1 Doxygen的简单使用
Doxygen是一个程序的文档产生工具,可以将程序中的注释转换成说明文档或者说是API参考手册,从而减少程序员整理文档的时间。当然这里程序中的注释需要遵循一定的规则书写,才能让Doxygen识别和转化。
目前Doxygen可处理的程序语言包含C/C++、Java、Objective-C、IDL等,可产生出来的文档格式有HTML、XML、LaTeX、RTF等,此外还可衍生出不少其它格式,如HTML可以打包成CHM格式,而LaTeX可以通过一些工具产生出PS或是PDF文档等。
1.1 Doxygen注释语法
- 单行注释:///或者//!
- 多行注释:/*或者/!
- @author 作者
- @brief 摘要
- @version 版本号
- @date 日期
- @file 文件名,可以默认为空,DoxyGen会自己加
- @class 类名
- @param 函数参数
- @return 函数返回值描述
- @exception 函数抛异常描述
- @warning 函数使用中需要注意的地方
- @remarks 备注
- @see see also字段
- @note brief下空一行后的内容表示详细描述,但也可以不空行用note表示
- @par 开始一个段落,段落名称描述由你自己指定,比如可以写一段示例代码
- @code 引用代码段
- @endcode 引用代码段结束
- @pre 函数前置条件,比如对输入参数的要求
- @post 函数后置条件,比如对系统状态的影响或返回参数的结果预期
附带我感觉不太会常用到的其他标记:
- @defgroup 模块名
- @name 分组名
- @{ 模块开始
- @} 模块结束
- @deprecated 今后可能将被废弃或已经有替代品的函数
- @todo 被标记的代码会在ToDo列表中出现
- @bug 被标记的代码会在Bug列表中出现
- @test 被标记的代码会在Test列表中出现
1.2 应用示例
使用doxygen解析之后,会生成html的文件,打开之后显示如下(简直就是API文档):/*** @brief main function* @details the program start point** @param argc input parameter counts* @param argv input parameters array* @return exec result* @retval 0 run OK* @retval 1 run failed* @note just a sample example*/int main(int argc, char* argv[]){return 0;};
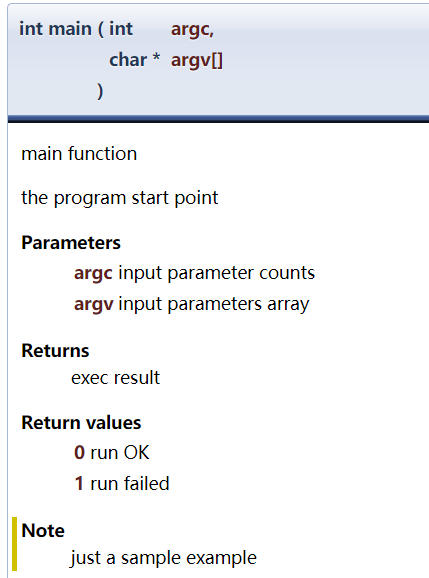
1.3 注意事项
- 不要使用@file
标签,因为文件名可能会变化;可以不带 ,让doxygen自动读取文件名 - 不要手动编辑@version、@author、@date标签,版本控制系统可以自动填充。
- 不要使用@bug、@todo标签,说明代码有缺陷或没有完成,应该由bug管理系统记录
- 建议使用@mainpage标签描述项目的主页
- 建议使用doxygen分组机制表达内聚的子模块,@defgroup、@addgroup、@ingroup
2 const的多种用途
- 将变量定义为常量:
const long double PI = 3.141592653589794; - 防止参数参数被修改:例如
- 输入指针参数指向Car的常量对象,对象不能被修改:
unsigned int determineWeightOfCar(Car ``const``* car); - 输入指针参数指向Car的指针常量,对象可以修改,指针的指向不能修改:
void lacquerCar(Car* ``const ``car); - 结合1&2,对象和指针指向都不能修改:
unsigned int determineWeightOfCar(Car const* const car); - const引用,message在函数内不能修改:
void printMessage(const std::string& message); - 也是const引用,效果一样:
void printMessage(std::string const& message);
- 输入指针参数指向Car的常量对象,对象不能被修改:
- 将类的成员函数声明为const,表示不能修改类中成员变量:
```cpp
class Car {
public:
std::string getRegistrationCode() const
{
}std::string toBeReturned = registrationCode;_registrationCode = "foo"; // 这里要修改成员变量,编译出错return toBeReturned;
private: std::string _registrationCode; };
> 记忆方法:> - **const总是修饰它左边的内容**> - **如果const在开头,则修饰它右边的内容**<a name="UXrye"></a># 3 C++ IO Stream<a name="LlL2f"></a>## 3.1 stringStream操作字符串[Cpp_sstream](https://www.yuque.com/barret/snelnn/gw1wee?view=doc_embed)<a name="oRiKN"></a>## 3.2 类重载<<运算符```cppclass Invoice{private://使用friend重载<<运算符,之后就可以用cout打印了friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& outstream, const Invoice& invoice){outstream << "Invoice No.: " << invoice.invoiceNumber << "\n";outstream << "Recipient: " << *(invoice.recipient) << "\n";outstream << "Date/time: " << invoice.getDateTimeOfInvoicingAsString() << "\n";outstream << "Items:" << "\n";for (const auto& item : invoice.invoiceLineItems){outstream << " " << *item << "\n";}outstream << "Amount invoiced: " << invoice.getSum() << std::endl;return outstream;}UniqueIdentifier invoiceNumber;DateTime dateTimeOfInvoicing;InvoiceRecipientPtr recipient;InvoiceLineItems invoiceLineItems;};
4 C++类型转换
C++的类型转换会在编译器编译期间进行检查,而C风格的强制转换不会做任何检查,所以在运行时会出错,导致严重问题或崩溃。
比如下面的例子:
#include <iostream>#include <string>#include <string.h>#include <stdio.h>using namespace std;int main(int argc, char* argv[]){int a = 200; //4个字节long* b = (long*)&a; //8个字节的指针,强制指向4字节内存地址cout<<*b<<endl;*b = 9223372036854775807; //这里数字会溢出,程序崩溃cout<<*b<<endl;return 0;};
将上面的强制转换用C++风格重新编写后,在编译时会检测到错误:long* b = static_cast<long*>(&a);a.cpp:10:36: error: invalid static_cast from type 'int*' to type 'long int*'
C++支持的cast类型转换如下:
1 变量定义与运算
使用建议如下:
- 不要使用dynamic_cast,它被认为时一个糟糕的设计,表明当前的特殊化层次结构出现了问题
- 永远不要使用reinterpret_cast,不安全、不可移植且依赖于实现
5 异常处理
5.1 自定义异常要简洁
第十八章 用于大型程序的工具5.2 throw new要释放资源
try{CFile f(_T("M_Cause_File.dat"), CFile::modeWrite);// If "M_Cause_File.dat" does not exist, the constructor of CFile throws an exceptionthrow new CFileException() //这里异常是在堆上new出来的}catch(CFileException* e){if( e->m_cause == CFileException::fileNotFound)TRACE(_T("ERROR: File not found\n"));e->Delete(); //堆上的内存要在catch中释放}