206-反转链表
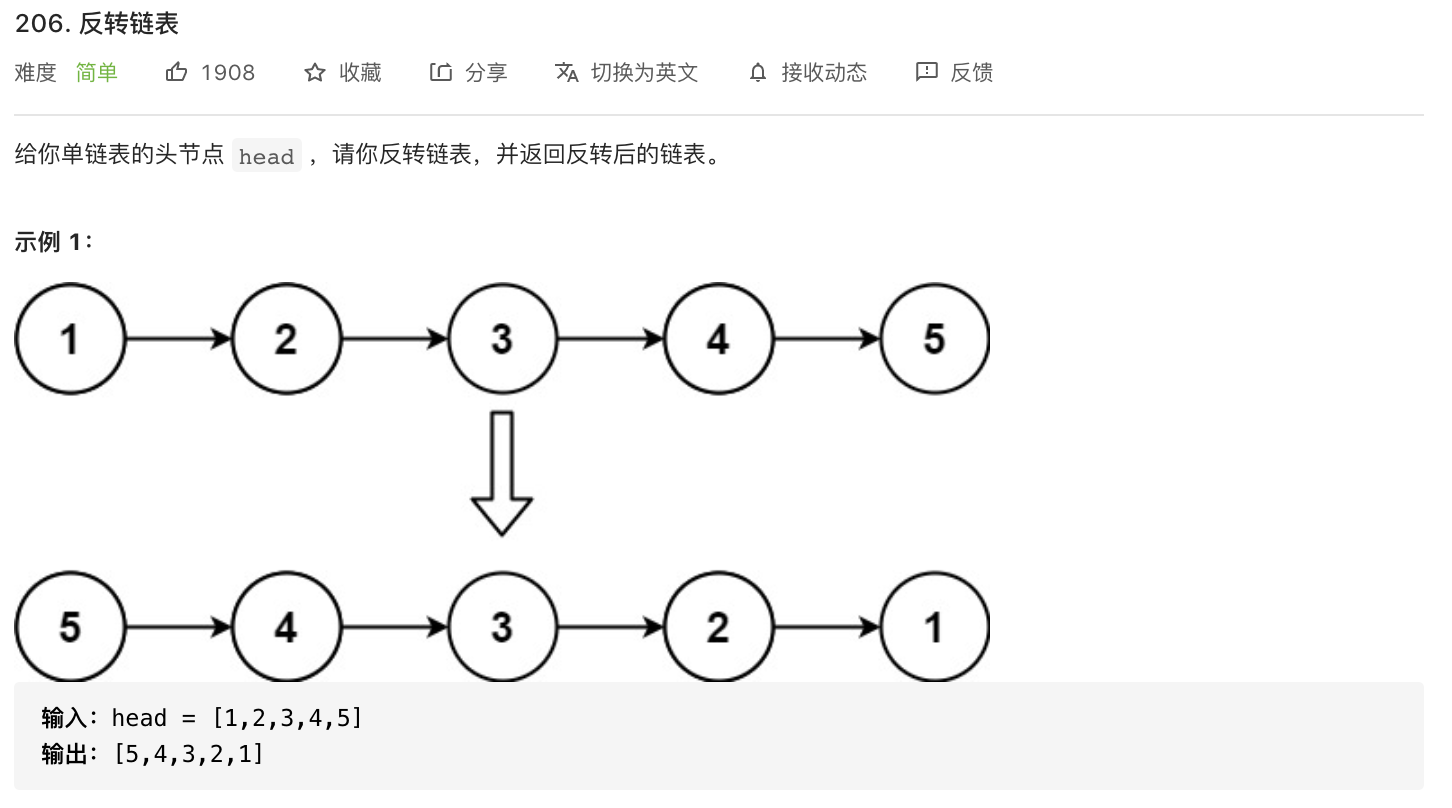
题意分析:
- 反转单链表所有节点。
解题思路:
- 迭代。指针一次遍历,迭代反转节点指向。
- 递归。针对每个节点递归调用。
注意点:
- 递归。
- 递归体和反转逻辑的先后顺序。
代码:
/*** 迭代思路。反转指针的指向。* @param head* @return*/public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {ListNode pre = null;ListNode curr = head;while (curr != null) {ListNode next = curr.next;curr.next = pre;pre = curr;curr = next;}return pre;}/*** 递归思路。* 1、找到递归体* 2、确定退出条件* @param head* @return*/public ListNode reverseList2(ListNode head) {if (head == null || head.next == null) {return head;}ListNode newHead = reverseList(head.next);head.next.next = head;head.next = null;return newHead;}
92-反转链表II
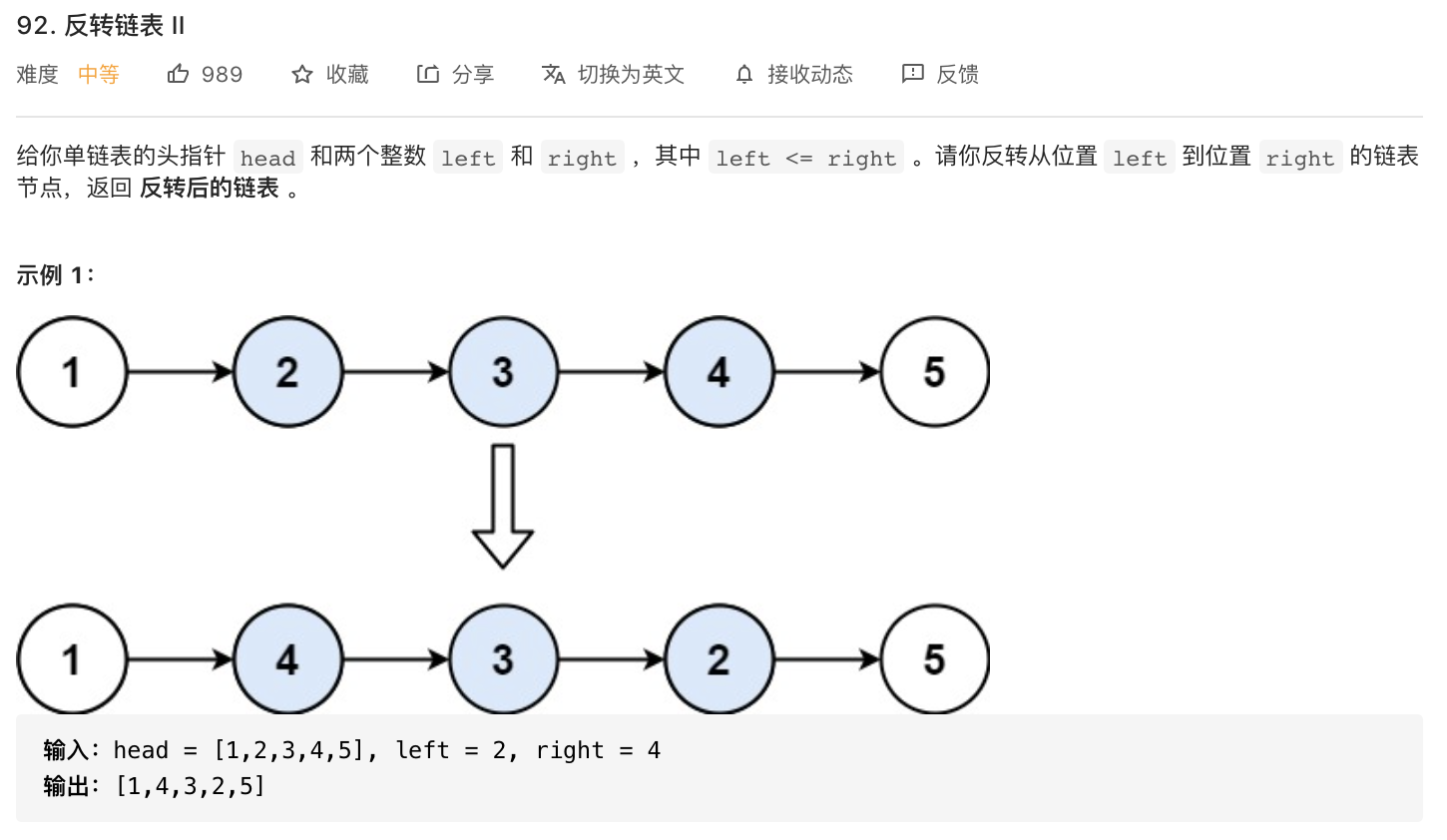
题意分析:
- 反转单链表中的一段节点。
解题思路:
- 插入排序思想。找到要反转链表节点区域的前驱节点,然后通过插入排序反转。
代码:
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int left, int right) {// 增加哑节点ListNode dummy = new ListNode();dummy.next = head;// 找到 left 处对应的节点,然后从这里开始插入排序逻辑反转ListNode curr = dummy;ListNode pre = null;int a = left;while (curr != null && a > 0) {pre = curr;curr = curr.next;a--;}System.out.println(pre.val + ": " + curr.val);ListNode next;// 遍历要插入排序的次数,即要执行插入操作的节点个数for (int i = 0; i < right - left; i++) {// System.out.println("i=" + i);if (curr.next != null) {next = curr.next;curr.next = next.next;next.next = pre.next;pre.next = next;}}return dummy.next;}
141-环形链表
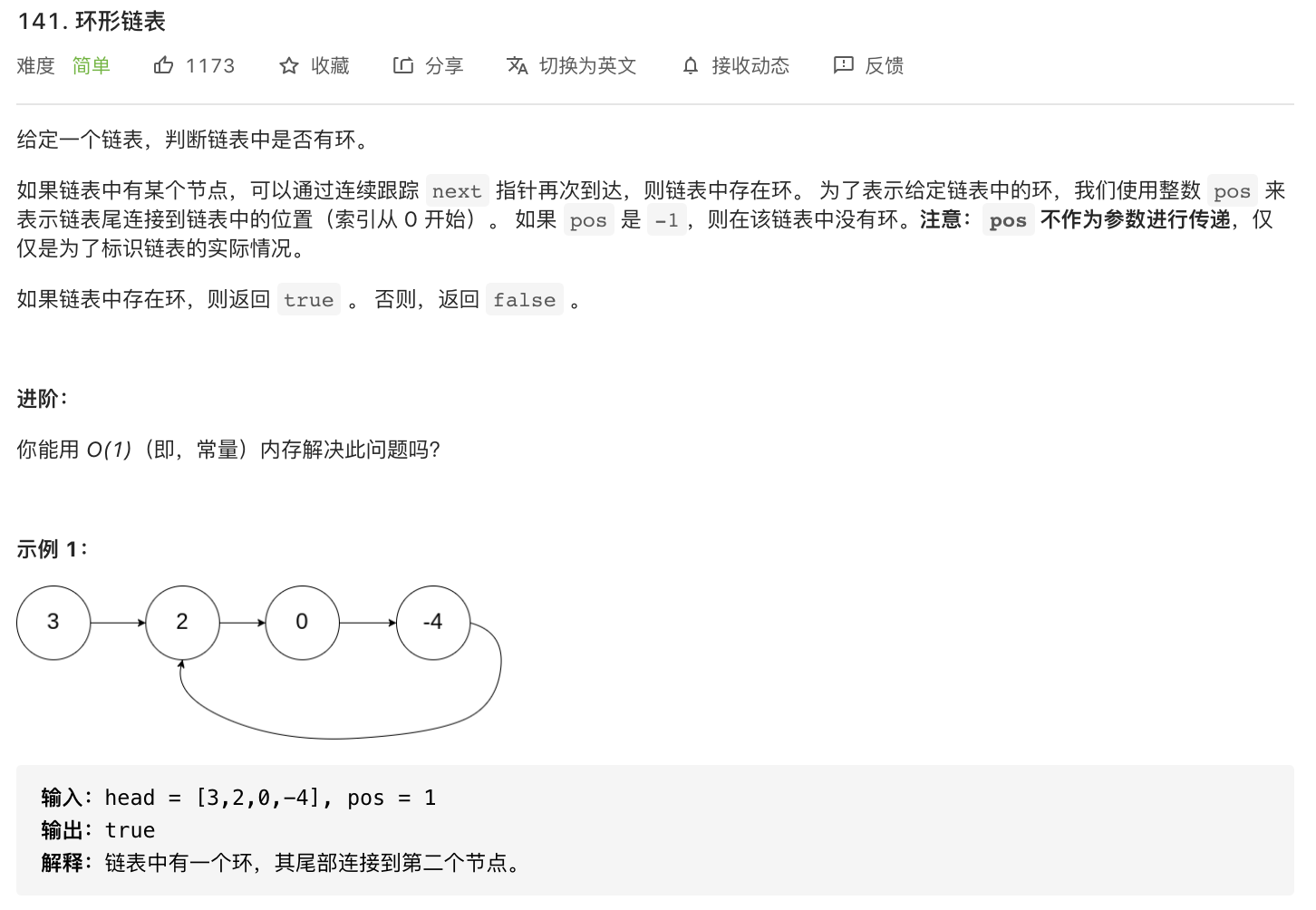
题意分析:
- 判断单链表中是否存在环。
解题思路:
- 快慢指针。
注意点:
- 特殊情况处理。比如空链表或者链表只有一个节点。
- while条件的判断。
- fast 指针走两次时第一次为 null 的处理。
代码:
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {if (head == null || head.next == null) {return false;}ListNode slow = head, fast = head.next;// 快慢指针扫描while (fast != null) {if (slow == fast) return true;slow = slow.next;// fast 走两次时容易空指针if (fast.next == null) return false;fast = fast.next.next;}return false;}
