引言
除了Synchronized和Volatile关键字,Java还提供了Lock显式锁来实现线程之间对共享资源的同步访问。这个系列,我们来研究Java中提供的各种锁。
Lock接口
Java提供的显式锁都在java.util.concurrent.locks包下面,其中Lock接口提供了所有显式锁必需的方法,例如lock()、tryLock()等。我们重点看一下这几个方法的含义。
Lock()方法
lock方法用来获取锁,获取到锁之后就能从lock方法返回并继续执行。我们重点看一下没有获取锁的线程的状态:
public class LockTest {Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();private void testLock(){lock.lock();System.out.println("我是线程"+Thread.currentThread());try {Thread.sleep(30000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}lock.unlock();}public static void main(String[] args) {LockTest lockTest = new LockTest();Thread thread1 = new Thread(lockTest::testLock,"thread1");Thread thread2 = new Thread(lockTest::testLock,"thread2");thread1.start();thread2.start();}}
这个例子中,thread1和thread2竞争锁,获取锁之后,持有锁的线程会sleep 30秒的时间,我们来看没有获得锁的线程的状态: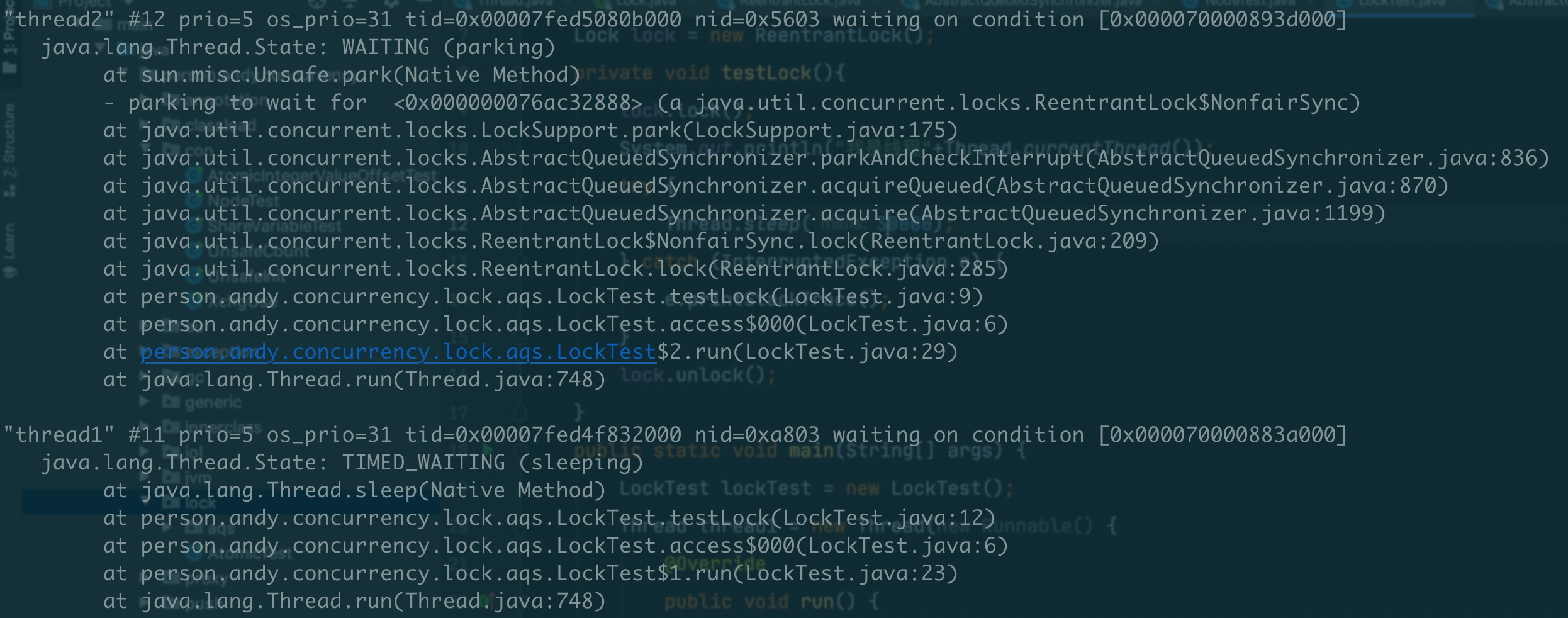
thread2没有获取到锁,状态是WAITING,注意不是阻塞状态。
lockInterruptibly()方法
void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException;
这个方法与lock方法不同的是它可以响应中断,如果一个线程在使用lockInterruptibly()方法获取锁的过程中被其他线程调用了Thread.interrupt()方法进行了中断,就会抛出InteruptedException异常,同时锁会被释放。注意是获取锁的过程中,如果该线程已经获取了锁在执行其他逻辑,就不会响应中断。看下面的例子:
public class LockTest {Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();private void testLock(){try {lock.lockInterruptibly();} catch (InterruptedException e) {System.out.println("获取锁的线程被中断了");e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("我是线程"+Thread.currentThread());while (true){}}public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {LockTest lockTest = new LockTest();Thread thread1 = new Thread(lockTest::testLock,"thread1");Thread thread2 = new Thread(lockTest::testLock,"thread2");thread1.start();Thread.sleep(3000);thread2.start();thread1.interrupt();thread2.interrupt();}}
main线程对线程1和线程2都进行了中断,但是中断时线程1已经获取到了锁而线程2正在等待锁,所以线程2会抛出InterruptedException异常而线程1没有影响,运行结果如下:
我是线程Thread[thread1,5,main]线程Thread[thread2,5,main]被中断了我是线程Thread[thread2,5,main]java.lang.InterruptedExceptionat java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.acquireInterruptibly(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.java:1220)at java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock.lockInterruptibly(ReentrantLock.java:335)at person.andy.concurrency.lock.aqs.LockTest.testLock(LockTest.java:10)at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748)
tryLock()方法
上面说的两个方法会一直尝试获取锁知道成功为止,所以没有返回值。而tryLock()方法则不同,如果锁可用就获取锁并返回true,否则直接返回false,这样,就能非阻塞地获取锁。
一个经典的使用tryLock()方法的模式如下:
public class LockTest {Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();private void testLock() {if(lock.tryLock()){System.out.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread()+"获取到了锁");try {Thread.sleep(3000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}finally {lock.unlock();}}else {System.out.println("线程"+Thread.currentThread()+"没有获取到锁");}}public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {LockTest lockTest = new LockTest();Thread thread1 = new Thread(lockTest::testLock,"thread1");Thread thread2 = new Thread(lockTest::testLock,"thread2");thread1.start();Thread.sleep(1000);thread2.start();}}
输出如下:
线程Thread[thread1,5,main]获取到了锁线程Thread[thread2,5,main]没有获取到锁
也就是在获取成功的情况下需要释放锁,没有获取成功就不需要进行锁的释放操作。
tryLock(long time,TimeUnit unit)方法
boolean tryLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException;
这个方法与tryLock()不同的是,它的获取锁的操作增加了时间范围,如果在参数指定的时间内获取到了锁,就返回true,没有获取到锁就返回false,这个方法同样也能响应中断。这里不再举例展示。
unLock()方法
这个方法用来释放锁。一般来说,只有持有锁的线程才能执行释放锁的操作。在上面的几个方法中,lock()、lockInterruptibly()都能正常获取到锁,所以要加unlock操作,tryLock()和tryLockInterruptibly()在返回true的情况下需要加unlock操作。
Lock接口还有一个newCondition()方法,这里我们先不介绍。
上面说的这几个就是Lock接口的重要方法,接下来,我们来看它的一个重要实现类:可重入锁ReentrantLock。

