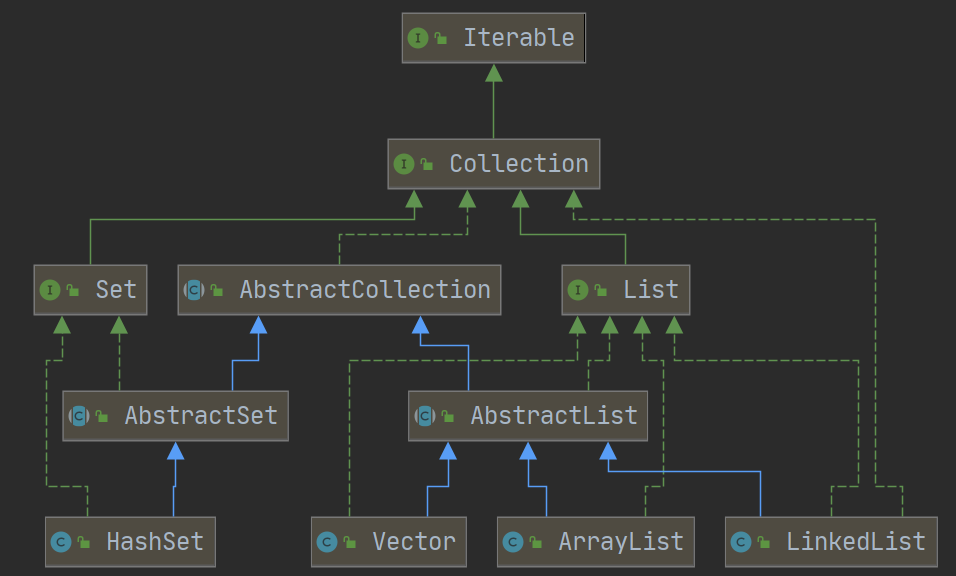
类关系图
功能介绍
包路径:java.util
功能描述: Collection 是最基本的集合接口,继承了Iterable**接口,一个 Collection 代表一组 Object,即 Collection 的元素, Java不提供直接继承自Collection的类,只提供继承于子接口(如List和set)。
Collection 接口存储一组不唯一,无序的对象。
The root interface in the collection hierarchy. A collection represents a group of objects, known as its elements
源码解析
Iterable
Iterable接口只有三个方法,实现了这个接口的集合对象支持迭代,也就是可迭代的。
/*** @since 1.5* @jls 14.14.2 The enhanced for statement*/public interface Iterable<T> {/*** 返回对应类型的迭代器* Iterator我们一般叫顺序遍历迭代器,它就是提供迭代机制的对象* 具体如何迭代,都是Iterator接口规范的。* @return an Iterator.*/Iterator<T> iterator();/*** 对集合元素执行传入函数* @since 1.8*/default void forEach(Consumer<? super T> action) {Objects.requireNonNull(action);for (T t : this) {action.accept(t);}}/*** 返回可以并行遍历元素的迭代器,以适应现在cpu多核时代并行遍历的需求。* 简单说:分割,增加并行处理能力* {@code Iterable}.* @since 1.8*/default Spliterator<T> spliterator() {return Spliterators.spliteratorUnknownSize(iterator(), 0);}}
Collection
package java.util;import java.util.function.Predicate;import java.util.stream.Stream;import java.util.stream.StreamSupport;/**** @param <E> the type of elements in this collection** @author Josh Bloch* @author Neal Gafter* @see Set* @see List* @see Map* @see SortedSet* @see SortedMap* @see HashSet* @see TreeSet* @see ArrayList* @see LinkedList* @see Vector* @see Collections* @see Arrays* @see AbstractCollection* @since 1.2*/public interface Collection<E> extends Iterable<E> {// Query Operations 查询操作/*** 返回该集合中元素的个数。如果超过了Integer.MAX_VALUE,那么返回Integer.MAX_VALUE* @return the number of elements in this collection*/int size();/*** 集合判空,如果集合中没有元素返回true。* @return <tt>true</tt> if this collection contains no elements*/boolean isEmpty();/*** 判断集合是否存在某元素* 如果集合中包含指定元素那么返回true。特别的,如果集合中也包含NULL元素的时候并且要查找的元素也是NULL的时候也返回true。* @param o element whose presence in this collection is to be tested* @return <tt>true</tt> if this collection contains the specified*/boolean contains(Object o);/*** 返回迭代器* @return an <tt>Iterator</tt> over the elements in this collection*/Iterator<E> iterator();/*** 将集合转化为数组,返回包含此集合中所有元素的数组。* @return an array containing all of the elements in this collection*/Object[] toArray();/*** 将集合转化为数组,返回集合中所有元素到传入的数组中* 该方法可以对返回的数组类型进行精确控制,而非像toArray方法一样返回Object[]** @param <T> the runtime type of the array to contain the collection* @param a the array into which the elements of this collection are to be* stored, if it is big enough; otherwise, a new array of the same* runtime type is allocated for this purpose.* @return an array containing all of the elements in this collection*/<T> T[] toArray(T[] a);// Modification Operations 更新操作/*** 向集合中添加一个元素。* 集合添加成功返回true,如果该集合不允许重复并且已经包含指定的元素。返回false* @param e element whose presence in this collection is to be ensured* @return <tt>true</tt> if this collection changed as a result of the* call*/boolean add(E e);/*** 删除集合中的指定的元素。如果存在NULL,也删除。* @param o element to be removed from this collection, if present* @return <tt>true</tt> if an element was removed as a result of this call**/boolean remove(Object o);// Bulk Operations 大量数据操作/*** 如果该集合中包含指定集合中的所有元素的时候返回true。* @param c collection to be checked for containment in this collection* @return <tt>true</tt> if this collection contains all of the elements* in the specified collection** @see #contains(Object)*/boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c);/*** 将指定集合中的所有元素添加到此集合中。* 在添加过程中如果被添加的集合发生了更改,addAll方法不具有幂等性。* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this collection* @return <tt>true</tt> if this collection changed as a result of the call** @see #add(Object)*/boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c);/*** 删除当前集合中所有等于指定集合中的元素。* @param c collection containing elements to be removed from this collection* @return <tt>true</tt> if this collection changed as a result of the* call* @see #remove(Object)* @see #contains(Object)*/boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c);/*** 删除所有匹配过滤器Predicate条件的元素* @param filter a predicate which returns {@code true} for elements to be* removed* @return {@code true} if any elements were removed* @since 1.8*/default boolean removeIf(Predicate<? super E> filter) {// 校验lambda是否为空Objects.requireNonNull(filter);boolean removed = false;// 获取迭代器final Iterator<E> each = iterator();while (each.hasNext()) {// 如果该方法执行返回true则移除该元素if (filter.test(each.next())) {each.remove();removed = true;}}return removed;}/*** 仅保留该指定集合中存在的所有元素。其余删除* @param c collection containing elements to be retained in this collection* @return <tt>true</tt> if this collection changed as a result of the call** @see #remove(Object)* @see #contains(Object)*/boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c);/*** 清空掉集合中的所有元素*/void clear();// Comparison and hashing/*** 比较是否相等* @see Object#equals(Object)* @see Set#equals(Object)* @see List#equals(Object)*/boolean equals(Object o);/**** @return the hash code value for this collection** @see Object#hashCode()* @see Object#equals(Object)*/int hashCode();/*** 返回Spliterator分割器,用于并发流式处理的时候调用* @return a {@code Spliterator} over the elements in this collection* @since 1.8*/@Overridedefault Spliterator<E> spliterator() {return Spliterators.spliterator(this, 0);}/*** 返回流对象* @return a sequential {@code Stream} over the elements in this collection* @since 1.8*/default Stream<E> stream() {return StreamSupport.stream(spliterator(), false);}/*** 返回并发流式对象* @return a possibly parallel {@code Stream} over the elements in this* collection* @since 1.8*/default Stream<E> parallelStream() {return StreamSupport.stream(spliterator(), true);}}
AbstractCollection
直接实现Collection接口的抽象类,实现基本方法,方便子类实现Collection功能
public abstract class AbstractCollection<E> implements Collection<E> {/****/protected AbstractCollection() {}// Query Operations/*** 返回迭代器* @return an iterator over the elements contained in this collection*/public abstract Iterator<E> iterator();// 获取集合元素总数public abstract int size();/*** 判断集合是否为空*/public boolean isEmpty() {return size() == 0;}/*** 判断元素是否存在于集合之中*/public boolean contains(Object o) {Iterator<E> it = iterator();if (o==null) {while (it.hasNext())if (it.next()==null)return true;} else {while (it.hasNext())if (o.equals(it.next()))return true;}return false;}/*** 将集合转为数组*/public Object[] toArray() {// Estimate size of array; be prepared to see more or fewer elements// 新建同等大小的Object数组Object[] r = new Object[size()];Iterator<E> it = iterator();// 遍历并填充元素for (int i = 0; i < r.length; i++) {if (! it.hasNext()) // fewer elements than expectedreturn Arrays.copyOf(r, i);r[i] = it.next();}// it.hasNext方法为true表明数组长度不足【可能在转换过程中有别的线程往里面加了元素】// 调用finishToArray对数组进行扩容并完成转换return it.hasNext() ? finishToArray(r, it) : r;}/*** 将集合转为数组*/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {// Estimate size of array; be prepared to see more or fewer elementsint size = size();// 构造足够大的数组T[] r = a.length >= size ? a :(T[])java.lang.reflect.Array.newInstance(a.getClass().getComponentType(), size);Iterator<E> it = iterator();// 遍历并填充元素for (int i = 0; i < r.length; i++) {if (! it.hasNext()) { // fewer elements than expectedif (a == r) {r[i] = null; // null-terminate} else if (a.length < i) {return Arrays.copyOf(r, i);} else {System.arraycopy(r, 0, a, 0, i);if (a.length > i) {a[i] = null;}}return a;}r[i] = (T)it.next();}// more elements than expected// it.hasNext方法为true表明数组长度不足【可能在转换过程中有别的线程往里面加了元素】// 调用finishToArray对数组进行扩容并完成转换return it.hasNext() ? finishToArray(r, it) : r;}/*** 最大数组容量限制*/private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;/*** 数组扩容* (1)当数组索引指向最后一个元素+1时,对数组进行扩容:即创建一个更长的数组,然后将原数组的内容复制到新数组中* (2)扩容大小:cap + cap/2 +1* (3)扩容前需要先判断数组长度是否溢出* 注意:这里的迭代器是从上层的方法(toArray)传过来的,并且这个迭代器已执行了一部分,而不是从头开始迭代的* @param r the array, replete with previously stored elements* @param it the in-progress iterator over this collection* @return array containing the elements in the given array, plus any* further elements returned by the iterator, trimmed to size*/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")private static <T> T[] finishToArray(T[] r, Iterator<?