- Concepts
- 94. 二叉树的中序遍历
- 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素">230.二叉搜索树中第K小的元素
- 98. 验证二叉搜索树">98. 验证二叉搜索树
- 04. 二叉树的最大深度">04. 二叉树的最大深度
- 110. 平衡二叉树">110. 平衡二叉树
- 538. 把二叉搜索树转换为累加树">538. 把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
- 654. 最大二叉树">654. 最大二叉树
- 543. 二叉树的直径">543. 二叉树的直径
- 112. 路径总和">112. 路径总和
- 437. 路径总和 III">437. 路径总和 III
- 101. 对称二叉树">101. 对称二叉树
- 剑指 Offer 32 - I. 从上到下打印二叉树">剑指 Offer 32 - I. 从上到下打印二叉树
- 236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先">236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
- 剑指 Offer 68 - I. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先">剑指 Offer 68 - I. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
- 剑指 Offer 26. 树的子结构">剑指 Offer 26. 树的子结构
- 572. 另一个树的子树">572. 另一个树的子树
- 103. 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历">103. 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历
- 116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针">116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
- 117. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II">117. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II
- 297. 二叉树的序列化与反序列化">297. 二叉树的序列化与反序列化
- 450. 删除二叉搜索树中的节点">450. 删除二叉搜索树中的节点
- 863. 二叉树中所有距离为 K 的结点">863. 二叉树中所有距离为 K 的结点
Concepts
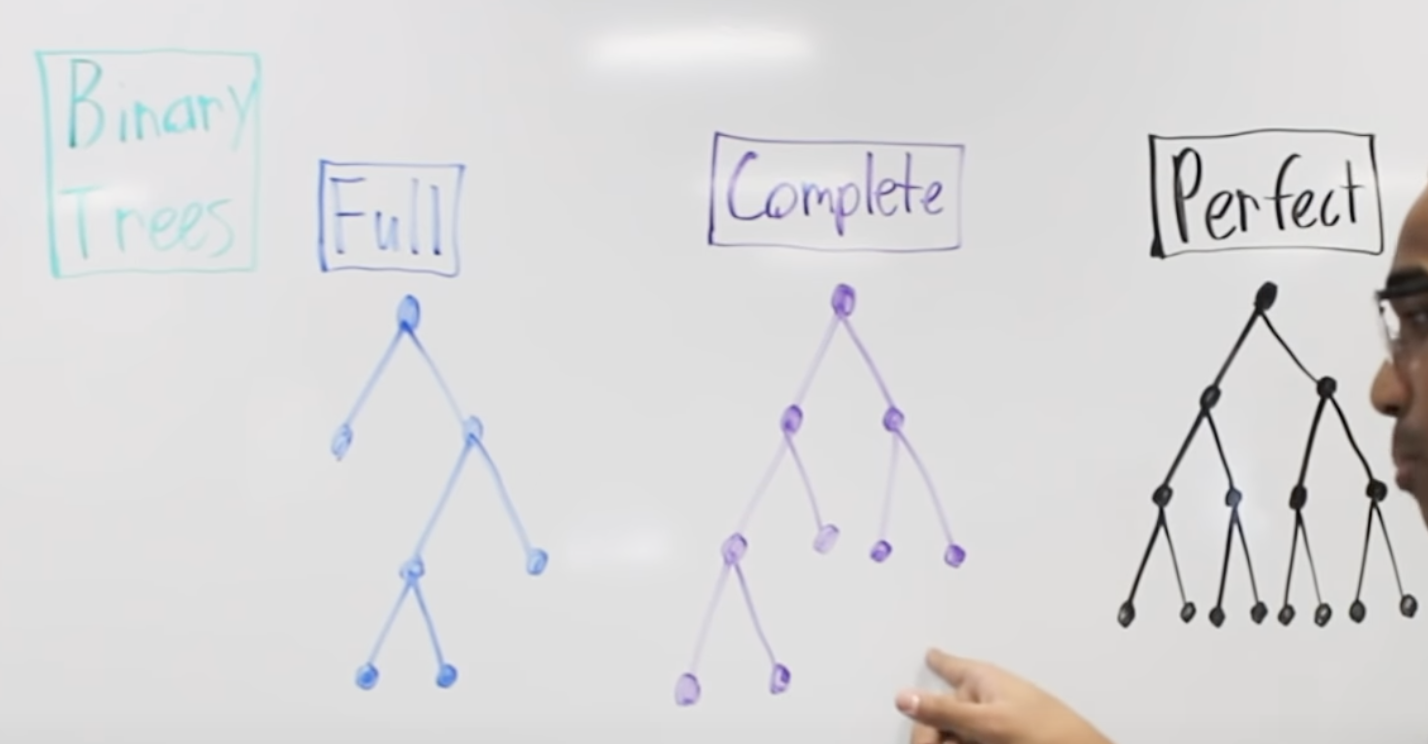
Full: 每个node只有0个或2个children
complete: 从上到下,从左到右
perfect: 每一层都是满的 2**k-1
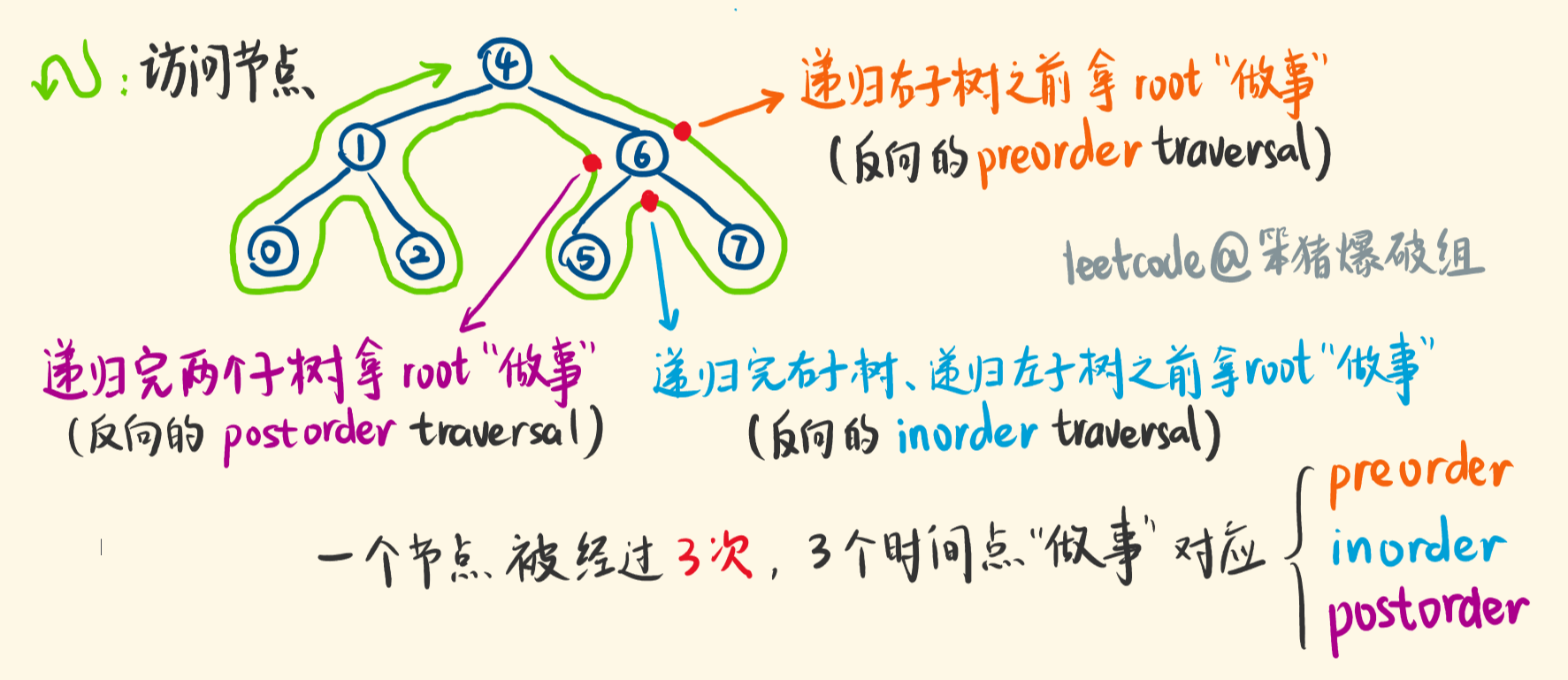
Focus on a Node! 不要去想递归的过程,不要去想整棵树,就想这一个node要做什么!
