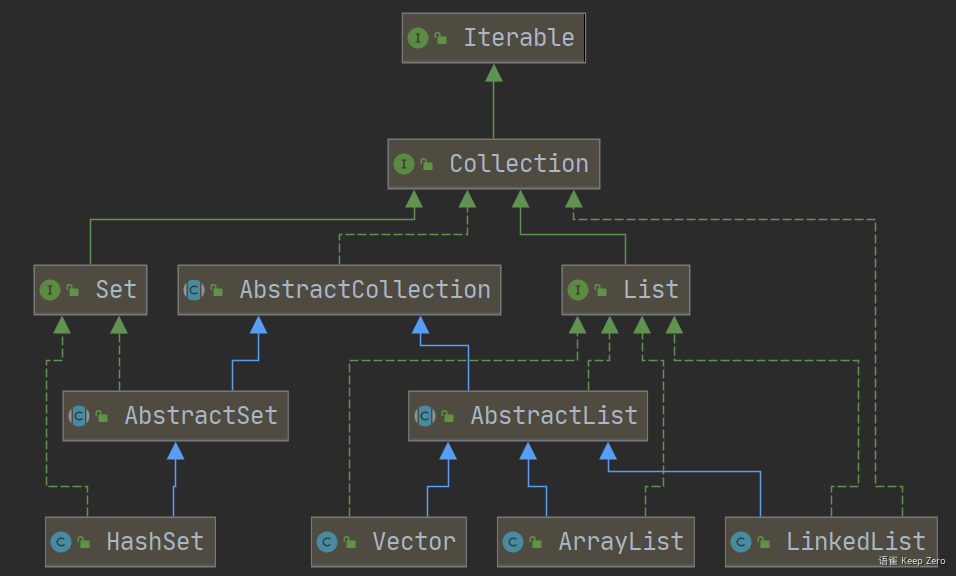
类关系图
功能介绍
包路径:java.util
功能描述: List **接口是一个有序的 Collection,直接继承Collection接口,使用此接口能够精确的控制每个元素插入的位置,能够通过索引(元素在List中位置,类似于数组的下标)来访问List中的元素,第一个元素的索引为 0,而且允许有相同的元素。
源码解析
List
public interface List<E> extends Collection<E> {// Query Operations/*** 获取集合元素总数* @return the number of elements in this list*/int size();/*** 判断集合是否为空* @return <tt>true</tt> if this list contains no elements*/boolean isEmpty();/*** 判断集合内是否存在传入元素* @param o element whose presence in this list is to be tested* @return <tt>true</tt> if this list contains the specified element*/boolean contains(Object o);/*** 获取迭代器* @return an iterator over the elements in this list in proper sequence*/Iterator<E> iterator();/*** 集合转化为Object数组* @return an array containing all of the elements in this list in proper* sequence* @see Arrays#asList(Object[])*/Object[] toArray();/*** 集合转化为数组* @param a the array into which the elements of this list are to* be stored, if it is big enough; otherwise, a new array of the* same runtime type is allocated for this purpose.* @return an array containing the elements of this list*/<T> T[] toArray(T[] a);// Modification Operations/*** 添加元素* @param e element to be appended to this list* @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add})*/boolean add(E e);/*** 移除元素* @param o element to be removed from this list, if present* @return <tt>true</tt> if this list contained the specified element*/boolean remove(Object o);// Bulk Modification Operations/*** 判断集合是否包含传入集合所有元素* @param c collection to be checked for containment in this list* @return <tt>true</tt> if this list contains all of the elements of the* specified collection* @see #contains(Object)*/boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c);/*** 将传入集合的元素全部添加到当前集合* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list* @return <tt>true</tt> if this list changed as a result of the call* @see #add(Object)*/boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c);/*** 在指定位置添加集合元素* @param index index at which to insert the first element from the* specified collection* @param c collection containing elements to be added to this list* @return <tt>true</tt> if this list changed as a result of the call*/boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c);/*** 从集合中移除传入集合的所有元素* @param c collection containing elements to be removed from this list* @return <tt>true</tt> if this list changed as a result of the call* @see #remove(Object)* @see #contains(Object)*/boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c);/*** 仅保留该指定集合中存在的所有元素。其余删除* @param c collection containing elements to be retained in this list* @return <tt>true</tt> if this list changed as a result of the call* @see #remove(Object)* @see #contains(Object)*/boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c);/*** 用函数接口的返回结果替代原集合中的值* UnaryOperator<T>继承于Function<T, T>,是一个对单个操作数的操作,该操作生成与其操作数类型相同的结果* @param operator the operator to apply to each element* @since 1.8*/default void replaceAll(UnaryOperator<E> operator) {Objects.requireNonNull(operator);final ListIterator<E> li = this.listIterator();while (li.hasNext()) {li.set(operator.apply(li.next()));}}/*** 对集合进行排序* @param c the {@code Comparator} used to compare list elements.