1 变量赋值的三种方式
从C++11开始,变量赋值有三种方式:
- 初始化列表(推荐):
int apple_count {15};,可以自动检测类型不匹配的赋值,编译时上报error或warning,并且使基本类型、结构体、类对象等初始化格式一致- 对于基本类型,
{}表示赋值该类型的默认值,此功能称为零值初始化
- 对于基本类型,
- 函数符号:
int apple_count (15);,没有检测功能,自动隐式转换 - 赋值运算符:
int apple_count = 15;,没有检测功能,自动隐式转换2 数学常量库
C++20开始提供了numbers库,可以引用标准的数学常量,比如常见的:
3 类型转换
隐式类型转换
对于不同类型的数的操作,编译器都会选择具有更有限值范围的操作数作为要转换为另一个操作数类型的操作数,其优先级为: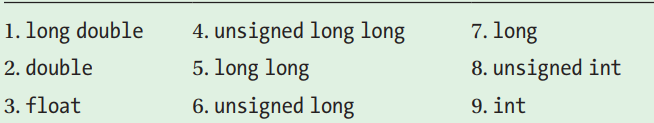
比如上面代码,执行unsigned int x {20u};int y {30};std::cout << x - y << std::endl;
x - y时,编译器优先把y隐式转换为unsigned int类型,之后继续计算,结果为-10。而unsigned int类型无法表示-10,所以结果会变为232 - 10, or 4294967286。cast类型转换
C++的cast类型转换会在编译器编译期间进行检查,而C风格的强制转换不会做任何检查,所以在运行时会出错,导致严重问题或崩溃。所以应该使用cast类型转换,杜绝强制类型转换。
截至C++20,提供了如下显示类型转换:
- static_cast:任何明确定义的类型转换,只要不包含底层const,都可以使用。
double slope = static_cast<double>(j); - const_cast:只能改变运算对象的底层const,一般可用于去除或添加const性质。
const char *pc; char *p = const_cast<char*>(pc)
- dynamic_cast:支持运行时类型识别。
- reinterpret_cast:通常为运算对象的位模式提供低层次上的重新解释。
- std::bit_cast:C++20新增,
4 基本类型的最大值最小值
<limits>库提供了std::numeric_limits类模板,可以获取指定类型的各种属性。其中最常用的式max()和min(),用于获取最大值和最小值。std::cout << "int\t"<< std::numeric_limits<int>::lowest() << '\t'<< std::numeric_limits<int>::min() << '\t'<< std::numeric_limits<int>::max() << '\n';
5 namespace与using
从C++17开始,对于嵌套的namespace,可以使用如下简化写法(在此之前只能使用多层作用域方式): ```cpp namespace MyLibraries::Networking::FTP { }
//旧写法,C++17之前编译错误 namespace MyLibraries { namespace Networking { namespace FTP { } } }
另外还可以直接定义已存在namespace的别名:```cppnamespace MyFTP = MyLibraries::Networking::FTP;
当然,最好还是使用using定义别名,using当前有如下三个功能:
using namespace xxx;:导入整个命名空间,这样空间中所有的变量和函数都可以直接使用using std::cout;:像这种格式,只导入某个name,仅仅该name可以直接使用。建议保持namespace导入的最小影响,将using语句放在最小最合适的范围内,尽量避免全局的导入。using new_name = name;:为某个内置或自定义的类型设置类型别名,忘记**typedef**吧。6 <=>运算符
从C++20开始,新增了<=>运算符,返回一个strong_ordering(int)或partial_ordering(浮点数)类型表示比较结果。我们可以通过判断result的值获取比较结果,不需要重复比较源数据: ```cpp //C++20新增三元比较运算符,一次比较得到得到结果,不需要重复比较原数据include
include
using namespace std;
int main() { int i{11}; //result保存比较结果,不能用switch比较 strong_ordering result{i <=> 0}; if (result == strong_ordering::less) { cout << “less” << endl; } if (result == strong_ordering::greater) { cout << “greater” << endl; } if (result == strong_ordering::equal) { cout << “equal” << endl; } //可以使用辅助函数比较result,不直接不叫枚举类 if (is_lt(result)) { cout << “less” << endl; } if (is_gt(result)) { cout << “greater” << endl; } if (is_eq(result)) { cout << “equal” << endl; } return 0; } ```