> it) {int i = r.length;while (it.hasNext()) {int cap = r.length;if (i == cap) {int newCap = cap + (cap >> 1) + 1;// overflow-conscious codeif (newCap - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)newCap = hugeCapacity(cap + 1);r = Arrays.copyOf(r, newCap);}r[i++] = (T)it.next();}// trim if overallocatedreturn (i == r.length) ? r : Arrays.copyOf(r, i);}/*** 判断数组容量是否溢出,最大为整型数据的最大值*/private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {if (minCapacity < 0) // overflowthrow new OutOfMemoryError("Required array size too large");return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?Integer.MAX_VALUE :MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;}// Modification Operations/*** 未移除指定元素实现*/public boolean add(E e) {throw new UnsupportedOperationException();}/*** 移除指定元素*/public boolean remove(Object o) {Iterator<E> it = iterator();if (o==null) {while (it.hasNext()) {if (it.next()==null) {it.remove();return true;}}} else {while (it.hasNext()) {if (o.equals(it.next())) {it.remove();return true;}}}return false;}// Bulk Operations/*** 如果该集合中包含指定集合中的所有元素的时候返回true。* @see #contains(Object)*/public boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) {for (Object e : c)if (!contains(e))return false;return true;}/*** 遍历参数集合,依次将参数集合中的元素添加当前集合中* @see #add(Object)*/public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {boolean modified = false;for (E e : c)if (add(e))modified = true;return modified;}/*** 移除参数集合的元素* @see #remove(Object)* @see #contains(Object)*/public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {Objects.requireNonNull(c);boolean modified = false;Iterator<?> it = iterator();while (it.hasNext()) {if (c.contains(it.next())) {it.remove();modified = true;}}return modified;}/*** 仅保留该指定集合中存在的所有元素。其余删除* @see #remove(Object)* @see #contains(Object)*/public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {Objects.requireNonNull(c);boolean modified = false;Iterator<E> it = iterator();while (it.hasNext()) {if (!c.contains(it.next())) {it.remove();modified = true;}}return modified;}/*** 删除所有元素*/public void clear() {Iterator<E> it = iterator();while (it.hasNext()) {it.next();it.remove();}}// String conversion/*** 重载toString方法* @return a string representation of this collection*/public String toString() {Iterator<E> it = iterator();if (! it.hasNext())return "[]";StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();sb.append('[');for (;;) {E e = it.next();sb.append(e == this ? "(this Collection)" : e);if (! it.hasNext())return sb.append(']').toString();sb.append(',').append(' ');}}}
简单使用
package com.java.list;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
/**
* @description Collection接口演示
* @auther: lai.guanfu
* @date: 2021-01-04 22:51
*/
public class CollectionCode {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<Integer> collection = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<20;i++){
collection.add(i);
}
System.out.println(collection);
System.out.println();
// ============= 移除大于10的元素
// 传统写法:
// Iterator<Integer> iterator = collection.iterator();
// while (iterator.hasNext()) {
// Integer item = iterator.next();
// if (item > 10)
// iterator.remove();
// }
// removeIf调用
collection.removeIf(item -> item>10);
System.out.println(collection);
}
}
输出如下:
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19]
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
总结
- Collection 是最基本的集合接口,继承了Iterable接口,一个 Collection 代表一组 Object,即 Collection 的元素, Java不提供直接继承自Collection的类,只提供继承于子接口(如List和set)
- Collection 接口存储一组不唯一,无序的对象。
- 在Collection中定义了一些常用的接口,供子类去实现
- 在JDK1.8中新增了一些方法,例如获取获取流式函数的方法在这个接口中引入了default方法