请注意,与有关EditContext、FieldIdentifier和FieldState的部分一样,这是一个高级主题。
如前所述,FieldState类保存表单数据的元状态。除了指示值是否已手动编辑外,Blazor还存储一组验证错误消息。为了理解它是如何工作的,本节将解释如何创建我们自己的自定义验证机制,该机制可以与Blazor一起用于验证用户输入。
下面的UML图显示了EditForm和存储此元状态的各种类(在图中分组)之间的关系。请记住,每当EditForm.Model更改时,EditForm都会创建EditContext的新实例。然后之前的EditContext(不再需要它,因为它包含关于以前模型的信息)会被垃圾回收,以及图中分组的类的所有实例。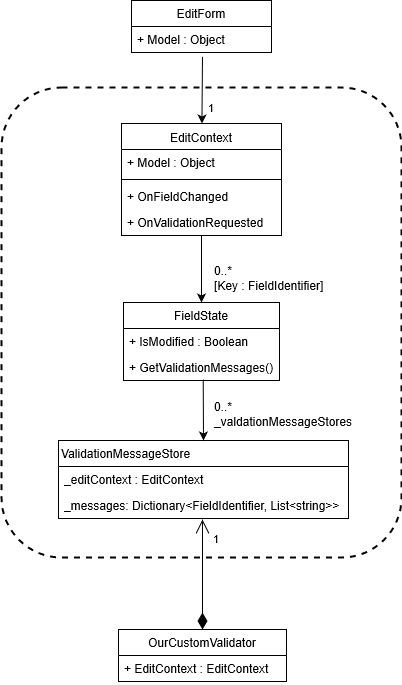
我们的自定义验证将基于FluentValidation。一旦你完成了这一部分(或者如果你只是想要一些你可以立即使用的东西),请看一看Blazor-Validation。
Creating a validator component
我们的验证器组件不必从任何特定类派生来提供验证。唯一的要求是它是从Blazor ComponentBase类派生出来的,这样我们就可以将它添加到视图中的<EditForm>标记中。嵌入到<EditForm>标记中的目的是,每当EditForm的Model参数更改时,我们可以定义一个级联参数来拾取EditForm创建的当前EditContext。
首先,创建一个新的Blazor应用程序,并添加对FluentValidation NuGet包的引用。然后创建一个名为FluentValidationValidator的类。
public class FluentValidationValidator : ComponentBase{[CascadingParameter]private EditContext EditContext { get; set; }[Parameter]public Type ValidatorType { get; set; }private IValidator Validator;private ValidationMessageStore ValidationMessageStore;[Inject]private IServiceProvider ServiceProvider { get; set; }}
- EditContext
从其父<EditForm>组件传递到组件的级联参数。每次EditForm.Model更改时,此设置都会更改。 - ValidatorType
这将指定用于执行实际验证的类类型。我们将检查这是否为IValidator(FluentValidation接口)。 - Validator
这将包含对指定ValidatorType的实例的引用,以执行实际的对象验证。 - ValidationMessageStore
每次EditContext更改时(因为EditForm.Model已经更改),我们都会创建一个新的。 ServiceProvider
对IServiceProvider的注入依赖项,我们可以使用它来创建ValidatorType的实例。public override async Task SetParametersAsync(ParameterView parameters){// Keep a reference to the original values so we can check if they have changedEditContext previousEditContext = EditContext;Type previousValidatorType = ValidatorType;await base.SetParametersAsync(parameters);if (EditContext == null)throw new NullReferenceException($"{nameof(FluentValidationValidator)} must be placed within an {nameof(EditForm)}");if (ValidatorType == null)throw new NullReferenceException($"{nameof(ValidatorType)} must be specified.");if (!typeof(IValidator).IsAssignableFrom(ValidatorType))throw new ArgumentException($"{ValidatorType.Name} must implement {typeof(IValidator).FullName}");if (ValidatorType != previousValidatorType)ValidatorTypeChanged();// If the EditForm.Model changes then we get a new EditContext// and need to hook it upif (EditContext != previousEditContext)EditContextChanged();}
LInes 4-5
每当我们的一个参数(包括EditContext级联参数)发生变化时,就会执行SetParametersAsync。我们需要做的第一件事是保持对一些原始值的引用,这样我们就可以看到它们是否发生了变化并做出相应的反应。
- Line 7
调用base.SetParametersAsync会将对象的属性更新为新值。
- Lines 9-16
确保我们有EditContext和作为IValidator的ValidatorType。
- Lines 18-19
如果ValidatorType已更改,则需要创建该类型的新实例,并将其分配给私有Validator字段以验证EditContext.Model。
- Lines 23-24
如果EditContext已经更改,那么我们需要连接到一些事件,以便可以验证用户输入,并且需要一个新的ValidationMessageStore来存储任何验证错误。
创建ValidatorType的新实例就像指示ServiceProvider检索实例一样简单。
private void ValidatorTypeChanged(){Validator = (IValidator)ServiceProvider.GetService(ValidatorType);}
要实现这一点,我们必须在应用程序的Startup.ConfigureServices方法中注册我们的验证器-一旦有了验证器和要验证的内容,我们就会这样做。
每当EditContext更改时,我们都需要一个新的ValidationMessagesStore来存储验证错误消息。
