1. IDEA的Structure中查看属性和字段
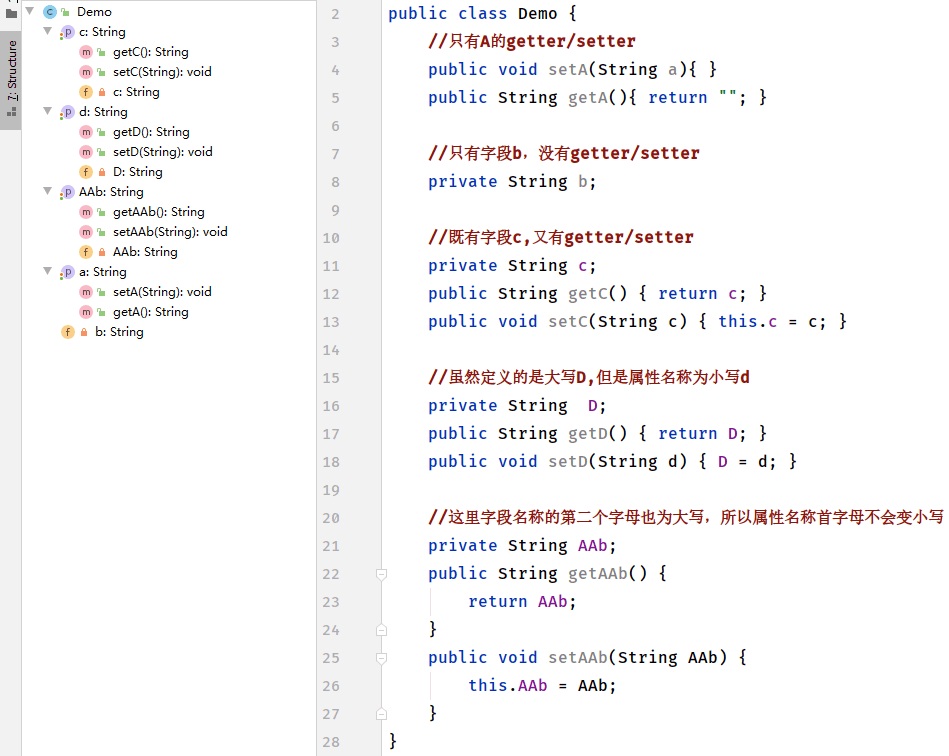
如上图所示:
- 属性c 由 getter/setter和字段 c 组成
- 属性a 由getter/setter组成
- b 没有getter和setter,所以是字段
- D和AAb用来验证属性名称
属性名称规则:去掉get或set后其剩余的字符串,如果第二个字母是小写的,则把第一个字母也变成小写,否则第一个字母也不变
Java中的属性(property),通常可以理解为get和set方法,而字段(field),通常叫做“类成员”,或 “类成员变量”,有时也叫“域”,理解为“数据成员”,用来承载数据的。
区别开属性与字段是为了更好的实现数据安全,比如当我们想给一个类的属性赋值或者其他类用到了,就需要将这个字段设置为public,然而这样可以对字段进行任意的读写操作,非常不利于数据安全。于是就加上了属性,简单说属性实现了字段的封装,属性有get、set 方法来控制字段,该字段的属性只有set方法没有get方法,就只可以对该方法进行赋值操作,没有读操作,反之亦然。就是对对字段的操作通过属性来控制。
突然想起2015年遇到的一个问题,当时给类起了个名字类似ABc(也就是首字母和第二个字母都是大写),然后用spring用类名注入时,我就把类名写成 aBc,当时就是无法注入,后来把类名改成Abc勉强解决这个问题,现在想想应该把注入的类名写成ABc就可以了。
2. Java 反省查看属性
通过Java 反省API证明属性
import java.beans.BeanInfo;import java.beans.IntrospectionException;import java.beans.Introspector;import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor;import java.lang.reflect.Method;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) throws IntrospectionException {BeanInfo beanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(Demo.class);PropertyDescriptor[] propertyDescriptors = beanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors();for (PropertyDescriptor propertyDescriptor : propertyDescriptors) {System.out.println(propertyDescriptor.getName());System.out.println(propertyDescriptor.getReadMethod().getName());Method writeMethod = propertyDescriptor.getWriteMethod();System.out.println(writeMethod != null ? writeMethod.getName():"");System.out.println("-----------------");}}}
AAb getAAb
setAAb
a getA
setA
c getC
setC
class getClass
d getD
setD
说明:class是Object中的方法,只有get,没有set.
public final native Class<?> getClass();
3. 验证Spring bean name也遵循这个规则
package cn.java.money.spring.bean;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Componentpublic class AAb {}
package cn.java.money.spring.bean;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Componentpublic class Bbc {}
package cn.java.money.spring;import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;@Configuration@ComponentScanpublic class Config {}
package cn.java.money.spring;import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) {AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac =new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Config.class);String[] beanDefinitionNames = ac.getBeanDefinitionNames();for (String name : beanDefinitionNames) {System.out.println(name);}}}
AAb
bbc

