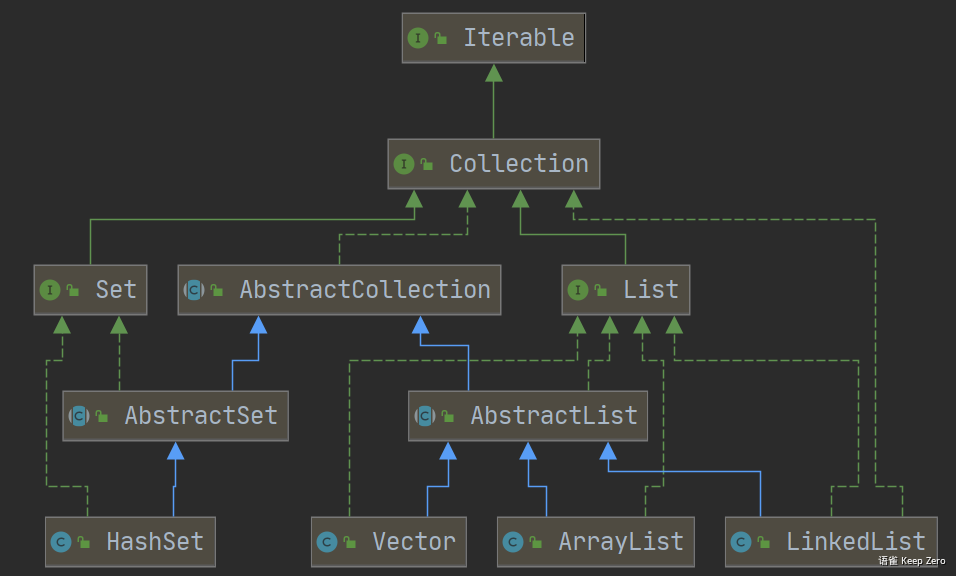
类关系图
功能介绍
包路径:java.util
功能描述: LinkedList 继承了AbstractSequentialList抽象类,同时实现了List的接口,允许有null(空)元素。主要用于创建双向链表数据结构**,该类没有同步方法,如果多个线程同时访问一个List,则必须自己实现访问同步,解决方法就是在创建List时候构造一个同步的List

LinkedList最主要的功能方面的增强是可以在List的头部和尾部添加、删除、获取元素,直接提供了这些方法的实现。可以非常方便的实现数据结构中常见的Stack(栈)和Queue(队列)
链表(Linked list)是一种常见的基础数据结构,是一种线性表,但是并不会按线性的顺序存储数据,而是在每一个节点里存到下一个节点的地址。
特点:非线程安全,查询慢,增删快(链表特性)
LinkedList 继承了 AbstractSequentialList 类,实现链式访问。
LinkedList 实现了 Deque 接口,可作为队列使用。
源码解析
AbstractSequentialList
AbstractSequentialList 继承于 AbstractList ,提供了对数据元素的链式访问而不是随机访问。
/*** @author Josh Bloch* @author Neal Gafter* @see Collection* @see List* @see AbstractList* @see AbstractCollection* @since 1.2*/public abstract class AbstractSequentialList<E> extends AbstractList<E> {/*** Sole constructor. (For invocation by subclass constructors, typically* implicit.)*/protected AbstractSequentialList() {}/*** 获取指定位置的元素*/public E get(int index) {try {// 直接获取以index为初始位置的ListIteratorreturn listIterator(index).next();} catch (NoSuchElementException exc) {throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index);}}/*** 设置指定位置元素*/public E set(int index, E element) {try {ListIterator<E> e = listIterator(index);E oldVal = e.next();e.set(element);return oldVal;} catch (NoSuchElementException exc) {throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index);}}/*** 在指定位置插入元素*/public void add(int index, E element) {try {listIterator(index).add(element);} catch (NoSuchElementException exc) {throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index);}}/*** 移除指定位置的元素*/public E remove(int index) {try {ListIterator<E> e = listIterator(index);E outCast = e.next();e.remove();return outCast;} catch (NoSuchElementException exc) {throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index);}}// Bulk Operations/*** 往指定位置插入集合所有元素*/public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {try {boolean modified = false;ListIterator<E> e1 = listIterator(index);Iterator<? extends E> e2 = c.iterator();while (e2.hasNext()) {e1.add(e2.next());modified = true;}return modified;} catch (NoSuchElementException exc) {throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: "+index);}}// Iterators/**** @return an iterator over the elements in this list (in proper sequence)*/public Iterator<E> iterator() {return listIterator();}/*** 返回ListIterator迭代器,未实现* @param index index of first element to be returned from the list* iterator (by a call to the <code>next</code> method)* @return a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper* sequence)*/public abstract ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index);}
Deque
LinkedList 实现了 Deque 接口,可作为队列使用。默认提供了头尾部插入和查找的方法
public interface Deque<E> extends Queue<E> {
/**
* 在头部插入元素
* @param e the element to add
*/
void addFirst(E e);
/**
* 在尾部追加元素
* @param e the element to add
*/
void addLast(E e);
/**
* 在头部插入元素,成功则返回true,否则返回false
* 和addFirst方法的区别在于不是通过引发异常来停止插入的,如容量限制原因,下同
* @param e the element to add
* @return {@code true} if the element was added to this deque, else
* {@code false}
*/
boolean offerFirst(E e);
/**
* 在尾部追加元素,成功则返回true,否则返回false
* @param e the element to add
