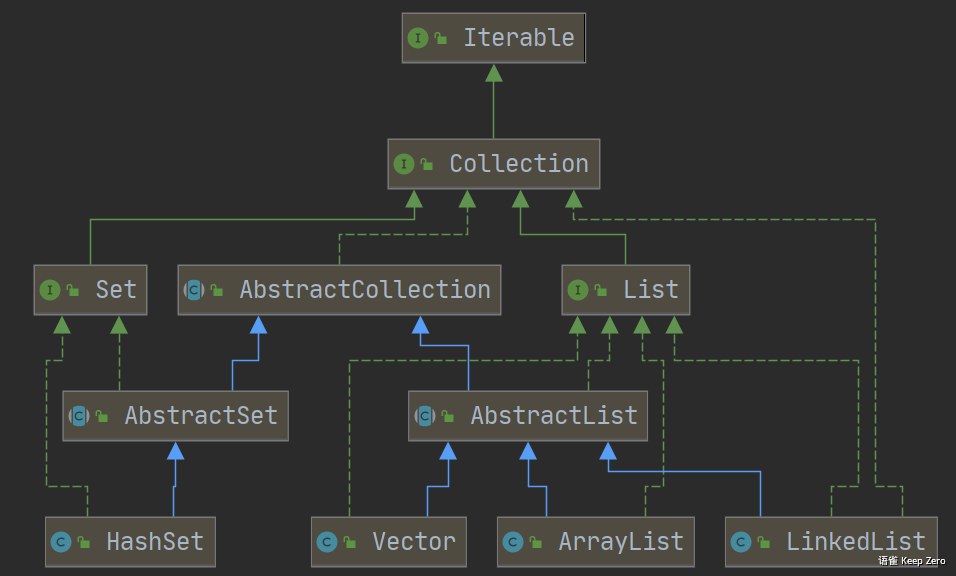
类关系图
功能介绍
包路径:java.util
功能描述: Vector类类和ArrayList非常相似,继承了AbstractList抽象类,同时实现了List的接口,**实现了一个动态数组,但是该类是同步的(内部使用syncronized同步锁实现),可以用在多线程的情况,该类允许设置增长长度,默认扩容方式为原来的2倍。
Vector 主要用在事先不知道数组的大小,或者只是需要一个可以改变大小的数组的情况。
源码解析
主要属性
public class Vector<E>extends AbstractList<E>implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable{// 存储数据的数组protected Object[] elementData;// 当前元素的个数protected int elementCount;// 容量增长系数,扩容时使用protected int capacityIncrement;// 最大数组容量private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;}
构造方法
public class Vector<E>extends AbstractList<E>implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable{/*** 指定初始容量以及增长系数* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the vector* @param capacityIncrement the amount by which the capacity is* increased when the vector overflows*/public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) {super();if (initialCapacity < 0)throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+initialCapacity);// 构建初始容量为initialCapacity的数组this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];// 设置增长系数this.capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement;}/*** 指定初始容量的构造方法* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the vector*/public Vector(int initialCapacity) {// 增长系数==0this(initialCapacity, 0);}/*** 无参构造方法*/public Vector() {// 初始容量==10,增长系数==0this(10);}/*** 构建Vector并传入元素* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this* vector*/public Vector(Collection<? extends E> c) {// 传入集合转为数组elementData = c.toArray();// 传入集合元素数量elementCount = elementData.length;// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, elementCount, Object[].class);}}
核心方法
(1) add方法—-添加元素
public class Vector<E>extends AbstractList<E>implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable{/*** 追加元素(synchronized方法)* @param e element to be appended to this Vector* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})* @since 1.2*/public synchronized boolean add(E e) {modCount++;// 判断是否需要扩容ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);// 添加元素elementData[elementCount++] = e;return true;}/*** 向指定位置插入元素* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted* @param element element to be inserted*/public void add(int index, E element) {// 向指定位置插入元素insertElementAt(element, index);}/*** 向指定位置插入元素(synchronized方法)* @param obj the component to insert* @param index where to insert the new component*/public synchronized void insertElementAt(E obj, int index) {modCount++;// 检测位置是否合法if (index > elementCount) {throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index+ " > " + elementCount);}// 判断是否需要扩容ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);// 移动元素,index后的元素都需要移动1位System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, elementCount - index);elementData[index] = obj;elementCount++;}/*** 追加集合所有元素(synchronized方法)* @param c elements to be inserted into this Vector* @return {@code true} if this Vector changed as a result of the call* @since 1.2*/public synchronized boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {modCount++;Object[] a = c.toArray();int numNew = a.length;// 判断是否需要扩容ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + numNew);System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, elementCount, numNew);elementCount += numNew;return numNew != 0;}/*** 向指定位置插入集合所有元素(synchronized方法)* @param index index at which to insert the first element from the* specified collection* @param c elements to be inserted into this Vector* @return {@code true} if this Vector changed as a result of the call* @since 1.2*/public synchronized boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {modCount++;// 判断位置是否合法if (index < 0 || index > elementCount)throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);Object[] a = c.toArray();int numNew = a.length;ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + numNew);int numMoved = elementCount - index;if (numMoved > 0)System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew,numMoved);System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew);elementCount += numNew;return numNew != 0;}/*** 追加元素(synchronized方法)* @param obj the component to be added*/public synchronized void addElement(E obj) {modCount++;// 判断是否需要扩容ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);// 设置elementCount位置元素,然后再+1elementData[elementCount++] = obj;}}