142-环形链表II

题意分析:
- 判断单链表是否存在环,找到环的入口
解题思路:
- 快慢指针。先找到快慢指针找到相遇点,然后分析相遇点到入口与head节点到入口的距离同时走向。(注意:fast 指针走的距离永远是 slow 指针的2倍)
注意点:
- 找到相遇点时,如果链表没有环,fast 指针为空,此时要先判断。
代码:
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {if (head == null || head.next == null) {return null;}// 快慢指针ListNode slow = head, fast = head.next;// 快慢指针扫描,找到相遇点while (fast != null) {// 存在环if (slow == fast) break;slow = slow.next;// fast 走两次时容易空指针if (fast.next == null) return null;fast = fast.next.next;}// System.out.println(slow.val + ": " + fast.val);// 找到环的入口 slow和fast相遇。fast走的距离始终等于slow的2倍: L(fast) = 2 L(slow)// [3,2,0,4,5]-(-1),该demo没有环fast为空if (fast == null) return null;fast = fast.next;ListNode p = head;while (p != fast) {p = p.next;fast = fast.next;}// 返回 fast 或者 preturn fast;}
86-分隔链表

题意解析:
- 将链表节点小于某个节点值的节点移动到该节点前面,并且整体节点顺序不变。
解题思路:
- 插入排序思想。由于要保证每个节点的初始相对位置,很容易想到插入排序,而插入排序思想的核心,无非就是要记录前面所有有序节点的最后一个节点,方便插入新数据。
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
- 合并两个链表。可以考虑将小于和大于等于x的节点单独维护一个链表,记录两个链表的头尾节点,然后合并。
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(n)
注意点:
- 插入排序思想。
- 扫描时要注意更新 curr 当前节点的前驱节点 pre 更新,会出现 curr 更新到下一个节点,但 pre 节点不变,这种情况要单独处理。
代码:
/*** 新构建两个链表,一个存储小于 x 的节点,一个存储大于 x 的节点* @param head* @param x* @return*/public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {ListNode small = new ListNode(Integer.MIN_VALUE);ListNode smallHead = small;ListNode large = new ListNode(Integer.MIN_VALUE);ListNode largeHead = large;while (head != null) {if (head.val < x) {small.next = head;small = small.next;} else {large.next = head;large = large.next;}head = head.next;}large.next = null;small.next = largeHead.next;return smallHead.next;}/*** 解题思路:插入排序保证有序。