原理: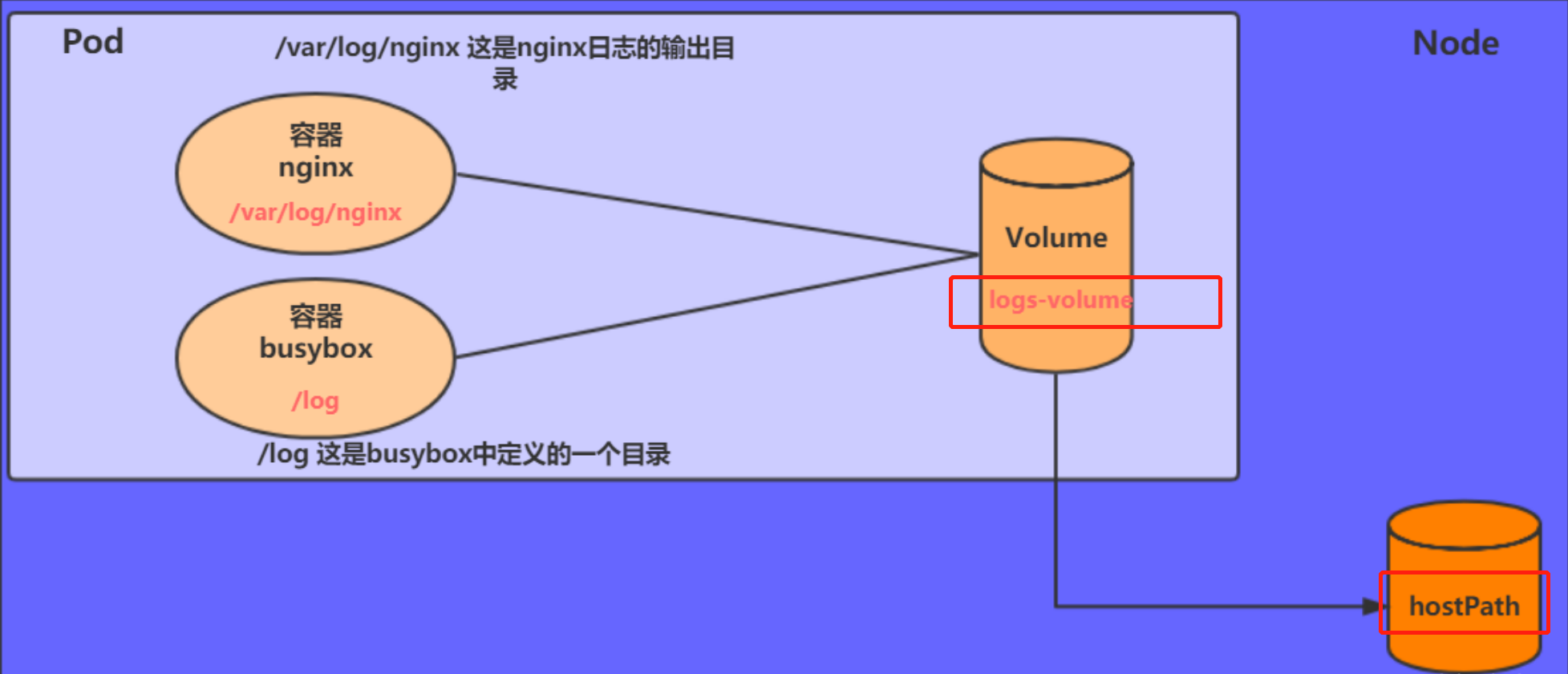
HostPath就是将Node主机中一个实际目录挂在到Pod中,以供容器使用,这样的设计就可以保证Pod销毁了,但是数据依据可以存在于Node主机上
配置清单:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: volume-hostpath
namespace: dev
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.17.1
ports:
- containerPort: 80
volumeMounts:
- name: logs-volume
mountPath: /var/log/nginx
- name: busybox
image: busybox:1.30
command: [“/bin/sh”,”-c”,”tail -f /logs/access.log”]
volumeMounts:
- name: logs-volume
mountPath: /logs
volumes:
- name: logs-volume
hostPath:
path: /root/logs
type: DirectoryOrCreate # 目录存在就使用,不存在就先创建后使用
Type参数值说明:
关于type的值的一点说明:
DirectoryOrCreate :目录存在就使用,不存在就先创建后使用
Directory :目录必须存在
FileOrCreate:文件存在就使用,不存在就先创建后使用
File:文件必须存在
Socket unix:套接字必须存在
CharDevice:字符设备必须存在
BlockDevice:块设备必须存在