* A {@code null} value indicates that the elements'* {@linkplain Comparable natural ordering} should be used* @since 1.8*/@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes"})default void sort(Comparator<? super E> c) {// 转为数组Object[] a = this.toArray();// 数组排序Arrays.sort(a, (Comparator) c);// 重设集合元素ListIterator<E> i = this.listIterator();for (Object e : a) {i.next();i.set((E) e);}}/*** 清空集合*/void clear();// Comparison and hashingboolean equals(Object o);int hashCode();// Positional Access Operations/*** 获取指定索引的元素* @param index index of the element to return* @return the element at the specified position in this list*/E get(int index);/*** 设置指定索引的元素,返回元素旧值* @param index index of the element to replace* @param element element to be stored at the specified position* @return the element previously at the specified position*/E set(int index, E element);/*** 向指定索引位置插入元素* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted* @param element element to be inserted*/void add(int index, E element);/*** 移除指定索引位置元素,返回指定位置元素* @param index the index of the element to be removed* @return the element previously at the specified position*/E remove(int index);// Search Operations/*** 查询传入元素在集合中第一次出现的索引,如果元素不存在返回-1* @param o element to search for* @return the index of the first occurrence of the specified element in* this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element*/int indexOf(Object o);/*** 查询传入元素在集合中最后一次出现的索引,如果元素不存在返回-1* @param o element to search for* @return the index of the last occurrence of the specified element in* this list, or -1 if this list does not contain the element*/int lastIndexOf(Object o);// List Iterators/*** 返回集合迭代器* ListIterator是一个功能更加强大的迭代器, 它继承于Iterator接口,只能用于各种List类型的访问* @return a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper* sequence)*/ListIterator<E> listIterator();/*** 返回从index开始的集合迭代器* @param index index of the first element to be returned from the* list iterator (by a call to {@link ListIterator#next next})* @return a list iterator over the elements in this list (in proper* sequence), starting at the specified position in the list*/ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index);// View/*** 截取并返回指定范围的元素集合* @param fromIndex low endpoint (inclusive) of the subList* @param toIndex high endpoint (exclusive) of the subList* @return a view of the specified range within this list*/List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex);/*** 返回分割器* @return a {@code Spliterator} over the elements in this list* @since 1.8*/@Overridedefault Spliterator<E> spliterator() {return Spliterators.spliterator(this, Spliterator.ORDERED);}}
AbstractList
AbstractList直接继承AbstractCollection抽象类,同时实现了List大部分接口,方便别的子类去实现List集合
AbstractList 虽然是抽象类,但其内部只有一个抽象方法 get(),从字面上看这是获取的方法,子类必须实现它,一般是作为获取元素的用途,除此之外,如果子类要操作元素,还需要重写 add(), set(), remove() 方法,因为 AbstractList 虽然定义了这几个方法,但默认是不支持的,
package java.util;
/**
* @author Josh Bloch
* @author Neal Gafter
* @since 1.2
*/
public abstract class AbstractList<E> extends AbstractCollection<E> implements List<E> {
/**
*
*/
protected AbstractList() {
}
/**
* 添加元素,添加成功则返回true
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
add(size(), e);
return true;
}
/**
* 获取指定位置的元素
*/
abstract public E get(int index);
/**
* 设置指定位置的元素,未实现
*/
public E set(int index, E element) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
/**
* 往指定位置插入元素,未实现
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
/**
* 移除指定位置的元素,未实现
*/
public E remove(int index) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
// Search Operations
/**
* 查找元素在集合中第一次出现的位置,如果不存在则返回-1
*/
public int indexOf(Object o) {
ListIterator<E> it = listIterator();
if (o==null) {
while (it.hasNext())
if (it.next()==null)
return it.previousIndex();
} else {
while (it.hasNext())
if (o.equals(it.next()))
return it.previousIndex();
}