* @return {@code true} if the element was added to this deque, else
* {@code false}
*/
boolean offerLast(E e);
/**
* 移除首元素
* @return the head of this deque
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this deque is empty
*/
E removeFirst();
/**
* 移除末尾元素
* @return the tail of this deque
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this deque is empty
*/
E removeLast();
/**
* 检索并删除此双端队列的第一个元素,如果此双端队列为空,则返回null
* @return the head of this deque, or {@code null} if this deque is empty
*/
E pollFirst();
/**
* 检索并删除此双端队列的最后一个元素,如果此双端队列为空,则返回null
* @return the tail of this deque, or {@code null} if this deque is empty
*/
E pollLast();
/**
* 获取首元素
* @return the head of this deque
*/
E getFirst();
/**
* 获取尾元素
* @return the tail of this deque
*/
E getLast();
/**
* 检索但不删除此双端队列的第一个元素,如果此双端队列为空,则返回null
* @return the head of this deque, or {@code null} if this deque is empty
*/
E peekFirst();
/**
* 检索但不删除此双端队列的最后一个元素,如果此双端队列为空,则返回null。
* @return the tail of this deque, or {@code null} if this deque is empty
*/
E peekLast();
/**
* 删除队列中第一次出现的指定元素,如果双端队列不包含元素,则它保持不变
* @param o element to be removed from this deque, if present
* @return {@code true} if an element was removed as a result of this call
*/
boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o);
/**
* 从此双端队列移除最后一次出现的指定元素。如果双端队列不包含元素,则它保持不变。
* @param o element to be removed from this deque, if present
* @return {@code true} if an element was removed as a result of this call
*/
boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o);
// *** Queue methods ***
/**
* 添加元素到队列末尾,此方法等效于addLast(E),通常最好使用offer。
* @param e the element to add
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
boolean add(E e);
/**
* 指定的元素插入此双端队列末尾,此方法等效于offerLast(E)
* @param e the element to add
* @return {@code true} if the element was added to this deque, else
* {@code false}
*/
boolean offer(E e);
/**
* 检索并删除此双端队列代表的队列的首元素
* @return the head of the queue represented by this deque
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this deque is empty
*/
E remove();
/**
* 检索并删除此双端队列表示的队列的首元素
* @return the first element of this deque, or {@code null} if
* this deque is empty
*/
E poll();
/**
* 检索但不删除此双端队列代表的队列的首元素,此方法等效于getFirst()。
* @return the head of the queue represented by this deque
*/
E element();
/**
* 检索但不删除此双端队列表示的队列的首元素,此方法等效于peekFirst()。
* @return the head of the queue represented by this deque, or
* {@code null} if this deque is empty
*/
E peek();
// *** Stack methods ***
/**
* 将一个元素压入此双端队列表示的头部,此方法等效于addFirst(E)。
* @param e the element to push
*/
void push(E e);
/**
* 删除并返回此双端队列的第一个元素,此方法等效于removeFirst()。
* @return the element at the front of this deque (which is the top
* of the stack represented by this deque)
*/
E pop();
// *** Collection methods ***
/**
* 移除第一次出现的指定元素,此方法等效于removeFirstOccurrence(java.lang.Object)
* @param o element to be removed from this deque, if present
* @return {@code true} if an element was removed as a result of this call
*/
boolean remove(Object o);
/**
* 如果此双端队列包含指定的元素,则返回true
* @param o element whose presence in this deque is to be tested
* @return {@code true} if this deque contains the specified element
*/
boolean contains(Object o);
/**
* 返回此双端队列的元素数量。
