二叉树理论基础
种类
- 满二叉树:如果一棵二叉树只有度为0的结点和度为2的结点,并且度为0的结点在同一层上,则这棵二叉树为满二叉树。深度为k,有2^k-1个节点的二叉树
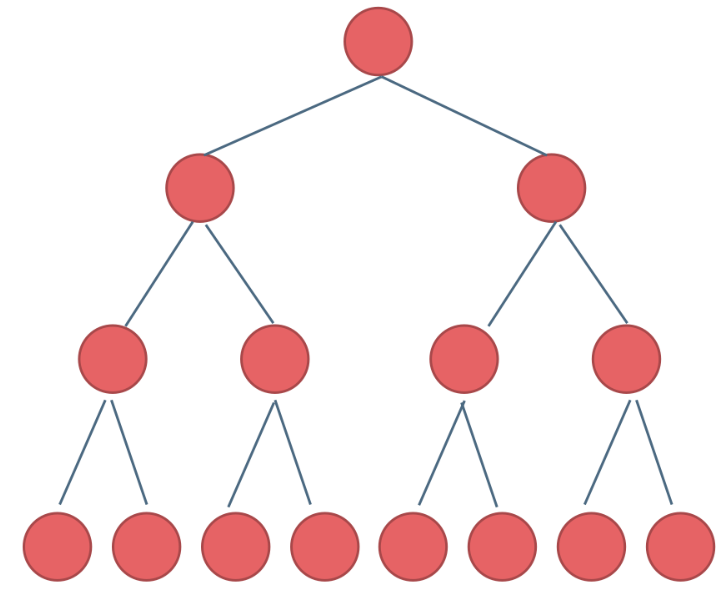
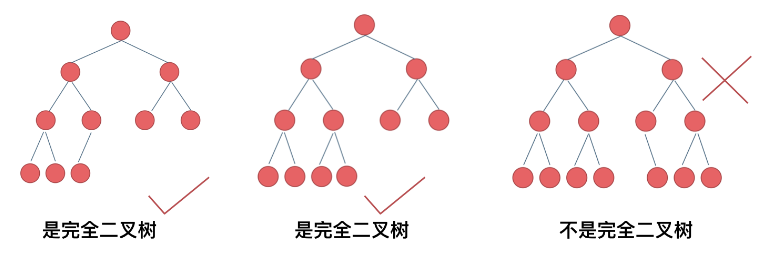
- 完全二叉树:在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层,则该层包含 1~ 2^(h-1) 个节点。
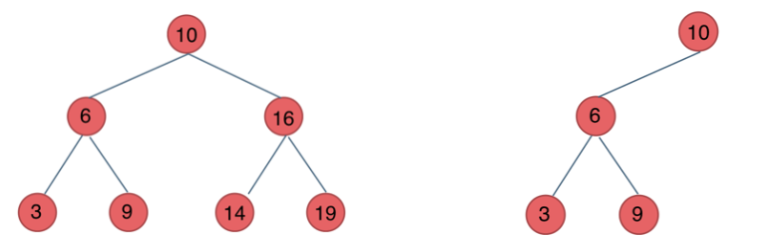
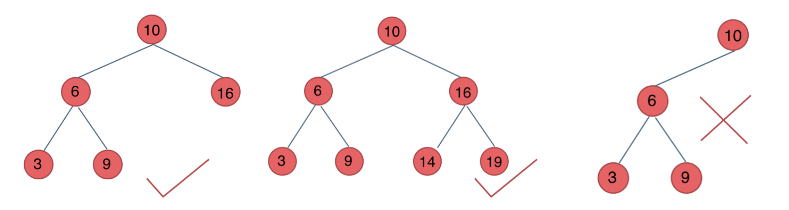
- 二叉搜索树:
- 若它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;
- 若它的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值;
- 它的左、右子树也分别为二叉排序树
平衡二叉搜索树:又被称为AVL(Adelson-Velsky and Landis)树,且具有以下性质:它是一棵空树或它的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1,并且左右两个子树都是一棵平衡二叉树。
存储方式
二叉树可以链式存储,也可以顺序存储。那么链式存储方式就用指针, 顺序存储的方式就是用数组。
- 顾名思义就是顺序存储的元素在内存是连续分布的,而链式存储则是通过指针把分布在散落在各个地址的节点串联一起。
- 链式存储(指针)
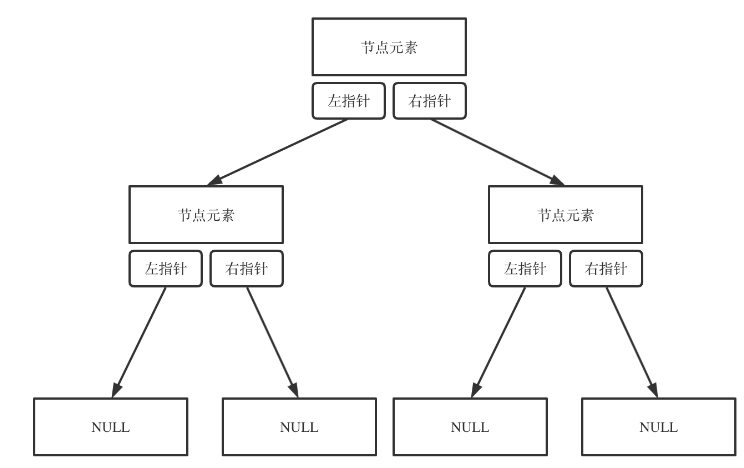
顺序存储(数组)
如果父节点的数组下标是 i,那么它的左孩子就是 i 2 + 1,右孩子就是 i 2 + 2。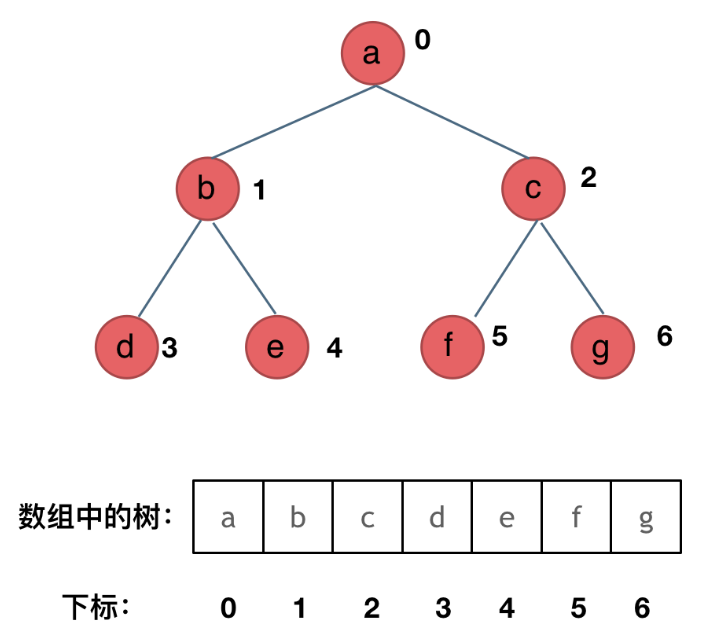
遍历方式
深度优先遍历
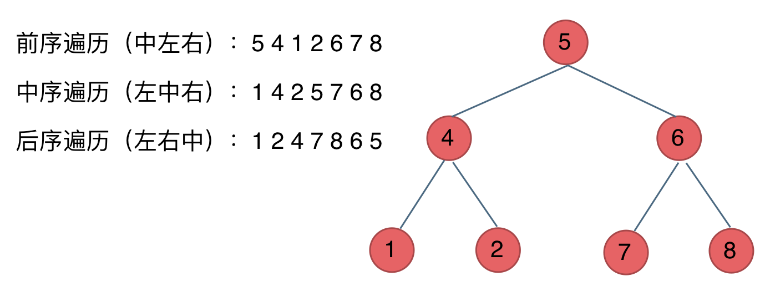
- 这里前中后,其实指的就是中间节点的遍历顺序
- 前序遍历(递归法,迭代法):中-左-右
- 中序遍历(递归法,迭代法):左-中-右
- 后序遍历(递归法,迭代法):左-右-中
- 广度优先遍历
- 层次遍历(迭代法)
- 一般使用递归的方式实现深度优先遍历。栈其实就是递归的一种是实现结构,也就说前中后序遍历的逻辑其实都是可以借助栈使用非递归的方式来实现的。
- 而广度优先遍历的实现一般使用队列来实现,这也是队列先进先出的特点所决定的,因为需要先进先出的结构,才能一层一层的来遍历二叉树。
二叉树的定义
function TreeNode(val, left, right) {this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)}
二叉树的递归遍历
递归的三要素
- 确定递归函数的参数和返回值: 确定哪些参数是递归的过程中需要处理的,那么就在递归函数里加上这个参数, 并且还要明确每次递归的返回值是什么进而确定递归函数的返回类型。
- 确定终止条件: 写完了递归算法, 运行的时候,经常会遇到栈溢出的错误,就是没写终止条件或者终止条件写的不对,操作系统也是用一个栈的结构来保存每一层递归的信息,如果递归没有终止,操作系统的内存栈必然就会溢出。
