问题:
1、常见的异常有哪些
2、遇到异常是如何解决的?有几种解决方式?
一、异常概述与异常体系结构
1、异常 :在Java语言中,将程序执行中发生的不正常情况称之为“异常”。
注:开发过程中的语法错误和逻辑错误不是属于异常
2、java程序在执行的过程中所发生的异常事件可分为两类:
2.1 Error
Java 虚拟机无法解决的严重问题。如: JVM 系统内部错误 、资源 耗尽等严重 情况 。比如: StackOverflowError 和 OOM 。一般不编写针对性 的代码进行处理 。
StackOverflowError
/*** StackOverflowError 栈溢出* @author dongxinxin* @create 2022-03-05 14:59*/public class ErrorTest01 {public static void main(String[] args) {main(args);}}Error 异常Exception in thread "main" java.lang.StackOverflowErrorat com.java.test01.ErrorDemo01.main(ErrorDemo01.java:9)
OOM
/*** OOM 异常* 堆内存不足* @author dongxinxin* @create 2022-03-05 15:13*/public class ErrorDemo01 {public static void main(String[] args) {Integer[] arr = new Integer[1024 * 1024 * 1024];}}OOM 异常Exception in thread "main" java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap spaceat com.java.test01.ErrorDemo01.main(ErrorDemo01.java:10)
2.2 Exception
其它因编程错误或偶然的外在素导致一般性问题 ,可以使 用针对性的代码进行处理 。例如:
空指针异常 如果创建一个对象,赋值为null,再用对象调用该类中的属性
IO异常
数组角标越界
3、如何解决这些写错误
对于这些错误 ,一般有两种 解决方法 :一是遇到错误就终止程序 的运行 。另一种方法是由程序员在编写时 ,就考虑到错误的检测 、错误消息的提示 ,以及错误的处理 。
捕获错误最理想的是在编译期间 ,但有的错误只在运行时才会发生 。 比如: 除数为 0,数组下标越界等
可分为:编译时异常和运行时异常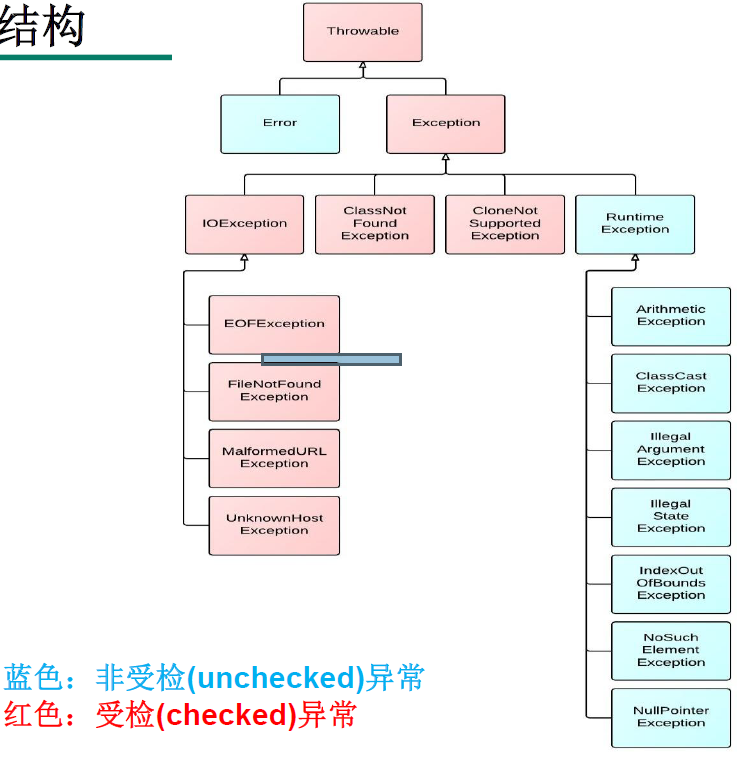
受检异常:编译异常
/*** 编译时异常的一种情况** 解决办法:使用try-catch-finally机制解决*/public static void test01(){File file = null;FileInputStream fis = null;try {file = new File("a.txt");fis = new FileInputStream(file);//读取数据int data = fis.read();while (data != -1) {// 读取数据的一个逻辑System.out.print((char)data);data = fis.read();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {try {if(fis != null){fis.close();}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
非受检异常:运行时异常
/*** 异常体系结构* java.lang.throwable* Error: 一般不需要编写代码去解决* Exception:可以进行异常处理,需要进行异常处理* 编译时异常(checked):* IOException* FileException* ClassNotFoundException* 运行时异常(unchecked):* NullPointException* ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException* ArithmeticException(算术异常)等* @author dongxinxin* @create 2022-03-05 15:25*/public class ExceptionTest01 {public static void main(String[] args) {Integer[] arr = new Integer[2];// System.out.println(arr[2]);// ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException// String[] str = null;// System.out.println(str[2]);// NullPointerExceptionObject date = new Date();// String str = (String)date;// ClassCastException 类型转换异常String str = "123";String str1 = "abc";// int parseInt = Integer.parseInt(str1);// NumberFormatException}
二、常见异常
三、异常处理机制:try-catch-finally
使用try-catch-finally处理编译时异常
/*** 异常的处理:抓抛模型** “抛”:程序在正常执行的过程中,一旦出现异常,就会在异常代码处生成一个对应异常类的对象,* 并将此对象抛出** “抓”:异常的处理方式:* 方式一:try-catch-finally* try {* // 可能出现异常的代码* } catch(异常类型1 变量名) {* //处理异常* }catch(异常类型2 变量名) {* //处理异常* }···{** } finally { // 不一定非得写* // 一定会执行的代码* }* 说明:* finally 可选* catch中的异常类型如果没有子父类关系,则谁声明在上,谁声明在下无所谓* 如果有子父类关系,则子类声明一定在父类的上面,否则报错* 在try结构中定义中的变量,try外不可以用,如果外面想用,我们可以在try外声明* 注:为了避免报错,要给try外定义的变量要进行初始化* 方式二:throws* @author dongxinxin* @create 2022-03-05 16:17*/public class ExceptionTest02 {public static void runExceptionTest(){String str = "123";str = "abc";try {int parseInt = Integer.parseInt(str);System.out.println("hello ------ 1"); // 不会去执行} catch (NumberFormatException e) {// e.printStackTrace();// System.out.println("出现数制转换异常");e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("hello ------ 2");}public static void main(String[] args) {runExceptionTest();}}
finally的使用
/*** try-catch-finally中的finally的使用* 1、finally是可选的* @author dongxinxin* @create 2022-03-05 20:29*/public class FinallyTest {/*** finally 必须执行的*/public static void finallyTest01(){try {int a = 10;int b = 0;System.out.println(a / b);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {System.out.println("你好");}}/*** finally 中的return的使用* @return*/public static int finallyTest02(){try {int a = 10;return a;} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {return 0;// 作为最终的返回值结果}}public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(finallyTest02());}}
一种关于finally的小注意点:
如果try中出现异常,我们在catch中解决异常,但是如果catch中出现异常,后面的finally中地代码是否会被执行?
/*** 如果try-catch中有异常我在catch中处理了,* 如果catch中有异常,按道理来说,程序应该结束,不应该再去执行了,* 但是这种情况下finally中的代码还回去执行,因为finally中表示的是最后一定要执行的* 如果没有finally则直接程序结束** 该方法的执行结果是:* 我是finally中的代码* Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 10*/public static void finallyTest03(){try{int a = 10;int b = 0;System.out.println("我是try中的代码:" + (a / b));}catch (ArithmeticException e){Integer[] arr = new Integer[10];System.out.println("我是catch中的代码:" + arr[10]);}finally {System.out.println("我是finally中的代码");}}/*** 如果try-catch中有异常我在catch中处理了,* 如果catch中有异常,按道理来说,程序应该结束,不应该再去执行了,* 但是这种情况下finally中的代码还回去执行,因为finally中表示的是最后一定要执行的 情况1* 但是如果没有finally,则程序结束,不会再去执行try-catch-finally之外的代码了 情况2* 如果有finally,则也不会执行finally之外的程序,但是finally之内的是要进行处理的 情况3** 执行结果:* 情况2 :Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 10* 情况3:我是finally中的代码* Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 10*/public static void finallyTest04(){try {int a = 10;int b = 0;System.out.println("我是try中的代码:" + (a / b));} catch (ArithmeticException e){Integer[] arr = new Integer[10];System.out.println("我是catch中的代码:" + arr[10]);// ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException} finally {System.out.println("我是finally中的代码");}System.out.println("我是try-catch执行完之后的代码");// 不会去执行的}public static void main(String[] args) {finallyTest04();}
什么情况下才把代码写在finally中呢?
1、比如像流操作
2、数据库中的连接资源
3、网络编程中的socket等
/*** finally中必须写的代码* 以下出现的错误都会在 catch 中处理* 情况一:* 如果在流操作当中try中的 1 出会出现错误,则 fis 流不会创建,直接到 5* 情况二:* 如果try中 1 没有出现错误,则 fis 创建成功,接着往下执行代码 执行到 2 ,* 如果 2 没有出现错误继续执行,执行到 3 ,有错误,则跳到 catch 当中,如果我将fis.close* 关闭操作放在 4,则是不是不会执行,因为刚才执行到 3 时,跳到 catch 当中处理了错误,* 因此岂不是造成了资源的浪费,只好将关闭资源的操作放在 finally 当中*/public static void finallyTest05(){File file = null;FileInputStream fis = null;try {file = new File("hello.txt");fis = new FileInputStream(file);// 会出现编译错误 1int read = fis.read();// 会出现编译错误 2while (read != -1) {System.out.println((char)read);read = fis.read();// 会出现编译错误 3}// fis.close();// 4} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();// 5} finally {try {if(fis != null){fis.close();// 会出现编译错误 4}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}
四、异常处理机制二:throws
throws跟在方法的括号后面,可以声明多个异常,以逗号分隔。这个声明的含义是说,我这个方法内可能抛出这些异常,我没有进行处理,至少没有处理完,调用者必须进行处理。这个声明没有说明,具体什么情况会抛出什么异常,作为一个良好的实践,应该将这些信息用注释的方式进行说明,这样调用者才能更好的处理异常。
一般对于运行时异常不要求使用throws进行声明的,但是对于编译异常则是必须进行生声明的。
对于一个方法调用了另一个声明抛出的编译异常,则此时的方法就应该处理这个编译异常,但是至于选择处理异常的方法,可以使用try-catch,也可以使用抛出的方式。
RuntimeException(unchecked)表示编程的逻辑错误,编程时应该检查以避免这些错误,比如说像空指针异常,如果真的出现了这些异常,程序退出也是正常的,程序员应该检查程序代码的bug而不是想办法处理这种异常。Checked exception表示程序本身没问题,但由于I/O、网络、数据库等其他不可预测的错误导致的异常,调用者应该进行适当处理。
五、手动抛出异常:throw
/*** @Description TODO* @Author dongxinxin@e6yun.com* @Created Date: 2022/3/8 16:55* @ClassName ThrowsTest* @Remark*/public class ThrowsTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Integer[] arr = {1,2,3};System.out.println(getArr(arr,4));}public static int getArr(Integer[] arr,int index){if(arr == null){throw new NullPointerException("有可能会导致空指针异常");}if(index < 1 || index > arr.length){throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException("请重新传参,角标越界");}return arr[index - 1];}}/**ArrayList 中添加的方法中判断*/private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {if (index > size || index < 0)throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));}
throws 和 throw 的区别:
1、throws:用来声明一个方法可能产生的所有异常,不做任何处理而是将异常往上传,谁调用我我就抛给谁。
用在方法声明后面,跟的是异常类名
可以跟多个异常类名,用逗号隔开
表示抛出异常,由该方法的调用者来处理
throws表示出现异常的一种可能性,并不一定会发生这些异常
2、throw:则是用来抛出一个具体的异常类型。
用在方法体内,跟的是异常对象名
只能抛出一个异常对象名
表示抛出异常,由方法体内的语句处理
throw则是抛出了异常,执行throw则一定抛出了某种异常
六、用户自定义异常类
/*** 自定义异常* 如何自定义异常类?* 1、继承现有的异常结构* 2、Exception 仿照现有异常类进行构造* 3、重载的构造器* @author dongxinxin* @create 2022-03-08 21:01*/public class MyExceptionTest extends Exception{static final long serialVersionUID = -3387516993124229948L;public MyExceptionTest(){}public MyExceptionTest(String msg){super(msg);}}class Demo01{public static void show(int index){try {if (index > 2){throw new MyExceptionTest("有异常了");} else {System.out.println("已解决");}} catch (Exception e){System.out.println(e.getMessage());}}}
七、练习
/*** 练习* @author dongxinxin* @create 2022-03-08 21:16*/public class DemoException {public static void methodA(){try {System.out.println("进入方法A");throw new RuntimeException("制造异常");} finally {System.out.println("A方法中的finally");}}public static void methodB(){try {System.out.println("进入方法B");return;} finally {System.out.println("B方法中的finally");}}public static void main(String[] args) {try {methodA();} catch (Exception e) {System.out.println(e.getMessage());}methodB();}}