* @param head* @param x* @return*/public ListNode partition2(ListNode head, int x) {// 创建哑节点ListNode dummy = new ListNode(Integer.MIN_VALUE, head);// small 记录前面小于 x 的最新节点,pre 为扫描指针 curr 的前驱指针ListNode small = dummy, pre = dummy, curr = head;while (curr != null) {if (curr.val < x) {ListNode newcurr = curr.next;pre.next = curr.next;curr.next = small.next;small.next = curr;// curr的pre节点更新需要特殊处理,比如 curr 节点原地更新,pre = curr,否则 pre 就不需要更新if (pre.next == curr) {pre = curr;}small = curr;curr = newcurr;} else {pre = curr;curr = curr.next;}}return dummy.next;}
1171-从链表中删去总和值为零的连续节点(*)
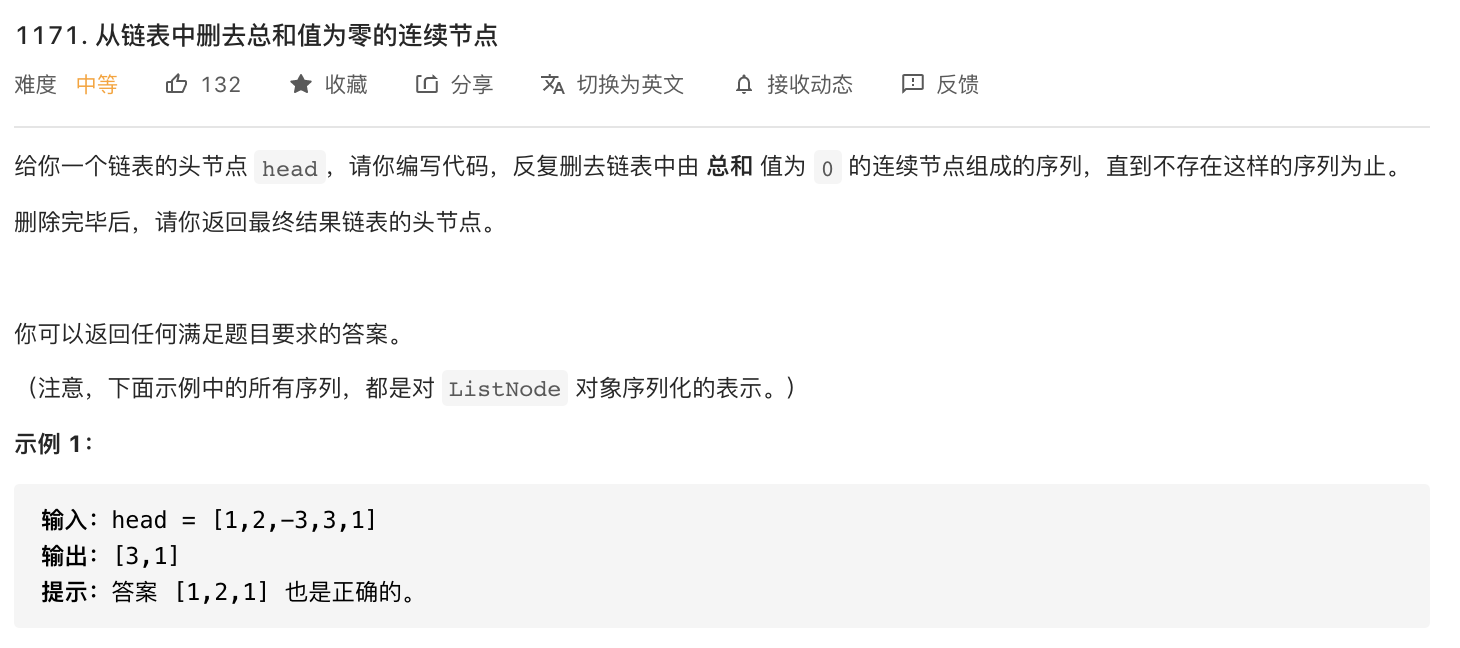
题意分析:
- 链表中连续节点(两个或者多个)如果和为零则删除,如果删除一次后还存在和为零的连续节点还需要继续删除。
解题思路:
- 哈希表记录(思路笔记特殊)。
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(n)
- 前缀和(待实现)。
注意点:
- 哈希表记录。
- 难点在于哈希表key覆盖时如何重构链表。
代码:
public ListNode removeZeroSumSublists(ListNode head) {ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0, head);Map<Integer, ListNode> map = new HashMap<>();// 第一次扫描,建立 当前节点和与当前节点 哈希表,若哈希表 节点和 相同则覆盖int sum = 0;for (ListNode curr = dummy; curr != null; curr = curr.next) {sum += curr.val;map.put(sum, curr);}// 根据第一次扫描的哈希表,如果哈希表的key更新过,则说明区间数据需要删除sum = 0;for (ListNode curr = dummy; curr != null; curr = curr.next) {sum += curr.val;curr.next = map.get(sum).next;}return dummy.next;}
160-相交链表

题意分析:
- 两个链表若相交,返回相交点,否则返回 null。
解题思路:
- 哈希集合。遍历 A 遍历并记录链表节点,然后遍历 B 节点,第一次出现对象值一样的节点则是相交节点。
- 时间复杂度:O(m+n)。
- 空间复杂度:O(m)