return -1;
}
/**
* 查找元素在集合中最后一次出现的位置,如果不存在则返回-1
*/
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
ListIterator<E> it = listIterator(size());
if (o==null) {
while (it.hasPrevious())
if (it.previous()==null)
return it.nextIndex();
} else {
while (it.hasPrevious())
if (o.equals(it.previous()))
return it.nextIndex();
}
return -1;
}
// Bulk Operations
/**
* 清空集合
*/
public void clear() {
removeRange(0, size());
}
/**
* 将传入集合的所有元素从当前集合的index位置开始插入
*/
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
boolean modified = false;
for (E e : c) {
add(index++, e);
modified = true;
}
return modified;
}
// Iterators
/**
* 返回迭代器
* @return an iterator over the elements in this list in proper sequence
*/
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
/**
* 返回初始位置为0的ListIterator
* @see #listIterator(int)
*/
public ListIterator<E> listIterator() {
return listIterator(0);
}
/**
* 返回初始位置为指定位置的ListIterator
*/
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(final int index) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
return new ListItr(index);
}
/**
* 内部类,迭代器实现
*/
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
/**
* 迭代器的游标
* Index of element to be returned by subsequent call to next.
*/
int cursor = 0;
/**
* 最近迭代的元素位置,每次使用完默认置为-1
*/
int lastRet = -1;
/**
* 记录容器被修改的次数,值不相等说明有并发操作
*/
int expectedModCount = modCount;
/**
* 是否存在下一个元素
*/
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != size();
}
/**
* 返回下一个元素
*/
public E next() {
checkForComodification();
try {
int i = cursor;
E next = get(i);
lastRet = i; // 本次操作的位置
cursor = i + 1; // 游标移动向下一节点
return next;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
checkForComodification();
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
}
/**
* 移除当前位置的元素
*/
public void remove() {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
// 移除当前位置的元素
AbstractList.this.remove(lastRet);
// 若当前位置小于游标位置,则游标前移
if (lastRet < cursor)
cursor--;
// 删除后,把最后迭代的记录位置置为-1
lastRet = -1;
// 赋值修改次数
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
/**
* 检查当前操作的合法性,即是否同时有其他已经对集合做了变更,如果发生并发更改则抛出异常
*/
final void checkForComodification() {
// 两个值不一致,说明有并发操作,抛出异常
if (modCount != expectedModCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
/**
* ListItr 是 Itr 的子类,在Itr 的基础上增强了对元素的操作
* 多了指定索引的赋值,以及向前读取,add 和 set 的方法
*/
private class ListItr extends Itr implements ListIterator<E> {
// 设置游标为指定值
ListItr(int index) {
cursor = index;
}
/**
* 判断前面是否还有元素,游标不为第一个的话,前面都有元素
*/
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return cursor != 0;
}
/**
* 获取前一个元素
*/
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
try {
// 获取游标的前一个元素
int i = cursor - 1;
E previous = get(i);
// 把最后操作的位置和游标都前移一位
lastRet = cursor = i;
return previous;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
checkForComodification();
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
}
/**
* 下一元素的位置
*/
public int nextIndex() {
return cursor;
}
/**
* 前一个元素的位置
*/
public int previousIndex() {
return cursor-1;
}
/**
* 设置当前位置元素
*/
public void set(E e) {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
AbstractList.this.set(lastRet, e);
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
/**
* 插入元素到当前位置
*/
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
try {
int i = cursor;
AbstractList.this.add(i, e);
lastRet = -1; // 最后操作位置置为-1
cursor = i + 1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
}
/**
* 获取指定范围的截取集合,返回RandomAccessSubList或SubList子类
*/
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
return (this instanceof RandomAccess ?
