24. 两两交换链表中的节点
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/
链表操作时尽量使用dummy节点
注意post节点更新的时机
class Solution:def swapPairs(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:if not head or not head.next:return headdummy = ListNode(-1)dummy.next = headpre = dummywhile head and head.next:post = head.next# swaphead.next = post.nextpost.next = headpre.next = post# update pointerpre = headhead = head.nextreturn dummy.next
206. 反转链表
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/
迭代
class Solution:def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:cur = Nonewhile head:tmp = head.nexthead.next = curcur = headhead = tmpreturn cur
递归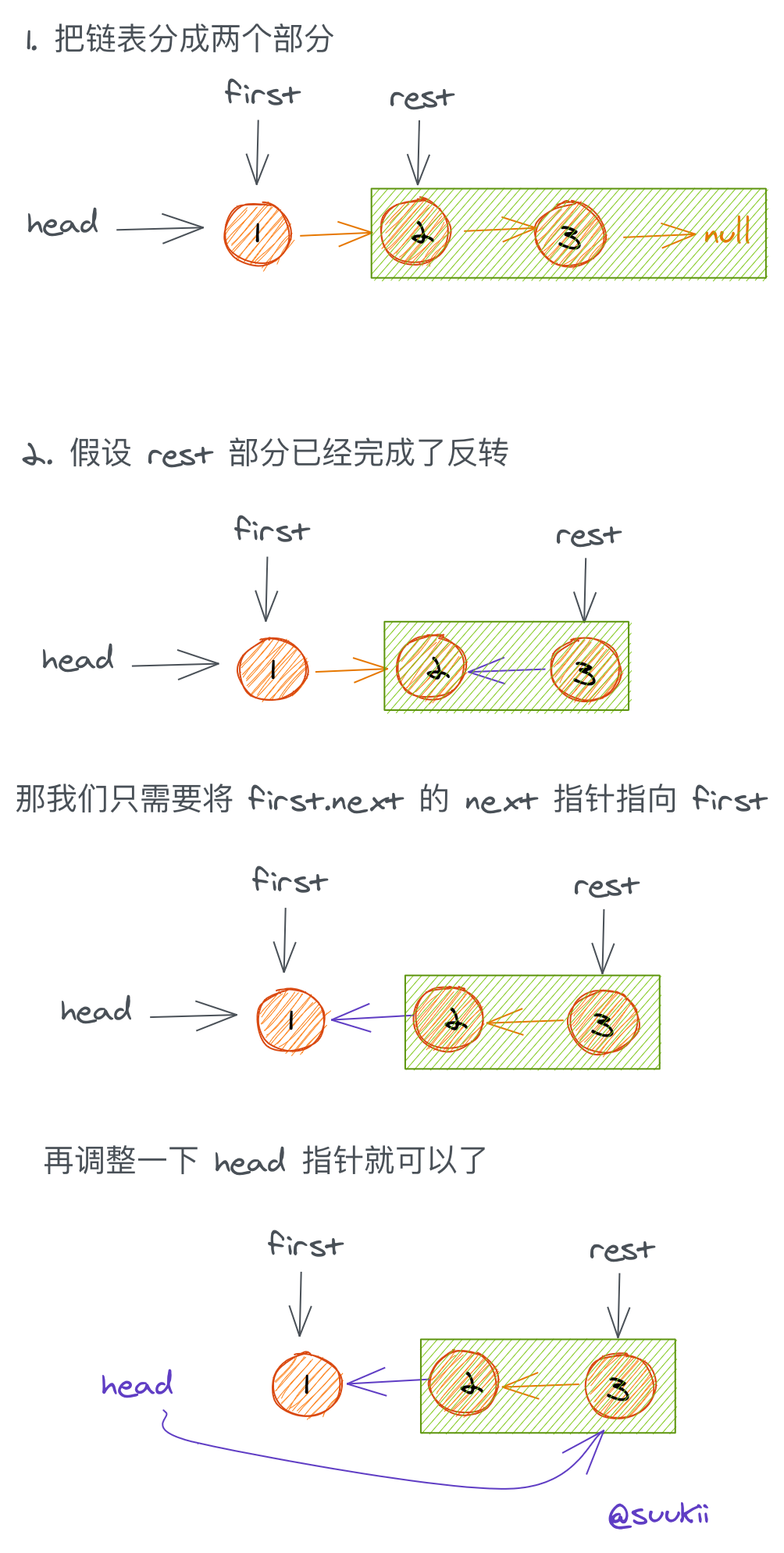
class Solution:def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:if not head or not head.next:return headnewHead = self.reverseList(head.next)head.next.next = headhead.next = Nonereturn newHead
92. 反转链表 II
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list-ii/
第一个版本写的比较丑,一个指针指向m的pre,一个指针指向n,一直把pre_m.next移动到n的后面就可以了
这种情况需要特殊考虑当m是1的时候,也就是要从第头指针开始反转的情况
第二种: 其实没有必要找到n点,只需要每次把m.next挪到m之前, pre_m之后即可
# Definition for singly-linked list.# class ListNode:# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):# self.val = val# self.next = nextclass Solution:def reverseBetween(self, head: ListNode, m: int, n: int) -> ListNode:if m == n:return headdummy = ListNode(-1)dummy.next = headpre = dummyi = 0while i < m-1:pre = pre.nexti += 1pre_m = prewhile i < n:pre = pre.nexti += 1node_n = prei = 0while i < n - m :# 从前面拿出来node = pre_m.nextpre_m.next = pre_m.next.next# 放到后面去tmp = node_n.nextnode_n.next = nodenode.next = tmpi += 1return dummy.next
只需要找到反转的起始位置, 使用头插法
用一个守卫节点指向反转起始位置,设为g
起始位置为p, 每次将p.next放到g.next. 循环m-n次
class Solution:def reverseBetween(self, head: ListNode, left: int, right: int) -> ListNode:if left == right:return headdummy = ListNode(-1)dummy.next = headpre = dummyi = 0while i < left-1:pre = pre.nexti += 1g = prep = g.nextfor i in range(right-left):tmp = p.nextp.next = tmp.nexttmp.next = g.nextg.next = tmpreturn dummy.next
445. 两数相加 II
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/add-two-numbers-ii/
class Solution:def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:stack_l1 = []stack_l2 = []while l1:stack_l1.append(l1.val)l1 = l1.nextwhile l2:stack_l2.append(l2.val)l2 = l2.nextcarry = 0while stack_l2 or stack_l1 or carry:a = stack_l2.pop() if stack_l2 else 0b = stack_l1.pop() if stack_l1 else 0summary = a+b+carrynode = ListNode(summary%10)carry = summary//10node.next = headhead = nodereturn head
21. 合并两个有序链表
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/
迭代
class Solution:def mergeTwoLists(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:dummy = ListNode(-1)res = dummywhile l1 and l2:if l2.val<l1.val:res.next = l2l2 = l2.nextelse:res.next = l1l1 = l1.nextres = res.nextres.next = l1 if l1 else l2return dummy.next
递归
class Solution:def mergeTwoLists(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:if not l1:return l2if not l2:return l1if l1.val<l2.val:l1.next = self.mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2)return l1else:l2.next = self.mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next)return l2
23. 合并K个升序链表
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-k-sorted-lists/
21的升级版
循环遍历k个链表, python会TLE
class Solution:def mergeKLists(self, lists: List[ListNode]) -> ListNode:if not lists:returndummy = ListNode(0)res = dummysize = len(lists)while True:minNode = NoneminPointer = -1for i in range(len(lists)):if not lists[i]:continueif not minNode or lists[i].val < minNode.val:minNode = lists[i]minPointer = iif minPointer==-1:breakres.next = minNoderes = res.nextlists[minPointer] = lists[minPointer].nextreturn dummy.next
分治, 归并排序应用于链表
class Solution:def mergeKLists(self, lists: List[ListNode]) -> ListNode:if not lists:returndef mergeTwoLists(l1,l2):dummy = ListNode(-1)res = dummywhile l1 and l2:if l2.val<l1.val:res.next = l2l2 = l2.nextelse:res.next = l1l1 = l1.nextres = res.nextres.next = l1 if l1 else l2return dummy.nextdef merge(lists, lo, hi):if lo==hi:return lists[lo]mid = lo + (hi-lo)//2l1 = merge(lists, lo, mid)l2 = merge(lists, mid+1, hi)return mergeTwoLists(l1,l2)return merge(lists, 0 , len(lists)-1)
拍案叫绝,给ListNode class增加lt方法, 就可以用来比较大小
class Solution:def mergeKLists(self, lists: List[ListNode]) -> ListNode:def __lt__(self, other):return self.val < other.valListNode.__lt__ = __lt__import heapqheap = []dummy = ListNode(-1)p = dummyfor l in lists:if l:heapq.heappush(heap, l)while heap:node = heapq.heappop(heap)p.next = ListNode(node.val)p = p.nextif node.next:heapq.heappush(heap, node.next)return dummy.next
25. K 个一组翻转链表
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-nodes-in-k-group/
一旦看到翻转顺序, 请第一时间先想到stack!160. 相交链表
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists/
我一开始想到的是用哈希表,两个链表都往哈希表里存,如果一个链表存的时候发现已经存在了,那么肯定是另外一个链表存进去的,此时返回这个节点
但是这样空间复杂度太高, 这道题可以用空间复杂度为0(1)的解法, 也就是长短链表拼接,假设两个链表相交,那么相交的部分长度是相等的,我们分为一个长链表一个短链表, 两个链表从表头开始循环,如果长的走完了,那么就走短的,如果短的走完了,那么就走长的; 如果有交点,那么他们会同时抵达交点,此刻走过的路程都是等于 长+短+相交, 顺序是 长+相交+短 和 短+相交+长。
这里最巧妙的地方在于边界条件的处理,要把最后一个节点之后的None也加到循环中来, 这样如果两个链表不相交,那么最终会在等于None的地方相交(满足退出条件)class Solution:def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> ListNode:ha, hb = headA, headBwhile ha!=hb:ha = ha.next if ha else headBhb = hb.next if hb else headAreturn ha
138. 复制带随机指针的链表
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer/ ```python “””
Definition for a Node.
class Node: def init(self, x: int, next: ‘Node’ = None, random: ‘Node’ = None):
self.val = int(x)self.next = nextself.random = random
“””
class Solution: def copyRandomList(self, head: ‘Node’) -> ‘Node’: lookup = {} if not head: return None p = head while p: lookup[p] = Node(p.val) p = p.next p = head while p: lookup[p].next = lookup[p.next] if p.next else None p = p.next p = head while p: lookup[p].random = lookup[p.random] if p.random else None p = p.next return lookup[head]
<a name="1lT4Q"></a>#### [234. 回文链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/palindrome-linked-list/)[https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/palindrome-linked-list/](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/palindrome-linked-list/)<br />简单的题不简单的做, 涉及快慢指针, 链表反转<br />用快慢指针找到链表的中间位置 ( 注意链表长度的奇偶分别判断)<br />反转链表后半部分<br />此时两个指针分别指向链表的开头 和 链表中间(后半部分已经翻转)<br />逐个对比, 判断回文```python# Definition for singly-linked list.# class ListNode:# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):# self.val = val# self.next = nextclass Solution:def isPalindrome(self, head: ListNode) -> bool:if not head or not head.next:return Truefast,slow = head,head# fast pointer is twice faster than slow pointerwhile fast and fast.next:slow = slow.nextfast = fast.next.next# if fast pointer is not None, it means the length of linkedlist is oddif fast:slow = slow.next# reverse the linkedlist leading by slow pointerpre = ListNode(-1)pre.next = slowwhile slow.next:post = slow.nextslow.next = post.nextpost.next = pre.nextpre.next = postslow = pre.next# compare from headwhile head and slow:if head.val!=slow.val:return Falsehead = head.nextslow = slow.nextreturn True

