解题思路1:哈希表
示例: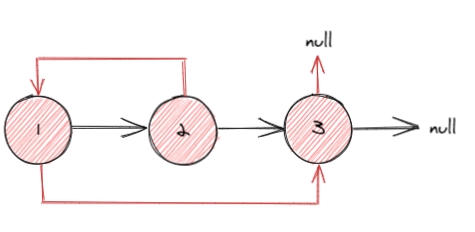
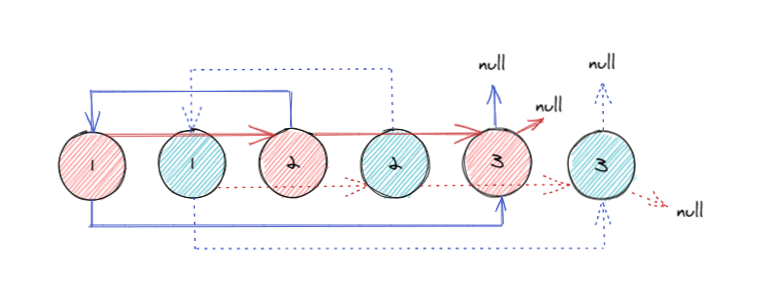
示例中,黑色的箭头表示为 next 指针,红色的箭头表示为 random 指针
我们可以使用哈希表,哈希表的键存储原链表的节点,哈希表的值存储复制后的节点。
链表中的原节点记作 node,复制后的节点记作 node’
两者之间具有如下关系:
node'.next = map.get(node.next)node'.random = map.get(node.random)
代码
/*// Definition for a Node.class Node {int val;Node next;Node random;public Node(int val) {this.val = val;this.next = null;this.random = null;}}*/class Solution {public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {Map<Node,Node> map = new HashMap<>();Node cur = head;while(cur != null){map.put(cur,new Node(cur.val));cur = cur.next;}cur = head;while(cur != null){map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next);map.get(cur).random = map.get(cur.random);cur = cur.next;}return map.get(head);}}
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:O(N)
使用哈希表,我们需要两轮遍历链表,所以时间复杂度为: O(N)
- 空间复杂度:O(N)
我们使用哈希表存储链表的节点,占用了 O(N) 的额外空间
解题思路2:拼接与拆分
第二种思路为拼接与拆分链表,可以分为三个步骤:
- 拼接链表,将复制后的节点放到原节点之后,使用 next 指针相关联
- 构建复制节点的 random 指针
- 将复制后的链表从原链表中拆分出去
拼接链表
我们首先不考虑 random 指针,将链表拼接至下图所示:
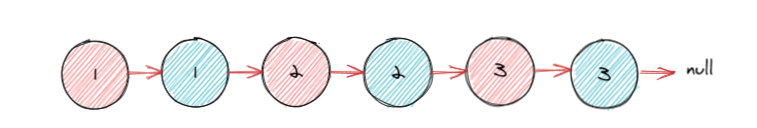
蓝色的节点为复制后的节点,我们将每一个复制后的节点都放在原节点之后,使用 next 指针相连接
构建 random 指针
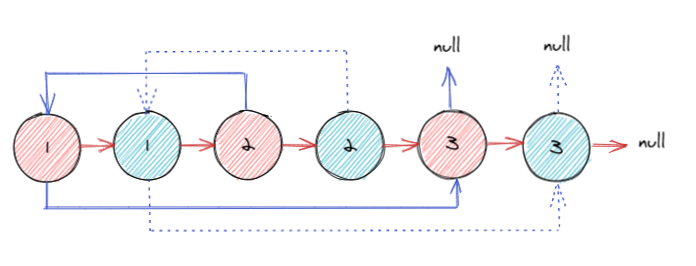
然后,我们构建复制后节点之间 random 指针的关联
原节点记作 node,复制后的节点记作 node’,二者之间满足:
node.next = node'node'.random = node.random.next
构建好 random 指针的关联后的链表如下图所示:
拆分链表
第三步,我们需要将复制后的链表从原链表中拆分出去
只需要将复制后的节点的 next 指针指向复制后的节点即可。同时我们为了不破坏原链表,还需要将原链表的节点的 next 指针指向原链表的节点。
代码
/*// Definition for a Node.class Node {int val;Node next;Node random;public Node(int val) {this.val = val;this.next = null;this.random = null;}}*/class Solution {public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {if(head == null){return null;}Node cur = head;while(cur != null){Node node = new Node(cur.val);node.next = cur.next;cur.next = node;cur = node.next;}cur = head;while(cur != null){cur.next.random = cur.random == null ? null :cur.random.next;cur = cur.next.next;}cur = head;Node res = head.next;Node cur2 = head.next;while(cur2.next != null){cur.next = cur.next.next;cur2.next = cur2.next.next;cur = cur.next;cur2 = cur2.next;}// 不要忘记处理原链表的尾节点cur.next = null;return res;}}
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度: O(N)
我们总共三轮遍历链表,使用 O(N) 的时间
- 空间复杂度: O(1)
我们仅使用了有限几个变量,使用了常数大小的额外空间,所以空间复杂度为 O(1)