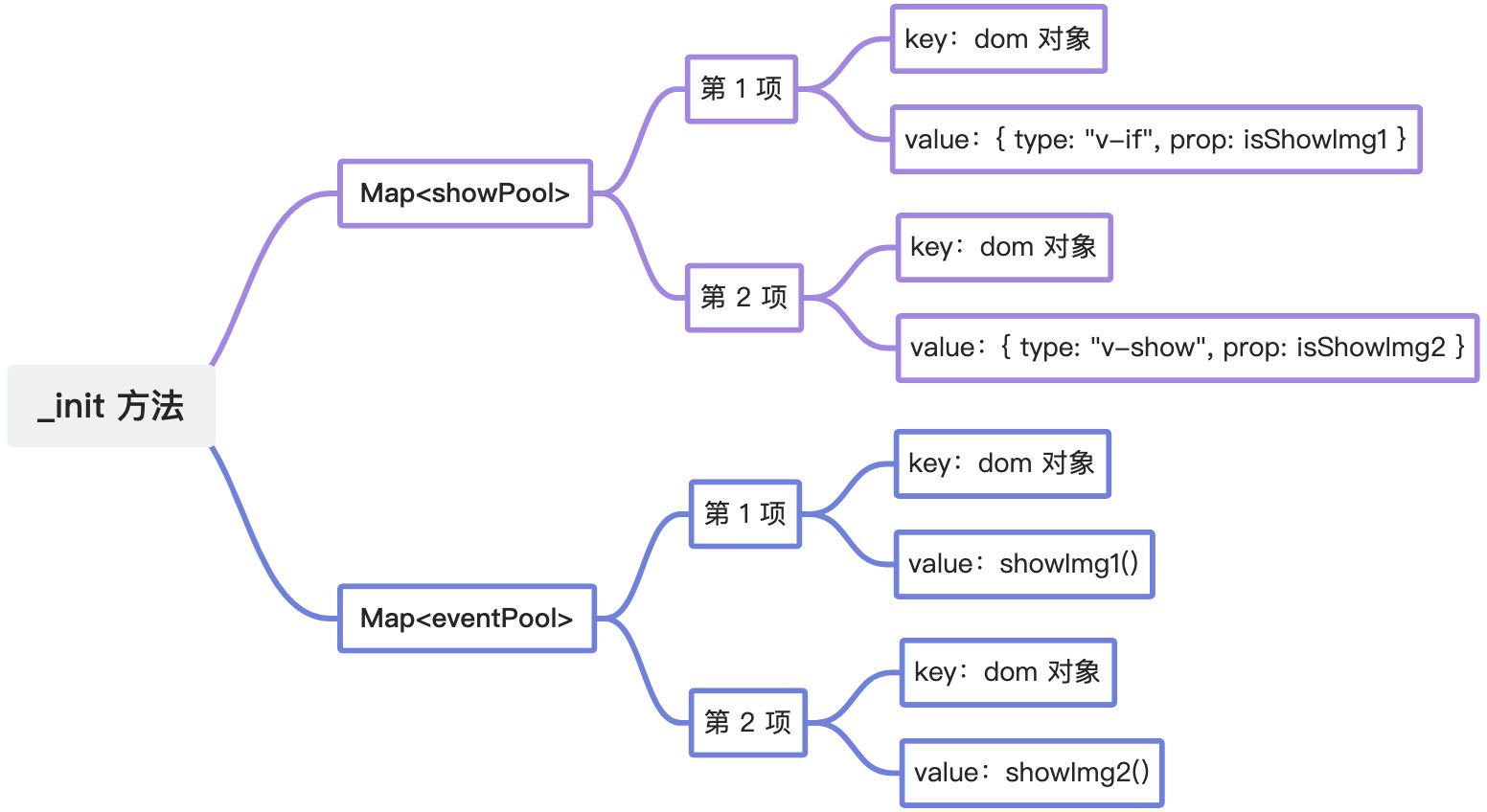
第一件事:数据拦截
到这里,基本的架子已经差不多了,下面我们先做第一件事,那就是对数据进行拦截:
var VueTest = (function () {function Vue(options) {this.$el = document.querySelector(options.el);this.$data = options.data();this._init();}Vue.prototype._init = function () {var showPool = new Map();var eventPool = new Map();// 把当前实例、dom和数据的对应关系传递过去initData(this, showPool);initPool();bindEvent();render();};function initData(vm, showPool) {var _data = vm.$data;for (const key in _data) {// 判断属性是不是 _data 的原生属性if (Object.hasOwnProperty.call(_data, key)) {// 对当前实例进行拦截,例如访问 vm.isShowImg1 就会被拦截Object.defineProperty(vm, key, {get: function () {return _data[key];},set: function (newVal) {_data[key] = newVal;// 当更改 data 的数据后,需要调用方法去更新数据和对应关系update(vm, key, showPool);}});}}}function initPool() {}function bindEvent() {}function render() {}function update() {}return Vue;})();export default VueTest;
第二件事:存储数据池
第二件事情,对数据池进行初始化(可以对应上面的思维导图去理解):
var VueTest = (function () {function Vue(options) {this.$el = document.querySelector(options.el);this.$data = options.data();this._init(options.template, options.methods);}// 把 template, methods 传递进来Vue.prototype._init = function (template, methods) {var showPool = new Map();var eventPool = new Map();// 创建一个 div 元素,把 template 的内容放进去var container = document.createElement("div");container.innerHTML = template;initData(this, showPool);// 把 template、methods 和数据池传递进去,绑定关系initPool(container, methods, showPool, eventPool);bindEvent();render();};function initData(vm, showPool) {var _data = vm.$data;for (const key in _data) {if (Object.hasOwnProperty.call(_data, key)) {Object.defineProperty(vm, key, {get: function () {return _data[key];},set: function (newVal) {_data[key] = newVal;update(vm, key, showPool);},});}}}function initPool(container, methods, showPool, eventPool) {var _allNodes = container.getElementsByTagName("*");var dom = null;console.log(container);console.log(_allNodes); // 获取 container 下所有的内容for (let i = 0; i < _allNodes.length; i++) {dom = _allNodes[i];// 获取所有元素上的 v-if、v-show 和 @click 属性var vIfData = dom.getAttribute("v-if");var vShowData = dom.getAttribute("v-show");var vEvent = dom.getAttribute("@click");}}function bindEvent() {}function render() {}function update() {}return Vue;})();export default VueTest;
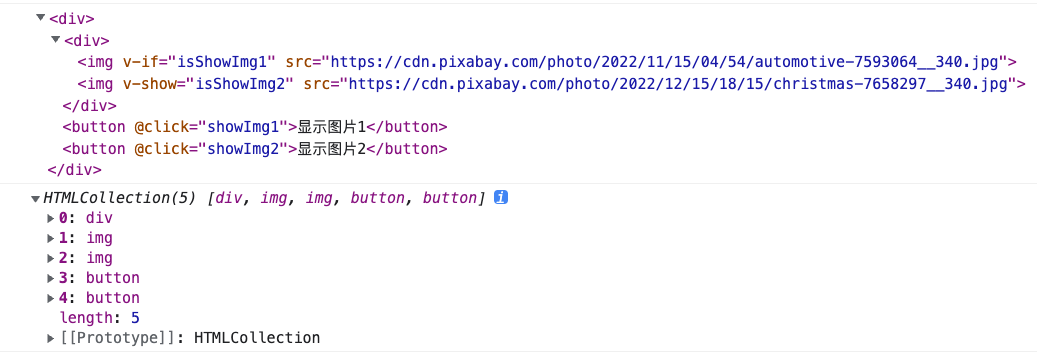
获取到这些属性之后,我们就可以存储到数据池啦:
var VueTest = (function () {function Vue(options) {this.$el = document.querySelector(options.el);this.$data = options.data();this._init(options.template, options.methods);}Vue.prototype._init = function (template, methods) {var showPool = new Map();var eventPool = new Map();var container = document.createElement("div");container.innerHTML = template;initData(this, showPool);initPool(container, methods, showPool, eventPool);bindEvent();render();};function initData(vm, showPool) {var _data = vm.$data;for (const key in _data) {if (Object.hasOwnProperty.call(_data, key)) {Object.defineProperty(vm, key, {get: function () {return _data[key];},set: function (newVal) {_data[key] = newVal;update(vm, key, showPool);},});}}}function initPool(container, methods, showPool, eventPool) {var _allNodes = container.getElementsByTagName("*");var dom = null;for (let i = 0; i < _allNodes.length; i++) {dom = _allNodes[i];var vIfData = dom.getAttribute("v-if");var vShowData = dom.getAttribute("v-show");var vEvent = dom.getAttribute("@click");if (vIfData) {showPool.set(dom, {type: "if",prop: vIfData,});dom.removeAttribute("v-if");} else if (vShowData) {showPool.set(dom, {type: "show",prop: vShowData,});dom.removeAttribute("v-show");}if (vEvent) {eventPool.set(dom, methods[vEvent]);dom.removeAttribute("@click");}}console.log(showPool);console.log(eventPool);}function bindEvent() {}function render() {}function update() {}return Vue;})();export default VueTest;
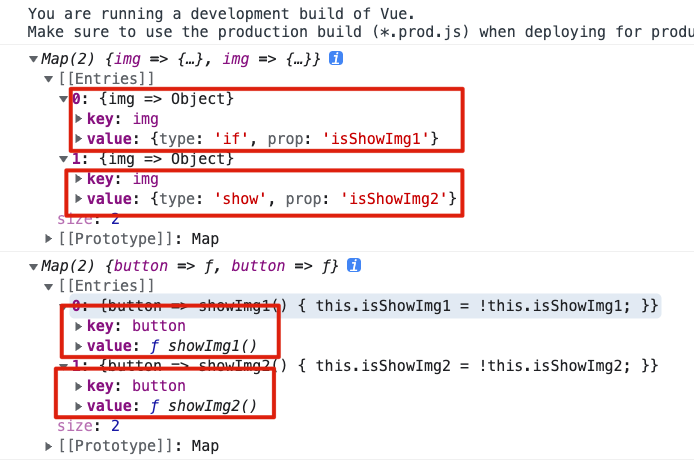
第三件事:绑定事件
到目前为止,数据拦截已经完成,dom和数据的对应关系也已经完成,接下来我们要绑定事件:
var VueTest = (function () {function Vue(options) {this.$el = document.querySelector(options.el);this.$data = options.data();this._init(options.template, options.methods);}Vue.prototype._init = function (template, methods) {var showPool = new Map();var eventPool = new Map();var container = document.createElement("div");container.innerHTML = template;initData(this, showPool);initPool(container, methods, showPool, eventPool);// 传递当前实例、事件池bindEvent(this, eventPool);render();};function initData(vm, showPool) {var _data = vm.$data;for (const key in _data) {if (Object.hasOwnProperty.call(_data, key)) {Object.defineProperty(vm, key, {get: function () {return _data[key];},set: function (newVal) {_data[key] = newVal;update(vm, key, showPool);},});}}}function initPool(container, methods, showPool, eventPool) {var _allNodes = container.getElementsByTagName("*");var dom = null;for (let i = 0; i < _allNodes.length; i++) {dom = _allNodes[i];var vIfData = dom.getAttribute("v-if");var