new RandomAccessSubList<>(this, fromIndex, toIndex) :
new SubList<>(this, fromIndex, toIndex));
}
// Comparison and hashing
/**
* 比较两个集合是否相等,每个元素都相等才是相等的
* @param o the object to be compared for equality with this list
* @return {@code true} if the specified object is equal to this list
*/
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (!(o instanceof List))
return false;
ListIterator<E> e1 = listIterator();
ListIterator<?> e2 = ((List<?>) o).listIterator();
// 迭代器遍历,比较每个元素是否相等
while (e1.hasNext() && e2.hasNext()) {
E o1 = e1.next();
Object o2 = e2.next();
if (!(o1==null ? o2==null : o1.equals(o2)))
return false;
}
return !(e1.hasNext() || e2.hasNext());
}
/**
*
* @return the hash code value for this list
*/
public int hashCode() {
int hashCode = 1;
for (E e : this)
hashCode = 31*hashCode + (e==null ? 0 : e.hashCode());
return hashCode;
}
/**
* 移除指定范围的元素
* @param fromIndex index of first element to be removed
* @param toIndex index after last element to be removed
*/
protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
ListIterator<E> it = listIterator(fromIndex);
for (int i=0, n=toIndex-fromIndex; i<n; i++) {
it.next();
it.remove();
}
}
/**
* 记录已对该列表进行结构修改的次数。结构修改是指更改列表大小或以其他方式干扰列表的方式,即正在进行的迭代可能会产生错误的结果。
* 检测并发的时候用
*/
protected transient int modCount = 0;
/**
* 检查索引是否<0或>list.size
*/
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > size())
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
/**
* 返回当前位置及集合大小信息
*/
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size();
}
}
/**
* 切割集合,并没有真的切割出来,仍旧在原集合进行操作
*/
class SubList<E> extends AbstractList<E> {
// 原始集合
private final AbstractList<E> l;
// 偏移量,切割的起始位置
private final int offset;
// 切割集合大小
private int size;
/**
* 构造方法
*/
SubList(AbstractList<E> list, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
if (fromIndex < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("fromIndex = " + fromIndex);
if (toIndex > list.size())
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("toIndex = " + toIndex);
if (fromIndex > toIndex)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromIndex(" + fromIndex +
") > toIndex(" + toIndex + ")");
l = list;
offset = fromIndex;
size = toIndex - fromIndex;
this.modCount = l.modCount;
}
/**
* 设置指定位置的元素(直接设置原集合对应位置的元素)
*/
public E set(int index, E element) {
rangeCheck(index);
checkForComodification();
return l.set(index+offset, element);
}
/**
* 获取指定位置的元素
*/
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
checkForComodification();
return l.get(index+offset);
}
/**
* 获取切割子集合大小
*/
public int size() {
checkForComodification();
return size;
}
/**
* 向指定位置插入元素
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
checkForComodification();
l.add(index+offset, element);
this.modCount = l.modCount;
size++;
}
/**
* 移除指定位置元素
*/
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
checkForComodification();
E result = l.remove(index+offset);
this.modCount = l.modCount;
size--;
return result;
}
/**
* 移除指定范围元素
*/
protected void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
checkForComodification();
l.removeRange(fromIndex+offset, toIndex+offset);
this.modCount = l.modCount;
size -= (toIndex-fromIndex);
}
/**
* 添加传入集合的所有元素
*/
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
return addAll(size, c);
}
/**
* 在指定位置插入传入集合的所有元素
*/
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
int cSize = c.size();
if (cSize==0)
return false;
checkForComodification();
l.addAll(offset+index, c);
this.modCount = l.modCount;
size += cSize;
return true;
}
/**
* 返回迭代器
*/
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return listIterator();
}
/**
* 返回从index开始的迭代器
*/
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(final int index) {