What needs to happen at this node?
中序遍历中的一些点
successor, 后驱节点,紧跟着当前节点比当前小的那个节点,先取root.right(如果root.right存在),然后一直取左子树
def succeesor(root):root = root.rightwhile root.left:root = root.leftreturn root
prece, 前驱,比当前节点大一个位置的节点
def predecessor(root):root = root.leftwhile root.right:root = root.rightreturn root
94. 二叉树的中序遍历
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-inorder-traversal/submissions/
# Definition for a binary tree node.# class TreeNode:# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):# self.val = val# self.left = left# self.right = rightclass Solution:def inorderTraversal(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[int]:stack = list()arr = list()while root or stack:while root:stack.append(root)root = root.leftroot = stack.pop()arr.append(root.val)root = root.rightreturn arr
230.二叉搜索树中第K小的元素
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/kth-smallest-element-in-a-bst/
class Solution:def kthSmallest(self, root: TreeNode, k: int) -> int:stack = list()while root or stack:while root:stack.append(root)root = root.leftroot = stack.pop()k -= 1if not k:return root.valelse:root = root.right
同理找第K大的
class Solution:def kthLargest(self, root: TreeNode, k: int) -> int:stack = list()while root or stack:while root:stack.append(root)root = root.rightroot = stack.pop()k-=1if k==0:return root.valroot = root.leftreturn
98. 验证二叉搜索树
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/validate-binary-search-tree/
Iteration
class Solution:def isValidBST(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:if not root:return Falsestack = list()pre = Nonewhile root or stack:while root:stack.append(root)root = root.leftroot = stack.pop()if pre and root.val<=pre.val:return Falsepre = rootroot = root.rightreturn True
Recursion
在纸上画一画,理解一下这个preNode的含义,出现的位置,preNode是如何保证整个左子树小于root,整个右子树都大于root的。
class Solution:pre = Nonedef isValidBST(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:if not root:return Trueleft = self.isValidBST(root.left)if self.pre and root.val<=self.pre.val:return Falseself.pre = rootright = self.isValidBST(root.right)return left and right
