A:Material nonpublic information
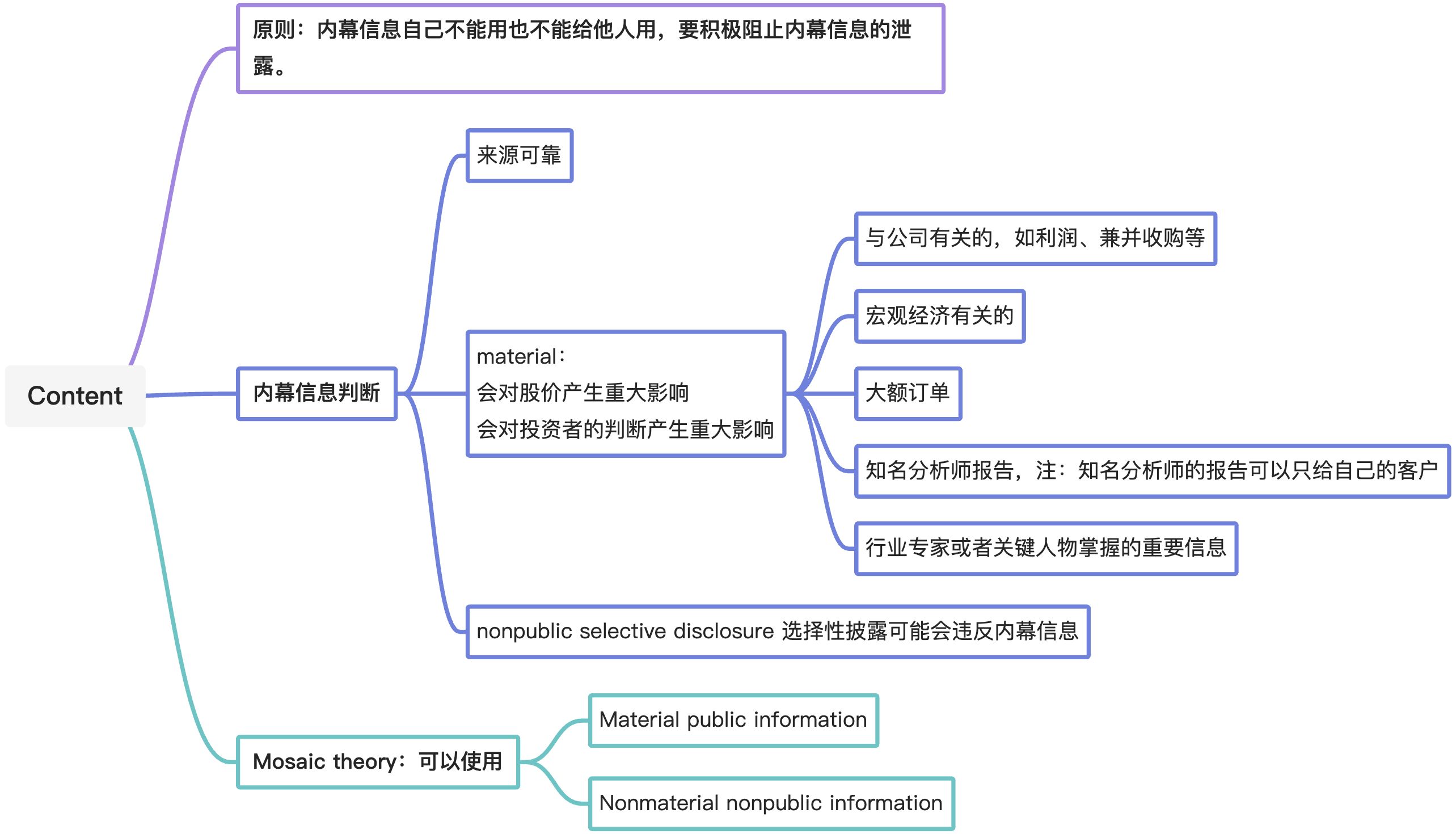
Members and Candidates who possess material nonpublic information that could affect the value of an investment must not act or cause others to act on the information.
(1)Guidance
Trading or inducing others to trade on material nonpublic information will cause investors to avoid capital markets because the markets are perceived to be “rigged” in favor of the knowledgeable insider.
Must not use such information to:
Material Nonpublic
- Information is “material” if its disclosure would likely have an impact on the price of a security or if reasonable investors would want to know the information before making an investment decision.
- Information is “nonpublic” until it has been disseminated or is available to the marketplace in general.

Substance and specificity([ˌspesɪˈfɪsəti] 独特性; 具体性; 明确性)determines the materiality
- Company-related information
- Earnings
- Mergers, acquisitions, tender offers, or joint ventures
- Changes in assets or asset quality
- Innovations products, processes, or discoveries
- New licenses, patents, registered trademarks, or regulatory approval/rejection of a product
- Developments regarding customers or suppliers (e.g.:the acquisition or loss of a contract)
- Changes in management
- Changes in auditor notification or the fact that the issuer may no longer rely on an auditor’s report or qualified opinion
- Events regarding the issuer’s securities
- Bankruptcies
- Significant legal disputes
- New or changing equity or debt rating issued by third party
- Macro-economy
- Government reports of economic trends (employment, housing starts, currency information, etc.)
- Large orders
- Orders for large trades before they are executed
- Well known analyst
- Reports from well known analyst
- Qualified personnel
- Information about trials of a new drug, product, or service under development from qualified personnel involved in the trials is likely to be material, whereas educated conjecture(猜想; 推测; 猜测; 臆测; 揣测) by subject experts not connected to the trials is unlikely to be material.
- Competitors
- Company-related information
Information is “nonpublic” until it has been disseminated or is available to the marketplace.
- Not necessary to wait for the slowest method of delivery.
- Once the information is disseminated to the market, it is public information that is no longer covered by this standard.
Selective disclosure
- Disclosure to a room full of analysts does not necessarily make the disclosed information “public”.
- Analysts should also be alert to the possibility that they are selectively receiving MNI when a company provides them with guidance or interpretation of financial statements or regulatory filings.
(c)When can use “nonpublic” Information?
A member or candidate may use insider information provided legitimately by the source company for the specific purpose of conducting due diligence according to the business agreement between the parties for such activities as mergers, loan underwriting, credit ratings, and offering engagements.
(d)Mosaic Theory

May use conclusions from the analysis of material public and nonmaterial nonpublic information even if those conclusions would have been material inside information had they been communicated directly to the analyst by a company.
- A perceptive analyst reaches a conclusion about a corporate action or event through an analysis of public information and items of nonmaterial nonpublic information.(not violate 2-A)
- perceptive:知觉的; 感觉的; 视觉的; 感性的; 听觉的; 有洞察力的; 理解力强的; 思维敏捷的
- Should save and document all the research when applying mosaic theory —> Standard 5-C.
- A perceptive analyst reaches a conclusion about a corporate action or event through an analysis of public information and items of nonmaterial nonpublic information.(not violate 2-A)
- 马赛克不是一种理论,而是一种理由。
- 如果你作为一名基金经理,跟某巨头公司的 CEO 是好哥们,该 CEO 告诉你他们明天准备以 50 元一股的价格发起一场对 XX 公司的收购,然后你马上以 30 元的价格大量买进了 XX 公司的股票,这就是妥妥的内幕交易,是违反 CFA 道德准则的行为。因为你是凭借一条既重大又来源可靠的内部信息做出的行动。注意这三个条件:既重大又可靠且非公开。
- 而另一个情形下,你还是作为一名基金经理,在某夜总会里正好碰到某巨头公司老板的儿子(一个知名花花公子富二代)在跟美女们吹嘘自己家的公司马上要花 20 个亿收购一家上市公司。但哪家公司、什么时候、什么价格富二代完全没透露。于是你从夜总会出来后立刻找到了自己在这家巨头公司里打印室的发小,发小说最近战略投资部的人经常在打印有一个缩写是 XX 的公司的材料,但具体哪家公司他不知道。这时你开始搜索公开资料,发现巨头公司的老板上个月正好在某个公开演讲中提到他们有意向布局直播行业,而直播行业里最火热的公司恰好缩写就是 XX 公司。于是你如获至宝开始研究 XX 公司的财务状况、商业模式,分析它和巨头公司潜在的 synergy,越看越觉得 XX 公司就是巨头公司将要收购的目标,而且根据富二代说到的20 亿元的信息,你判断出收购的目标价格是 50 元,于是你很快以 30 元的价格大量买入了 XX 公司的股票。
第二个情形并没有违反 CFA 的内幕交易规定,因为你并不是根据任何一个既重大又可靠且非公开的信息做出的判断。而是通过拼凑两条并不可靠的内部信息和两条可靠的公开信息才得出了结论。这就是所谓的马赛克方式。
(e)Social Media
It is important for investment professionals to understand the implications of using information from the internet and social media platforms because all such information may not actually be considered public.
- Members and candidates participating in groups with membership limitations should verify that material information obtained from these sources can also be accessed from a source that would be considered available to the public (e.g.:company filings, webpages, and press releases).
- As long as the information reaches all clients or is open to the investing public, the use of these platforms would be comparable with other traditional forms of communications, such as e-mails and press releases. Members and candidates, as required by Standard 1-A, should also complete all appropriate regulatory filings related to information distributed through social media platforms.
(f)Using industry expert
Members and candidates may provide compensation to individuals for their insights without violating this standard. However, members and candidates are ultimately responsible for ensuring the information they receive does not constitute material nonpublic information.
- members and candidates would be prohibited from taking investment actions on the associated firm until the information became publicly known to the market
- Firms connecting experts with members or candidates often require both parties to sign agreements concerning the disclosure of material nonpublic information.
(g)Investment Research Reports
When a well-known or respected analyst issues a report or makes changes to his or her recommendation, that information alone may have an effect on the market and thus may be considered material. Such a report would have to be made public before it was distributed to clients. The analyst’s hard work, paid for by the client, generated the conclusions.
- Simply because the public in general find the conclusions material does not require that the analyst make his/her work public.
Investors who are not clients of the analyst can either do the work themselves or become clients of the analyst for access to the analyst’s expertise.
(2)Recommended Procedures for compliance
Achieve public dissemination
- Adopt compliance procedures
- Adopt disclosure procedures
- Issue press releases
- Firewall elements
- Appropriate interdepartmental communications
- Physical separation of departments
- Prevention of personnel overlap
- A reporting system
- Personal trading limitations
- Record maintenance
- Proprietary trading procedures (自营业务)
Communication to all employees
(a)A reporting system
Primary objective of effective firewall procedure:
- establish a reporting system in which authorized people review and approve communications between departments
- Inter-department communication:
- should consult a designated compliance officer to determine whether sharing the information is necessary and how much to be shared.
- If sharing is necessary, the compliance officer should coordinate the process of “looking over the wall” so that the necessary information will be shared and the integrity of the procedure will be maintained.
- A single supervisor or compliance officer should decide whether or not information is material and whether it is sufficiently public to be used as the basis for investment decisions.
Ideally, the supervisor or compliance officer responsible for communicating information to a firm’s research or brokerage area would not be a member of that area. (independent)
(b)Personal trading limitations
Firms should consider restrictions or prohibitions on personal trading and should carefully monitor proprietary trading.
- proprietary:
- adj. 专有的; 专利的; 所有的; 所有权的; 专卖的; 专营的
- n. 所有权; 所有人; 所有物; 专卖药品; 独家制造(及销售)的产品
- proprietary:
- Should require employees to make periodic reports (to the extent that such reporting is not already required by securities laws) of their own transactions and transactions made for the benefit of family members.
Securities should be placed on a restricted list when a firm has or may have MNI. The broad distribution of a restricted list often triggers the sort of trading the list was developed to avoid.
Multi-service firms should maintain written records of the communications between various departments. Firms should place a high priority on training and consider instituting comprehensive training programs, particularly for employees in sensitive areas.
(d)Proprietary trading procedures(自营业务)
Monitor and restrict proprietary trading when holding MNI
Prohibition on all proprietary activity when owning MNI is not appropriate. —> depend on the types of proprietary trading.
- Market maker in possession of MNI, withdrawal from market making will be a clear tip to market. Remain passive to market (take only contra side of unsolicited customer’s trades).
- Risk-arbitrage trading:Best to stop; If not stop, prove the adequacy of their internal procedures, and must demonstrate stringent(严格的; 严厉的) review and documentation of firm trades.
B:Market manipulation

Must not engage in practices that:
- distort prices or artificially inflate trading volume
- with the intent to mislead market participants
- Market manipulation includes:
- Info-based:Dissemination of false or misleading information
- Pump up prices by issuing misleading positive info, then dump.
- Transaction-based:Members or candidates knew or should have known that transactions deceive(欺骗、误导)or would be likely to mislead market participants by distorting the price-setting mechanism. It includes:
- Info-based:Dissemination of false or misleading information
The intent of the action is critical to determining whether it is a violation
- Not prohibit legitimate trading strategies that exploit a diff in market power, info, or other inefficiency.
- Not prohibit trade for tax purposes, selling then buying back.
- To increase liquidity, Futures Exchange made agreements with members to insure the minimum trading volume in exchange for reduction of commission. —> If for the interest of clients and disclosed, not violate.