- 双指针。A 指针走完 A 链表所有节点和 B 链表相交前的节点距离,B 指针走完 B 链表所有节点和 A 链表相交前的节点距离,两个距离是相等的,也是交叉点位置。
- 时间复杂度:O(m+n)。
- 空间复杂度:O(1)。
注意点:
- 哈希集合。
- 本地测试不太好测试,可能在相交点之前 A 和 B 中也存在相同元素,但元素的哈希值是不同的,这一点在相交情况下也是一致的。
代码:
/*** 哈希集合(List集合)*/public ListNode getIntersectionNode2(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {if (headA == null || headB == null) {return null;}List<ListNode> list = new ArrayList<>();for (ListNode p = headA; p != null; p = p.next) {list.add(p);}for (ListNode q = headB; q != null; q = q.next) {if (list.contains(q)) {return q;}}return null;}/*** 双指针。* 当存在交叉,两个指针分别走完两个链表的距离一定是相等的。*/public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {ListNode pa = headA, pb = headB;while (pa != pb) {pa = pa != null ? pa.next : headB;pb = pb != null ? pb.next : headA;}return pa;}
147-对链表进行插入排序

题意分析:
- 数组的插入排序。
解题思路:
- 参考数组插入排序。
注意点:
- 插入排序时要考虑前面节点有序时插入的位置单独处理。
代码:
public ListNode insertionSortList(ListNode head) {if (head == null || head.next == null) {return head;}// 增加哑节点,方便统一处理ListNode dummy = new ListNode(Integer.MIN_VALUE);dummy.next = head;// 从第二个节点开始处理ListNode curr = head.next;ListNode sort_last = head;while (curr != null) {int curr_val = curr.val;// 两种情况,前面节点有序,一种不修改前面排序状态,一种要修改前面排序状态if (curr_val >= sort_last.val) {sort_last = sort_last.next;} else {// 从第一个节点开始遍历ListNode p = dummy;// 这个位置判断 p.next.val 比较巧妙,这样找不大于 curr_val 的节点时不要单独申请空间记录其前驱节点while (p.next.val <= curr_val) {p = p.next;}sort_last.next = curr.next;curr.next = p.next;p.next = curr;}// Utils.printList(dummy.next);curr = sort_last.next;}return dummy.next;}
148-排序链表(归并排序)

题意分析:
解题思路:
注意点:
代码:
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {if (head == null || head.next == null) {return head;}// 寻找链表中节点ListNode slow = head, fast = head;while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next.next;}// System.out.println("slow = " + slow.val);ListNode mid = slow;ListNode right = mid.next;mid.next = null;ListNode l1 = sortList(head);ListNode l2 = sortList(right);return merge(l1, l2);}/*** 合并两个有序链表* @param l1* @param l2* @return*/public ListNode merge(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {ListNode head = new ListNode(Integer.MAX_VALUE);ListNode cur = head;ListNode p1 = l1, p2 = l2;while (p1 != null && p2 != null) {ListNode tmp;if (p1.val < p2.val) {tmp = p1;p1 = p1.next;} else {tmp = p2;p2 = p2.next;}cur.next = tmp;cur = cur.next;}if (p1 != null) cur.next = p1;if (p2 != null) cur.next = p2;return head.next;}
19-删除链表的倒数第 N 个节点
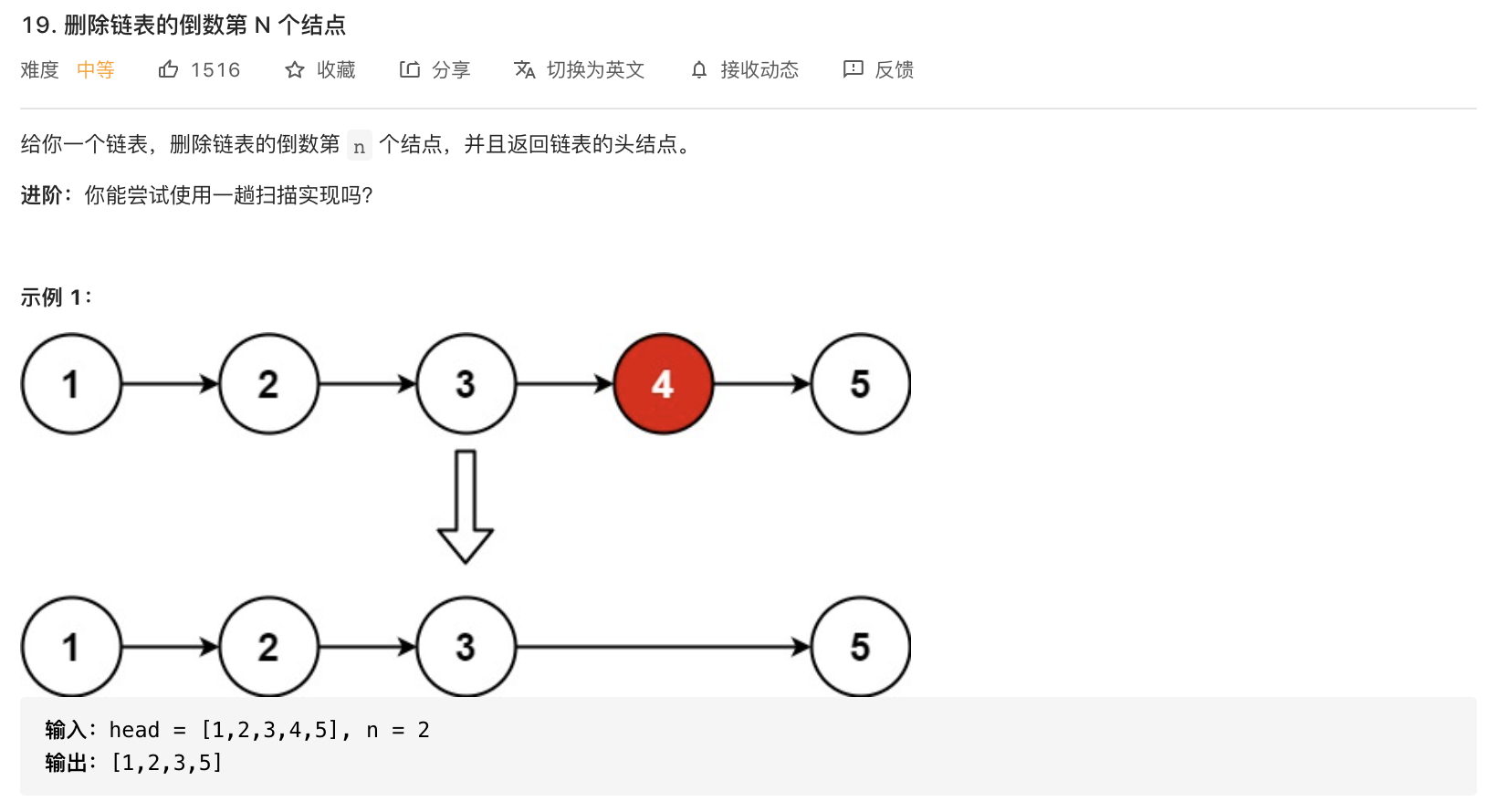
题意分析:
- 给定链表,删除倒数的某一个节点。
解题思路:
- 两次扫描。第一次计算链表长度,第二次找到要删除的节点。
- 时间复杂度:O(2n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
- 双指针。快慢指针同时扫描,快指针先走 n 个节点,然后快慢指针同时走,但快指针走到尾节点时,满指针就是倒数第 n 个节点(快慢指针始终相差 n 个节点)。
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
- 辅助栈。先将链表元素都入栈,然后依次出栈元素到倒数第 n 个节点。
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(n)
注意点:
代码:
/*** 思路一:两次扫描链表,第一次获取链表长度,第二次找到要删除的节点* @param head* @param n* @return*/public ListNode removeNthFromEnd1(ListNode head, int n) {ListNode nHead = new ListNode(-1, head);ListNode p = nHead;ListNode idx = nHead, idxPre = nHead;int len = 0;// 统计链表长度while (p != null) {p = p.next;len++;}// 要遍历的元素位置int k = len - n + 1;int i = 1;while (i++ < k) {idxPre = idx;idx = idx.next;}if (idxPre == nHead) {idxPre.next = null;} else {idxPre.next = idx.next;}return nHead.next;}/*** 