包装类
概述
为了对基本数据类型进行更多更方便的操作,Java就针对每一种基本数据类型提供了对应的包装类类型
将基本数据类型封装成对象的好处在于可以在对象中定义更多的功能方法操作该数据
基本类型和包装类的对应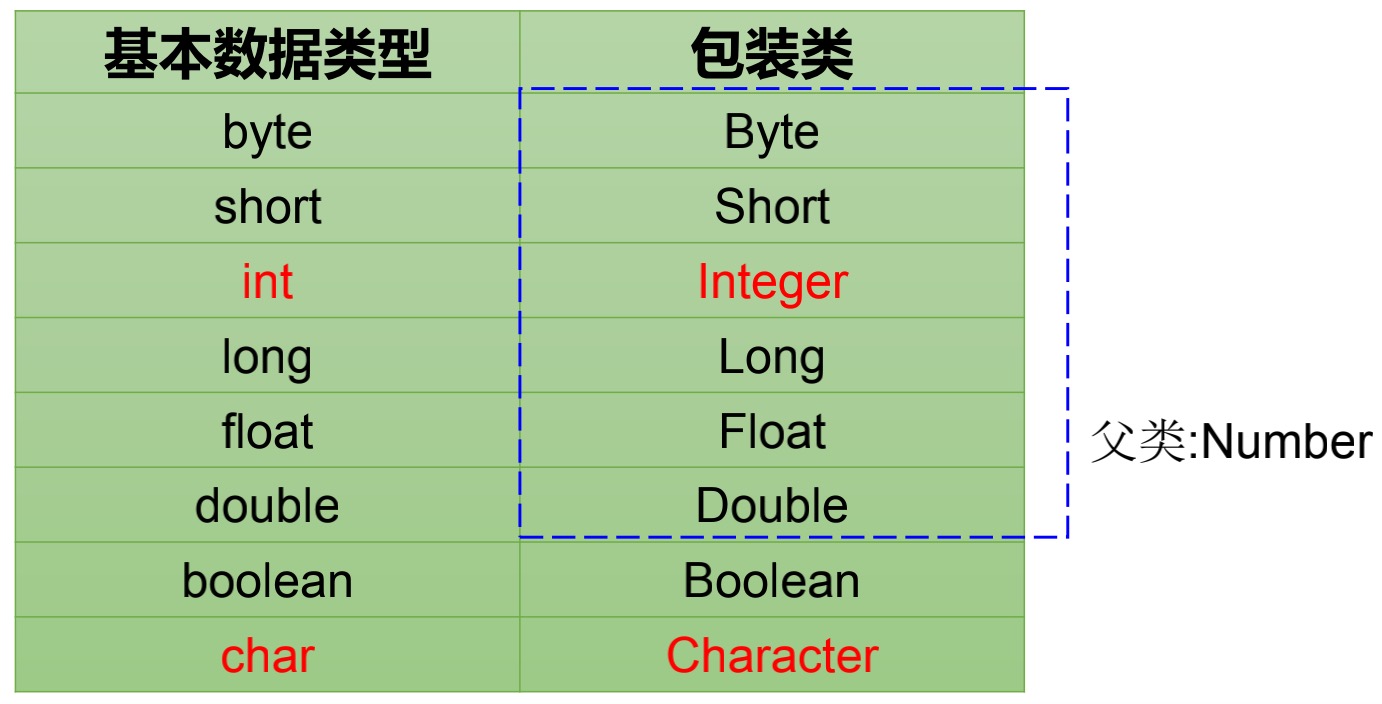
以Integer类例
构造方法**public Integer(int value)**将int型转化为Integer对象**public Integer(String s)**将String型转化为Integer对象
成员方法
int——Integer |
**public int intValue()**| 将Integer转成int | | —- | —- | |**public static Integer valueOf(int i)**
public Integer(int value) | 将int转成Integer | | 直接自动装箱拆箱 | |int——String |
**public static int parseInt(String s)**| 将String转成int | | —- | —- | |**public static String valueOf(int i)****public static String toString(int i)**
String s = “” + i |
将int转成十进制String |- Integer——String
|
**public String valueOf(Integer i)**String的方法**public static String toString(Integer i)****public String toString()**|
将Ingeger转成String | | —- | —- | |**public static Integer valueOf(String s)****public static int parseInt(String s)**| 将String转成Integer |
- Integer——String
|
综上(int Integer)与String相互转换用 valueOf(),一个String的一个Integer的
- 基本进制转换
public static String toBinaryString(int i)public static String toOctalString(int i)public static String toHexString(int i)public static String toString(int i, int radix)
- 十进制到其他进制
**public static int parseInt(String s, int radix)**
- 其他进制到十进制
(int Integer)与String转换用 valueOf()
自动装箱和拆箱
自动装箱:把基本类型转换为包装类型
自动拆箱:把包装类类型转换为基本类型
JDK1.5以后, 简化了定义方式
- Integer x = new Integer(4);可以直接写成
- Integer x = 4; 自动装箱
- x = x + 5; 自动拆箱。通过intValue方法
- 在使用时,Integer x = null;上面的代码就会出现NullPointerException
- 建议先判断是否为null,然后再使用
例题
```java @Test public void test1() { Object o1 = true ?new Integer(1) :new Double(2.0); //冒号前后会转成相同类型 System.out.println(o1); // 1.0 }
@Test public void test2() { Object o2; if (true) o2 = new Integer(1); else o2 = new Double(2.0); System.out.println(o2); // 1 }
@Test public void test3() { Integer i = new Integer(1); Integer j = new Integer(1); System.out.println(i == j); //false // Integer内部定义了IntegerCache 结构,IntegerCache 中定义了Integer[], // 保存了从-128~127范围的整数。如果我们使用自动装箱的方式,给Integer赋值的范围在 // -128~127范围内时,可以直接使用数组中的元素,不用再去new了。目的:提高效率 Integer m = 1; Integer n = 1; System.out.println(m == n); //true
Integer x = 128; //相当于new了一个Integer对象Integer y = 128; //相当于new了一个Integer对象System.out.println(x == y); //false
}
<a name="6qYW0"></a>### Character类Character 类在对象中包装一个基本类型 char 的值<br />该类提供了几种方法,以确定字符的类别(小写字母 数字 等等),并将字符从大写转换成小写,反之亦然<br />构造方法<br />`**Character(char value)**`<br />常用方法<br />`**public static boolean isUpperCase(char ch)**`判断给定的字符是否是大写字符<br />`**public static boolean isLowerCase(char ch)**`判断给定的字符是否是小写字符<br />`**public static boolean isDigit(char ch)**`判断给定的字符是否是数字字符<br />`**public static char toUpperCase(char ch)**`把给定的字符转换为大写字符<br />`**public static char toLowerCase(char ch)**`把给定的字符转换为小写字符---<a name="ejaKa"></a>## BigIntegerjava.math包的 BigInteger 可以表示不可变的任意精度的整数<br />BigInteger 提供所有Java的基本整数操作符的对应物,并提供 java.lang.Math 的所有相关方法<br />另外BigInteger还提供以下运算:模算术、GCD计算、质数测试、素数生成、位操作以及一些其他操作<br />构造器<br />`**BigInteger(String val)**`根据字符串构建 BigInteger对象<br />方法<br />`**public BigInteger abs()**`<br />`**BigInteger add(BigInteger val)**`<br />`**BigInteger subtract(BigInteger val)**`<br />`**BigInteger multiply(BigInteger val)**`<br />`**BigInteger divide(BigInteger val)**`<br />`**BigInteger remainder(BigInteger val)**`<br />`**BigInteger[] divideAndRemainder(BigInteger val)**`返回商和余数的两个BigInteger数组<br />`**BigInteger pow(int exponent)**`返回其值为 (thisexponent)的BigInteger---<a name="KmPRb"></a>## BigDecimal要求数字精度比较高,用到java.math.BigDecimal类<br />BigDecimal类支持不可变的、任意精度的有符号十进制定点数<br />**构造器**<br />`**public BigDecimal(double val)**`<br />`**public BigDecimal(String val)**`<br />**常用方法**<br />`**public BigDecimal add(BigDecimal augend)**`<br />`**public BigDecimal subtract(BigDecimal subtrahend)**`<br />`**public BigDecimal multiply(BigDecimal multiplicand)**`<br />`**public BigDecimal divide(BigDecimal divisor, int scale, int rounding Mode)**````javaBigInteger bi = new BigInteger("1243324112234324324325235245346567657653");BigDecimal bd = new BigDecimal("12435.351");BigDecimal bd2 = new BigDecimal("11");System.out.println(bi);//System.out.println(bd.divide(bd2)); // 报错System.out.println(bd.divide(bd2, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP));System.out.println(bd.divide(bd2, 25, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP));