vShowData = dom.getAttribute("v-show");var vEvent = dom.getAttribute("@click");if (vIfData) {showPool.set(dom, {type: "if",prop: vIfData,});dom.removeAttribute("v-if");} else if (vShowData) {showPool.set(dom, {type: "show",prop: vShowData,});dom.removeAttribute("v-show");}if (vEvent) {eventPool.set(dom, methods[vEvent]);dom.removeAttribute("@click");}}}function bindEvent(vm, eventPool) {for (var [dom, handler] of eventPool) {// 把方法挂载到实例上vm[handler.name] = handler;// 给 dom 添加事件处理// 利用 bind 把 this 指向当前实例对象dom.addEventListener("click", vm[handler.name].bind(vm), false);}}function render() {}function update() {}return Vue;})();export default VueTest;
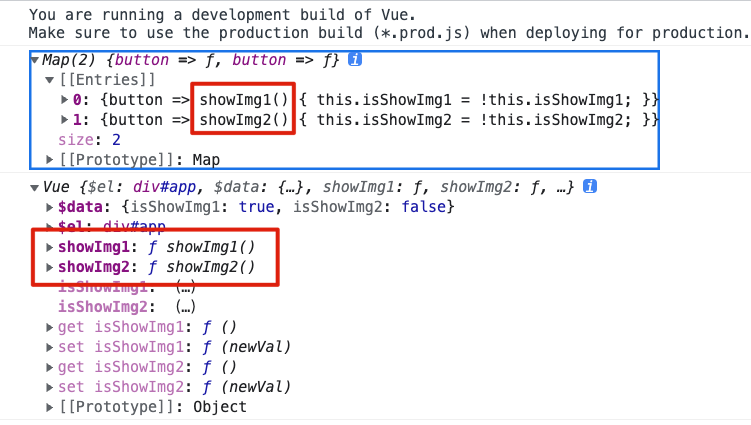
可以看到实例对象上有了showImg1和showImg2这两个方法啦。
第四件事:渲染 dom
最重要的事情来了,那就是渲染dom,我们要判断dom对应的指令是v-if还是v-show来决定如何隐藏dom。
var VueTest = (function () {function Vue(options) {this.$el = document.querySelector(options.el);this.$data = options.data();this._init(options.template, options.methods);}Vue.prototype._init = function (template, methods) {var showPool = new Map();var eventPool = new Map();var container = document.createElement("div");container.innerHTML = template;initData(this, showPool);initPool(container, methods, showPool, eventPool);bindEvent(this, eventPool);// 把当前实例、数据池、dom 内容传递过去render(this, showPool, container);};function initData(vm, showPool) {var _data = vm.$data;for (const key in _data) {if (Object.hasOwnProperty.call(_data, key)) {Object.defineProperty(vm, key, {get: function () {return _data[key];},set: function (newVal) {_data[key] = newVal;update(vm, key, showPool);},});}}}function initPool(container, methods, showPool, eventPool) {var _allNodes = container.getElementsByTagName("*");var dom = null;for (let i = 0; i < _allNodes.length; i++) {dom = _allNodes[i];var vIfData = dom.getAttribute("v-if");var vShowData = dom.getAttribute("v-show");var vEvent = dom.getAttribute("@click");if (vIfData) {showPool.set(dom, {type: "if",prop: vIfData,});dom.removeAttribute("v-if");} else if (vShowData) {showPool.set(dom, {type: "show",prop: vShowData,});dom.removeAttribute("v-show");}if (vEvent) {eventPool.set(dom, methods[vEvent]);dom.removeAttribute("@click");}}}function bindEvent(vm, eventPool) {console.log(eventPool);for (var [dom, handler] of eventPool) {vm[handler.name] = handler;dom.addEventListener("click", vm[handler.name].bind(vm), false);}}function render(vm, showPool, container) {var _data = vm.