* @return the number of elements in this deque
*/
public int size();
/**
* 以适当的顺序返回此双端队列中的元素的迭代器。元素将按照从头(头)到后(尾)的顺序返回。
* @return an iterator over the elements in this deque in proper sequence
*/
Iterator<E> iterator();
/**
* 以相反的顺序返回此双端队列中的元素的迭代器。元素将按从最后(尾)到第一个(头)的顺序返回。
* @return an iterator over the elements in this deque in reverse
* sequence
*/
Iterator<E> descendingIterator();
}
可以看到,Deque继承了Queue接口,作为队列的代表,提供了大量关于首位元素和末尾元素的直接操作方法。
LinkedList
主要属性
// 用来记录元素个数
transient int size = 0;
// 记录链表/队列头节点
transient Node<E> first;
// 记录链表/队列尾节点
transient Node<E> last;
构造方法
public LinkedList() {
}
/**
* 构建LinkedList同时添加集合元素
*/
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}
核心子类—Node
Node子类代表了LinkedList的一个元素封装
private static class Node<E> {
// 元素本身
E item;
// 前一个结点
Node<E> prev;
// 后一节点
Node<E> next;
/**
* 构造函数,构建一个节点,指定其前一节点以及后一节点
*/
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
核心方法
(1) 连接与解除连接
只有节点里面的item为空值,不可能存在空节点,当链表中first节点为null,代表链表没有任何节点
public class LinkedList<E> extends AbstractSequentialList<E> implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
/**
* 将传入元素连接到链表首元素前面,也就是成为首元素
* Links e as first element.
*/
private void linkFirst(E e) {
final Node<E> f = first;
// null <- e -> f
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);
// 传入元素作为首节点
first = newNode;
// 如果原本首节点就是空的,则现在链表只有一个元素
if (f == null)
last = newNode; // 尾元素就是首元素
else
f.prev = newNode; // 否则f关联前一个元素:e <-> f
// 元素数量+1
size++;
// 修改次数+1
modCount++;
}
/**
* 插入到last节点的后面
* Links e as last element.
*/
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
// l <- e -> null
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
// 新插入的节点成为尾节点
last = newNode;
// 如果原本last就是空的,证明之前没有元素,现在只有一个元素
if (l == null)
first = newNode; // 首节点即尾节点
else
l.next = newNode; // l <-> e
// 元素数量+1
size++;
// 修改次数+1
modCount++;
}
/**
* 将e插入到succ节点之前
* Inserts element e before non-null Node succ.
*/
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {
// assert succ != null;
// 获取succ节点的前一节点
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;
// 构造节点:pred <- e -> succ
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
// e <-> succ
succ.prev = newNode;
// 如果pred为null节点,证明succ之前为首节点
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode; // pred <-> e
// 元素数量+1
size++;
// 修改次数+1
modCount++;
}
/**
* 解除首位元素关联,也就是删除首元素
* Unlinks non-null first node f.
*/
private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {
// assert f == first && f != null;
// 获取首节点内容
final E element = f.item;
// 获取首节点下一节点
final Node<E> next = f.next;
// f节点置空,以便回收空间
f.item = null;
f.next = null; // help GC
// 下一节点转为首节点
first = next;
// 如果下一节点本就为null,证明原本就只有一个节点
if (next == null)
last = null;
else
next.prev = null;
// 元素数量-1
size--;
// 修改次数+1
modCount++;
return element;
}
/**
* 解除末尾元素关联,也就是删除尾元素
* Unlinks non-null last node l.
*/
private E unlinkLast(Node<E> l) {
// assert l == last && l != null;
// 获取尾节点内容
final E element = l.item;
// 获取尾节点前一节点
final Node<E> prev = l.prev;
// 尾节点置空
l.item = null;
l.prev = null; // help GC
// prev成为尾节点
last = prev;
if (prev == null)
first = null;
else
prev.next = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
/**
* 删除指定节点
* Unlinks non-null node x.