思路二:利用辅助栈,出栈时找对要删除的元素* @param head* @param n* @return*/public ListNode removeNthFromEnd2(ListNode head, int n) {ListNode nHead = new ListNode(-1, head);Deque<ListNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();ListNode p = nHead;while (p != null) {stack.push(p);p = p.next;}ListNode idx = nHead;// 退到要删除的元素为止for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {idx = stack.pop();}ListNode idxPre = nHead;if (stack.isEmpty()) {idx.next = null;} else {idxPre = stack.pop();idxPre.next = idx.next;}return nHead.next;}/*** 思路三:利用快慢指针,两个指针始终相差n个元素,当快指针扫描到链表最后一个元素,此时慢指针所在的元素就是要删除的元素* @param head* @param n* @return*/public ListNode removeNthFromEnd3(ListNode head, int n) {ListNode nHead = new ListNode(-1, head);// 快慢指针ListNode fast = nHead, slow = nHead;// 辅助指针ListNode p = nHead, slowPre = nHead;// 快指针先走了n个位置for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){fast = p;p = p.next;}while (fast.next != null) {fast = fast.next;slowPre = slow;slow = slow.next;}// 特殊情况,如果链表只有一个元素,slowPre 其实和 slow 指针是对等的,无法按照正常逻辑去处理if (slowPre == slow) {slowPre.next = null;} else {slowPre.next = slow.next;}return nHead.next;}
61-旋转链表
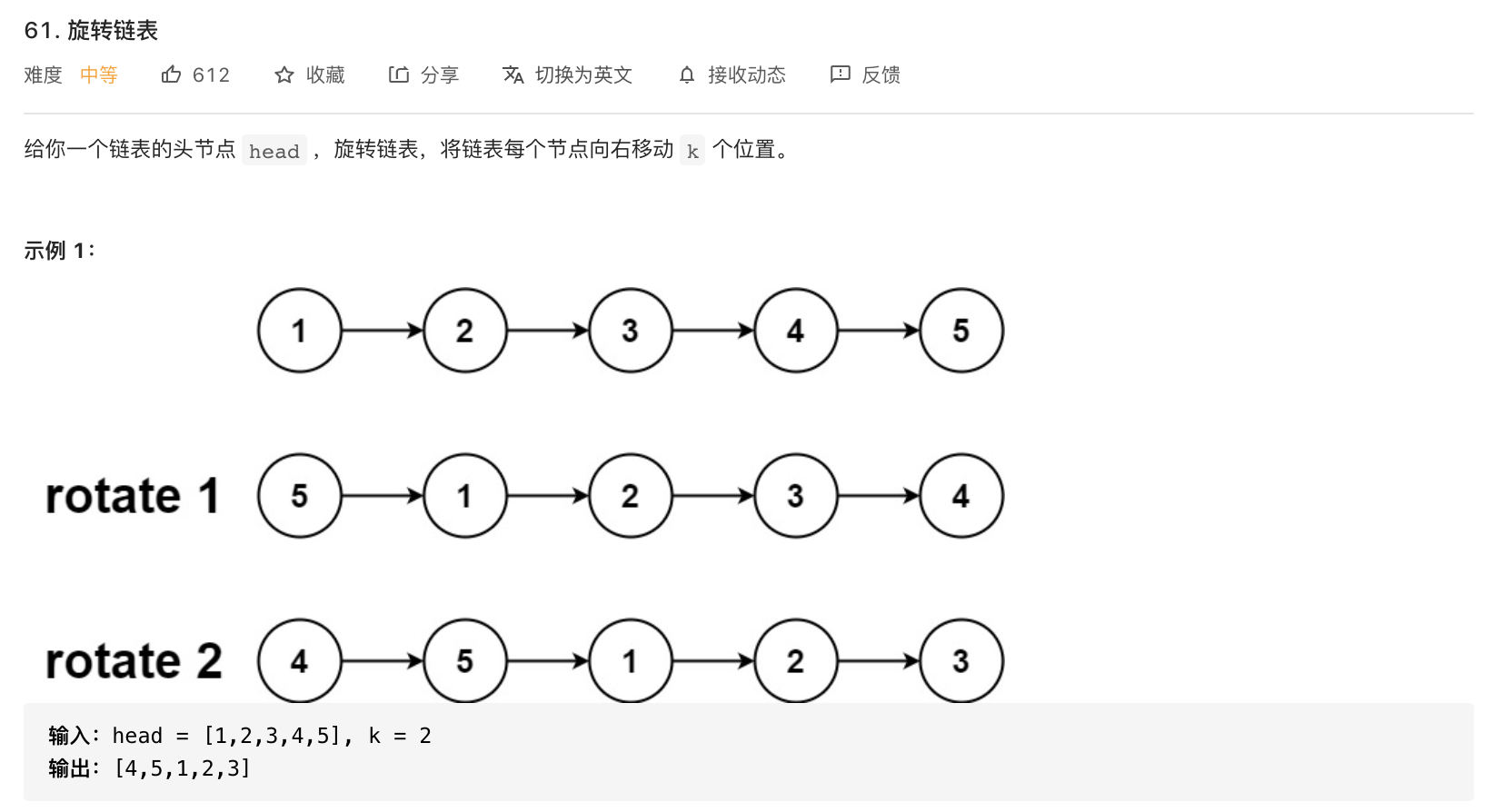
题意分析:
解题思路:
注意点:
代码:
public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) {if (k == 0 || head == null || head.next == null) {return head;}int len = 1;ListNode p = head;// 遍历到链表尾节点while (p.next != null) {len++;p = p.next;}// 链表尾部和头部形成闭环p.next = head;// 记录从尾部指针移动多少次走到新尾部节点int mvLen = len - k % len;while (mvLen-- > 0) {p = p.next;}ListNode newHead = p.next;p.next = null;return newHead;}
去重问题
83-删除排序链表中的重复元素
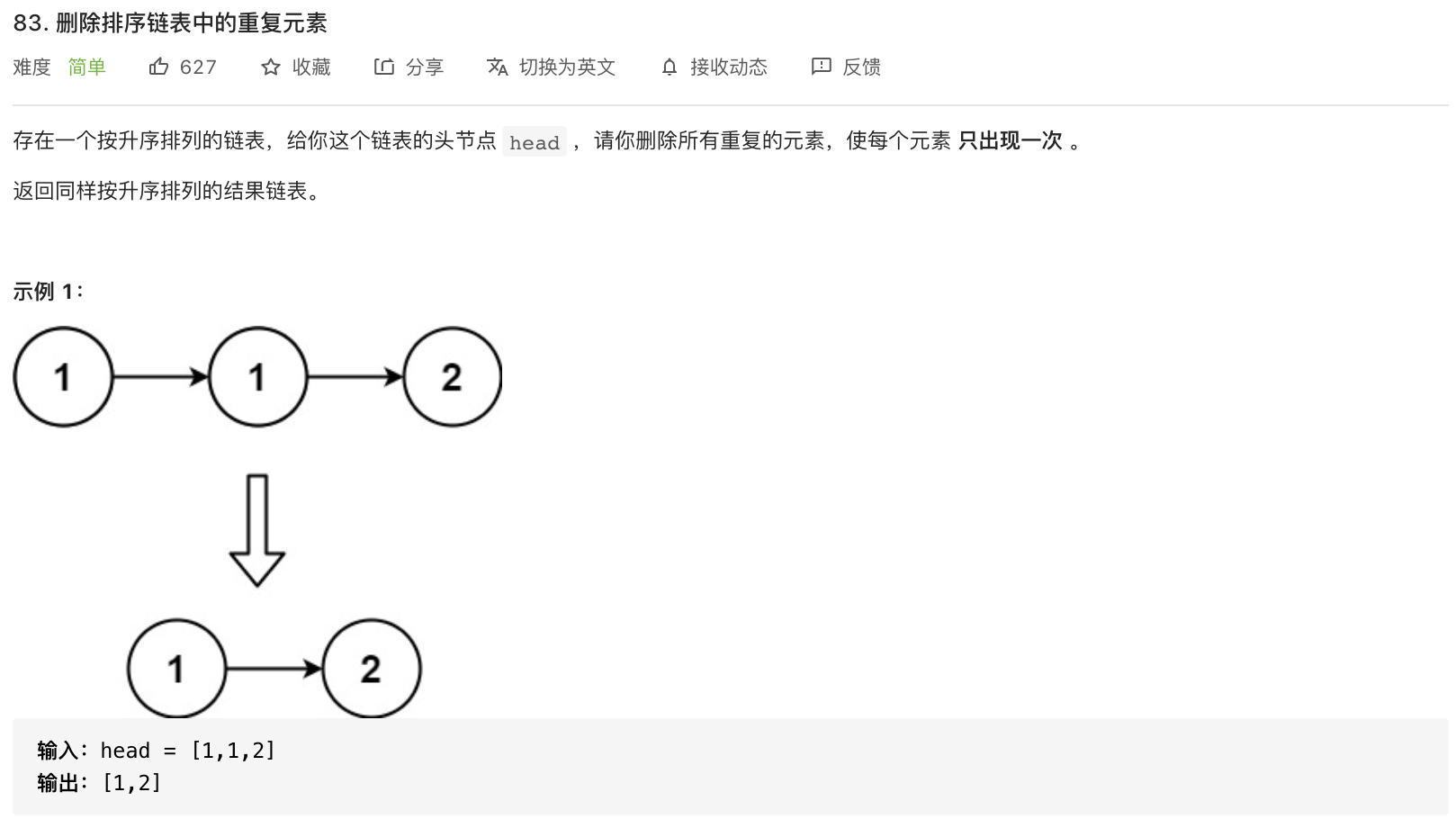
题意分析:
解题思路:
注意点:
代码:
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {if (head == null) {return head;}ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-101, head);ListNode cur = dummy;while (cur.next != null) {if (cur.val == cur.next.val) {cur.next = cur.next.next;} else {cur = cur.next;}}return dummy.next;}
82-删除排序链表中的重复元素II

题意分析:
解题思路:
注意点:
代码:
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {if (head == null) {return head;}ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-101, head);ListNode cur = dummy;while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null) {if (cur.next.val == cur.next.next.val) {// 开始遍历重复元素个数,并删除int tmp = cur.next.val;while (cur.next != null && cur.next.val == tmp) {cur.next = cur.next.next;}} else {cur = cur.next;}}return dummy.next;}
未分类
24-两两交换链表中的节点

题意分析:
解题思路:
注意点:
代码:
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);dummyHead.next = head;ListNode temp = dummyHead;while (temp.next != null && temp.next.next != null) {ListNode node1 = temp.next;ListNode node2 = temp.next.next;temp.next = node2;node1.next = node2.next;node2.next = node1;temp = node1;}return dummyHead.next;}
21-合并两个有序链表
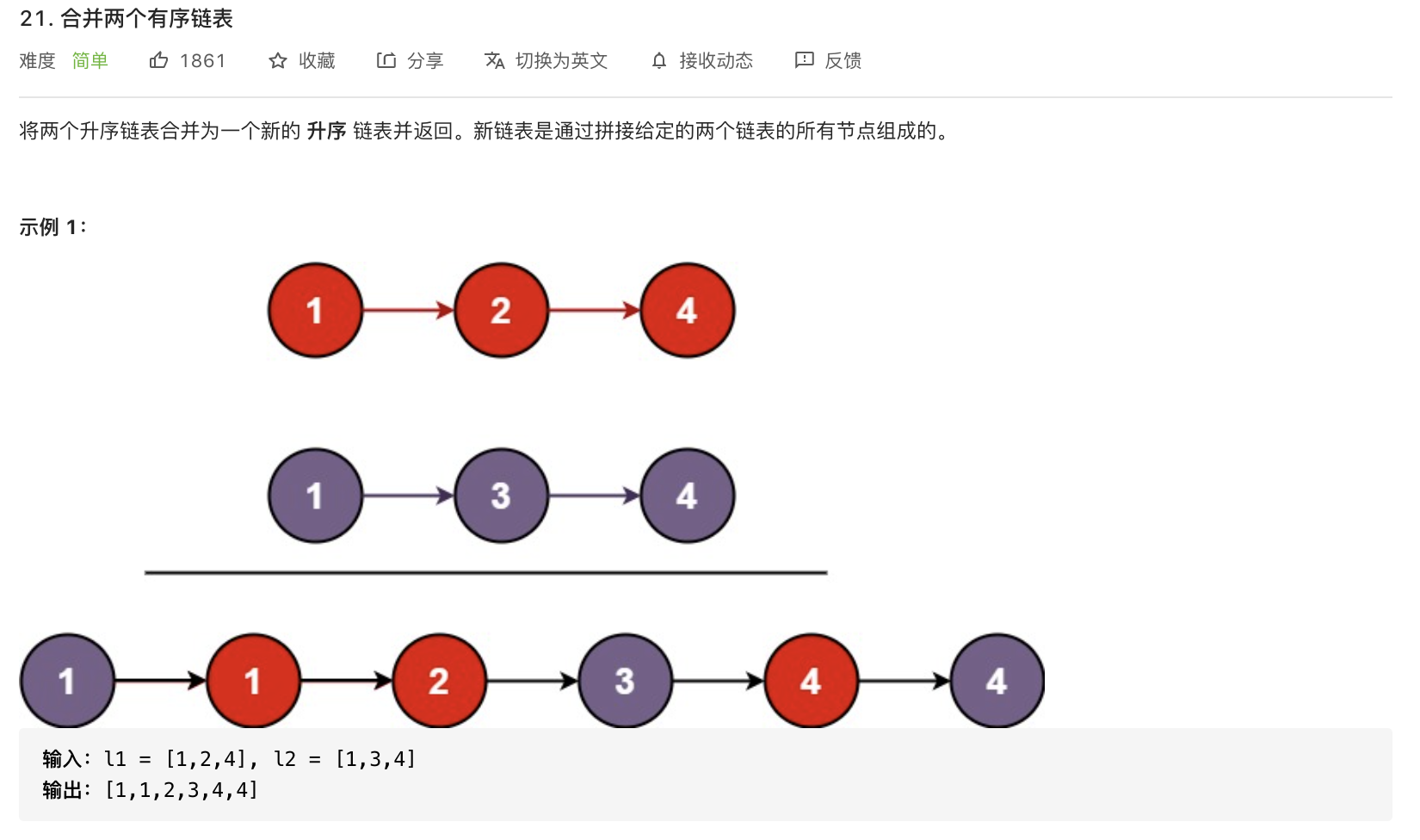
题意分析:
解题思路:
注意点:
代码:
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {ListNode head = new ListNode(Integer.MAX_VALUE);ListNode cur = head;ListNode p1 = l1, p2 = l2;while (p1 != null && p2 != null) {ListNode tmp;if (p1.val < p2.val) {tmp = p1;p1 = p1.next;} else {tmp = p2;p2 = p2.next;}cur.next = tmp;cur = cur.next;}if (p1 != null) cur.next = p1;if (p2 != null) cur.next = p2;return head.next;}
23-合并K个升序链表
题意分析:
- 合并 K 个升序链表。
解题思路:
- 优先级队列(最小堆)。队列先添加所有链表的 head 节点(每次添加都是最小节点),然后取队列元素并添加其 next 元素到队列中。
