引言
使用反射API可以获取在运行期间仍然被保留的注解信息进而拿到了注解元素的值,java将获取注解的功能融合在反射机制中,通过简单的API调用,我们就能够发挥注解的强大能力。这篇文章,我们来看这种融合是怎样做到的。
getAnnotation方法在哪里定义
在使用注解处理器来处理注解这篇文章中,我们通过调用Method类的getAnnotation方法获取了方法上的注解,Method为什么有这个方法呢?我们来看Method的定义:
public final class Method extends Executable {}
它继承了Executable这个抽象类,Executable类的声明:
/*** A shared superclass for the common functionality of {@link Method}* and {@link Constructor}.** @since 1.8*/public abstract class Executable extends AccessibleObjectimplements Member, GenericDeclaration {}
Executable是Method和Constructor的公共父类,它继承了AccessibleObject类,实现了Member和GenericDeclaration,我们主要来看AccessibleObject:
public class AccessibleObject implements AnnotatedElement {}
它实现了AnnotatedElement接口,而AnnotatedElement接口就是我们要找的getAnnotation方法的来源。
下面,我们就来详细分析一下这个接口。
详解AnnotatedElement
根据注释,AnnotatedElement代表在当前运行的java虚拟机中一个可以被注解的元素,这个接口允许通过反射读取元素上面的注解,这与我们之前的理解是一致的。
AnnotatedElement提供了7个方法: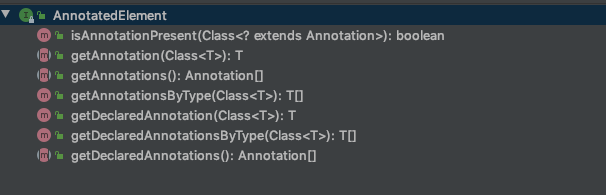
这几个方法可以分为三类,第一类就是isAnnotationPresent()方法,第二类就是 getAnnotationXXX方法,第三类就是getDeclaredAnnotationXXX方法。
四个限定词
在分析这几个方法之前我们先给定四个限定词:directly present、indrectly present、present和associated。必须注意这四个限定词存在的前提是注解是运行时被保留的注解,也就是我们这里讨论的注解,@Retention的取值都是RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME。这四个限定词的含义如下:
如果一个注解A是直接添加(声明)在一个元素E上面的,那么这个注解A就是directly present在这个元素上。
如果一个注解A是可重复(repetable)的,并且另外一个注解A1直接出现在元素E上,并且A1是A的包含注解类型,那么注解A就是indrectly present在元素E上。
present有两种情况:
- 注解A是directly present在元素E上。
- 元素E是一个类,并且注解A不是directly present在元素E上,并且A是可以继承(inheritable)的,并且A是present在E的父类上。
associated有两种情况:
- 注解A是directly或者indirectly present在元素E上。
- 上面的判断为false,并且E是一个类,并且注解A是可以继承(inheritable)的,并且A是associated 在E的父类上。
可以看出,Directly present是范围最小的,只能是元素上显式声明的注解,Indirectly present针对可重复注解和包含注解类型的情况,present在Directly present基础上增加了继承的情况,associated在Directly present和Indirectly的基础上增加了继承的情况。
实际上AnnotatedElement中的方法都是根据这些限定词来返回注解的,也就是说,不同的方法可能返回不同限定词指定的注解。下面我们来将方法与限定词一一对应起来。
限定词与方法的对应
下面这个表格总结了AnnotatedElement不同方法返回的注解的present情况:
| 方法 | Directly Present | Indirectly Present | Present | Associated |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T getAnnotation(Class |
✅ | |||
| Annotation[] getAnnotations | ✅ | |||
| T[] getAnnotationsByType(Class |
✅ | |||
| T getDeclaredAnnotation(Class |
✅ | |||
| T[] getDeclaredAnnotationsByType(Class |
✅ | ✅ | ||
| Annotation[] getDeclaredAnnotations() | ✅ |
所以,如果我们只想获取Directly Present的注解,就使用getDeclaredAnnotations和getDeclaredAnnotation这两个方法,如果也想获取Indirectly Present也就是没有直接声明在元素上的可重复注解,就使用getDeclaredAnnotationsByType,如果想获取直接声明的加上继承的注解,就使用getAnnotation或者getAnnotations方法,如果想获取所有这些情况下的注解,就使用getDeclaredAnnotation方法。
我们将这几个方法分类并分别举例来演示。
示例
首先,getDeclaredAnnotation(Class
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Target(ElementType.TYPE)public @interface DirectlyPresent {int id() ;String description() default "this is a common description";}@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME )@Target(ElementType.TYPE)@Repeatable(IndirectlyPresent.class)public @interface IndirectlyPresentValue {String name();}@Target(ElementType.TYPE)@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)public @interface IndirectlyPresent {IndirectlyPresentValue[] value();}@Target(ElementType.TYPE)@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Inheritedpublic @interface InheritablePresent {}@InheritablePresent()public class ParentPresentElement {}@DirectlyPresent(id=2,description = "this is a DirectlyPresentElement")@IndirectlyPresent({@IndirectlyPresentValue(name = "firstName")})public class PresentElement extends ParentPresentElement {public static void main(String[] args) {Class<PresentElement> directlyPresentElementClass = PresentElement.class;DirectlyPresent annotation = directlyPresentElementClass.getDeclaredAnnotation(DirectlyPresent.class);System.out.println(annotation.description());System.out.println(annotation.id());}}
输出结果为:
Directly Present的注解有:@person.andy.concurrency.annotation.annotetedelements.DirectlyPresent(description=this is a DirectlyPresentElement, id=2)@person.andy.concurrency.annotation.annotetedelements.IndirectlyPresent(value=[@person.andy.concurrency.annotation.annotetedelements.IndirectlyPresentValue(name=firstName)])Indirectly Present的注解有:[@person.andy.concurrency.annotation.annotetedelements.IndirectlyPresentValue(name=firstName)][][@person.andy.concurrency.annotation.annotetedelements.DirectlyPresent(description=this is a DirectlyPresentElement, id=2)]Present注解有:@person.andy.concurrency.annotation.annotetedelements.InheritablePresent()@person.andy.concurrency.annotation.annotetedelements.DirectlyPresent(description=this is a DirectlyPresentElement, id=2)@person.andy.concurrency.annotation.annotetedelements.IndirectlyPresent(value=[@person.andy.concurrency.annotation.annotetedelements.IndirectlyPresentValue(name=firstName)])Associated注解有:[@person.andy.concurrency.annotation.annotetedelements.IndirectlyPresentValue(name=firstName)]
小结
这篇文章,我们主要学习了AnnotationElement这个接口以及它与注解相关的限定词和概念,这个接口在很多地方例如Class、Method、Field等都有用到,在学习反射的时候,我们还会看到它的身影。

