Files类专门的静态方法用来操作文件、目录等。通过Files,我们可以删除、创建、复制、移动文件,能够创建针对文件的InputStream、OutputStream、BufferedReader、BufferedWriter、channel等。
创建InputStream、BufferedReader、Channel
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {Path path = Paths.get("/Users", "cuihualong", "Desktop", "monitor.sql");InputStream inputStream = Files.newInputStream(path, StandardOpenOption.READ);BufferedReader bufferedReader = Files.newBufferedReader(path);SeekableByteChannel seekableByteChannel = Files.newByteChannel(path, StandardOpenOption.READ);}
创建OutputStream、BufferedWriter与InputStream、BufferedReader基本类似,这里就不罗列了。
读取文件
Files提供了三个方法用于读取整个文件,可以读取为字节数组和String列表: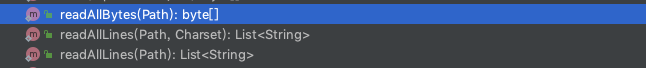
读取整个文件到字节数组
第一个方法readAllBytes用来读取整个文件的内容到一个字节数组。想想一下之前我们要想使用InputStream来读取整个文件到一个字节数组,需要循环读取,现在有了这个方法就简单多了,它的实现如下:
public static byte[] readAllBytes(Path path) throws IOException {try (SeekableByteChannel sbc = Files.newByteChannel(path);InputStream in = Channels.newInputStream(sbc)) {long size = sbc.size();if (size > (long)MAX_BUFFER_SIZE)throw new OutOfMemoryError("Required array size too large");return read(in, (int)size);}}
它首先获取了channel,然后通过Channels工具类将Channel映射为流,然后通过流来读取。
读取整个文件到List
public static List<String> readAllLines(Path path, Charset cs) throws IOException {try (BufferedReader reader = newBufferedReader(path, cs)) {List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();for (;;) {String line = reader.readLine();if (line == null)break;result.add(line);}return result;}}
这个方法接收一个Path和一个字符集,它是通过BufferedReader来实现的。方式就是在循环中取调用BufferedReader的readLine方法。
写入文件
对于写入文件,Files同样提供了三个方法: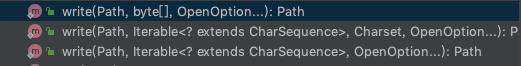
我们来重点看第一个:
public static Path write(Path path, byte[] bytes, OpenOption... options)throws IOException{// ensure bytes is not null before opening fileObjects.requireNonNull(bytes);try (OutputStream out = Files.newOutputStream(path, options)) {int len = bytes.length;int rem = len;while (rem > 0) {int n = Math.min(rem, BUFFER_SIZE);out.write(bytes, (len-rem), n);rem -= n;}}return path;}
复制、删除、移动文件
copy方法可以复制文件,它接收三个参数,前两个都是Path,表示源文件Path和目标文件Path,第三个是复制的选项。
public static Path copy(Path source, Path target, CopyOption... options)throws IOException{FileSystemProvider provider = provider(source);if (provider(target) == provider) {// same providerprovider.copy(source, target, options);} else {// different providersCopyMoveHelper.copyToForeignTarget(source, target, options);}return target;}
move方法用来移动文件,它和copy一样,也接收三个参数,并且含义一致。
public static Path move(Path source, Path target, CopyOption... options)throws IOException{FileSystemProvider provider = provider(source);if (provider(target) == provider) {// same providerprovider.move(source, target, options);} else {// different providersCopyMoveHelper.moveToForeignTarget(source, target, options);}return target;}
delete方法用来删除文件,它只需要一个参数,即代表文件的Path。
public static void delete(Path path) throws IOException {provider(path).delete(path);}
除了上面这些方法,files还有很多其他实用的方法,这里我就不多介绍了。