- 时间复杂度:优先级队列中最多有 k 个元素,单个节点插入和删除的时间复杂度为 O(logk),总共有 kn 个节点,每个节点都要被插入和删除一次,故总的时间复杂度为 O(kn * logk)。
- 空间复杂度:优先级队列的大小 O(k)。
注意点:
- 优先级队列添加对象时需要实现 Compartor 对象。
- TreeSet 可以实现按顺序添加元素和取最小元素,但不能添加重复元素。
扩展:
代码:
/*** 合并 k 个升序链表** 思路:* 1、添加所有链表的 head 节点* 2、循环从中拿到最小节点,然后添加其 next 元素*/public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {// 构建优先级队列(最小堆),队列元素添加排序规则Queue<ListNode> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<ListNode>() {// 升序排序器,默认就是最小堆@Overridepublic int compare(ListNode o1, ListNode o2) {return o1.val - o2.val;}});// 添加所有链表的 head 节点for (ListNode list : lists) {if (list != null)queue.offer(list);}// 增加哨兵节点ListNode newHead = new ListNode(-1);ListNode currTail = newHead;// 循环出队列,并添加新元素到队列while (!queue.isEmpty()) {ListNode node = queue.poll();if (node.next != null) {queue.offer(node.next);}currTail.next = node;currTail = node;node.next = null;}return newHead.next != null ? newHead.next : null;}
1669-合并两个链表
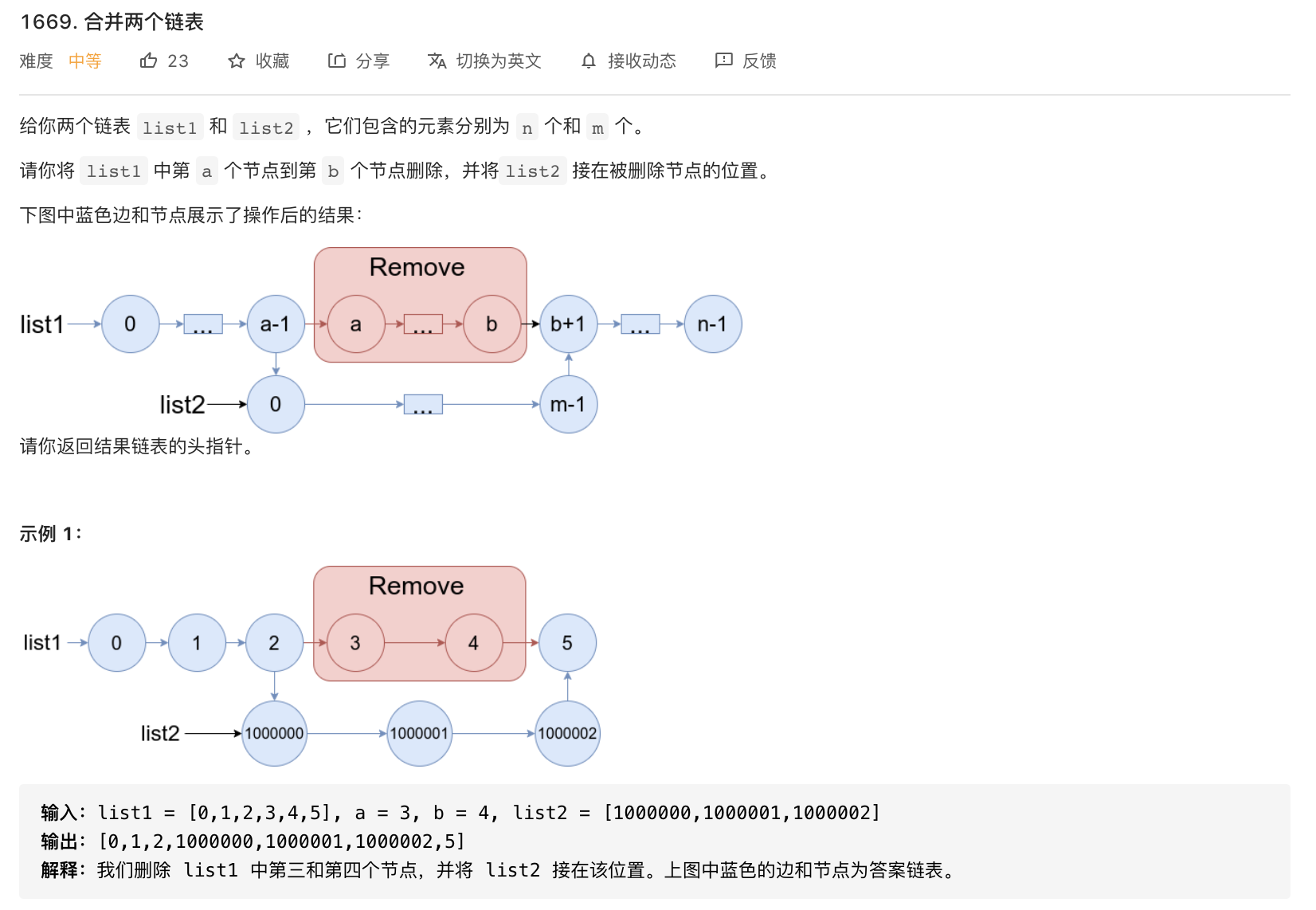
题意分析:
解题思路:
注意点:
代码:
public ListNode mergeInBetween(ListNode list1, int a, int b, ListNode list2) {// 获取链表 1 的前半部分结束节点 和 后半部分的开始节点ListNode head1 = list1, tail1 = list1;ListNode curr1 = list1;while (curr1 != null && b > 0) {if (a > 0) {head1 = curr1;a--;}curr1 = curr1.next;b--;}tail1 = curr1.next;System.out.println("head1 = " + head1.val + "; tail1 = " + tail1.val);// 获取链表 2 的头节点和尾节点ListNode head2 = list2;while (list2.next != null) {list2 = list2.next;}ListNode tail2 = list2;System.out.println("head2 = " + head2.val + "; tail2 = " + tail2.val);// 连接链表head1.next = head2;tail2.next = tail1;return list1;}
模版
题意分析:
解题思路:
注意点:
扩展:
代码:

