遍历问题
105-从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
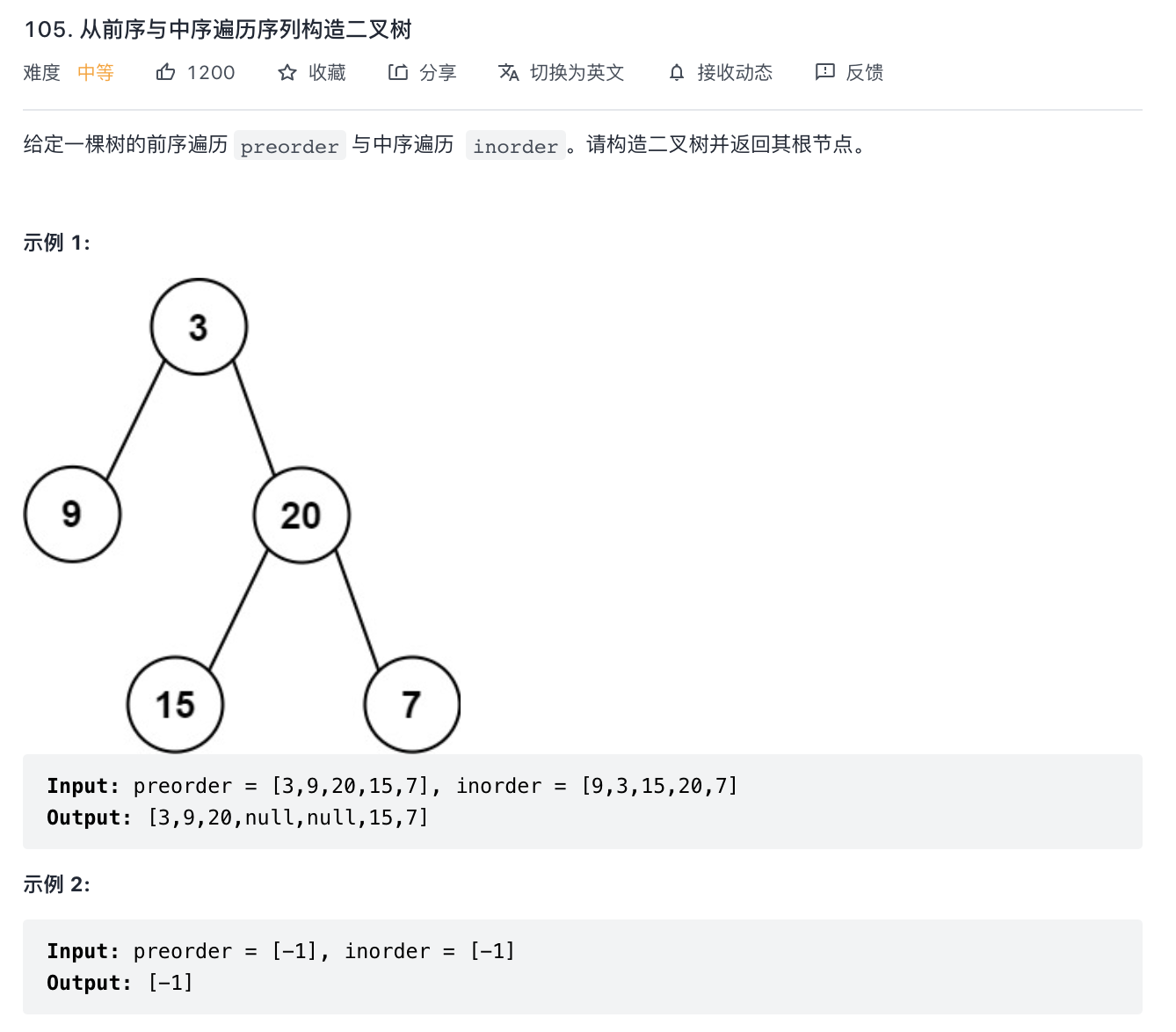
题意分析:
- 根据树的遍历重构二叉树。
解题思路:
- 先根据 preorder 遍历找到 root 节点,找到 root 节点在 inorder 的索引位置 idx,然后递归构造左右子树(难点在于如何根据 idx 分隔左右子树区间)。
注意点:
扩展:
代码:
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {return build(preorder, 0, preorder.length - 1, inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1);}private TreeNode build(int[] preorder, int preStart, int preEnd, int[] inorder, int inStart, int inEnd) {// 递归结束条件if (preStart > preEnd) {return null;}System.out.println(Arrays.toString(preorder) + ": prestart=" + preStart + "; preend=" + preEnd);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(inorder) + " instart=" + inStart +"; inend=" + inEnd);System.out.println();int rootVal = preorder[preStart];// 记录中序遍历中rootVal 对应的位置int idx = -1;// 这里每次递归调用时都会重复遍历inorder 数组,可以通过 HashMap 保持 val 对应的 idx 信息for (int i = inStart; i <= inEnd; i++) {if (inorder[i] == rootVal) {idx = i;break;}}// 根据先序遍历找到新树的 root 节点TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootVal);// left_len = idx - inStartroot.left = build(preorder, preStart + 1, preStart + (idx - inStart), inorder, inStart, idx - 1);root.right = build(preorder, preStart + (idx - inStart) + 1, preEnd, inorder, idx + 1, inEnd);if (root.left != null && root.right != null)System.out.println("root=" + root.val + "; root.left=" + root.left.val + "; root.right=" + root.right.val);return root;}
106-从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
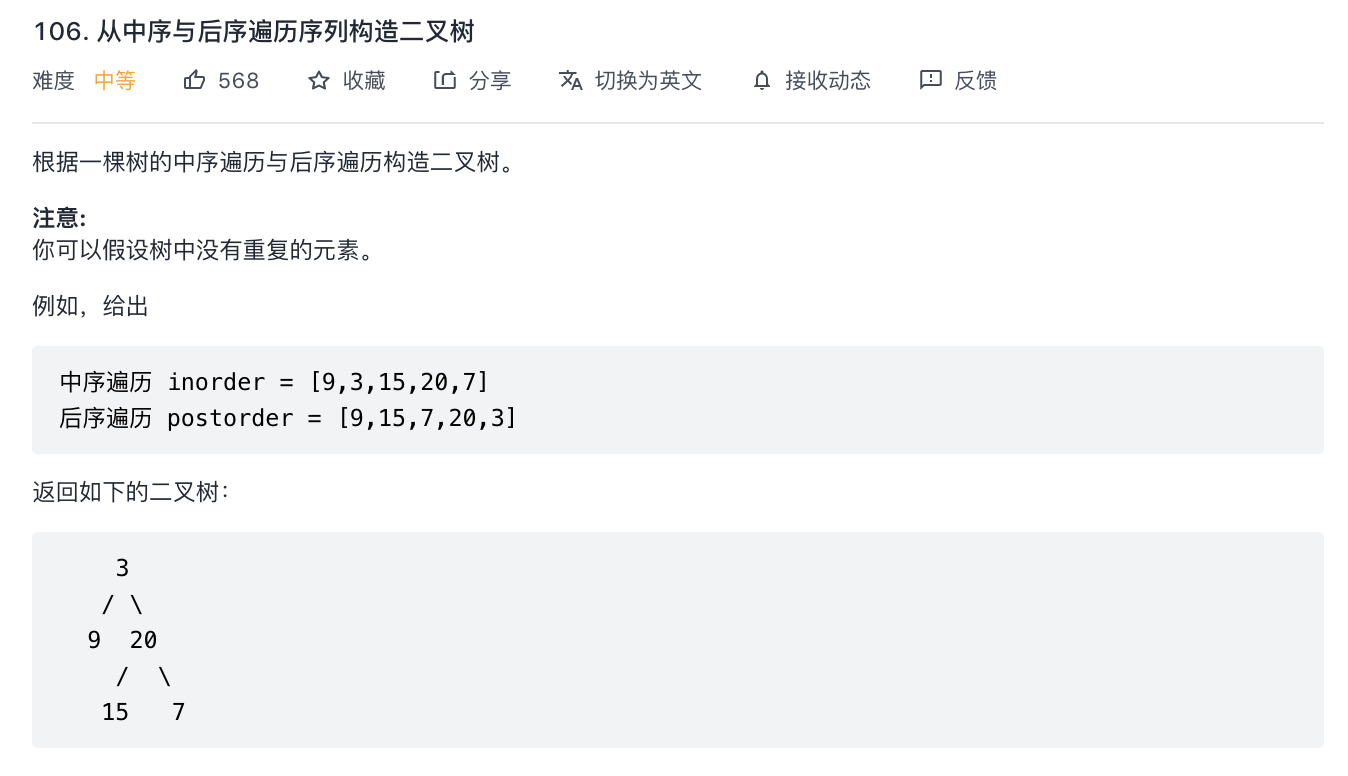
题意分析:
- 和 105 题目差不多,条件序列不同而已。
解题思路:
- 先根据 postorder 遍历找到 root 节点,找到 root 节点在 inorder 的索引位置 idx,然后递归构造左右子树(难点在于如何根据 idx 分隔左右子树区间)。
注意点:
扩展:
代码:
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {return build(inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1, postorder, 0, postorder.length - 1);}private TreeNode build(int[] inorder, int inStart, int inEnd, int[] postorder, int postStart, int postEnd) {if (postStart > postEnd) {return null;}System.out.println(Arrays.toString(inorder) + ": inStart=" + inStart + "; inEnd=" + inEnd);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(postorder) + " postStart=" + postStart +"; postEnd=" + postEnd);System.out.println();int rootVal = postorder[postEnd];// 记录中序遍历中rootVal 对应的位置int idx = -1;for (int i = inStart; i <= inEnd; i++) {if (inorder[i] == rootVal) {idx = i;break;}}// 根据先序遍历找到新树的 root 节点TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootVal);root.left = build(inorder, inStart, idx - 1, postorder, postStart, postStart + (idx - inStart) - 1);root.right = build(inorder, idx + 1, inEnd, postorder, postStart + (idx - inStart), postEnd - 1);System.out.println("root=" + root.val + "; root.left=" + root.left + "; root.right=" + root.right);if (root.left != null && root.right != null)System.out.println("root=" + root.val + "; root.left=" + root.left.val + "; root.right=" + root.right.val);return root;}
二叉树的先序遍历
代码:
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();preorder(root, res);return res;}public void preorder(TreeNode root, List res) {if (root == null) {return;}res.add(root.val);preorder(root.left, res);preorder(root.right, res);}public List<Integer> preorderTraversal2(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();if (root == null) {return res;}stack.push(root);while (!stack.isEmpty()) {TreeNode node = stack.pop();res.add(node.val);if (node.right != null) {stack.push(node.right);}if (node.left != null) {stack.push(node.left);}}return res;}
94-二叉树的中序遍历
代码:
/*** 递归思路:* 1、递归退出条件* 2、递归体*/public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();inorder(root, res);return res;}private void inorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> res) {if (root == null) {return;}inorder(root.left, res);res.add(root.val);inorder(root.right, res);}/*** 非递归思路:* 1、手动维护栈,什么时候进栈,什么时候出栈* @param root* @return*/public List<Integer> inorderTraversal2(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {while (root != null) {stack.push(root);root = root.left;}TreeNode node = stack.pop();res.add(node.val);root = node.right;}return res;}
二叉树的后序遍历
代码:
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();postorder(root, res);return res;}public void postorder(TreeNode root, List res) {if (root == null) {return;}postorder(root.left, res);postorder(root.right, res);res.add(root.val);}public List<Integer> postorderTraversal2(TreeNode root) {List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();Deque<TreeNode> stack = new LinkedList<>();TreeNode pre = null; // 用于记录上一次访问的节点while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {while (root != null) {stack.push(root);root = root.left;}TreeNode node = stack.pop();if (node.right != null) {stack.push(node);root = node.right;} else if (node.right == null || node.right == pre){res.add(node.val);pre = node;root = null;}}return res;}
102-二叉树的层序遍历
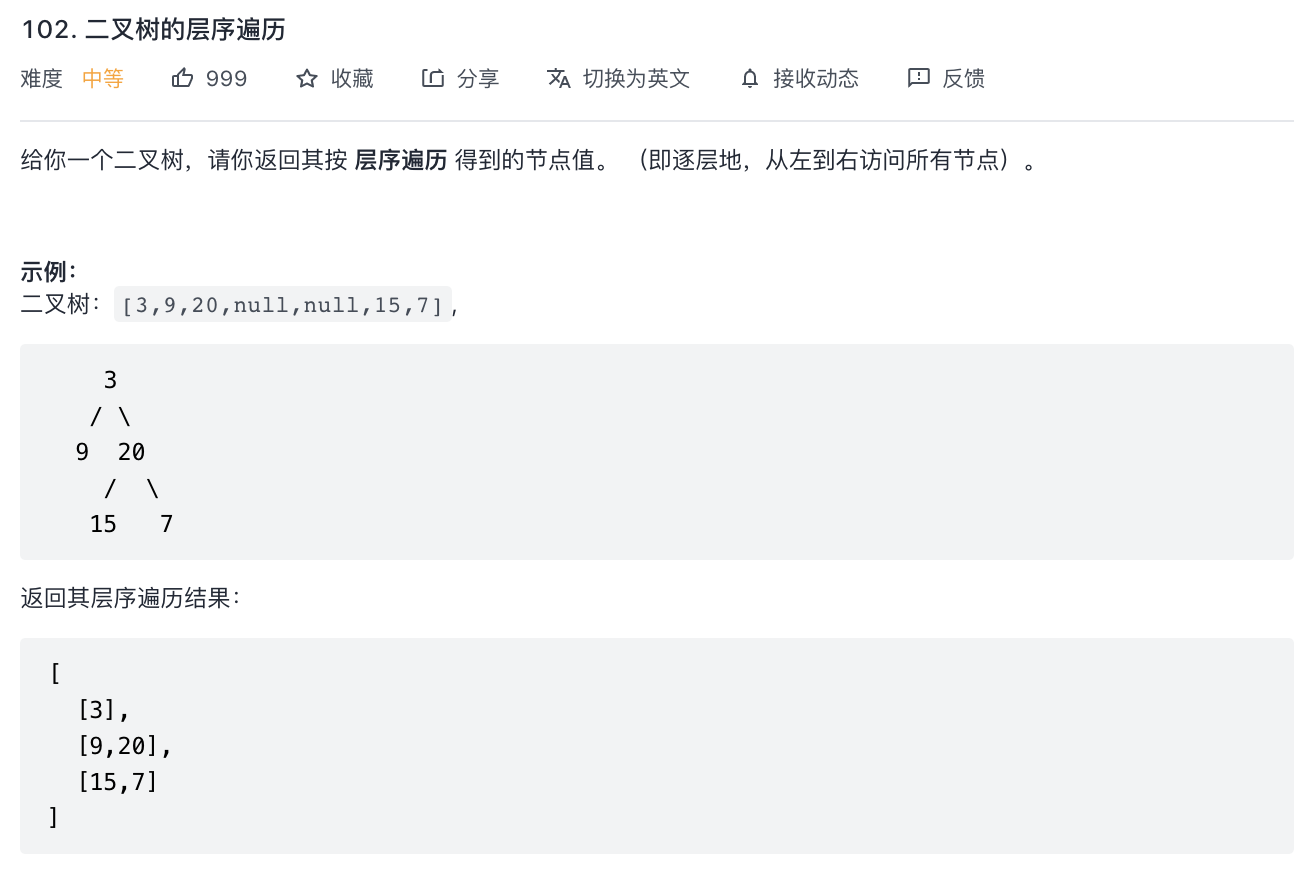
代码:
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();if (root == null) {return res;}Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);while (!queue.isEmpty()) {int size = queue.size();List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();// 逐层记录元素while (size > 0) {TreeNode node = queue.poll();list.add(node.val);if (node.left != null) {queue.offer(node.left);}if (node.right != null) {queue.offer(node.right);}size--;}// 一层元素遍历完了添加到 res 中res.add(list);}return res;}
路径问题
1104-二叉树寻路
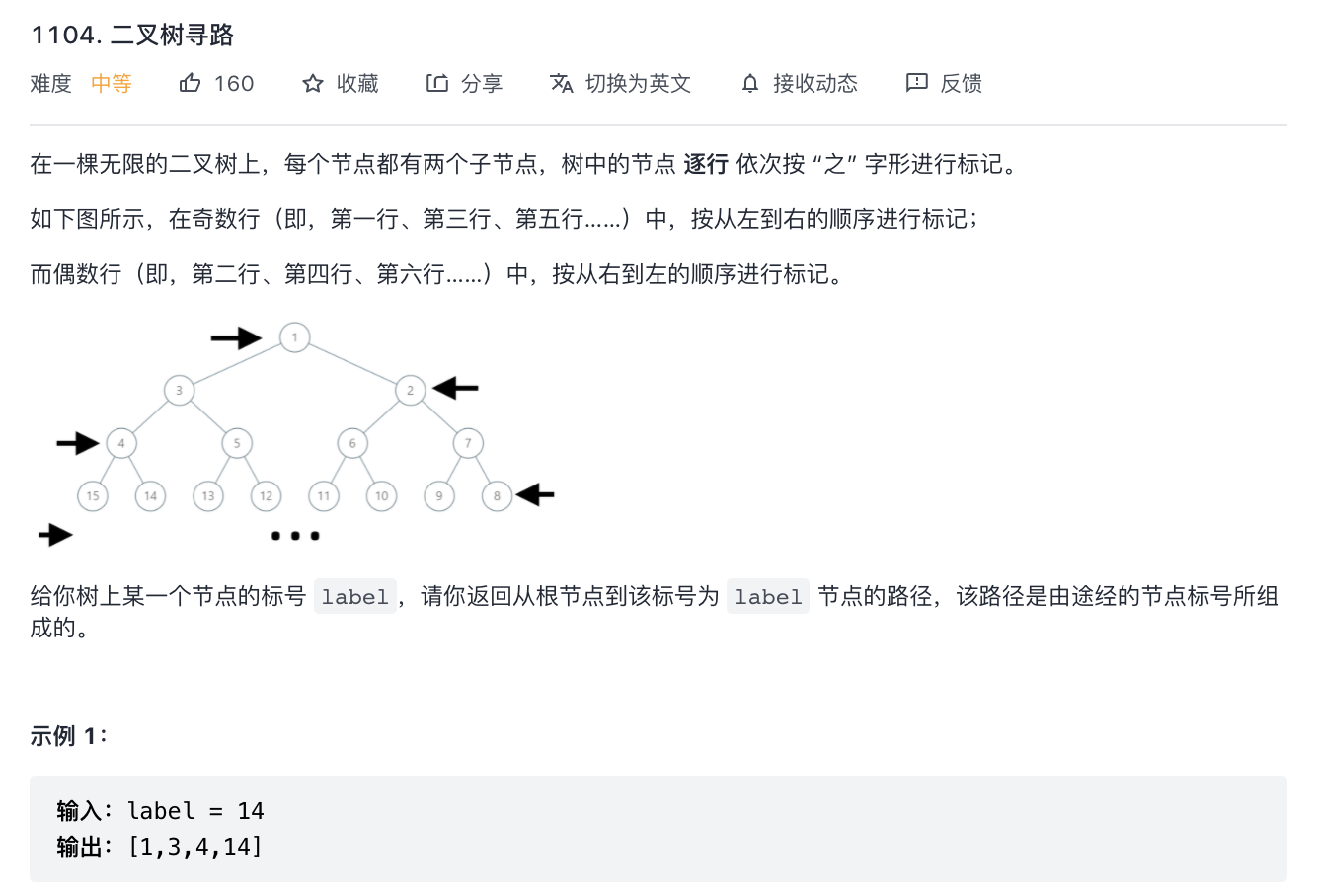
题意分析:
- 打印树根节点到 label 的路径,只不过是树奇偶层级数据进行了反向。
解题思路:
- 按层级遍历完全二叉树,根据对称关系对树进行处理。
注意点:
扩展:
代码:
/*** 解题思路* 特点:完全二叉树* 1、每一行的元素区间为 [2^(level-1), 2^level -1]* @param label* @return*/public List<Integer> pathInZigZagTree(int label) {// 根据 label 得到所在行数int level = 1;// 每一行的最大元素为 2^(row) - 1while (label > (Math.pow(2, level) - 1)) {level++;}// 因为偶数行是反着的,所以在寻路前先和对称元素交换,在处理偶数行时再交换过来。if (level % 2 == 0) {label = (int)(Math.pow(2, level - 1) + Math.pow(2, level)) - 1 -label;}List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();while (level > 0) {// 奇偶行分别处理,奇数行正常处理,偶数行对称处理if (level % 2 == 0) {// 拿到对称的元素。(对称两个元素和是固定的)int val = (int)(Math.pow(2, level - 1) + Math.pow(2, level)) - 1 -label;path.add(val);} else {path.add(label);}// label 往父节点走一次,并且行数减 1label = label / 2;level--;}Collections.reverse(path);return path;}
257-二叉树的所有路径
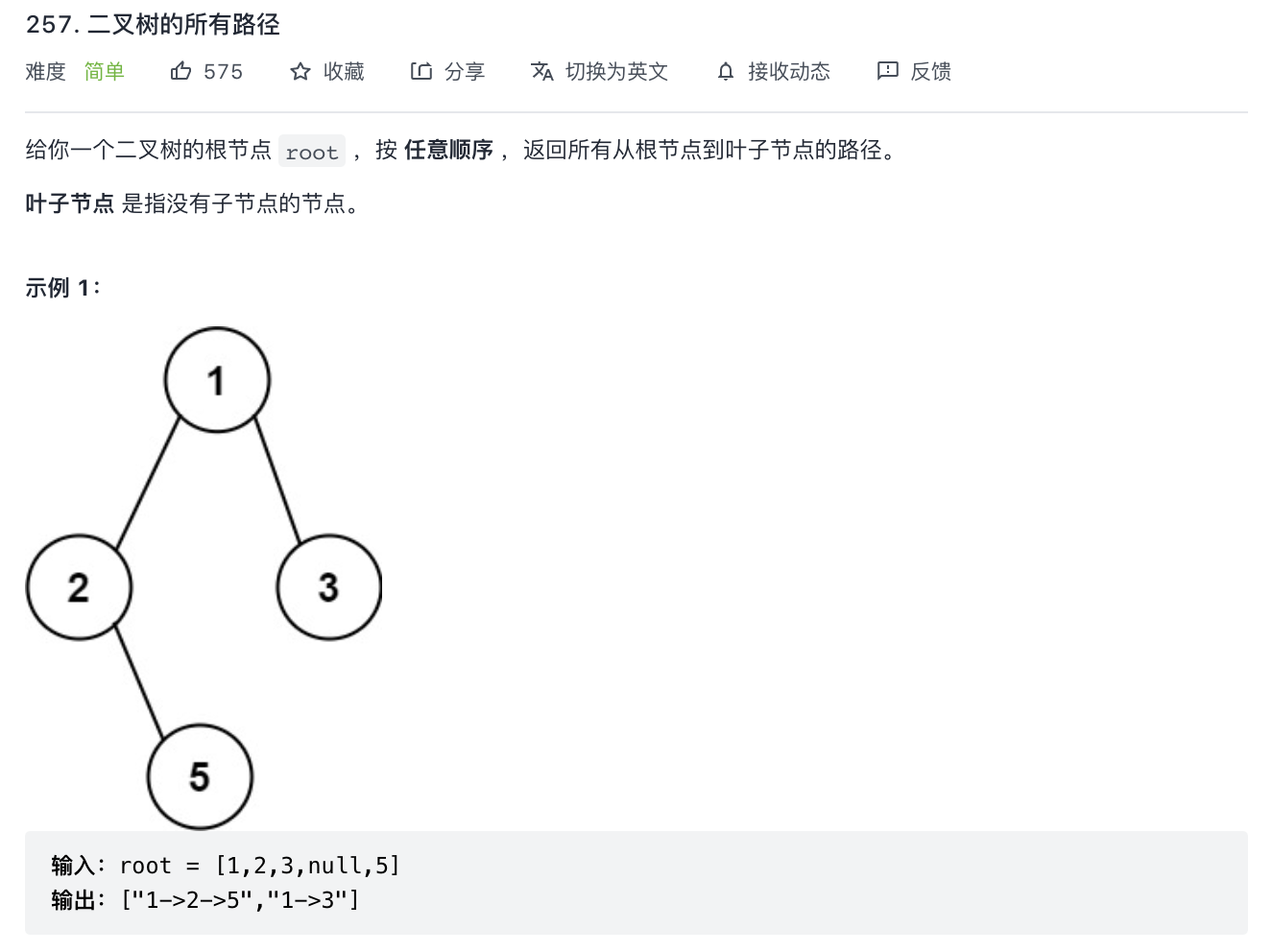
题意分析:
- 打印数的所有路径,显然是要遍历树。
解题思路:
- dfs 深度遍历,遍历到树节点开始回溯。
注意点:
扩展:
- 能否使用 bfs 广度遍历实现?
代码:
/*** dfs深度遍历 + 回溯思想(找完一个往回找)*/List<List<Integer>> res = new LinkedList<>();public List<List<Integer>> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();dfs(root, path);return res;}public void dfs(TreeNode root, LinkedList path) {if (root == null) {return;}path.offer(root.val);if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {res.add(new LinkedList<>(path));// return;}dfs(root.left, path);dfs(root.right, path);path.pollLast();}
112-路径总和 I
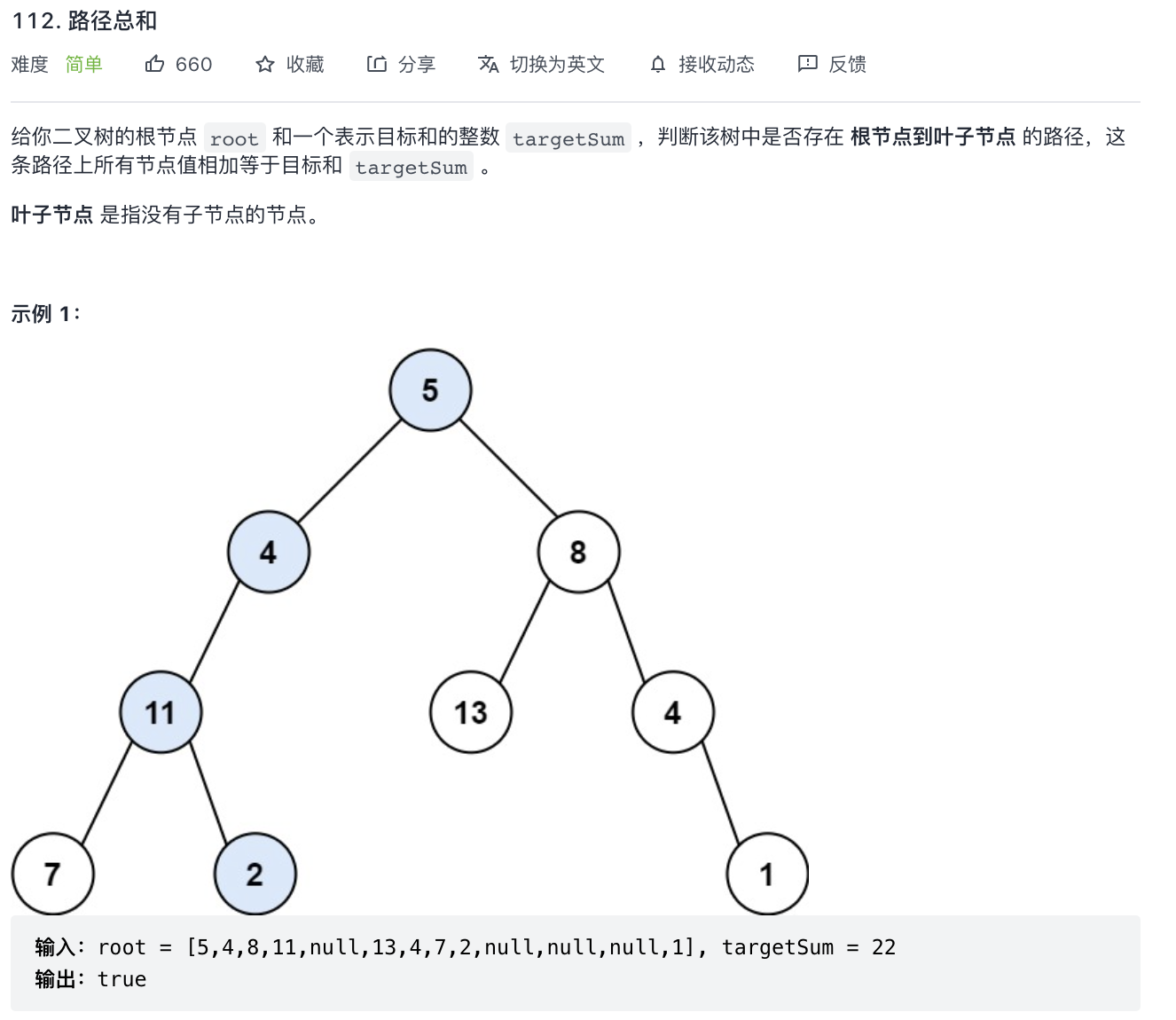
题意分析:
- 判断是否存在从根节点到叶子节点存在和为 sum 的路径。
解题思路:
- dfs 递归遍历,不断减去节点值递归。
- 层序遍历,记录每一层所有节点的和,直到叶子节点,判断是否存在和为 sum 的叶子节点。
注意点:
扩展:
- 如何输出所有路径?
代码:
/*** 先序遍历。** 思考:如果存在路径,如何打印出路径?** @param root* @param sum* @return*/public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {// base caseif (root == null) {return false;}sum -= root.val;if (root.left == null && root.right == null && sum == 0) {return true;}boolean left = hasPathSum(root.left, sum);boolean right = hasPathSum(root.right, sum);return left || right;}
113-路径总和 II
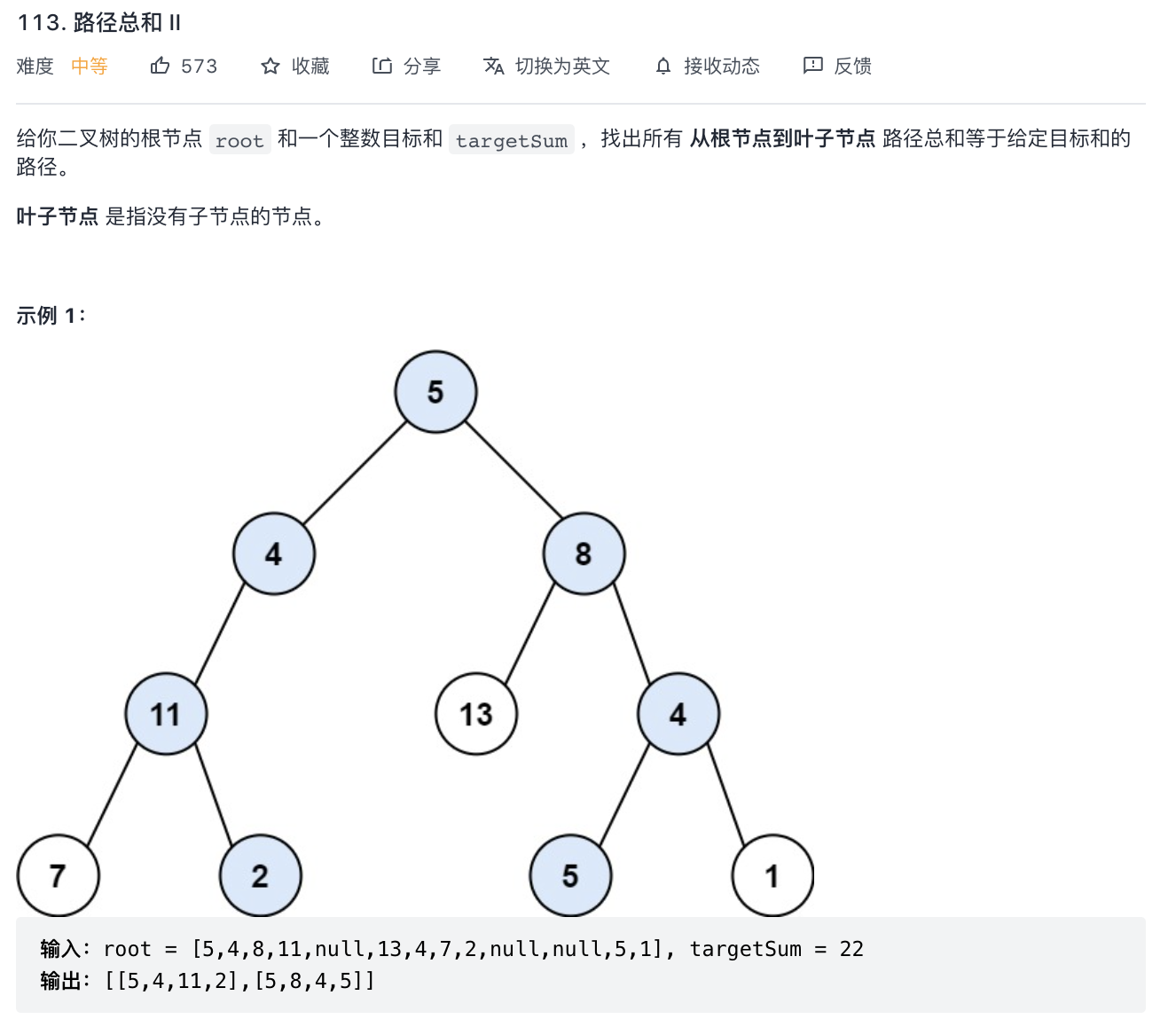
题意分析:
- 输出所有和为 sum 的路径,该路径从根节点到叶子节点。
解题思路:
- dfs。路径问题建议 dfs 算法,可以结合回溯思想遍历到每个叶子节点。
- bfs(层序遍历)。记录每一层节点中到达该节点的路径总和,并且还要记录其父亲节点。
注意点:
- bfs 思路要记录父亲节点,方便在找到节点后输出路径。
扩展:
代码:
// bfs// 记录所有path路径List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();// path:找到预期节点后向上父节点寻找(树特点:一个节点只有一个父亲节点)Map<TreeNode, TreeNode> map = new HashMap<>();public List<List<Integer>> pathSum2(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {if (root == null) {return res;}// 这两个队列元素是一一对应的// 记录层序遍历节点(BFS思想)Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();// 记录当前层级所有节点的和Queue<Integer> sumQueue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);sumQueue.offer(root.val);map.put(root, null);while (!queue.isEmpty()) {int size = queue.size();while (size > 0) {TreeNode curr = queue.poll();int val = sumQueue.poll();if (curr.left == null && curr.right == null && val == targetSum) {getPath(curr);}if (curr.left != null) {queue.offer(curr.left);sumQueue.offer(val + curr.left.val);map.put(curr.left, curr);}if (curr.right != null) {queue.offer(curr.right);sumQueue.offer(val + curr.right.val);map.put(curr.right, curr);}size--;}}return res;}/*** 寻找父亲节点路径* @param leaf*/public void getPath(TreeNode leaf) {List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();while (leaf != null) {list.add(leaf.val);leaf = map.get(leaf);}Collections.reverse(list);res.add(list);}// dfs// 记录所有path路径List<List<Integer>> res2 = new LinkedList<>();public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {dfs(root, targetSum, new LinkedList());return res2;}public void dfs(TreeNode root, int sum, LinkedList path) {if (root == null) {return;}sum -= root.val;path.offer(root.val);if (root.left == null && root.right == null && sum == 0) {res2.add(new LinkedList<>(path));}dfs(root.left, sum, path);dfs(root.right, sum, path);path.pollLast();}
437-路径总和 III

题意分析:
- 输出和为 sum 的路径,该路径不一定包含根节点或叶子节点,只有和为 sum 的节点都可以,且不跨越根节点。
解题思路:
- 结合路径总和II 解法,对所有节点递归调用 II 的逻辑,退出条件为 sum=0 即可。
注意点:
- 递归的退出条件。
扩展:
代码:
// 记录所有path路径List<List<Integer>> res = new LinkedList<>();public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {if (root == null) {return res;}dfs(root, targetSum, new LinkedList<>());// 由于总和不一定包括根节点,对左右孩子节点也要递归遍历pathSum(root.left, targetSum);pathSum(root.right, targetSum);return res;}public void dfs(TreeNode root, int sum, LinkedList path) {if (root == null) {return;}sum -= root.val;path.offer(root.val);// 和路径总和II 问题的区别是这里不用判断节点是否是叶子节点if (sum == 0) {res.add(new LinkedList<>(path));}dfs(root.left, sum, path);dfs(root.right, sum, path);path.pollLast();}
687-最长同值路径(?)

题意分析:
- 树中最长的包含相同 val 的节点,路径可以包含根节点。
解题思路:
- dfs 后序遍历,计算每个节点的左右最大同值数量。
注意点:
扩展:
代码:
int res = 0;public int longestUnivaluePath(TreeNode root) {longestPath(root);return res;}public int longestPath(TreeNode root){if (root == null) {return 0;}int left = longestPath(root.left);int right = longestPath(root.right);if (root.left != null && root.val == root.left.val) {left++;} else {left = 0;}if (root.right != null && root.val == root.right.val) {right++;} else {right = 0;}// 打印当前root节点的左右子树值都最好。// System.out.println(root.val + ": left = " + left +"; right = " + right);// 如果根节点的左右子树res都为1,则表示根节点和左右节点的值 val 相等。res = Math.max(res, left + right);// 返回左右子树的最长同值路径return Math.max(left, right);}
124-二叉树中的最大路径和(?)
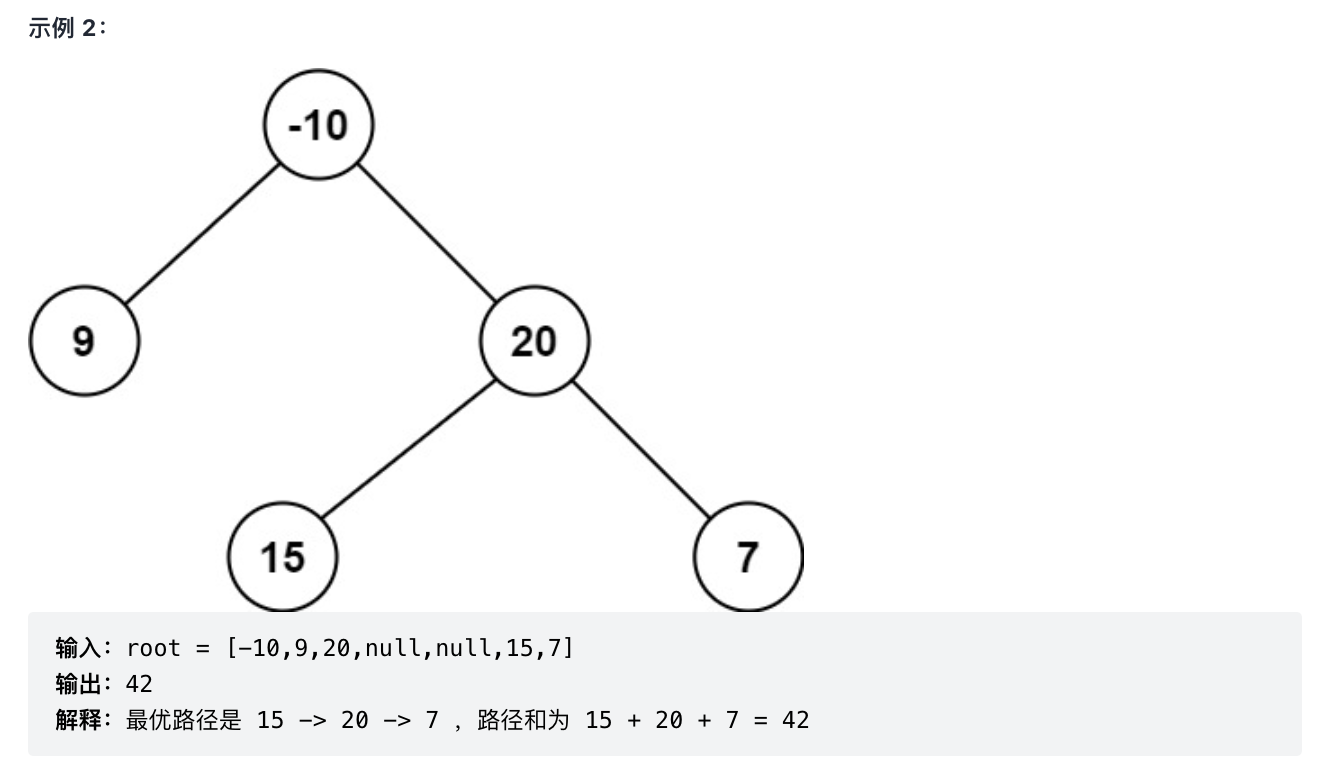
题意分析:
- 二叉树中节点包含负数情况下最大的路径和,可以经过或不经过根节点。
解题思路:
- dfs 遍历分别计算每个节点的左右子树的最大路径和。
注意点:
扩展:
代码:
int maxSum = Integer.MIN_VALUE;public int maxPathSum(TreeNode root) {maxPath(root);return maxSum;}public int maxPath(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) {return 0;}// 如果某个路径小于0,则改路径是无增益路径int left = Math.max(maxPath(root.left), 0);int right = Math.max(maxPath(root.right), 0);System.out.println(root.val + ": left = " + left +"; right = " + right);maxSum = Math.max(maxSum, left + right + root.val);return root.val + Math.max(left, right);}
988-从叶节点开始的最小字符串
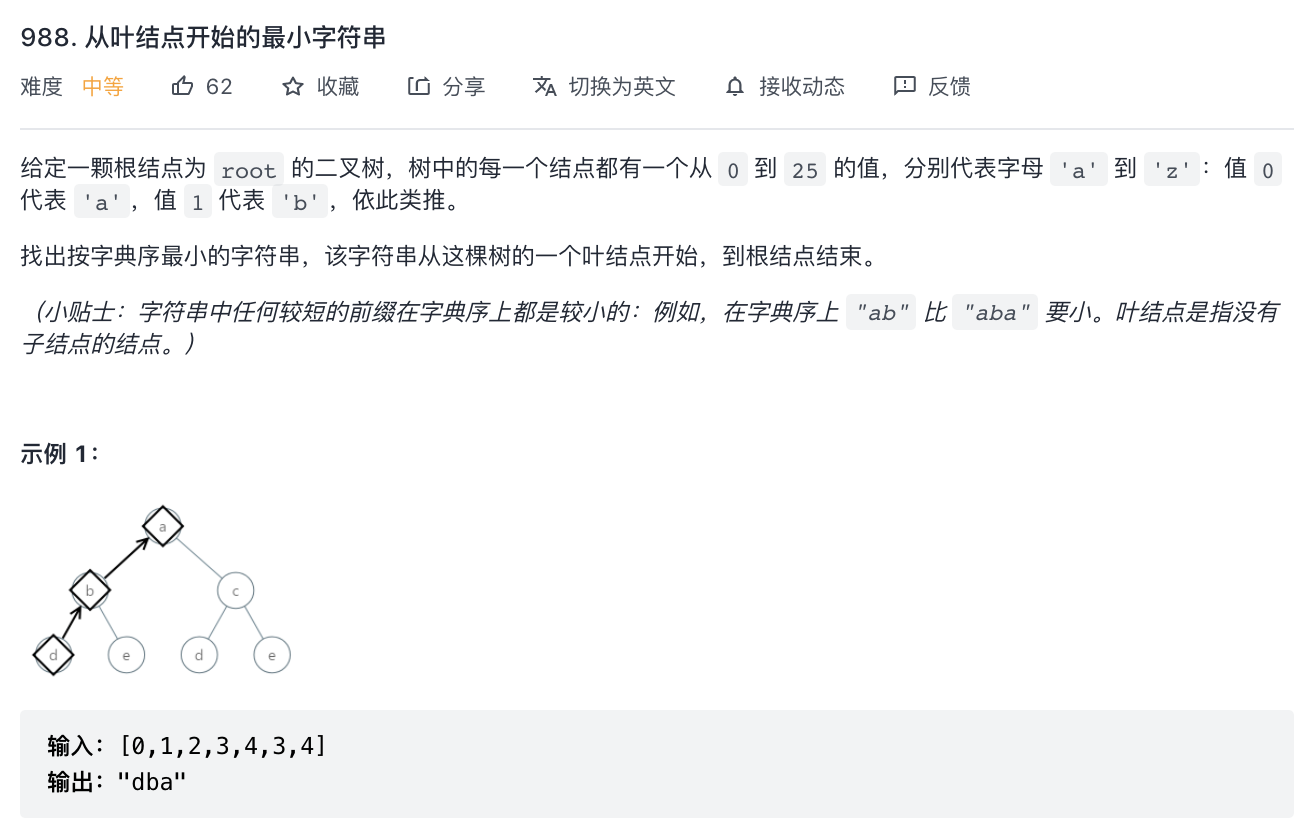
题意分析:
- 从所有叶子节点到根节点的路径中,找到字符串值最小的字符串。
解题思路:
- 类似 路径总和II 问题思路,找到所有路径,比较路径字符串大小。
注意点:
扩展:
代码:
String maxStr = "~";public String smallestFromLeaf(TreeNode root) {dfs(root, new StringBuilder());return maxStr;}public void dfs(TreeNode root, StringBuilder path) {if (root == null) {return;}path.append((char)('a' + root.val));if (root.left == null && root.right == null){path.reverse();String tmp = path.toString();path.reverse();if (tmp.compareTo(maxStr) < 0 ) {maxStr = tmp;}}dfs(root.left, path);dfs(root.right, path);// 回溯,删除 path 中最后一个节点,类似 路径总和II 问题思路path.deleteCharAt(path.length() - 1);}
前缀树
208-实现前缀树
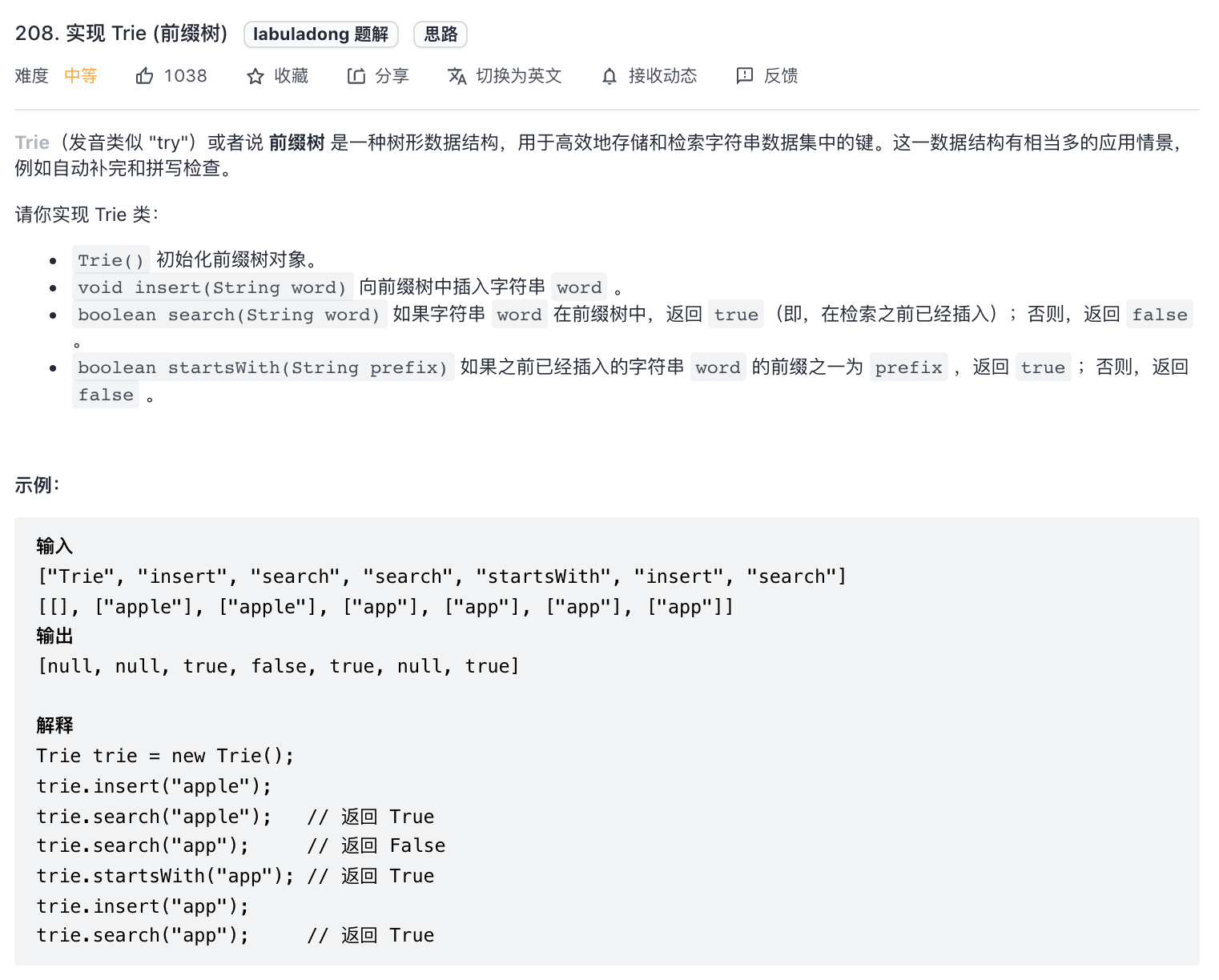
题意分析:
- 前缀树的新增、查找和前缀判断功能。
解题思路:
- 定义前缀树,清楚前缀树的属性功能实现就相对容易。
注意点:
- search() 方法实现的return逻辑,需要判断字符是否是前缀的特殊情况。
扩展:
代码:
public class TreeTrieImpl_208 {TrieNode root;class TrieNode {int pass;int end;TrieNode[] childs;public TrieNode() {pass = 0;end = 0;childs = new TrieNode[26];}}public TreeTrieImpl_208() {root = new TrieNode();}public void insert(String word) {TrieNode node = root;int idx;char[] chs = word.toCharArray();for (int i = 0; i < chs.length; i++) {idx = chs[i] - 'a';if (node.childs[idx] == null) {node.childs[idx] = new TrieNode();}node.childs[idx].pass++;node = node.childs[idx];}node.end++;}public boolean search(String word) {TrieNode node = root;int idx;char[] chs = word.toCharArray();for (int i = 0; i < chs.length; i++) {idx = chs[i] - 'a';if (node.childs[idx] == null) {return false;}node = node.childs[idx];}// 不能直接返回ture,比如'apple'串中搜索'app',要判断是否结束字符return node.end != 0;}public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {TrieNode node = root;int idx;char[] chs = prefix.toCharArray();for (int i = 0; i < chs.length; i++) {idx = chs[i] - 'a';if (node.childs[idx] == null) {return false;}node = node.childs[idx];}return true;}public static void main(String[] args) {TreeTrieImpl_208 treeTrieImpl208 = new TreeTrieImpl_208();treeTrieImpl208.insert("apple");System.out.println(treeTrieImpl208.search("apple")); // 返回 TrueSystem.out.println(treeTrieImpl208.search("app")); // 返回 FalseSystem.out.println(treeTrieImpl208.startsWith("app")); // 返回 TruetreeTrieImpl208.insert("app");System.out.println(treeTrieImpl208.search("app")); // 返回 True}}
648-单词替换
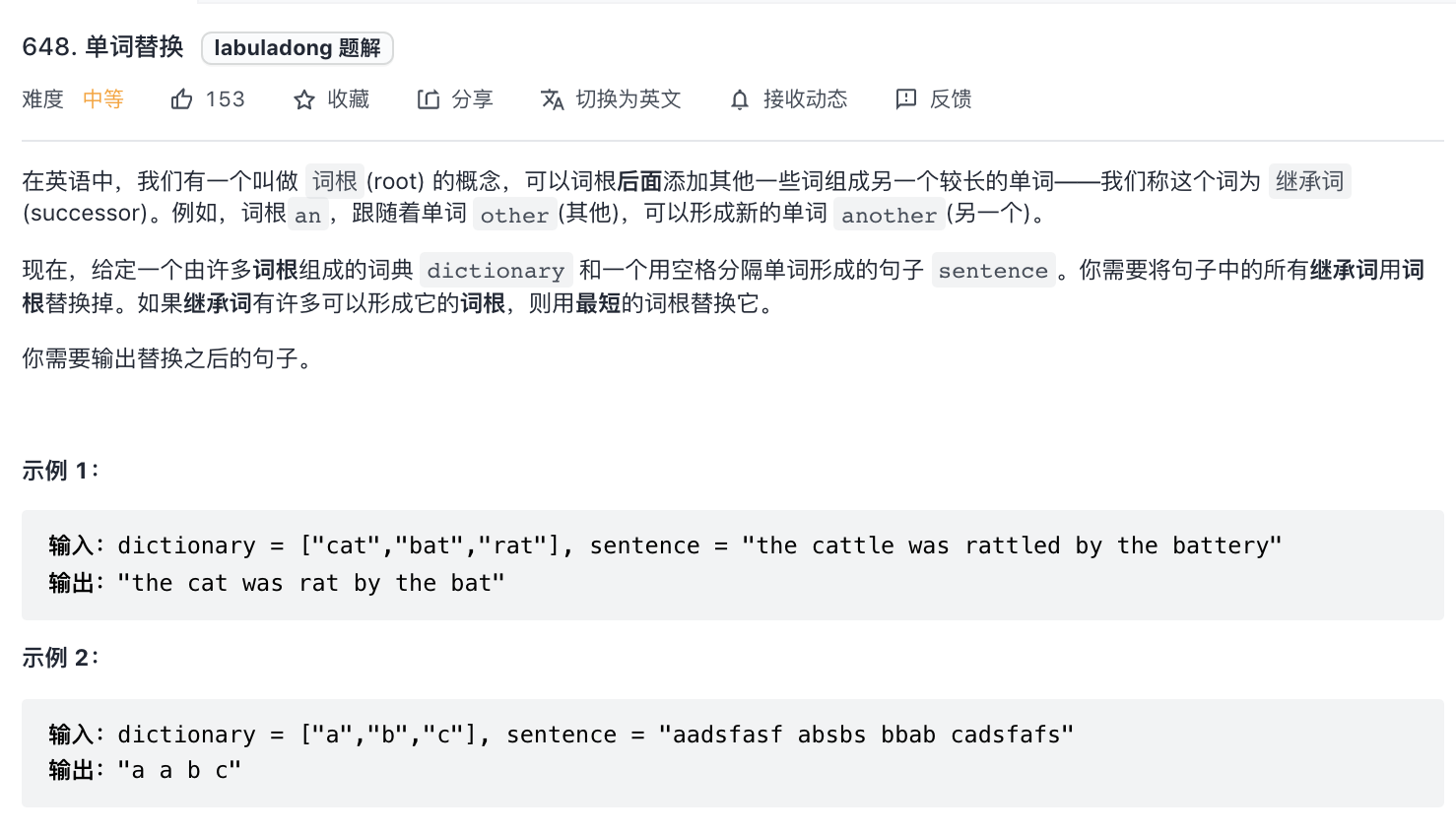
题意分析:
- 如果一个单词在前缀词字典中存在前缀词,则用前缀词替换。
解题思路:
- 选择字典还是句子作为前缀树是关键,然后判断前缀是否存在。
注意点:
扩展:
代码:
public class WordReplace_648 {TrieNode root = new TrieNode();public void insert(String word) {TrieNode node = root;int idx;char[] chs = word.toCharArray();for (int i = 0; i < chs.length; i++) {idx = chs[i] - 'a';if (node.childs[idx] == null) {node.childs[idx] = new TrieNode();}node.pass++;node = node.childs[idx];}node.end++;}public String shortestPrefix(String word) {TrieNode node = root;int idx;char[] chs = word.toCharArray();StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();for (int i = 0; i < chs.length; i++) {if (node.end != 0) { // 找到了存在的前缀break;}idx = chs[i] - 'a';if (node.childs[idx] == null) {return "";}sb.append(chs[i]);node = node.childs[idx];}return sb.toString();}public String replaceWords(List<String> dictionary, String sentence) {String[] strs = sentence.split(" ");// 将 dictionary 中单词构建成前缀树for (int i = 0; i < dictionary.size(); i++) {insert(dictionary.get(i));}StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();for (int i = 0; i < strs.length; i++) {String prefix = shortestPrefix(strs[i]);if (!prefix.isEmpty()) {sb.append(prefix);} else {sb.append(strs[i]);}if (i != strs.length -1) {sb.append(" ");}}return sb.toString();}public static void main(String[] args) {WordReplace_648 obj = new WordReplace_648();List<String> dictionary = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList("cat","bat","rat"));String sentence = "the cattle was rattled by the battery";System.out.println(obj.replaceWords(dictionary, sentence));}}
211-添加与搜索
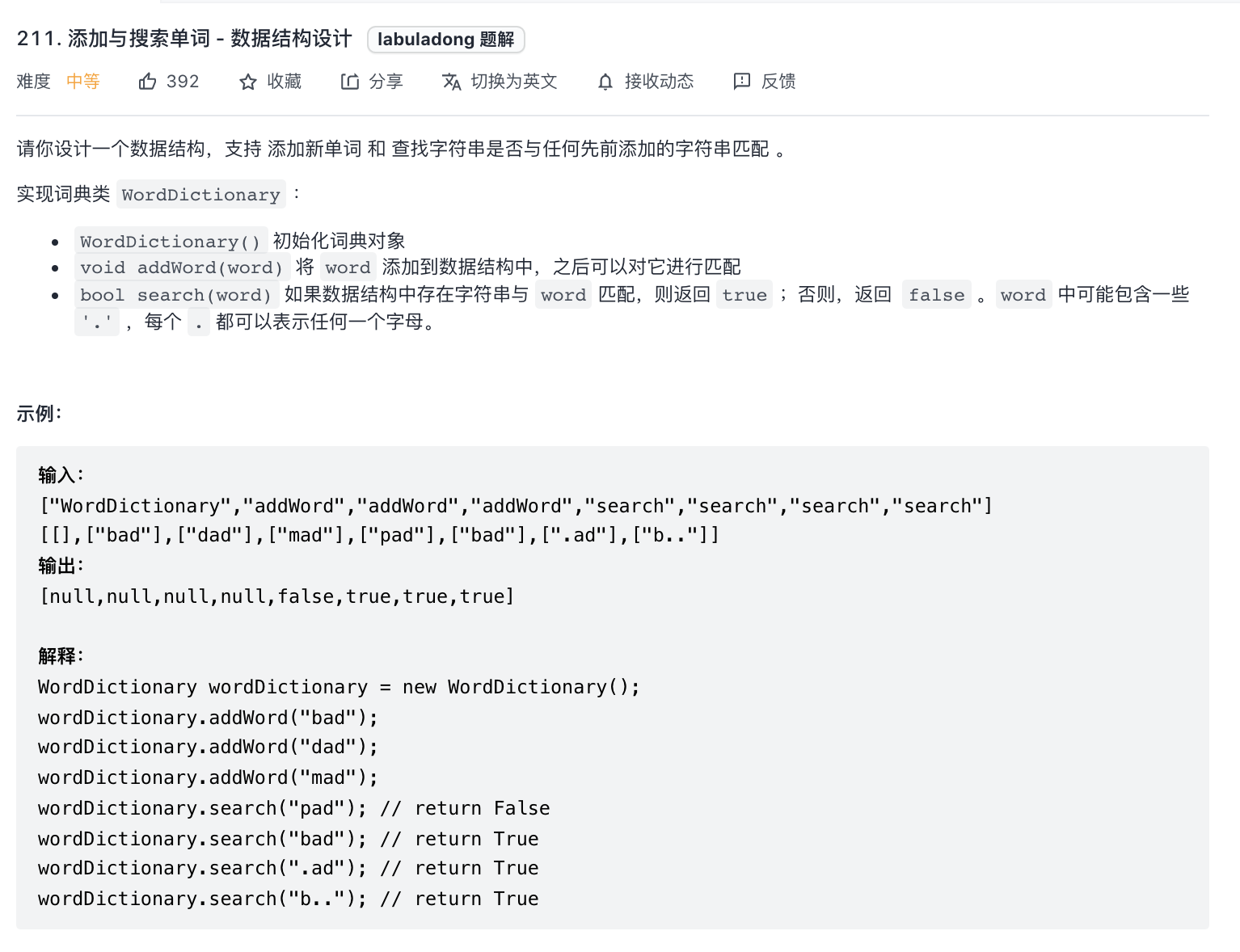
题意分析:
- 前缀树的应用,向前缀树中添加字符串,然后查询prefix前缀是否存在,也存在模式匹配的前缀。
解题思路:
- 构建前缀树,然后采用 dfs + 回溯 方式遍历。
注意点:
- dfs 遍历添加参数 pattern 和 idx 表示递归体在向前遍历。这种递归走向还不是特别容易理解。
扩展:
代码:
public class WordDictionary {TrieNode root;public WordDictionary() {root = new TrieNode();}public void addWord(String word) {if (word == null) {return;}char[] chs = word.toCharArray();TrieNode node = root;node.pass++;int idx;// 遍历每一个字符,两种选择:有路径或者没有路径for (int i = 0; i < chs.length; i++) {idx = chs[i] - 'a';if (node.childs[idx] == null) {// 没有路径则新建路径node.childs[idx] = new TrieNode();}node = node.childs[idx];node.pass++;}node.end++;}public boolean search(String word) {return hasKeyWithPattern(root, word, 0);}private boolean hasKeyWithPattern(TrieNode node, String pattern, int idx) {if (node == null) {return false;}if (idx == pattern.length()) {return node.end != 0;}char ch = pattern.charAt(idx);if (ch == '.') {// '.' 符号则遍历所有子树for (int i = 0; i < node.childs.length; i++) {if (node.childs[i] != null) {if (hasKeyWithPattern(node.childs[i], pattern, idx + 1))return true;}}} else {return hasKeyWithPattern(node.childs[ch - 'a'], pattern, idx + 1);}return false;}public static void main(String[] args) {WordDictionary wordDictionary = new WordDictionary();wordDictionary.addWord("at");wordDictionary.addWord("and");wordDictionary.addWord("an");wordDictionary.addWord("add");System.out.println(wordDictionary.search("a")); // return FalseSystem.out.println(wordDictionary.search(".at")); // return FalsewordDictionary.addWord("bat");System.out.println(wordDictionary.search(".at")); // return true}}
677-键值映射