(2) remove方法—-删除元素
public class Vector<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
/**
* 移除指定位置上的元素,返回元素旧值(synchronized方法)
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return element that was removed
* @since 1.2
*/
public synchronized E remove(int index) {
modCount++;
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
// 获取指定位置的元素
E oldValue = elementData(index);
// 判断是否需要移动元素
int numMoved = elementCount - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
// 位置置空,以便gc回收内存
elementData[--elementCount] = null; // Let gc do its work
return oldValue;
}
/**
* 移除元素
* @param o element to be removed from this Vector, if present
* @return true if the Vector contained the specified element
* @since 1.2
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return removeElement(o);
}
/**
* 移除传入的所有元素(synchronized方法)
* @param c a collection of elements to be removed from the Vector
* @return true if this Vector changed as a result of the call
* @since 1.2
*/
public synchronized boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {
return super.removeAll(c);
}
/**
* 仅保留传入的所有元素(synchronized方法)
* @param c a collection of elements to be retained in this Vector
* (all other elements are removed)
* @return true if this Vector changed as a result of the call
* @since 1.2
*/
public synchronized boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {
return super.retainAll(c);
}
/**
* 移除元素(synchronized方法)
* @param obj the component to be removed
* @return {@code true} if the argument was a component of this
* vector; {@code false} otherwise.
*/
public synchronized boolean removeElement(Object obj) {
modCount++;
// 寻找目标元素在集合中的位置
int i = indexOf(obj);
// i > =0 代表元素存在
if (i >= 0) {
removeElementAt(i);
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 移除所有元素(synchronized方法)
*/
public synchronized void removeAllElements() {
modCount++;
// 遍历数组置空
// Let gc do its work
for (int i = 0; i < elementCount; i++)
elementData[i] = null;
// 元素数量==0
elementCount = 0;
}
/**
* 移除指定位置元素(synchronized方法)
* @param index the index of the object to remove
*/
public synchronized void removeElementAt(int index) {
modCount++;
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " +
elementCount);
}
else if (index < 0) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
int j = elementCount - index - 1;
if (j > 0) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1, elementData, index, j);
}
elementCount--;
elementData[elementCount] = null; /* to let gc do its work */
}
}
(3) set方法—-设置元素
public class Vector<E>
extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
/**
* 设置指定位置的元素(synchronized方法)
* @param index index of the element to replace
* @param element element to be stored at the specified position
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @since 1.2
*/
public synchronized E set(int index, E element) {
// 如果传入index不合法,抛出异常
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
// 获取指定位置的元素
E oldValue = elementData(index);
// 设置新值
elementData[index] = element;
// 返回旧值
return oldValue;
}
}
(4) get方法—-获取元素
public class Vector<E>
extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
/**
* 获取指定位置的元素(synchronized方法)
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return object at the specified index
* @since 1.2
*/
public synchronized E get(int index) {
if (index >= elementCount)
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
