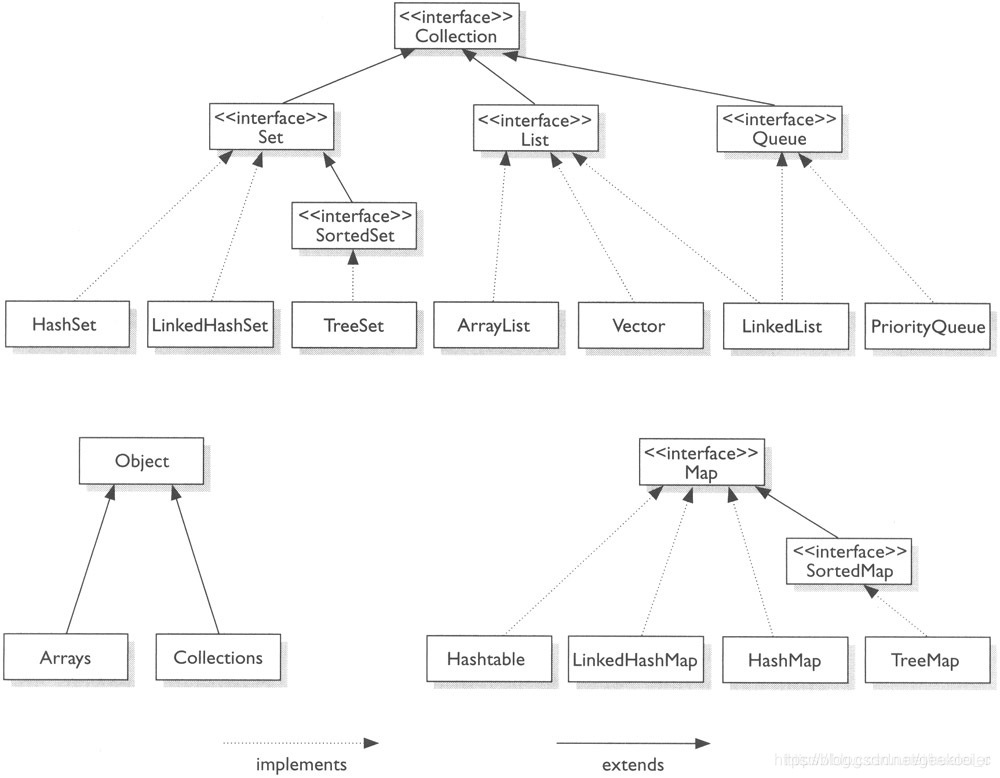
Map 接口
- 与前面的接口不同,为双列
- set 接口实际上也是kv 但是 k为值,v为present常量
Map 接口实现类总结
1 map 与 collection并列存在, 用于保存映射关系的数据 key-value
2 map 中的key 和 value 可以是任何引用类型的数据,会封装到 hashMap$Node对象中
3 map 的key 不允许重续 ,原因和hashSet一样,hash值唯一索引,可以参考前面hashSet底层
4 map 中的value可以重复
5 map 的key 可以为 null ,value 也可为 null, 注意key 为null 只能有一个,value为null可以有多个
6 常用String类作为 map 的key
7 key 和 value 中间存在 单向1对1关系,即通过制定的key 总能找到 对应的value
8 map存放数据的 kv 一堆 kv 是放在一个node中的,有因为node实现了 Entry接口, 也有书说 一对kv就是一个entryEntrySet
```java package map_;
- set 接口实际上也是kv 但是 k为值,v为present常量
import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map;
public class MapSource_01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {Map hashMap = new HashMap();hashMap.put("no1","addicated");hashMap.put("no2","addicated");hashMap.put("no3","addicated");// 1 HashMap$Node node// tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);// 2 k-v 为了方便程序员遍历,还会创建 entrySet集合 该集合存放元素的类型 Entry// 而一个entry对象,对象就有 k,v, EntrySet<Entry<k,v>> 即 transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet// 3 entrySet 中,定义的类型 是 Map.Entry ,但是实际上存放的还是 HashMap@Node// 这是因为 static class Node<k,v> implements Map.Entry<k,v>// 4 当吧 HashMap$Node 对象存放到 entrySet 就方便我们的遍历 因为 map.Entry 提供了 getkey getvalue 方法
// 已经老生畅谈了,因为 hashSet的底层实现即是hashMap 所以在聊hashMap的时候会略一些内容过去,
// 首先 hashMap 底层添加到 hashtable 中的是一个HashMap$Node对象,但是这个node对象 实现了 Map.Entry
}
}
/*** Basic hash bin node, used for most entries. (See below for* TreeNode subclass, and in LinkedHashMap for its Entry subclass.)*/static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {final int hash;final K key;V value;Node<K,V> next;Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> next) {this.hash = hash;this.key = key;this.value = value;this.next = next;}public final K getKey() { return key; }public final V getValue() { return value; }public final String toString() { return key + "=" + value; }public final int hashCode() {return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value);}public final V setValue(V newValue) {V oldValue = value;value = newValue;return oldValue;}public final boolean equals(Object o) {if (o == this)return true;if (o instanceof Map.Entry) {Map.Entry<?,?> e = (Map.Entry<?,?>)o;if (Objects.equals(key, e.getKey()) &&Objects.equals(value, e.getValue()))return true;}return false;}}
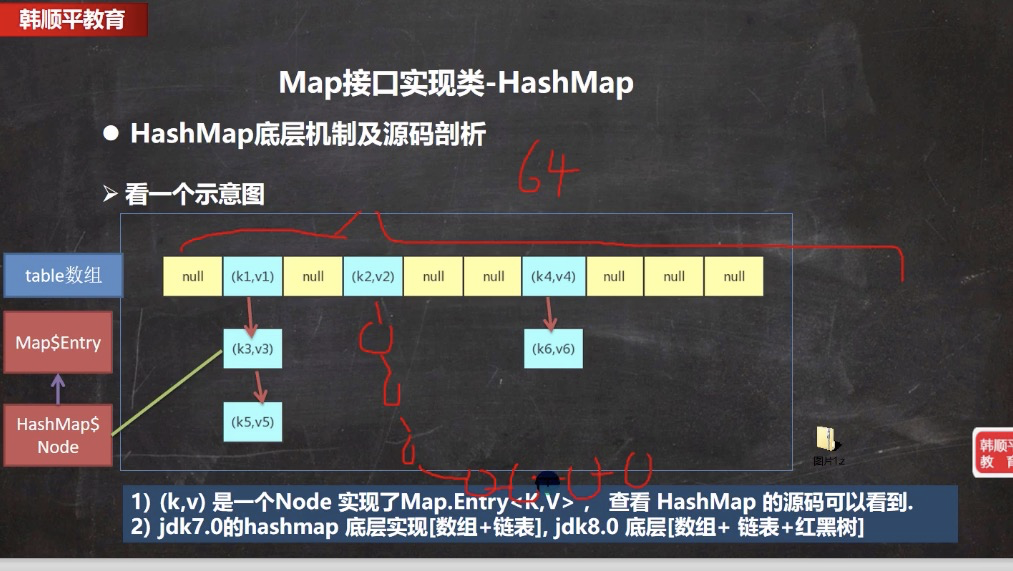- 如上图所示- 某个链表元素大于8个 且整个数组长度大于64 就会树化<a name="I10wE"></a># 扩容机制- 与hashSet完全一致,再复习一遍- hashMap 底层维护了 Node类型的数组table 默认为null- 当创建对象的时候,将加载因子 loadfactor 初始化为0.75- 当添加k -v 的时候- 首先通过 key 的 hash值得到在table 的索引,即 hashSet文章中的那个 hash算法方法- 然后判断该索引处是否有元素。- 没有则直接添加。- 有则判断该元素的key是否和准备加入的key是否相等,如果相等,直接替换val- 如果不相等,判断是树结构还是链表结构,进行对应处理。- 如果添加时发现容量不够,则扩容- 第一次添加,直接扩容table为16 临界值 threshold 即下次扩容的临界点为12- 之后再次扩容则扩容table容量为原来的2倍,临界值为原来的2倍,即24,以此类推- java8中,如果一条链表元素 超过 TREEIFY_THRESHOLD 默认为8,并且table大小超过 MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY 默认为64 就进行树化<a name="FMF6d"></a># 源码解读```java构造器/*** Constructs an empty <tt>HashMap</tt> with the default initial capacity* (16) and the default load factor (0.75).*/public HashMap() {this.loadFactor = DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; // all other fields defaulted}// 初始化加载因子 0.75HashMap$Node[] table = null执行put 注意点,此处与hashSet 不同 ,k 为 hashMap.put(k,v) 传入的值,hashSet 此处 v 为 PRESENT 常量public V put(K key, V value) {return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);}老生畅谈的 putvalfinal V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,boolean evict) {Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;//辅助变量//如果底层的table 数组为null, 或者 length =0 , 就扩容到16if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)n = (tab = resize()).length;//取出hash值对应的table的索引位置的Node, 如果为null, 就直接把加入的k-v//, 创建成一个 Node ,加入该位置即可if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);else {Node<K,V> e; K k;//辅助变量// 如果table的索引位置的key的hash相同和新的key的hash值相同,// 并 满足(table现有的结点的key和准备添加的key是同一个对象 || equals返回真)// 就认为不能加入新的k-vif (p.hash == hash &&((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))e = p;else if (p instanceof TreeNode)//如果当前的table的已有的Node 是红黑树,就按照红黑树的方式处理e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);else {//如果找到的结点,后面是链表,就循环比较for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {//死循环if ((e = p.next) == null) {//如果整个链表,没有和他相同,就加到该链表的最后p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);//加入后,判断当前链表的个数,是否已经到8个,到8个,后//就调用 treeifyBin 方法进行红黑树的转换if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1sttreeifyBin(tab, hash);break;}if (e.hash == hash && //如果在循环比较过程中,发现有相同,就break,就只是替换value((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))break;p = e;}}if (e != null) { // existing mapping for keyV oldValue = e.value;if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)e.value = value; //替换,key对应valueafterNodeAccess(e);return oldValue;}}++modCount;//每增加一个Node ,就size++if (++size > threshold[12-24-48])//如size > 临界值,就扩容resize();afterNodeInsertion(evict);return null;}5. 关于树化(转成红黑树)//如果table 为null ,或者大小还没有到 64,暂时不树化,而是进行扩容.//否则才会真正的树化 -> 剪枝final void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] tab, int hash) {int n, index; Node<K,V> e;if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) < MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY)resize();}