$data;var _el = vm.$el;// 迭代 showPool 对象for (const [dom, info] of showPool) {// 判断dom和数据的对应关系switch (info.type) {// 如果是 if 指令case "if":// 创建一个注释节点info.comment = document.createComment(["v-if"]);// 如果数据为假,也就是 isShowImg1,那么就把 dom 替换为注释节点!_data[info.prop] && dom.parentNode.replaceChild(info.comment, dom);break;case "show":// 如果数据为假,也就是 isShowImg2,那么就把 dom 的样式设置为隐藏!_data[info.prop] && (dom.style.display = "none");break;}}// 最后把 container 渲染到 el 节点上_el.appendChild(container);}function update() {}return Vue;})();export default VueTest;
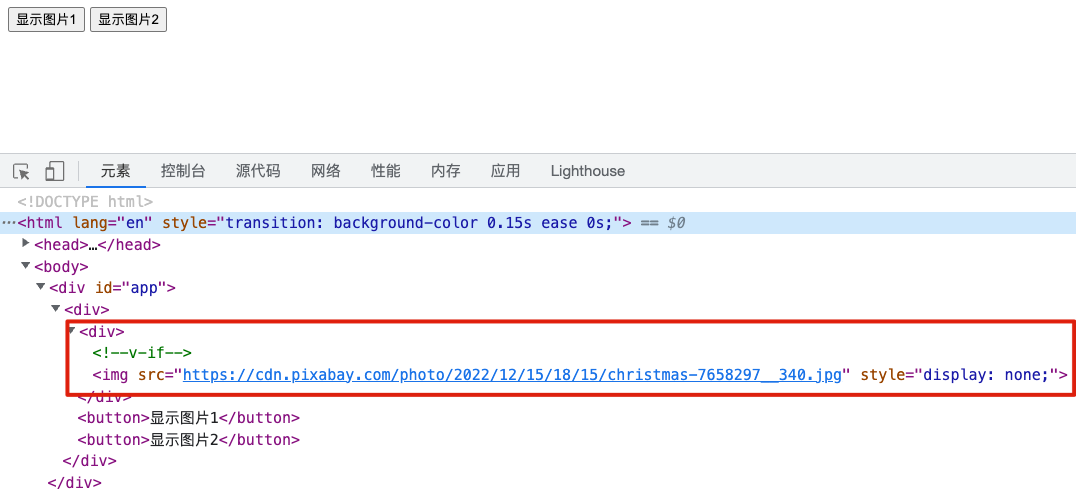
这样页面第一次加载就会触发render函数,该函数内负责对dom的隐藏/显示进行控制。
第五件事:更新视图
最后一件事就是在调用methods的方法后,去更新视图,更改isShowImg1或isShowImg2的时候就会触发initData里面的拦截器,拦截器在set处理函数中又调用了update函数。
new VueTest({// 其他的配置选项methods: {showImg1() {this.isShowImg1 = !this.isShowImg1;},showImg2() {this.isShowImg2 = !this.isShowImg2;}}})
var VueTest = (function () {// ...function initData(vm, showPool) {var _data = vm.$data;for (const key in _data) {if (Object.hasOwnProperty.call(_data, key)) {Object.defineProperty(vm, key, {get: function () {return _data[key];},set: function (newVal) {_data[key] = newVal;// 更新视图update(vm, key, showPool);},});}}}// ...function update(vm, key, showPool) {}return Vue;})();export default VueTest;
update方法和render方法基本类似:
var VueTest = (function () {function Vue(options) {this.$el = document.querySelector(options.el);this.$data = options.data();this._init(options.template, options.methods);}Vue.prototype._init = function (template, methods) {var showPool = new Map();var eventPool = new Map();var container = document.createElement("div");container.innerHTML = template;initData(this, showPool);initPool(container, methods, showPool, eventPool);bindEvent(this, eventPool);render(this, showPool, container);};function initData(vm, showPool) {var _data = vm.$data;for (const key in _data) {if (Object.hasOwnProperty.call(_data, key)) {Object.defineProperty(vm, key, {get: function () {return _data[key];},set: function (newVal) {_data[key] = newVal;update(vm, key, showPool);},});}}}function initPool(container, methods, showPool, eventPool) {var _allNodes = container.getElementsByTagName("*");var dom = null;for (let i = 0; i < _allNodes.length; i++) {dom = _allNodes[i];var vIfData = dom.getAttribute("v-if");var vShowData = dom.getAttribute("v-show");var vEvent = dom.getAttribute("@click");if (vIfData) {showPool.set(dom, {type: "if",prop: vIfData,});dom.removeAttribute("v-if");} else if (vShowData) {showPool.set(dom, {type: "show",prop: vShowData,});dom.removeAttribute("v-show");}if (vEvent) {eventPool.set(dom, methods[vEvent]);dom.removeAttribute("@click");}}}function bindEvent(vm, eventPool) {console.log(eventPool);for (var [dom, handler] of eventPool) {vm[handler.name] = handler;dom.addEventListener("click", vm[handler.name].bind(vm), false);}}function render(vm, showPool, container) {var _data = vm.$data;var _el = vm.$el;for (const [dom, info] of showPool) {switch (info.type) {case "if":info.comment = document.createComment(["v-if"]);!_data[info.prop] && dom.parentNode.replaceChild(info.comment, dom);break;case "show":!_data[info.prop] && (dom.style.display = "none");break;}}_el.appendChild(container);}function update(vm, key, showPool) {var _data = vm.$data;// 遍历 showPool 对象for (const [dom, info] of showPool) {// 如果 dom 的数据和被拦截到的 key 相等if (info.prop === key) {switch (info.type) {case "show":// 如果为假那么就设置样式为隐藏,否则就移除样式!_data[key] ? (dom.style.display = "none") : dom.removeAttribute("style");break;case "if":// 如果为假就用注释节点替换dom,否则就用dom替换注释节点!_data[key]? dom.parentNode.replaceChild(info.comment, dom): info.comment.parentNode.replaceChild(dom, info.comment);break;}}}}return Vue;})();export default VueTest;
到这里我们的模拟就已经完成了,下面去看看效果。
添加声明周期函数
我们还可以添加一些生命周期函数,在相应的阶段进行执行。
import VueTest from "./Vue.js";const vm2 = new VueTest({el: "#app",template: `<div><img v-if="isShowImg1" src="https://cdn.pixabay.com/photo/2022/11/15/04/54/automotive-7593064__340.jpg" /><img v-show="isShowImg2" src="https://cdn.pixabay.com/photo/2022/12/15/18/15/christmas-7658297__340.jpg" /></div><button @click="showImg1">显示图片1</button><button @click="showImg2">显示图片2</button>`,data() {return {isShowImg1: false,isShowImg2: false,};},beforeCreate() {console.log("beforeCreate", this);},created() {console.log("created", this);},beforeMount() {console.log("beforeMount", this);},mounted() {console.log("mounted", this);this.isShowImg1 = false;},methods: {showImg1() {this.isShowImg1 = !this.isShowImg1;},showImg2() {this.isShowImg2 = !this.isShowImg2;},},});console.log(vm2);
var VueTest = (function () {function Vue(options) {// 保存所有的生命周期函数,并且改变 this 指向为 当前实例var recycles = {beforeCreate: options.beforeCreate.bind(this),created: options.created.bind(this),beforeMount: options.beforeMount.bind(this),mounted: options.mounted.bind(this),};// 初始化数据之前调用recycles.beforeCreate();this.$el = document.querySelector(options.el);this.$data = options.data();// 传递 recyclesthis._init(options.template, options.methods, recycles);}Vue.prototype._init = function (template, methods, recycles) {// 初始化数据之后调用recycles.created();var showPool = new Map();var eventPool = new Map();var container = document.createElement("div");container.innerHTML = template;initData(this, showPool);initPool(container, methods, showPool, eventPool);bindEvent(this, eventPool);// 传递 recyclesrender(this, showPool, container, recycles);};function initData(vm, showPool) {var _data = vm.$data;for (const key in _data) {if (Object.hasOwnProperty.call(_data, key)) {Object.defineProperty(vm, key, {get: function () {return _data[key];},set: function (newVal) {_data[key] = newVal;update(vm, key, showPool);},});}}}function initPool(container, methods, showPool, eventPool) {var _allNodes = container.getElementsByTagName("*");var dom = null;for (let i = 0; i < _allNodes.length; i++) {dom = _allNodes[i];var vIfData = dom.getAttribute("v-if");var vShowData = dom.getAttribute("v-show");var vEvent = dom.getAttribute("@click");if (vIfData) {showPool.set(dom, {type: "if",prop: vIfData,});dom.removeAttribute("v-if");} else if (vShowData) {showPool.set(dom, {type: "show",prop: vShowData,});dom.removeAttribute("v-show");}if (vEvent) {eventPool.set(dom, methods[vEvent]);dom.removeAttribute("@click");}}}function bindEvent(vm, eventPool) {for (var [dom, handler] of eventPool) {vm[handler.name] = handler;dom.addEventListener("click", vm[handler.name].bind(vm), false);}}function render(vm, showPool, container, recycles) {var _data = vm.$data;var _el = vm.$el;for (const [dom, info] of showPool) {switch (info.type) {case "if":info.comment = document.createComment(["v-if"]);!_data[info.prop] && dom.parentNode.replaceChild(info.comment, dom);break;case "show":!_data[info.prop] && (dom.style.display = "none");break;}}// 挂载之前调用recycles.beforeMount();_el.appendChild(container);// 挂载之后调用recycles.mounted();}function update(vm, key, showPool) {var _data = vm.$data;for (const [dom, info] of showPool) {if (info.prop === key) {switch (info.type) {case "show":!_data[key] ? (dom.style.display = "none") : dom.removeAttribute("style");break;case "if":!_data[key]? dom.parentNode.replaceChild(info.comment, dom): info.comment.parentNode.replaceChild(dom, info.comment);break;}}}}return Vue;})();export default VueTest;
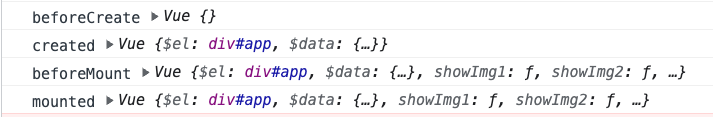
这些生命周期方法的this都指向当前实例!!!