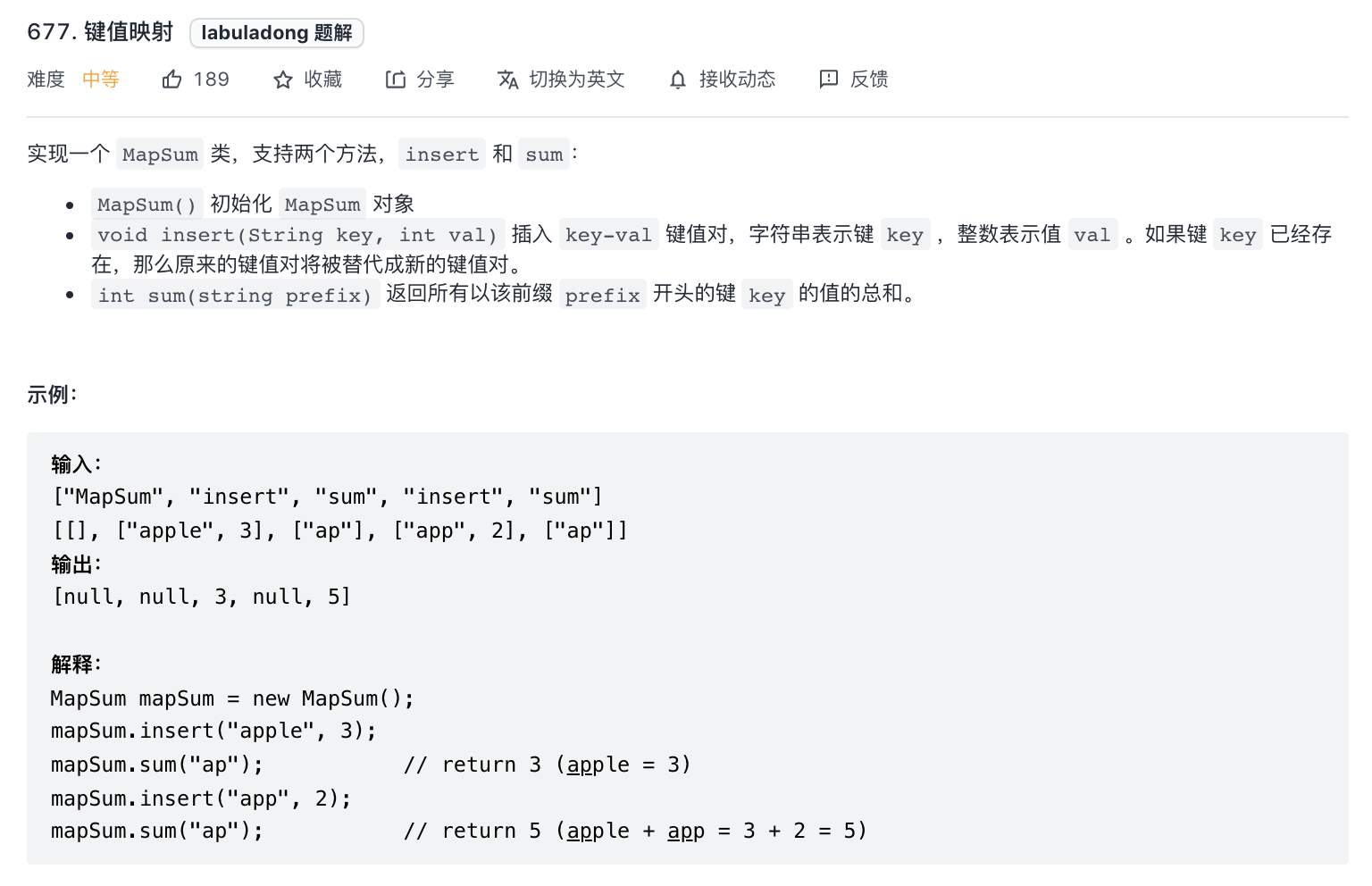
题意分析:
- 首先是判断前缀prefix是否是存在字符串的前缀,如果是,求所有以 prefix 为前缀的字符的 val 的和。
解题思路:
- 熟悉前缀树的基本操作就比较容易,首先构建前缀树,然后判断前缀 prefix 是否是合法的(即 getNode 判断前缀是否存在对应的路径节点),最后从 prefix 的路径结束节点开始 dfs 遍历,求所有叶子节点的 val 和。
注意点:
扩展:
代码:
public class TrieMapSum_677 {TrieNode root;public TrieMapSum_677() {root = new TrieNode();}public void insert(String key, int val) {TrieNode node = root;node.pass++;int idx;char[] chs = key.toCharArray();for (int i = 0; i < chs.length; i++) {idx = chs[i] - 'a';if (node.childs[idx] == null) {node.childs[idx] = new TrieNode();}node = node.childs[idx];node.pass++;}node.end++;node.val = val;}int sum = 0;public int sum(String prefix) {sum = 0;TrieNode node = getNode(prefix);if (node == null) {return 0;}// 以node为根节点递归遍历,求其子树下所有叶子节点的和dfs(node);return sum;}public void dfs(TrieNode node) {if (node == null) {return;}if (node.end != 0) {sum += node.val;}// 树的先序遍历。(多叉树)for (int i = 0; i < node.childs.length; i++) {if (node.childs[i] != null) {dfs(node.childs[i]);}}}public TrieNode getNode(String prefix) {TrieNode node = root;int idx;char[] chs = prefix.toCharArray();for (int i = 0; i < chs.length; i++) {idx = chs[i] - 'a';if (node.childs[idx] == null) {return null;}node = node.childs[idx];}return node;}public static void main(String[] args) {TrieMapSum_677 mapSum = new TrieMapSum_677();mapSum.insert("apple", 3);System.out.println(mapSum.sum("ap")); // return 3 (apple = 3)mapSum.insert("app", 2);System.out.println(mapSum.sum("ap")); // return 5 (apple + app = 3 + 2 = 5)}}
未分类
543-二叉树的直径

题意分析:
- 直径定义:无非就是判断根节点的左右子树深度,两者和即为直径。
解题思路:
- 后序遍历,计算每个节点的左右子树深度。
注意点:
扩展:
代码:
int res = 0;public int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {diameter(root);return res;}public int diameter(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) {return 0;}int left = diameter(root.left);int right = diameter(root.right);if (root.left != null) {left++;} else {left = 0;}if (root.right != null) {right++;} else {right = 0;}System.out.println(root.val + ": left = " + left +"; right = " + right);// 统计最长路径。如果是统计节点: left + right + 1res = Math.max(res, left + right);return Math.max(left, right);}
101-对称二叉树
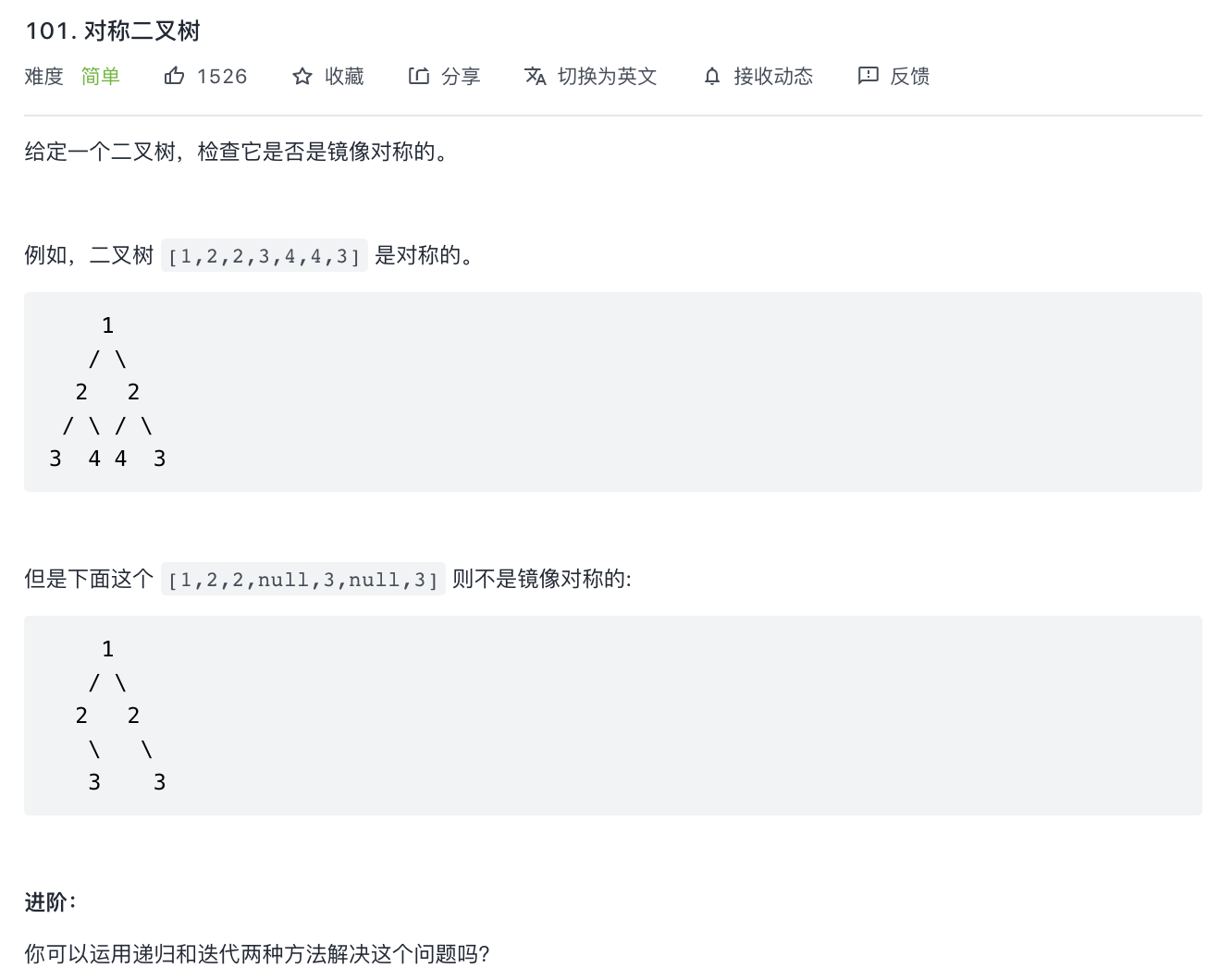
题意分析:
- 判断 p.left 和 q.right 元素是否是一致的
解题思路:
- bfs 遍历。每次入队两个元素,即对称的两个节点元素,判断是否对称。
- dfs 遍历。递归判断两个节点。
注意点:
扩展:
代码:
/*** bfs 遍历* @param root* @return*/public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);queue.offer(root);while (!queue.isEmpty()) {TreeNode p = queue.poll();TreeNode q = queue.poll();if (p == null && q == null) {continue;}if (p == null || q == null || p.val != q.val) {return false;}queue.offer(p.left);queue.offer(q.right);queue.offer(p.right);queue.offer(q.left);}return true;}/*** dfs 遍历* @param root* @return*/public boolean isSymmetric2(TreeNode root) {return check(root, root);}private boolean check(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {if (p == null && q == null) {return true;}if (p == null || q == null)return false;return (p.val == q.val) && check(p.left, q.right) && check(p.right, q.left);}
104-二叉树的最大深度
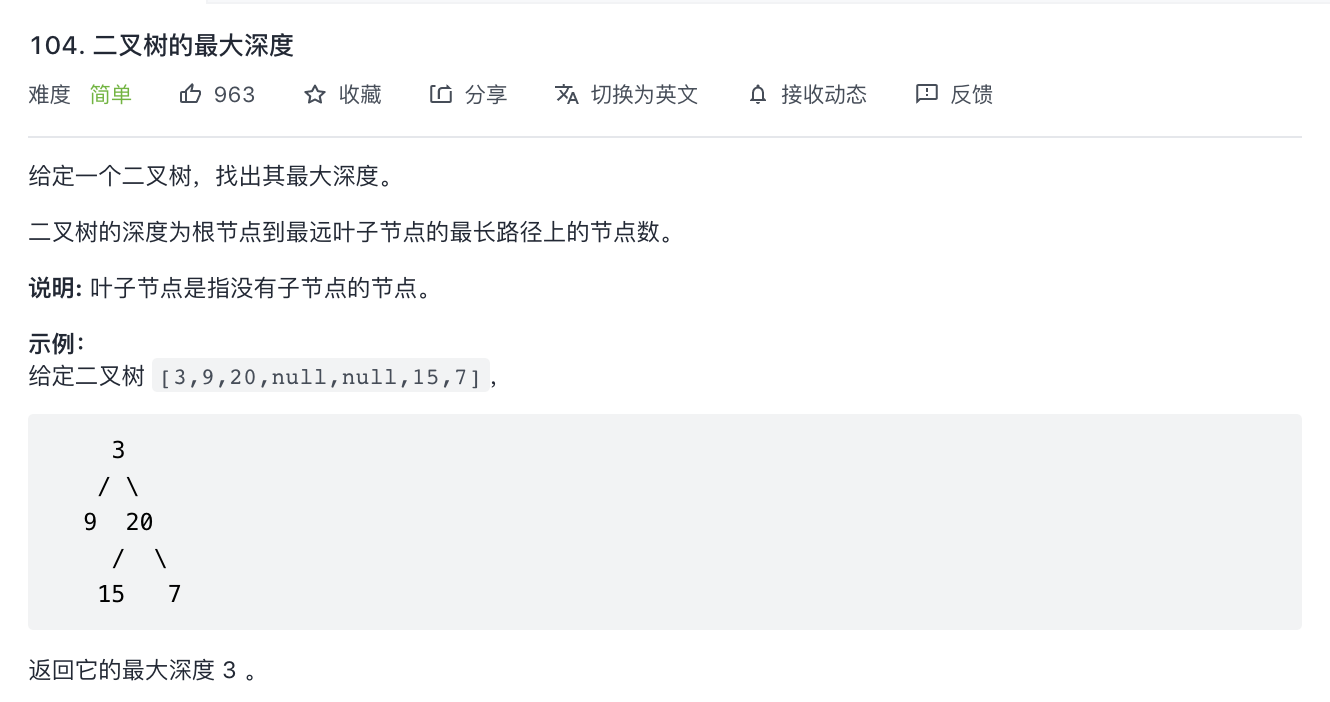
题意分析:
- 树的最大深度。
解题思路:
- bfs 最直观,遍历每一层的节点。
- dfs 后序(自底向上)遍历记录每个节点的左右最大深度。
注意点:
扩展:
代码:
/*** 树的深度优先遍历* @param root* @return*/public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) {return 0;}int leftDepth = maxDepth(root.left);int rightDepth = maxDepth(root.right);return Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;}public int maxDepth2(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) {return 0;}Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);int depth = 0;while (!queue.isEmpty()) {// size 记录每一层节点的数量,一层节点出队列完毕后深度+1int size = queue.size();while (size > 0 ) {TreeNode node = queue.poll();if (node.left != null) {queue.offer(node.left);}if (node.right != null) {queue.offer(node.right);}size--;}depth++;}return depth;}
111-二叉树的最小深度
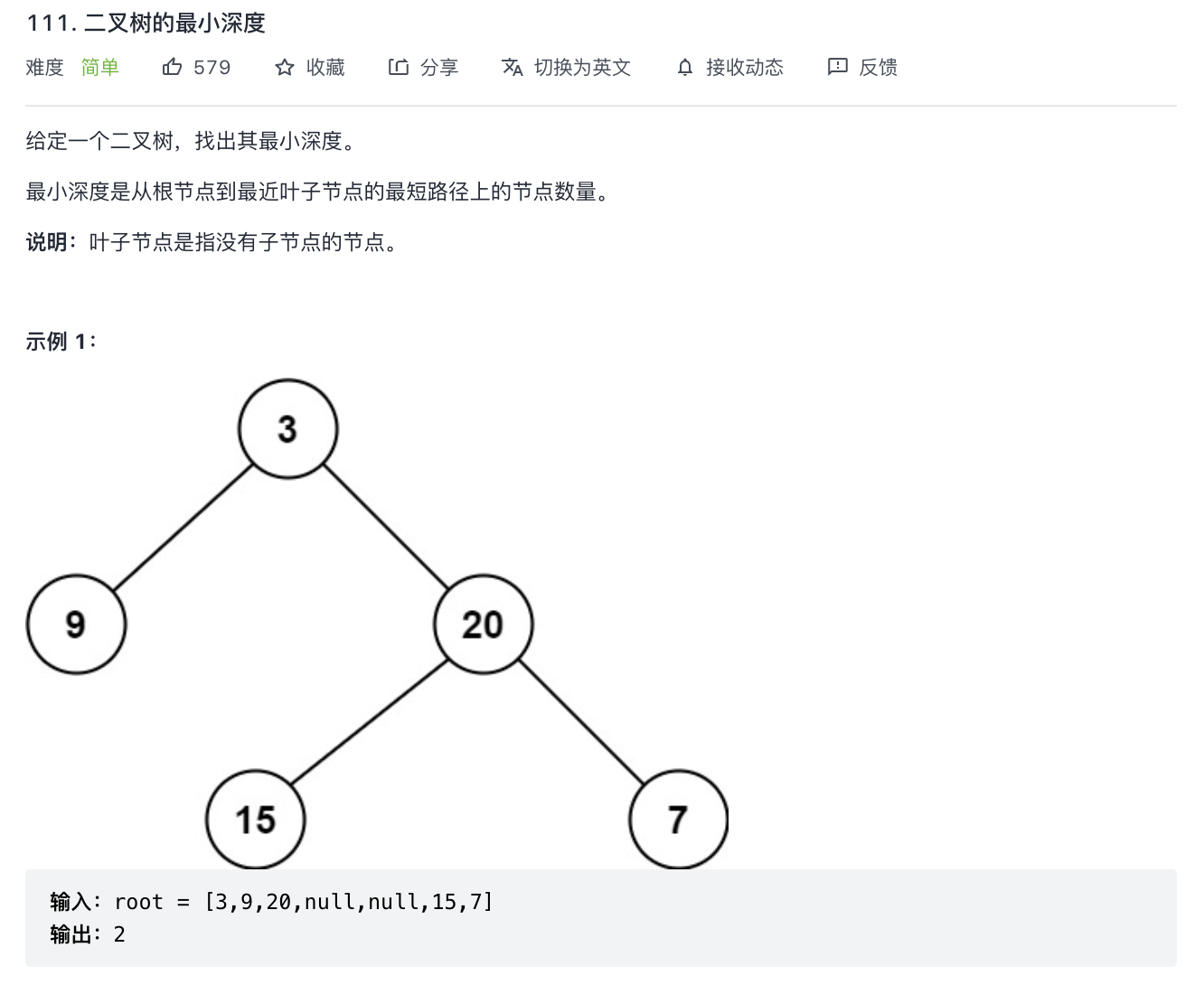
题意分析:
- 和最大深度差不多。
解题思路:
- bfs 遍历最简单,遇到叶子节点直接返回深度。
注意点:
扩展:
代码:
int res = Integer.MAX_VALUE;public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {if (root == null) {return 0;}Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();queue.offer(root);int depth = 0;while (!queue.isEmpty()) {// size 记录每一层节点的数量,一层节点出队列完毕后深度+1int size = queue.size();while (size > 0 ) {TreeNode node = queue.poll();if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {return ++depth;}if (node.left != null) {queue.offer(node.left);}if (node.right != null) {queue.offer(node.right);}size--;}depth++;}return depth;}
987-二叉树的垂序遍历

题意分析:
- 根据每个节点 x/y 值对树节点进行遍历。
解题思路:
- 逻辑思路比较清晰。
- 先遍历树,计算每个节点的 x 和 y 值。
- 然后对所有节点排序,自定义排序器,分别按 y、x、val 升序遍历。
- 分组输出节点元素。
注意点:
扩展:
代码:
/*** 题目考查的知识点:* 1、二叉树的遍历;* 2、Java 比较器的实现;* 3、数组/List 的遍历技巧。* List[1,2,3,3,3,4,4,5] = 统计每个单词出现的次数,并放在不同集合中。[[1],[2],[3,3,3],[4,4],[5]]*/public class VerticalTraversal_987 {List<VerticalNode> nodeList = new ArrayList<>();public List<List<Integer>> verticalTraversal(TreeNode root) {// 遍历树节点,获得每个节点的 [x, y , val] 组值dfs(root, 0, 0);// System.out.println("----------排序前--------");// for (VerticalNode node : nodeList) {// System.out.println(node.val + ": " + node.x + ": " + node.y);// }// 排序,先根据列 y 升序排序,如果 y 相同,则按照 val 升序排序Collections.sort(nodeList, new Comparator<VerticalNode>() {@Overridepublic int compare(VerticalNode o1, VerticalNode o2) {if (o1.y != o2.y) {return o1.y - o2.y; // 按 y 升序} else if (o1.x != o2.x) {return o1.x - o2.x; // 按 x 升序} else {return o1.val - o2.val;}}});System.out.println("----------排序后--------");for (VerticalNode node : nodeList) {System.out.println(node.val + ": " + node.x + ": " + node.y);}// 排序后输出结果List<List<Integer>> retList = new ArrayList<>();List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();int last_y = Integer.MIN_VALUE;// 记录有多少组不同 y 元素int size = -1;// 此时遍历可忽略 行x 的影响,因为 x 是有序的,List 也是有序的,根据 y 遍历输出 val 的值即可。for (VerticalNode node : nodeList) {if (node.y != last_y) {size++;last_y = node.y;list.add(node.val);retList.add(list);list = new ArrayList<>();} else {retList.get(size).add(node.val);}}System.out.println(retList);return retList;}public void dfs(TreeNode root, int x, int y) {if (root == null) {return;}nodeList.add(new VerticalNode(root.val, x, y));// 对左右子树递归遍历dfs(root.left, x+1, y-1);dfs(root.right, x+1, y+1);}/*** 1* 2 3* 4 5*/public static void main(String[] args) {VerticalTraversal_987 obj = new VerticalTraversal_987();System.out.println(obj.verticalTraversal(Utils.createTree2()));}class VerticalNode {int val;int x;int y;public VerticalNode(int val, int x, int y) {this.val = val;this.x = x;this.y = y;}}}
模版
题意分析:
解题思路:
注意点:
扩展:
代码:

