
Overview
Pocket Shield is equipped with a built-in rechargeable battery that can supply power for CyberPi and provides 2-pin and 3-pin interfaces that can be used to connect servos, LED strips, and motors, which significantly improves the extensibility of CyberPi.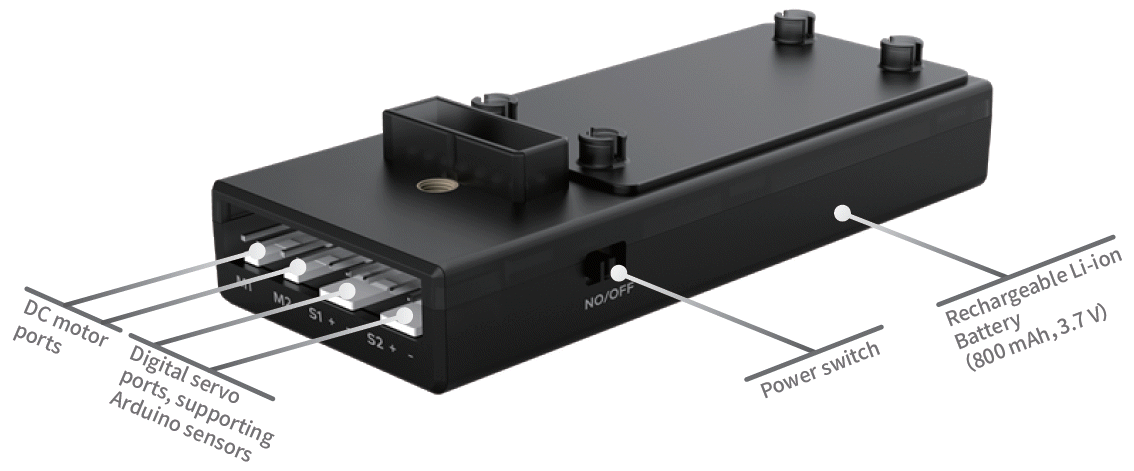
Features
- Built-in rechargeable Li-ion battery, used to supply power for CyberPi
- Two DC motor ports, used to connect and drive DC motors
- Two digital servo ports, used to connect and drive servos or LED strips
- One main control board port, allowing you to easily connect Pocket Shield to CyberPi
- Supporting mBlock 5 programming, which is intended for users of all ages, including those without any programming experience
- Supporting Python programming, for which the
cyberpilibrary is providedSpecifications
| Product parameters | description |
|---|---|
| Micro-processor | GD32 |
| Battery Parameter | 3.7V 800mAh |
| Input voltage/current | 5V 700mA |
| Output voltage/current | 5V 2A |
| Battery life | 4 hours( in general application scenarios, just for reference) |
| Charging time | 1~2 hours |
| Communication mode | Serial communication: between the main control board and extension board Digital signals: at the digital servo port PWM signals: at the DC motor port |
| Hardware version | V1.1 |
| Dimension | 84×35×19mm |
| Weight | 48g |
Note:
- Self-discharge occurs in the lithium-ion battery. If you store mBot2 Shield with the battery voltage lower than 3.6 V for a long time, the battery will be over-discharged and its internal structure may be damaged, which reduces the endurance of the battery. Therefore, to store mBot2 Shield for a long time while keeping the battery intact, you need to charge the battery once every three to six months to 3.8–3.9 V (the best voltage for storage is 3.85 V), which allows the discharge depth of 40% to 60%.
- Store mBot2 Shield at 4℃ to 35℃ in a dry place or keep it away from moisture through packaging.
- Keep it away from heat or direct sunlight.
Firmware update
After a new firmware version is released, you can connect Pocket Shield to mBlock 5 through CyberPi to view and update its firmware. For details about how to update the firmware, see “How to update the firmware?“
Programming
You can use mBlock 5 to program Pocket Shield. mBlock 5 provides two editors, namely the block-based graphical editor (the default editor, referred to as mBlock 5) and Python editor (referred to as mBlock-Python Editor).
For details about programming, see “Programming Software.”
Take Pocket Shield home
- Contact the local dealer to purchase CyberPi series products and their educational packages.
2. Contact us to become our dealer.More information
CyberPi Operation Guide
Pocket Shield Operation Guide
CyberPi Series User Manual
Python API Documentation for CyberPi
mBlock 5 Online Help
mBlock-Python Editor Online Help