04. 二叉树的最大深度
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/
class Solution:def maxDepth(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:if not root:return 0return 1+max(self.maxDepth(root.left),self.maxDepth(root.right))
110. 平衡二叉树
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/balanced-binary-tree/
自顶向下
O(n), O(n)
class Solution:def isBalanced(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:def recur(root):if not root:return 0left = recur(root.left)if left == -1:return -1right = recur(root.right)if right == -1:return -1return max(left,right) + 1 if abs(left-right)<2 else -1return recur(root)!=-1
自底向上
O(NlogN), O(N)
class Solution:def maxDepth(self,root):if not root:return 0return 1+max(self.maxDepth(root.left),self.maxDepth(root.right))def isBalanced(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:if not root:return Truereturn abs(self.maxDepth(root.left)-self.maxDepth(root.right))<2 and self.isBalanced(root.left) and self.isBalanced(root.right) # 先序遍历,判断当前子树是否二叉平衡树, 判断当前左子树是否二叉平衡树, 判断当前右子树是否二叉平衡树
538. 把二叉搜索树转换为累加树
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/convert-bst-to-greater-tree/
因为每个节点要之后它右边所有子树之和,所以这道题是inorder的反向操作
访问每一个节点时,我们希望维护一个变量 sum,保存「比当前节点值大的所有节点值的和」。
二叉搜索树的中序遍历,访问的节点值是递增的。
如果先访问右子树,反向的中序遍历,访问的节点值是递减的,之前访问的节点值都比当前的大,每次累加给 sum 即可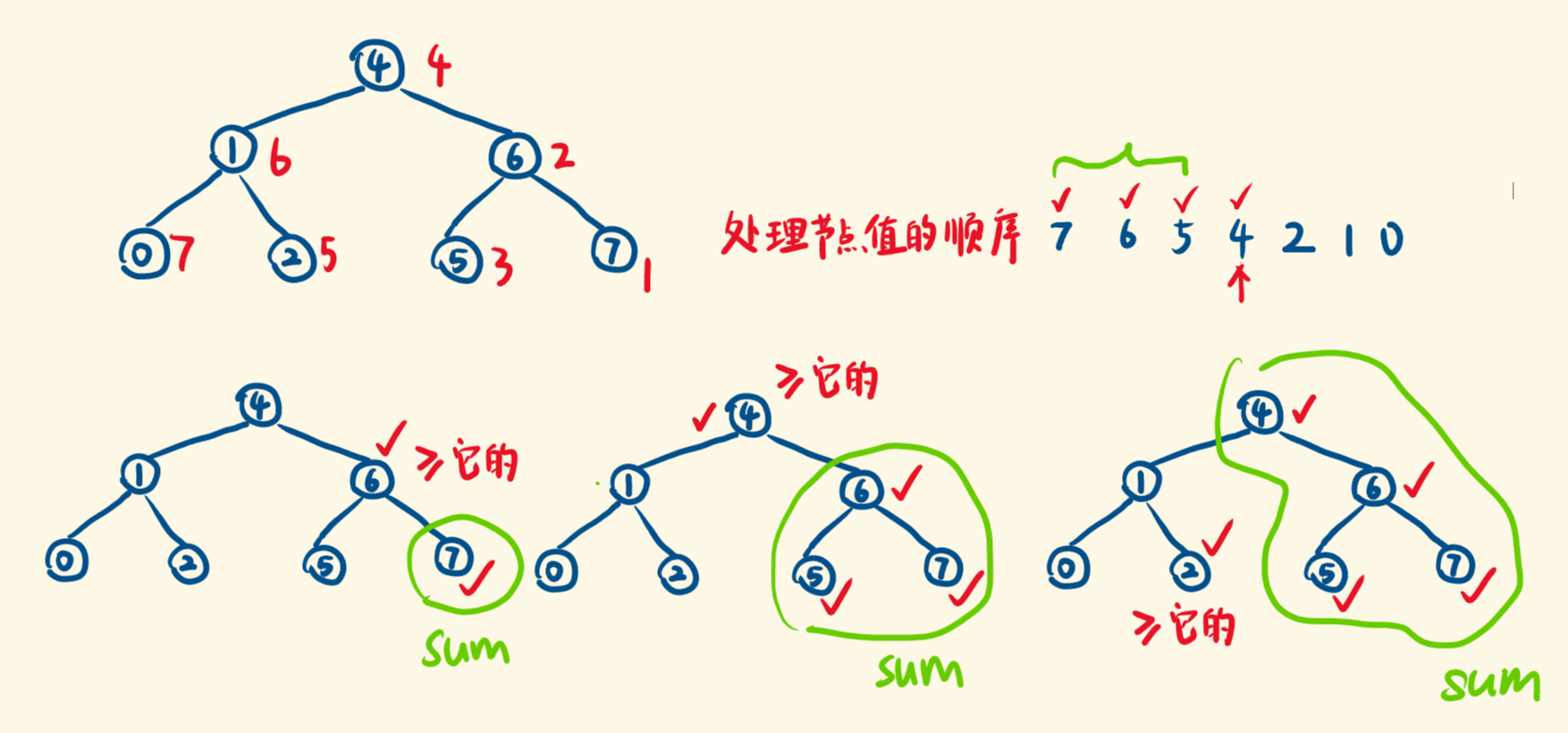
class Solution:total = 0def convertBST(self, root: TreeNode) -> TreeNode:if root:self.convertBST(root.right)self.total += root.valroot.val = self.totalself.convertBST(root.left)return root
654. 最大二叉树
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-binary-tree/
第一次秒做出来二叉树的medium题目
class Solution:def constructMaximumBinaryTree(self, nums: List[int]) -> TreeNode:if not nums:returnmax_val = max(nums)max_idx = nums.index(max_val)root = TreeNode(max_val)root.left = self.constructMaximumBinaryTree(nums[:max_idx])root.right = self.constructMaximumBinaryTree(nums[max_idx+1:])return root
543. 二叉树的直径
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/diameter-of-binary-tree/
这道题更新diameter的方式和最后的返回值是一个关键点,返回给节点的是这个节点的最大深度,而不是diameter
每次在root计算左右子树的深度加起来有多长,这个是diameter,但是返回的时候是返回这个节点的最大深度
class Solution:diameter = 0def diameterOfBinaryTree(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:def helper(root,diameter):if not root:return 0left = helper(root.left,diameter)right = helper(root.right,diameter)self.diameter = max(left+right,self.diameter)return max(left,right)+1helper(root,self.diameter)return self.diameter
112. 路径总和
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/path-sum/
class Solution:def hasPathSum(self, root: TreeNode, targetSum: int) -> bool:if not root:# 注意这个返回值,如果可以一直到none节点,那说明这条路径上没找到,所以返回falsereturn Falseif root.val == targetSum and not root.left and not root.right:return Truereturn self.hasPathSum(root.left, targetSum-root.val) or self.hasPathSum(root.right, targetSum-root.val)
437. 路径总和 III
这道题还有1 和 2
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/path-sum-iii/
先序遍历,用一个list把这条路径上所有可能的加和都存下来,相对好理解一些,但是时间复杂度比较高,每一层都要对sumlist进行两次遍历, 第一次对每个元素加一,第二次算count
class Solution:def pathSum(self, root: TreeNode, sum: int) -> int:def dfs(root, sumlist):if root is None:return 0sumlist = [num+root.val for num in sumlist]sumlist.append(root.val)count = sumlist.count(sum)return count+dfs(root.left, sumlist)+dfs(root.right, sumlist)return dfs(root, [])
前缀和,晚上状态不太好,理解不了这个了,迷迷糊糊的
当前节点的前缀和减去target如果存在在hashmap中,说明这条路径之前有个节点的前缀和是presum-target
那当前节点减去那个节点就是 presum - (presum-target) = target
这个思路有点像经典的twoSum
用一个HashMap来存前缀和记录,key是前缀和,value是这个前缀和出现过几次,注意关键是在这条路径上出现过几次,因为从一个节点回到root只有一条路径,这个路径上同一个前缀和可能多次出现。
所以关键的那一步 返回本层,就是把当前前缀和出现的次数减一,因为我们退回去了。
def pathSum(root,sum):#思路:前缀和#递归进入左右子树后,回到当前层,要把当前节点添加的前缀和去除,避免回溯之后影响上一层。def dfs(root, hashmap, target,presum):#终止条件if not root:return 0#本层要做的事情cnt=0presum += root.valif presum - target in hashmap:cnt += hashmap[presum - target]if presum not in hashmap:hashmap[presum] = 1else:hashmap[presum]+=1#进入下一层cnt+=dfs(root.left, hashmap, target,presum)cnt+=dfs(root.right, hashmap, target,presum)#!!!重要:回到本层hashmap[presum]-=1return cnthashmap = {0:1}r = dfs(root, hashmap,sum,0)return r
101. 对称二叉树
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/symmetric-tree/
或者叫做镜像二叉树
这道题的关键在于递归函数返回值和输入值的设计!
class Solution:def isSymmetric(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:def helper(left, right):if not left and not right:return Trueif not left or not right:return False# left is left's left or left's right# right is right's right or right's leftif left.val !=right.val:return Falsereturn helper(left.left, right.right) and helper(left.right,right.left)if not root:return Trueelse:return helper(root.left, root.right)
BFS, 层序遍历
from collections import dequeclass Solution:def isSymmetric(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:if not root:return Truequeue = deque()queue.append(root)while queue:level_list=[]for _ in range(len(queue)):tmp = queue.popleft() # 注意这里是先进先出,所以是popleft()if not tmp:level_list.append(-1)else:level_list.append(tmp.val)# 下面这两句要放在else的逻辑下,因为如果是一个node是None,那么它的左右节点不能继续#往list里放,否则程序无法终止queue.append(tmp.left)queue.append(tmp.right)if level_list[:] == level_list[::-1]:continueelse:return Falsereturn True
剑指 Offer 32 - I. 从上到下打印二叉树
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/cong-shang-dao-xia-da-yin-er-cha-shu-lcof/
上一题如果children是none也要继续往queue里放是因为我们要把空children用-1来补位置,来确保对称检查;但是如果节点本身是none,则不能继续放入queue,这样会死循环
from collections import dequeclass Solution:def levelOrder(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[int]:queue = deque()if not root:return []res = []queue.append(root)while queue:for _ in range(len(queue)):tmp = queue.popleft()res.append(tmp.val)if tmp.left:queue.append(tmp.left)if tmp.right:queue.append(tmp.right)return res
236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree/
class Solution:def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root: 'TreeNode', p: 'TreeNode', q: 'TreeNode') -> 'TreeNode':if not root or root==p or root==q:return rootleft = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q)right = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)if not left:return rightif not right:return leftreturn root
剑指 Offer 68 - I. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/er-cha-sou-suo-shu-de-zui-jin-gong-gong-zu-xian-lcof/
注意这道题和上一题的区别 这道题是二叉搜索树,可以利用二叉搜索树的特性,让题目变的更简单
# 迭代class Solution:def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root: 'TreeNode', p: 'TreeNode', q: 'TreeNode') -> 'TreeNode':# 确保p <= qif p.val > q.val:p,q=q,pwhile root:if root.val < p.val:root=root.rightelif root.val > q.val:root=root.leftelse:breakreturn root# 递归class Solution:def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root: 'TreeNode', p: 'TreeNode', q: 'TreeNode') -> 'TreeNode':if not root:returnif root.val > q.val and root.val > p.val:return self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q)if root.val<q.val and root.val < p.val:return self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q)return root
二叉树序列化和反序列化
from collections import dequeclass Codec:def serialize(self, root):if not root:return "[]"res = []queue = deque()queue.append(root)while queue:node = queue.popleft()if node:res.append(str(root.val))queue.append(root.left)queue.append(root.right)else:res.append('null')return '[' + ','.join(res) + ']'def deserialize(self, data):if data=='[]':returndataList = data[1:-1].split(",")root = TreeNode(int(dataList[0]))queue = deque()queue.append(root)i = 1while queue:node = queue.popleft()if dataList[i]!='null':node.left = TreeNode(int(dataList[i]))queue.append(node.left)i+=1if dataList[i]!='null':node.right = TreeNode(int(dataList[i]))queue.append(node.right)i+=1return root
剑指 Offer 26. 树的子结构
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/shu-de-zi-jie-gou-lcof/
树的匹配类问题,两步:
- 找到A里和B的根节点相等的点C
- 从C开始匹配
- 两个递归函数
主函数是用来找那个相等的C点,先进去check,如果不相等会进到or的下一个条件left,去left找,找不到去right找,如果找到了就会在check里递归
class Solution:def check(self, t, s):'''if s is a subtree of t'''if not s: return Trueif not t: return Falsereturn t.val==s.val and self.check(t.left,s.left) and self.check(t.right, s.right)def isSubStructure(self, A: TreeNode, B: TreeNode) -> bool:if not A or not B: return Falsereturn self.check(A,B) or self.isSubStructure(A.left, B) or self.isSubStructure(A.right, B)
572. 另一个树的子树
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/subtree-of-another-tree/
注意这一题和上一题判断条件的不同之处
这道题必须同时遍历结束才算匹配class Solution:def check(self,s,t):if not s and not t:return Trueif not s or not t:return Falseif s.val!=t.val:return Falsereturn s.val==t.val and self.check(s.left,t.left) and self.check(s.right,t.right)def isSubtree(self, s: TreeNode, t: TreeNode) -> bool:if not s or not t:return Falsereturn self.check(s,t) or self.isSubtree(s.left, t) or self.isSubtree(s.right, t)
103. 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-zigzag-level-order-traversal/
注意改变打印方向的时候,改的是往result里放的顺序,是尾插入还是头插入,而不是改变放队列里放的顺序from collections import dequeclass Solution:def zigzagLevelOrder(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[List[int]]:queue = deque()if not root:return []res = []queue.append(root)flag = Truewhile queue:level_list = deque()flag = not flagfor _ in range(len(queue)):tmp = queue.popleft()if flag:level_list.appendleft(tmp.val)else:level_list.append(tmp.val)if tmp.left:queue.append(tmp.left)if tmp.right:queue.append(tmp.right)res.append(list(level_list))return res
116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node/
层序遍历class Solution:def connect(self, root: 'Node') -> 'Node':res = rootwhile root and root.left:# 保留下一层最左边节点next = root.left# 遍历当前层,但是在给下一层节点的next赋值# 每次当前层横向遍历,从左到右while root:root.left.next = root.right# 下面这句等价于:# if root.next:# root.right.next = root.next.left# else:# root.right.next = None# OR# root.right.next = root.next.left if root.next else Noneroot.right.next = root.next and root.next.leftroot = root.nextroot = next #去到下一层最左边return res
递归 dfs
class Solution:def connect(self, root: 'Node') -> 'Node':def dfs(root):if not root.left and not root.right:returnroot.left.next = root.rightroot.right.next = root.next.left if root.next else Nonedfs(root.left)dfs(root.right)return rootif not root:return rootelif not root.left:root.next = Nonereturn rootelse:return dfs(root)
拉拉链的递归
class Solution:def connect(self, root: 'Node') -> 'Node':def dfs(root):if not root:returnleft = root.leftright = root.rightwhile left:left.next = rightleft = left.rightright = right.leftdfs(root.left)dfs(root.right)return rootreturn dfs(root)
117. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node-ii/
上一题的拓展,此时不是完全二叉树,那么下一层的第一个节点就不是每层开始的节点的left
需要更巧妙的办法来保存下一层的起始点class Solution:def connect(self, root: 'Node') -> 'Node':first = rootwhile first:head = tail = Node()cur = firstwhile cur:if cur.left:tail.next = cur.lefttail = tail.nextif cur.right:tail.next = cur.righttail = tail.nextcur = cur.nextfirst = head.nextreturn root
上面的写法看着简洁,但是理解起来不是很直观, head=tail=Node() 这种赋值方式,第一次tail.next更新时,head是跟着一起更新的,之后tail再更新,就和head的索引不一样了
def connect(self, root: 'Node') -> 'Node':first = rootwhile first:head = Nonetail = Node()cur = firstwhile cur:if cur.left:if not head:head = cur.lefttail.next = cur.lefttail = tail.nextif cur.right:if not head:head = cur.righttail.next = cur.righttail = tail.nextcur = cur.nextfirst = headreturn root
297. 二叉树的序列化与反序列化
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/serialize-and-deserialize-binary-tree/
递归,也就是dfs的序列化是按照 root,left,right三大块的顺序存储的
而迭代,也就是bfs的序列化是按照一层一层的顺序存储的
递归写法from collections import dequeclass Codec:def serialize(self, root):"""Encodes a tree to a single string.:type root: TreeNode:rtype: str"""if not root:return 'X,'leftStr = self.serialize(root.left)rightStr = self.serialize(root.right)return str(root.val) + ',' + leftStr + rightStrdef deserialize(self, data):"""Decodes your encoded data to tree.:type data: str:rtype: TreeNode"""queue = deque(data.split(","))return self.helper(queue)def helper(self,queue):cur_node = queue.popleft()if cur_node == 'X':return NonenewNode = TreeNode(cur_node)newNode.left = self.helper(queue)newNode.right = self.helper(queue)return newNode
迭代
deserialize的时候,如果弹出来的是X,那么就不用管这个child了,初始化时就是nonefrom collections import dequeclass Codec:def serialize(self, root):"""Encodes a tree to a single string.:type root: TreeNode:rtype: str"""if not root:return ''queue = deque()queue.append(root)res = ''while queue:for _ in range(len(queue)):node = queue.popleft()if not node:res +='X,'else:res +=str(node.val) + ','queue.append(node.left)queue.append(node.right)return resdef deserialize(self, data):"""Decodes your encoded data to tree.:type data: str:rtype: TreeNode"""if not data:returndata = deque(data.split(","))root = TreeNode(data.popleft())queue = deque()queue.append(root)while queue:for _ in range(len(queue)):node = queue.popleft()if data:val = data.popleft()if val!='X':node.left = TreeNode(val)queue.append(node.left)if data:val = data.popleft()if val!='X':node.right = TreeNode(val)queue.append(node.right)return root
450. 删除二叉搜索树中的节点
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/delete-node-in-a-bst/
这道题一开始困惑的地方在于,如果是链表的删除,那么是用这个点之前的点指向这个点next的点。用这样的思路解决这道题会发现找不到当前节点的父节点,所以不能按照链表的思路去修改指针,而要去修改的是节点的值,让值修改完之后保持BST的特性就可以了,那么关键就在于这个值用哪个值,根据节点不同的情况,选择直接删除或者前驱或者后继根据当前root.val和key的大小判断决定取左边删还是右边删,记得递归函数返回的是删除掉目标节点后的子树,所以最后是返回了root,所以取哪边找要重新复制给那个方向left or right
- 如果是叶子节点最简单,直接删除,注意删除操作是置为None
- 如果right存在,说明是有后继的,不管left有没有,因为即便left有,也要把right那边的最小值拿过来。所以如果right存在,就去right找right子树的最小值,也就是当前子树的后继, 从当前子树的right一直找左子树找到最后一个
如果没有right,有left,那么就去拿当前节点的前驱,用前驱的值覆盖,然后删除前驱
class Solution:def successor(self, root):root = root.rightwhile root.left:root = root.leftreturn root.valdef predecessor(self, root):root = root.leftwhile root.right:root = root.rightreturn root.valdef deleteNode(self, root: TreeNode, key: int) -> TreeNode:if not root:returnif root.val > key:# search in left subtreeroot.left = self.deleteNode(root.left, key)elif root.val < key:root.right = self.deleteNode(root.right, key)else:#如果是叶子节点,直接删除if not root.left and not root.right:root = None#如果有右子树elif root.right:root.val = self.successor(root)root.right = self.deleteNode(root.right, root.val)else:root.val = self.predecessor(root)root.left = self.deleteNode(root.left, root.val)return root
863. 二叉树中所有距离为 K 的结点
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/all-nodes-distance-k-in-binary-tree/
可以添加父节点指针的例子