checkForComodification();
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
return new ListIterator<E>() {
private final ListIterator<E> i = l.listIterator(index+offset);
public boolean hasNext() {
return nextIndex() < size;
}
public E next() {
if (hasNext())
return i.next();
else
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return previousIndex() >= 0;
}
public E previous() {
if (hasPrevious())
return i.previous();
else
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
public int nextIndex() {
return i.nextIndex() - offset;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return i.previousIndex() - offset;
}
public void remove() {
i.remove();
SubList.this.modCount = l.modCount;
size--;
}
public void set(E e) {
i.set(e);
}
public void add(E e) {
i.add(e);
SubList.this.modCount = l.modCount;
size++;
}
};
}
/**
* 内部切割
*/
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
return new SubList<>(this, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
/**
* 检查索引位置是否越界
*/
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
/**
* 检查索引位置是否越界
*/
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
/**
* 返回索引位置以及集合大小信息
*/
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size;
}
/**
* 并发检查
*/
private void checkForComodification() {
if (this.modCount != l.modCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
/**
* RandomAccessSubList 是 SubList 的子类,内部实现直接沿用父类,只是实现了RandomAccess接口
*/
class RandomAccessSubList<E> extends SubList<E> implements RandomAccess {
RandomAccessSubList(AbstractList<E> list, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
super(list, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
return new RandomAccessSubList<>(this, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
}
可以看到AbstractList内部还包含了两个迭代器实现类(Itr 和其子类 ListItr)和两个子类(SubList 和 其子类RandomAccessSubList)。
其中,Itr 实现了 Iterator 接口,重写了 next() 和 remove() 方法,Abstract使用iterator() 获取该对象
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
ListItr 是 Itr 的子类,同时实现了ListIterator接口,在Itr 的基础上增强了对元素的操作,多了指定索引的赋值,以及向前读取,add 和 set 的方法。Abstract使用listIterator() 获取该对象
public ListIterator<E> listIterator() {
return listIterator(0);
}
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(final int index) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
return new ListItr(index);
}
简单使用
package com.java.list;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ListIterator;
/**
* @description List接口演示
* @date: 2021-01-06 11:09
*/
public class ListCode {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
list.add(i);
}
System.out.println(list.get(0));
// 获取子集合,子集合区间为[5,10],共5个元素
List<Integer> subList = list.subList(5, 10);
System.out.println("subList = "+subList);
System.out.println("list = "+list);
// 更新子集合内容,以子集合的第五个元素(也就是最后一个元素)为起始获取迭代器
ListIterator<Integer> subListIterator = subList.listIterator(5);
while (subListIterator.hasPrevious()){
Integer previous = subListIterator.previous();
subListIterator.set(previous+100); // 每个元素+100
}
System.out.println("执行修改之后========");
System.out.println("subList = "+subList);
System.out.println("list = "+list);
}
}
输出:
0
subList = [5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
list = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
执行修改之后========
subList = [105, 106, 107, 108, 109]
list = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 105, 106, 107, 108, 109]
总结
1、List **接口是一个有序的 Collection**,直接继承Collection接口,使用此接口能够精确的控制每个元素插入的位置,能够通过索引(元素在List中位置,类似于数组的下标)来访问List中的元素,第一个元素的索引为 0,而且允许有相同的元素。
2、List 接口存储一组不唯一,有序(插入顺序)的对象。
3、AbstractList直接继承AbstractCollection抽象类,同时实现了List大部分接口**,方便别的子类去实现List集合
4、AbstractList内部还包含了两个迭代器实现类(Itr 和其子类 ListItr)和两个子类(SubList 和 其子类RandomAccessSubList)。