HashMap 遍历方式
共三组 ```java public class Map_for {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Object o1 = new Object();Map hashMap = new HashMap();hashMap.put("key1","addicated");hashMap.put("key2","mengnan");hashMap.put("key3","rebot");hashMap.put(null,"rebot");// 1组 先取出所有的key ,通过key 取到对应的valueSet keySet = hashMap.keySet();// 1 增强for// 增强for循环 快捷键 为 I 大写的 Ifor (Object o :keySet) {System.out.println(hashMap.get(o));}System.out.println("----------- 使用迭代器来进行遍历");// 2 迭代器进行遍历 ititIterator iterator = keySet.iterator();while (iterator.hasNext()) {Object next = iterator.next();System.out.println(hashMap.get(next));}// 第二组 包所有的value 取出Collection values = hashMap.values();for (Object o :values) {System.out.println(o);}// 迭代器System.out.println("---------- 值 ");Iterator iterator1 = values.iterator();while (iterator1.hasNext()) {Object next = iterator1.next();System.out.println(next);}// 通过entrySet来进行遍历Set set = hashMap.entrySet();
// 增强for循环遍历
for (Object o :set) {
// 实际上每一个o 都是一个 entry 即一个kv对 // 要将entry 转换成map.entry Map.Entry o2 = (Map.Entry) o; System.out.println(o2.getKey()+ “——“ + o2.getValue());
}
// 迭代器
Iterator iterator2 = set.iterator();
while (iterator2.hasNext()) {
Object next = iterator2.next();
System.out.println(next.getClass()); // 其实是一个个的hashmap$node对象
Map.Entry next1 = (Map.Entry) next;
System.out.println(next1.getKey());
System.out.println(next1.getValue());
}
// person person1 = new person(“猛男”,18); // person person2 = new person(“猛男”,18); // // System.out.println(person1.hashCode()); // System.out.println(person2.hashCode()); // System.out.println(person1.equals(person2)); // person1.setAge(22); // System.out.println(person2.getAge()); }
<a name="CiInc"></a>
# Hashtable
- 同hashMap一样作为map的一个实现子类
- 有以下特点
- 1 存放的元素是kv 对<br />2 hashtable 的 k v 都不能为null<br />3 hashTable 的使用方法基本上hashMap一致<br />4 hashTable 是线程安全的,hashMap是线程不安全的
<a name="TYinG"></a>
# 源码分析
```java
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hashtable hashtable = new Hashtable();
hashtable.put(1, "addicated");
hashtable.put(2, "addicated");
hashtable.put(3, "addicated");
hashtable.put(4, "addicated");
hashtable.put(5, "addicated");
}
// 构造方法 初始容量为 11 扩容系数为0.75
public Hashtable() {
this(11, 0.75f);
}
// 底层解析 下见图
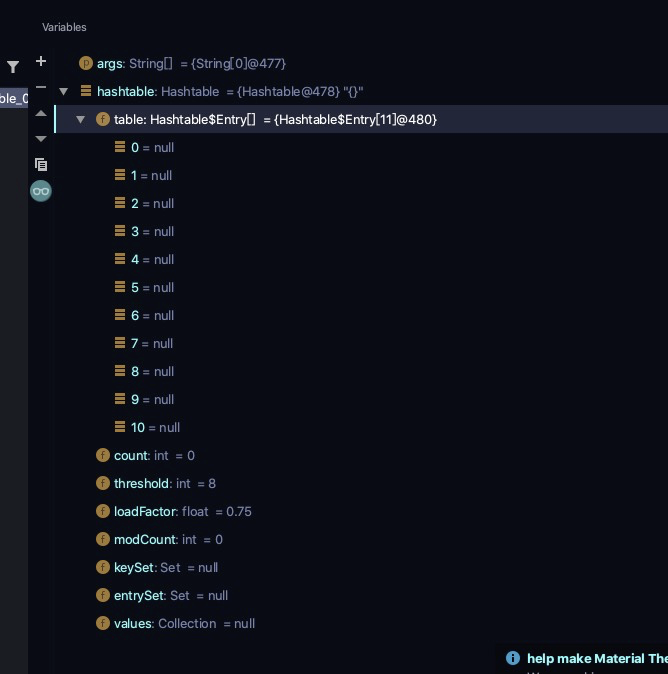
为一个 Hashtable$Entry[] 数组 里面存放的为entry对象 ```java // put 方法解析 public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {
// Make sure the value is not null if (value == null) { // 这里是为什么 hashtable 不允许null key null value的代码层原因 throw new NullPointerException(); } // Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable. Entry<?,?> tab[] = table; int hash = key.hashCode(); int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length; @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Entry<K,V> entry = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index]; for(; entry != null ; entry = entry.next) { if ((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) { V old = entry.value; entry.value = value; return old; } } addEntry(hash, key, value, index); return null;}
// 追入 addEntry private void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int index) { modCount++;
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
if (count >= threshold) {
// Rehash the table if the threshold is exceeded
rehash(); // 判断当前数组长度是否超过扩容临界值 ,超过则扩容,
tab = table;
hash = key.hashCode();
index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
}
// Creates the new entry.
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>) tab[index];
tab[index] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
count++;
}
// rehash 方法, hashtable 独有 @SuppressWarnings(“unchecked”) protected void rehash() { int oldCapacity = table.length; Entry<?,?>[] oldMap = table;
// overflow-conscious code 关键点, 为 旧容量向左位移1位之后 +1 相当于*2 +1
int newCapacity = (oldCapacity << 1) + 1;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) {
if (oldCapacity == MAX_ARRAY_SIZE)
// Keep running with MAX_ARRAY_SIZE buckets
return;
newCapacity = MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
Entry<?,?>[] newMap = new Entry<?,?>[newCapacity];
modCount++;
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1);
table = newMap;
for (int i = oldCapacity ; i-- > 0 ;) {
for (Entry<K,V> old = (Entry<K,V>)oldMap[i] ; old != null ; ) {
Entry<K,V> e = old;
old = old.next;
int index = (e.hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % newCapacity;
e.next = (Entry<K,V>)newMap[index];
newMap[index] = e;
}
}
}
```
- hashtable 总结
- 1 底层有数组 HashTable$Entry[] 初始化大小为 11 系数为0。75
2 threshold 为8 = 11 *0。75
3 按照自己的扩容机制来进行扩容 4 put 底层执行 addEntry(hash, key, value, index);
当达到8个以上之后开始扩容,扩容调用的方法为 rehash
5 按照 if (count >= threshold )满足时就进行扩容_hashTable 和 hashMap 的对比__hashMap | 1。2 | 线程不安全 | 效率搞 | 允许 nullkey null value
hashTable | 1。0 | 线程安全 | 效率低 | 不允许 null key null value
- 1 底层有数组 HashTable$Entry[] 初始化大小为 11 系数为0。75
_