*/
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
}
(2) add方法—添加元素
public class LinkedList<E> extends AbstractSequentialList<E> implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
/**
* 将元素追加到链表结尾
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
/**
* 向指定位置插入元素
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
// 检查位置是否合法,index不可以<0 也不可以>size
checkPositionIndex(index);
if (index == size)
linkLast(element);
else
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}
/**
* 将元素添加到首节点前
* @param e the element to add
*/
public void addFirst(E e) {
linkFirst(e);
}
/**
* 将元素添加到末尾
*
* @param e the element to add
*/
public void addLast(E e) {
linkLast(e);
}
/**
* 添加传入集合全部元素
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
*/
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
return addAll(size, c);
}
/**
* 在指定位置插入集合全部元素
* @param index index at which to insert the first element
* from the specified collection
* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list
* @return {@code true} if this list changed as a result of the call
*/
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
// 检查位置是否合法,index不可以<0 也不可以>size
checkPositionIndex(index);
// 传入集合转为数组
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
// 找到指定位置的节点和前一节点
Node<E> pred, succ;
if (index == size) {
succ = null;
pred = last;
} else {
succ = node(index);
pred = succ.prev;
}
// 遍历传入元素
for (Object o : a) {
// 构造节点
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o;
Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null);
// 如果前一节点为null,表明index位置为首元素位置
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
pred = newNode;
}
// 如果原位置节点为null,则表明原先链表为空
if (succ == null) {
last = pred;
} else {
pred.next = succ;
succ.prev = pred;
}
size += numNew;
modCount++;
return true;
}
}
(3) remove方法—-删除元素
public class LinkedList<E> extends AbstractSequentialList<E> implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
/**
* 移除指定位置元素
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return the element previously at the specified position
*/
public E remove(int index) {
// 检查位置是否合法
checkElementIndex(index);
// 解除元素关联,即移除
return unlink(node(index));
}
/**
* 移除最先出现的指定元素,如果存在且移除成功则返回true
* @param o element to be removed from this list, if present
* @return {@code true} if this list contained the specified element
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
// 如果传入元素为null,则匹配item为null的节点
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 移除首节点
* @return the first element from this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
*/
public E removeFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
/**
* 移除末尾节点
* @return the last element from this list
* @throws NoSuchElementException if this list is empty
*/
public E removeLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkLast(l);
}
/**
* 移除第一个出现的指定元素
* @param o element to be removed from this list, if present
* @return {@code true} if the list contained the specified element
*/
public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) {
return remove(o);
}
/**
* 移除最后一个出现的指定元素
* @param o element to be removed from this list, if present
* @return {@code true} if the list contained the specified element