return elementData(index);
}
}
(5) forEach方法—-遍历元素
public class Vector<E>
extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
/**
* 遍历元素并对元素执行传入函数(synchronized方法)
* @param action
* @since 1.2
*/
@Override
public synchronized void forEach(Consumer<? super E> action) {
Objects.requireNonNull(action);
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
final E[] elementData = (E[]) this.elementData;
final int elementCount = this.elementCount;
// 遍历数组执行函数
for (int i=0; modCount == expectedModCount && i < elementCount; i++) {
action.accept(elementData[i]);
}
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
}
(6) sort方法—-排序
public class Vector<E>
extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
/**
* 根据传入的比较器规则排序(synchronized方法)
* @param c
* @since 1.2
*/
@Override
public synchronized void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) {
final int expectedModCount = modCount;
Arrays.sort((E[]) elementData, 0, elementCount, c);
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
modCount++;
}
}
(7) ensureCapacityHelper方法—-扩容
添加元素的时候会涉及到数组容量的判断与扩容操作,我们看一下具体源码:
public class Vector<E>
extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
/**
* 判断是否需要扩容
* @param minCapacity 最小需要的容量
* @see #ensureCapacity(int)
*/
private void ensureCapacityHelper(int minCapacity) {
// 如果当前数组长度比所需容量小,则调用grow方法执行扩容
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
/**
* 执行扩容
* @param minCapacity 最小需要的容量
* @see #ensureCapacity(int)
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
// 如果增长系数>0,则优先使用增长系数+旧长度的方式增长,否则扩大为两倍
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?
capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);
// 扩大之后还是比minCapacity小,则直接将新长度定为目标长度
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
// 如果新长度超过了最大允许长度,则调用hugeCapacity计算最终长度
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// 数组扩容
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
/**
* 计算返回最大的数组长度
* @param minCapacity 本次扩容最小的目标长度
* @see #ensureCapacity(int)
*/
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
// 如果最小目标长度比最大允许容量还大,那就使用Integer.MAX_VALUE,否则使用最大的允许容量
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
/**
* 额外提供给外界的手动扩容方法
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
*/
public synchronized void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity > 0) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(minCapacity);
}
}
/**
* 直接设置vector的size,可以用来手动扩容或强行缩减数组
* @param newSize the new size of this vector
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if the new size is negative
*/
public synchronized void setSize(int newSize) {
modCount++;
if (newSize > elementCount) {
ensureCapacityHelper(newSize);
} else {
for (int i = newSize ; i < elementCount ; i++) {
elementData[i] = null;
}
}
elementCount = newSize;
}
}
也就是说,最核心的方法实际上是grow方法,正常情况下数组会扩容1.5倍,特殊情况下(新扩展数组大小已经达到了最大值)则只取最大值。
简单使用
public class VectorCode {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
commonExample();
}
public static void commonExample(){
Vector<Integer> vector = new Vector<>();
for(int i=0;i<20;i++){
vector.add(i);
}
System.out.println("vector = "+vector);
System.out.println("vector.size() = "+vector.size());
// 强行扩容,并用null填充多出来的部分
vector.setSize(25);
System.out.println("\n=============扩容后=============");
System.out.println("vector = "+vector);
System.out.println("vector.size() = "+vector.size());
}
}
输出:
vector = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19]
vector.size() = 20
=============扩容后=============
vector = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, null, null, null, null, null]
vector.size() = 25
总结
1、Vector类类和ArrayList非常相似,继承了AbstractList抽象类,同时实现了List的接口,**实现了一个动态数组,但是该类是同步的(内部使用syncronized同步锁实现),可以用在多线程的情况,该类允许设置增长长度,默认扩容方式为原来的2倍**。
2、Vector类的特点是线程安全,查询快,增删慢(涉及数组扩容)
3、Vector类内部大多数方法都使用了**syncronized关键字修饰
4、Vector 主要用在事先不知道数组的大小,或者只是需要一个可以改变大小的数组的情况。**