void EditContextChanged(){ValidationMessageStore = new ValidationMessageStore(EditContext);HookUpEditContextEvents();}
我们还需要连接一些事件,以便验证用户输入并将错误添加到ValidationMessageStore。
private void HookUpEditContextEvents(){EditContext.OnValidationRequested += ValidationRequested;EditContext.OnFieldChanged += FieldChanged;}
- OnValidationRequested
此事件在需要验证EditContext.Model的所有属性时触发。当用户尝试发布EditForm以便Blazor可以确定输入是否有效时,就会发生这种情况。
- OnFieldChanged
只要用户通过在Blazor的InputBase<T>子代组件之一中编辑EditContext.Model的属性值来更改该属性值,就会触发此事件。
async void ValidationRequested(object sender, ValidationRequestedEventArgs args){ValidationMessageStore.Clear();var validationContext =new ValidationContext<object>(EditContext.Model);ValidationResult result =await Validator.ValidateAsync(validationContext);AddValidationResult(EditContext.Model, result);}
- Line 3
首先,我们从之前的任何验证中清除所有错误消息。
- Line 4
接下来,我们指示FluentValidation.IValidator验证正在EditForm(我们通过EditContext.Model访问)中编辑的模型。
- Line 5
最后,我们将所有验证错误添加到ValidationMessageStore中,这是在一个单独的方法中完成的,因为我们将在验证整个对象以及在通过EditContext.OnFieldChanged通知时验证单个更改的属性时使用它。
将错误消息添加到ValidationMessageStore只需创建一个FieldIdentifier来准确标识哪个对象/属性有错误,并使用该标识符来添加任何错误消息,然后让EditContext知道验证状态已更改。
请注意,当验证涉及长时间运行的异步调用时(例如,对WebApi进行检查用户名可用性的调用),我们可以更新验证错误并多次调用EditContext.NotifyValidationStateChanged,以在用户界面中提供验证状态的增量显示。
void AddValidationResult(object model, ValidationResult validationResult){foreach (ValidationFailure error in validationResult.Errors){var fieldIdentifier = new FieldIdentifier(model, error.PropertyName);ValidationMessageStore.Add(fieldIdentifier, error.ErrorMessage);}EditContext.NotifyValidationStateChanged();}
最后,当用户编辑表单输入控件中的值时,我们需要验证单个对象/属性。发生这种情况时,会通过EditContext.OnFieldChanged事件通知我们。除了前两行和最后一行之外,以下代码是特定于FluentValidator的。
async void FieldChanged(object sender, FieldChangedEventArgs args){FieldIdentifier fieldIdentifier = args.FieldIdentifier;ValidationMessageStore.Clear(fieldIdentifier);var propertiesToValidate = new string[] { fieldIdentifier.FieldName };var fluentValidationContext =new ValidationContext<object>(instanceToValidate: fieldIdentifier.Model,propertyChain: new FluentValidation.Internal.PropertyChain(),validatorSelector: new FluentValidation.Internal.MemberNameValidatorSelector(propertiesToValidate));ValidationResult result = await Validator.ValidateAsync(fluentValidationContext);AddValidationResult(fieldIdentifier.Model, result);}
- LInes 3-4
从事件参数中获取FieldIdentifier(ObjectInstance/PropertyName对),并仅清除该属性以前的所有错误消息。
- Line 16
使用与ValidationRequsted相同的方法将错误从FluentValidation添加到我们的ValidationMessageStore。
Using the component
首先创建一个模型供我们的用户编辑。
namespace CustomValidation.Models{public class Person{public string Name { get; set; }public int Age { get; set; }}}
接下来,使用FluentValidation为Person创建验证器。
using CustomValidation.Models;using FluentValidation;namespace CustomValidation.Validators{public class PersonValidator : AbstractValidator<Person>{public PersonValidator(){RuleFor(x => x.Name).NotEmpty();RuleFor(x => x.Age).InclusiveBetween(18, 80);}}}
因为我们的验证组件使用IServiceProvider来创建验证器的实例,所以我们需要在Startup.ConfigureServices中注册它。
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services){services.AddScoped<Validators.PersonValidator>();}
最后,我们需要设置用户界面来编辑Person类的实例。
@page "/"@using Models<EditForm Model=@Person OnValidSubmit=@ValidFormSubmitted><FluentValidationValidator ValidatorType=typeof(Validators.PersonValidator)/><p>Validation summary</p><ValidationSummary /><p>Edit object</p><div class="form-group"><label for="Name">Name</label><InputText @bind-Value=Person.Name class="form-control" id="Name" /><ValidationMessage For="() => Person.Name" /></div><div class="form-group"><label for="Age">Age</label><InputNumber @bind-Value=Person.Age class="form-control" id="Age" /><ValidationMessage For=@(() => Person.Age) /></div><input type="submit" class="btn btn-primary" value="Save" /></EditForm>@code {Person Person = new Person();void ValidFormSubmitted(){Person = new Person();}}
Process flow
Page is displayed
- 我们的
EditForm组件是从<EditForm Model=@Person>标记创建的。 - 执行
EditForm.OnParametersSet,因为EditForm.Model已从null更改为OurPerson,它将创建一个新的EditContext实例。 - 新的
EditContext实例通过级联值向下级联到所有子组件。 作为这种级联值更改的结果,
InputBase<T>的每个子代都执行了其SetParametersAsync,并通过创建一个新的FieldIdentifier实例进行响应。Our validation component is initialised
我们的验证组件的
SetParametersAsync方法通过引用新的EditContext来执行。- 我们的组件创建一个新的
ValidationMessageStore。 我们的组件侦听
EditContext上的事件,以获取验证请求和输入更改通知。User alters data
用户编辑
InputBase<T>子体中的数据。- 该组件通过
EditContext.NotifyFieldChanged通知此状态更改(从未修改到已修改),并传递其FieldIdentifier。 EditContext通过传递FieldIdentifier来触发其OnFieldChanged。- 组件的事件订阅告诉
ValidationMessageStore清除由FieldIdentifier的Model和FieldName属性标识的状态的所有错误消息。 - 我们的组件对单个属性执行自定义验证。
- 验证错误被添加到组件的
ValidationMessageStore中,以FieldIdentifier为关键字。 ValidationMessageStore执行EditContext.GetFieldState以检索当前FieldIdentifier的FieldState。- 将
ValidationMessageStore添加到FieldState,以便FieldState.GetValidationMessages能够从所有ValidationMessageStore实例检索所有错误消息。步骤8特别重要,因为Blazor需要能够检索特定输入的所有验证错误消息,而不管它们被添加到哪个ValidationMessageStore。
User submits the form
<EditForm>执行EditContext.Validate。EditContext触发其OnValidationRequsted事件。- 我们组件的订阅告诉我们的
ValidationMessageStore清除所有字段以前的所有验证错误消息。 - 组件对整个
EditContext.Model对象执行其自定义验证。 - 与单个更改的验证一样,错误被添加到
ValidationMessageStore,该存储库向EditContext中的所有相关FieldState实例注册自身。 <EditForm>根据是否有错误消息触发相关的有效/无效事件。EditForm.Model is changed
如果这是一个用于创建新人的用户界面,那么在成功地将我们的新Person提交到服务器之后,我们的应用程序可能会为我们的表单创建一个要编辑的新Person。这将丢弃与前一个Person实例相关联的所有状态(在虚线框中指示),并从新实例重新开始。
- EditContext
- FieldState
- ValidationMessageStore
在演示源代码中添加了一些日志记录后,我们可以看到以下输出。
WASM: EditContext has changedWASM: New ValidationMessageStore createdWASM: Hooked up EditContext events (OnValidationRequested and OnFieldChanged)WASM: OnFieldChanged triggered: Validating a single property named Name on class PersonWASM: OnFieldChanged triggered: Validating a single property named Age on class PersonWASM: OnValidationRequested triggered: Validating whole objectWASM: EditContext has changedWASM: New ValidationMessageStore createdWASM: Hooked up EditContext events (OnValidationRequested and OnFieldChanged)
- Lines 1-3
创建相关的状态实例以支持编辑Person实例。
- Line 4
输入了一个名称
- Line 5
输入了年龄
- Line 6
用户提交表单
- Line 7
Index.razor中的Person实例被更改,导致元状态实例被丢弃,并为新的EditForm.Model创建新实例。