* @since 1.6
*/
public boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
if (x.item == null) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
} else {
for (Node<E> x = last; x != null; x = x.prev) {
if (o.equals(x.item)) {
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
(4) set/get方法-设置与获取
public class LinkedList<E> extends AbstractSequentialList<E> implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
{
/**
* 设置指定位置元素
* @param index index of the element to replace
* @param element element to be stored at the specified position
* @return the element previously at the specified position
*/
public E set(int index, E element) {
// 检查位置合法性
checkElementIndex(index);
// 获取指定位置节点
Node<E> x = node(index);
// 获取旧值
E oldVal = x.item;
// 设定新值
x.item = element;
// 返回旧值
return oldVal;
}
/**
* 获取指定位置元素
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return the element at the specified position in this list
*/
public E get(int index) {
// 检查位置合法性
checkElementIndex(index);
// 返回节点值
return node(index).item;
}
/**
* 获取首节点值
* @return the first element in this list
*/
public E getFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return f.item;
}
/**
* 获取尾节点值
* @return the last element in this list
*/
public E getLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return l.item;
}
/**
* 获取指定位置的节点对象
*/
Node<E> node(int index) {
// assert isElementIndex(index);
// 如果index < size/2,也就是离开头更近
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
// 从开头往后遍历
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else { // 如果index离结尾更近
Node<E> x = last;
// 从结尾往前遍历
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}
}
我们可以看到,需要查找指定位置的元素(除了首尾元素),我们只能通过遍历链表的方式去获取,所以查询起来相对较慢。
简单使用
public class LinkedListCode {
public static void main(String[] args) {
commonExample();
}
public static void commonExample(){
LinkedList<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
linkedList.add(i);
}
System.out.println("原始链表:"+linkedList);
System.out.println("首元素:"+linkedList.getFirst());
System.out.println("尾元素:"+linkedList.getLast());
// 在首节点前插入元素
linkedList.addFirst(-1);
System.out.println("前插数据后:"+linkedList);
// 在尾节点后追加元素
linkedList.addLast(10);
System.out.println("后加数据后:"+linkedList);
}
}
输出:
原始链表:[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
首元素:0
尾元素:9
前插数据后:[-1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
后加数据后:[-1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
总结
1、LinkedList 继承了AbstractSequentialList抽象类,同时实现了List的接口,允许有null(空)元素。主要用于创建双向链表数据结构,该类没有同步方法,如果多个线程同时访问一个List,则必须自己实现访问同步,解决方法就是在创建List时候构造一个同步的List
2、LinkedList的特点是非线程安全,查询慢,增删快(链表特性)
3、LinkedList 继承了 AbstractSequentialList 类,实现链式访问。LinkedList还 实现了 Deque 接口,可作为队列使用。
4、LinkedList内部使用Node子类作为一个元素的封装
思考
什么时候用ArrayList,什么时候用LinkedList?
以下情况使用 ArrayList :
- 频繁访问列表中的某一个元素。
- 只需要在列表末尾进行添加和删除元素操作。
以下情况使用 LinkedList :
- 你需要通过循环迭代来访问列表中的某些元素。
- 需要频繁的在列表开头、中间、末尾等位置进行添加和删除元素操作。
为什么说LinkedList是线程不安全的?
和ArrayList一样,我们在LinkedList的add、set、remove等非原子性操作上都没有看到任何关于并发锁的代码,这就已经表明了它是非线程安全的
如何解决这个线程安全问题:
1、使用线程安全的队列:ConcurrentLinkedQueue【内部使用CAS安全算法保证线程安全】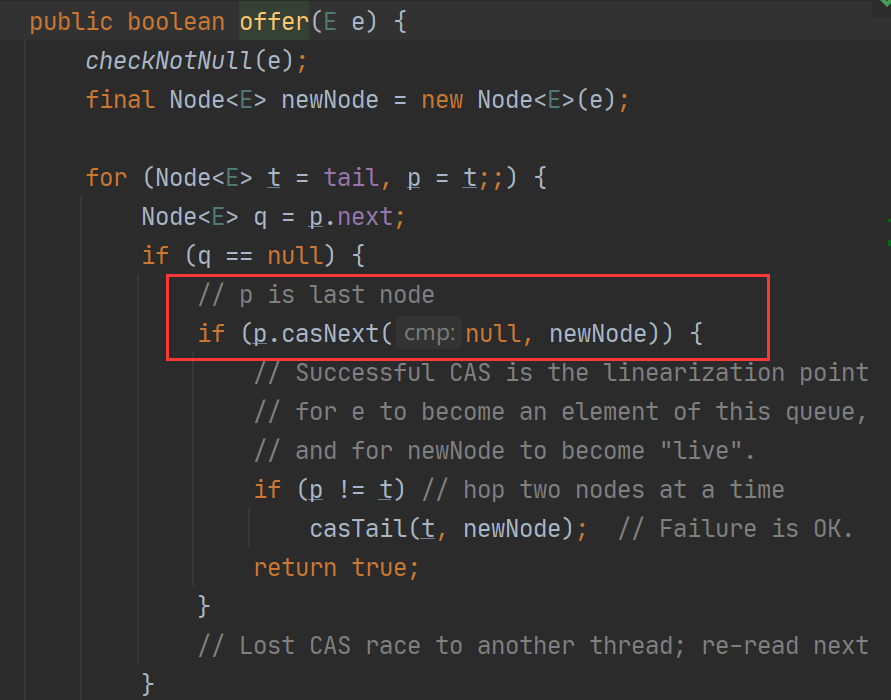
2、使用Collections.synchronizedList(new LinkedList
3、使用Vector(内部主要使用synchronized关键字实现同步)

