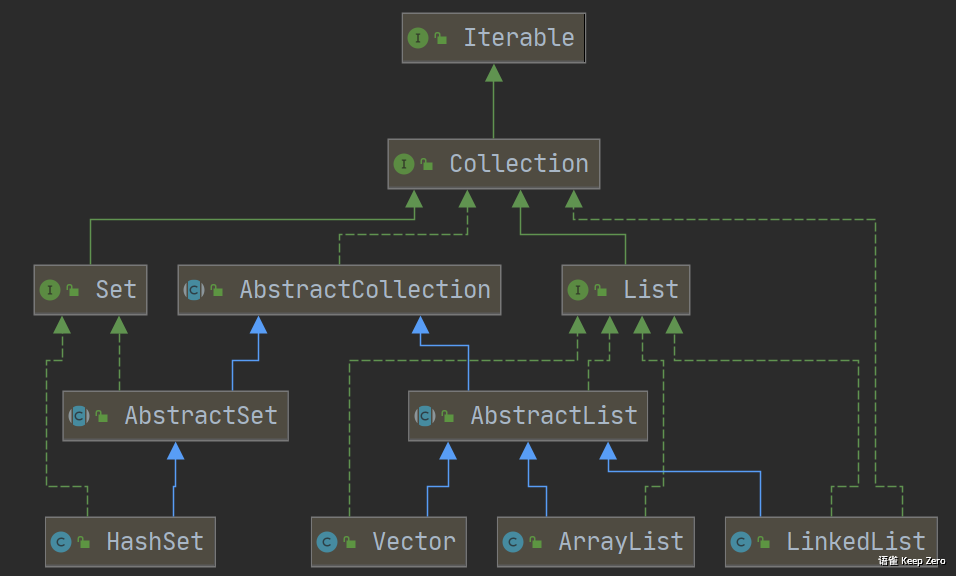
类关系图
功能介绍
包路径:java.util
功能描述: HashSet 继承了AbstractSet抽象类,同时实现了Set接口,内部使用HashMap作为容器装载元素,以元素本身为key,一个空对象为值**
特点:线程不安全;**不允许出现重复元素;不保证集合中元素的顺序;允许包含值为null的元素,但最多只能一个。**
源码解析
核心属性
public class HashSet<E>extends AbstractSet<E>implements Set<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable{// 存放数据的容器private transient HashMap<E,Object> map;// PRESENT 空对象作为 hashmap 的value,不使用 null 是为了与获取key为null区分开// Dummy value to associate with an Object in the backing Mapprivate static final Object PRESENT = new Object();}
构造方法
public class HashSet<E>
extends AbstractSet<E>
implements Set<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
/**
* 默认构造方法,构造hashMap对象,默认初始容量16,负载因子 0.75
*/
public HashSet() {
map = new HashMap<>();
}
/**
* 初始化一个集合,默认负载因子为0.75,容量看情况定义足够存储的大小
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this set
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public HashSet(Collection<? extends E> c) {
map = new HashMap<>(Math.max((int) (c.size()/.75f) + 1, 16));
addAll(c);
}
/**
* 创建一个空集合,但是指定 容量大小 与 负载因子
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the hash map
* @param loadFactor the load factor of the hash map
*/
public HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
map = new HashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
}
/**
* 构建空集合,指定 容量大小,使用默认的 负载因子 0.75
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the hash table
*/
public HashSet(int initialCapacity) {
map = new HashMap<>(initialCapacity);
}
/**
* 不对外开放的构造函数,指定 容量大小 与 负载因子,参数 dummy 只是为了重载构造,没有意义
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the hash map
* @param loadFactor the load factor of the hash map
* @param dummy ignored (distinguishes this
*/
HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean dummy) {
map = new LinkedHashMap<>(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
}
}
核心方法
(1) add方法—-添加元素
public class HashSet<E>
extends AbstractSet<E>
implements Set<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
/**
* 添加元素
* @param e element to be added to this set
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this set did not already contain the specified
* element
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
// 以传入元素为key,PRESENT空对象为值存入map中
return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
}
(2) remove方法—-删除元素
public class HashSet<E>
extends AbstractSet<E>
implements Set<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
/**
* 移除元素
* @param o object to be removed from this set, if present
* @return <tt>true</tt> if the set contained the specified element
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
// 从map中移除元素并返回旧值判断是否移除成功
return map.remove(o)==PRESENT;
}
}
(3) contains方法—-判断是否存在指定元素
public class HashSet<E>
extends AbstractSet<E>
implements Set<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
/**
* 判断set集合是否存在指定元素
* @param o element whose presence in this set is to be tested
* @return <tt>true</tt> if this set contains the specified element
*/
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return map.containsKey(o);
}
}
(4) iterator方法—-迭代器
public class HashSet<E>
extends AbstractSet<E>
implements Set<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
/**
* 返回迭代器,实际上返回的是HashMap的keySet迭代器
* @return an Iterator over the elements in this set
* @see ConcurrentModificationException
*/
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return map.keySet().iterator();
}
}
简单使用
package com.java.collection.set;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @description Set接口演示
* @date: 2021-01-09 15:45
*/
public class SetCode {
public static void main(String[] args) {
commonExample();
}
public static void commonExample(){
Set<Integer> mySet = new HashSet<>();
for(int i=0;i<20;i++){
mySet.add(i);
}
System.out.println("mySet = "+mySet);
System.out.println("mySet.size() = "+mySet.size());
Set<Integer> subSet = new HashSet<>();
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
subSet.add(i);
}
System.out.println("subSet = "+subSet);
System.out.println("mySet.containsAll(subSet) = "+mySet.containsAll(subSet));
// 移除元素
mySet.removeAll(subSet);
// 利用迭代器迭代集合元素
Iterator<Integer> iterator = mySet.iterator();
StringBuilder outStr = new StringBuilder("[");
while (iterator.hasNext()){
outStr.append(iterator.next()+",");
}
outStr.deleteCharAt(outStr.length()-1);// 删除字符串最后一个逗号
outStr.append("]");
System.out.println("mySet = "+outStr);
}
}
输出结果:
mySet = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19]
mySet.size() = 20
subSet = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
mySet.containsAll(subSet) = true
mySet = [10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19]
总结
1、 HashSet 继承了AbstractSet抽象类,同时实现了Set接口,内部使用HashMap作为容器装载元素,以元素本身为key,一个空对象为值
2、HashSet的特点是线程不安全;**不允许出现重复元素;不保证集合中元素的顺序;允许包含值为null的元素,但最多只能一个
思考
怎么解决HashSet线程不安全问题?
我们知道,HashSet内部使用HashMap来实现存储和插入更新等操作,HashMap是线程不安全的,自然就使得HashSet也是线程不安全的(在其相关方法也未见任何关于并发锁机制的处理)。
解决方案:
- 使用 Collections.synchronizedSet()【内部通过syncronized实现线程安全】
**
- 使用CopyOnWriteArraySet线程安全集合(内部使用CopyOnWriteArrayList存放元素)

