12 线程池
12.1 线程池介绍
第四种获取线程的方法:线程池。线程池提供了一个线程队列,队列中保存着所有等待状态的线程。避免了创建与销毁额外开销,提高了响应的速度。通常使用 Executors 工厂方法配置
线程池可以解决两个不同问题:由于减少了每个任务调用的开销,它们通常可以在执行大量异步任务时提供增强的性能,并且还可以提供绑定和管理资源(包括执行任务集时使用的线程)的方法
12.2 线程池的体系结构
java.util.concurrent.Executor : 负责线程的使用与调度的根接口|--ExecutorService 子接口: 线程池的主要接口|--ThreadPoolExecutor 线程池的实现类|--ScheduledExecutorService 子接口:负责线程的调度|--ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor:继承ThreadPoolExecutor,实现ScheduledExecutorService
12.3 工具类 : Executors
为了便于跨大量上下文使用,此类提供了很多可调整的参数和扩展钩子 (hook)。但是,强烈建议程序员使用较为方便的 Executors 工厂方法 **ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool()**创建固定大小的线程池**ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool()**缓存线程池,线程池的数量不固定,可以根据需求自动的更改数量**ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor()**创建单个线程池。线程池中只有一个线程**ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool()**创建固定大小的线程,可以延迟或定时的执行任务
public class TestThreadPool {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {// 1. 创建线程池ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);List<Future<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {Future<Integer> future = pool.submit(new Callable<Integer>() {@Overridepublic Integer call() throws Exception {int sum = 0;for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {sum += i;}return sum;}});list.add(future);}pool.shutdown();for (Future<Integer> future : list) {System.out.println(future.get());}// ThreadPoolDemo tpd = new ThreadPoolDemo();// // 2. 为线程池中的线程分配任务// for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {// pool.submit(tpd);// }// // 3. 关闭线程池// pool.shutdown();}}class ThreadPoolDemo implements Runnable {private int i = 0;@Overridepublic void run() {while (i <= 100) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " : " + i++);}}}
12.4 线程调度
ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool() 创建固定大小的线程,可以延迟或定时的执行任务
public class TestScheduledThreadPool {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {ScheduledExecutorService pool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(5);for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {Future<Integer> result = pool.schedule(new Callable<Integer>() {@Overridepublic Integer call() throws Exception {int num = new Random().nextInt(100); // 生成随机数System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " : " + num);return num;}}, 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 延迟线程,延迟时间,时间单位System.out.println(result.get());}pool.shutdown(); // 关闭线程池}}
13 ForkJoinPool 分支/合并框架 工作窃取
13.1 Fork/Join 框架
Fork/Join 框架:就是在必要的情况下,将一个大任务,进行拆分(fork)成 若干个小任务(拆到不可再拆时),再将一个个的小任务运算的结果进 行 join 汇总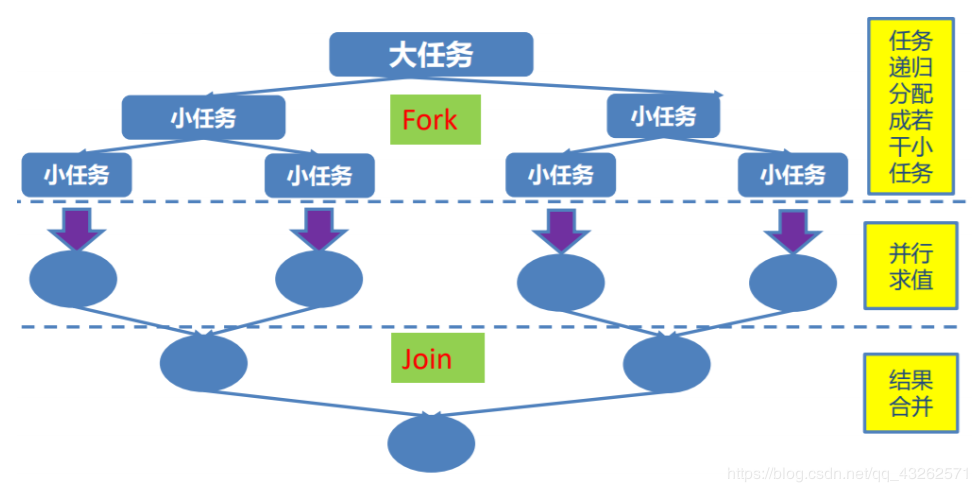
13.2 Fork/Join 框架与线程池的区别
采用 “工作窃取”模式(work-stealing)
当执行新的任务时它可以将其拆分分成更小的任务执行,并将小任务加到线程队列中,然后再从一个随机线程的队列中偷一个并把它放在自己的队列中
相对于一般的线程池实现,fork/join框架的优势体现在对其中包含的任务的处理方式上。在一般的线程池中,如果一个线程正在执行的任务由于某些原因无法继续运行,那么该线程会处于等待状态。而在fork/join框架实现中, 如果某个子问题由于等待另外一个子问题的完成而无法继续运行。那么处理该子问题的线程会主动寻找其他尚未运行的子问题来执行。这种方式减少了 线程的等待时间,提高了性能
public class TestForkJoinPool {public static void main(String[] args) {Instant start = Instant.now();ForkJoinPool pool = new ForkJoinPool();ForkJoinTask<Long> task = new ForkJoinSumCalculate(0L, 5000000000L);Long sum = pool.invoke(task);System.out.println(sum);Instant end = Instant.now();System.out.println("耗费时间为:" + Duration.between(start, end).toMillis());//2709 拆分也需要时间}@Testpublic void test1(){Instant start = Instant.now();long sum = 0L;for (long i = 0L; i <= 5000000000L; i++) {sum += i;}System.out.println(sum);Instant end = Instant.now();System.out.println("for耗费时间为:" + Duration.between(start, end).toMillis());//2057}//java8 新特性@Testpublic void test2(){Instant start = Instant.now();Long sum = LongStream.rangeClosed(0L, 5000000000L).parallel().reduce(0L, Long::sum);System.out.println(sum);Instant end = Instant.now();System.out.println("java8 新特性耗费时间为:" + Duration.between(start, end).toMillis());//1607}}class ForkJoinSumCalculate extends RecursiveTask<Long>{/****/private static final long serialVersionUID = -259195479995561737L;private long start;private long end;private static final long THURSHOLD = 10000L; //临界值public ForkJoinSumCalculate(long start, long end) {this.start = start;this.end = end;}@Overrideprotected Long compute() {long length = end - start;if(length <= THURSHOLD){long sum = 0L;for (long i = start; i <= end; i++) {sum += i;}return sum;}else{long middle = (start + end) / 2;ForkJoinSumCalculate left = new ForkJoinSumCalculate(start, middle);left.fork(); //进行拆分,同时压入线程队列ForkJoinSumCalculate right = new ForkJoinSumCalculate(middle+1, end);right.fork(); //进行拆分,同时压入线程队列return left.join() + right.join();}}}