效果验证: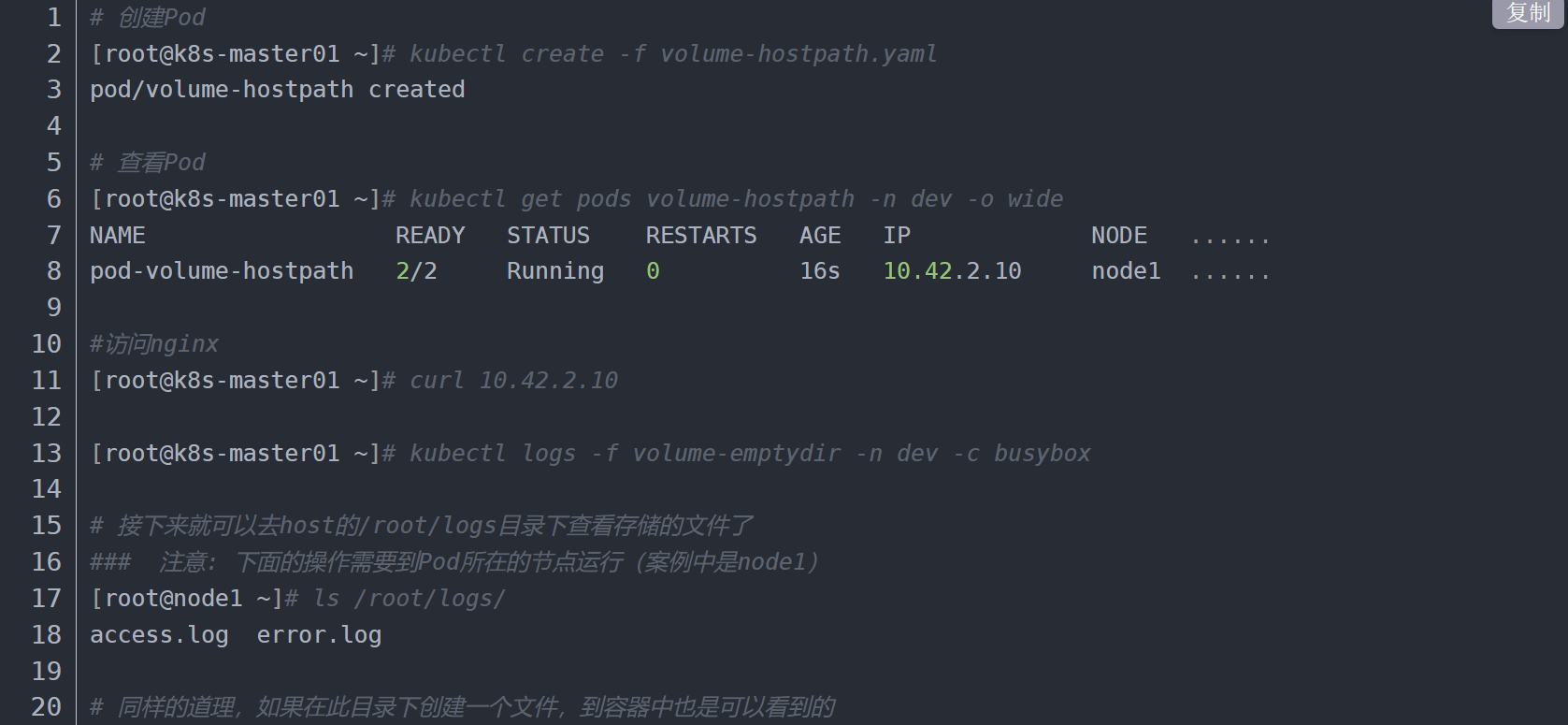
# 创建Pod
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl create -f volume-hostpath.yaml
pod/volume-hostpath created
# 查看Pod
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl get pods volume-hostpath -n dev -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE ……
pod-volume-hostpath 2/2 Running 0 16s 10.42.2.10 node1 ……
#访问nginx
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# curl 10.42.2.10
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# kubectl logs -f volume-emptydir -n dev -c busybox
# 接下来就可以去host的/root/logs目录下查看存储的文件了
### 注意: 下面的操作需要到Pod所在的节点运行(案例中是node1)
[root@node1 ~]# ls /root/logs/
access.log error.log
# 同样的道理,如果在此目录下创建一个文件,到容器中也是可以看到的
相关文档:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_27184497/article/details/121764723