确定单层递归的逻辑: 确定每一层递归需要处理的信息。在这里也就会重复调用自己来实现递归的过程。
前中后序遍历
递归是常规的解法,需要记住。基本代码差不多,只是递归的时候左右子树和父节点的顺序不一样。
var preorderTraversal = function (root) {let res = []const dfs = function (root) {if (root == null) return// 先把父节点的值加进去res.push(root.val)// 递归左子树dfs(root.left)// 递归右子树dfs(root.right)}dfs(root)return res};
var inorderTraversal = function (root) {let res = []const dfs = function (root) {if (root == null) return// 递归左子树dfs(root.left)// 把父节点的值加进去res.push(root.val)// 递归右子树dfs(root.right)}dfs(root)return res};
var postorderTraversal = function (root) {let res = []const dfs = function (root) {if (root == null) return// 递归左子树dfs(root.left)// 递归右子树dfs(root.right)// 把父节点的值加进去res.push(root.val)}dfs(root)return res};
二叉树的迭代遍历
- 前序和后序的思路差不多,中序因为访问节点和处理节点不能同时进行所以更复杂。
var preorderTraversal = function (root) {let res = []if (root == null) return resconst stack = [root]while (stack.length) {let current = stack.pop()res.push(current.val)// 入栈 右 -> 左// 出栈 中 -> 左 -> 右if (current.right) {stack.push(current.right)}if (current.left) {stack.push(current.left)}}return res}
var inorderTraversal = function (root) {let res = []const stack = []let current = rootwhile (stack.length || current) {if (current) {// 先一路向左,把途径的节点都压入栈中,直到左子树为空stack.push(current)// 左current = current.left} else {// 左子树为空的时候开始弹栈// 弹出 中current = stack.pop()res.push(current.val)// 再将右子树压入栈中,为空时继续弹栈// 右current = current.right}}return res}
var postorderTraversal = function (root) {let res = []if (root == null) return resconst stack = [root]while (stack.length) {let current = stack.pop()// 入栈 左 -> 右// 出栈 中 -> 右 -> 左 结果翻转 左 -> 右 -> 中res.push(current.val)if (current.left) {stack.push(current.left)}if (current.right) {stack.push(current.right)}}return res.reverse()}
二叉树的统一迭代法
- 统一了三种遍历方式的写法。更难理解
- 在上面迭代遍历中提到:中序因为访问节点和处理节点不能同时进行所以更复杂。
- 那我们就将访问的节点放入栈中,把要处理的节点也放入栈中但是要做标记。
- 如何标记呢,就是要处理的节点放入栈之后,紧接着放入一个空指针作为标记。 这种方法也可以叫做标记法。 ```javascript // 前序遍历:中左右 // 压栈顺序:右左中
var preorderTraversal = function(root, res = []) { const stack = []; if (root) stack.push(root); while(stack.length) { const node = stack.pop(); if(!node) { res.push(stack.pop().val); continue; } if (node.right) stack.push(node.right); // 右 if (node.left) stack.push(node.left); // 左 stack.push(node); // 中 stack.push(null); }; return res; };
```javascript// 中序遍历:左中右// 压栈顺序:右中左var inorderTraversal = function(root, res = []) {const stack = [];if (root) stack.push(root);while(stack.length) {const node = stack.pop();if(!node) {res.push(stack.pop().val);continue;}if (node.right) stack.push(node.right); // 右stack.push(node); // 中stack.push(null);if (node.left) stack.push(node.left); // 左};return res;};
// 后续遍历:左右中// 压栈顺序:中右左var postorderTraversal = function(root, res = []) {const stack = [];if (root) stack.push(root);while(stack.length) {const node = stack.pop();if(!node) {res.push(stack.pop().val);continue;}stack.push(node); // 中stack.push(null);if (node.right) stack.push(node.right); // 右if (node.left) stack.push(node.left); // 左};return res;};

