原文参考: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/341692197
一:整体
1、单文件组件(SFC,.vue 文件)
以 Webpack4 为例
<template></template><script>export default {}</script><style></style>
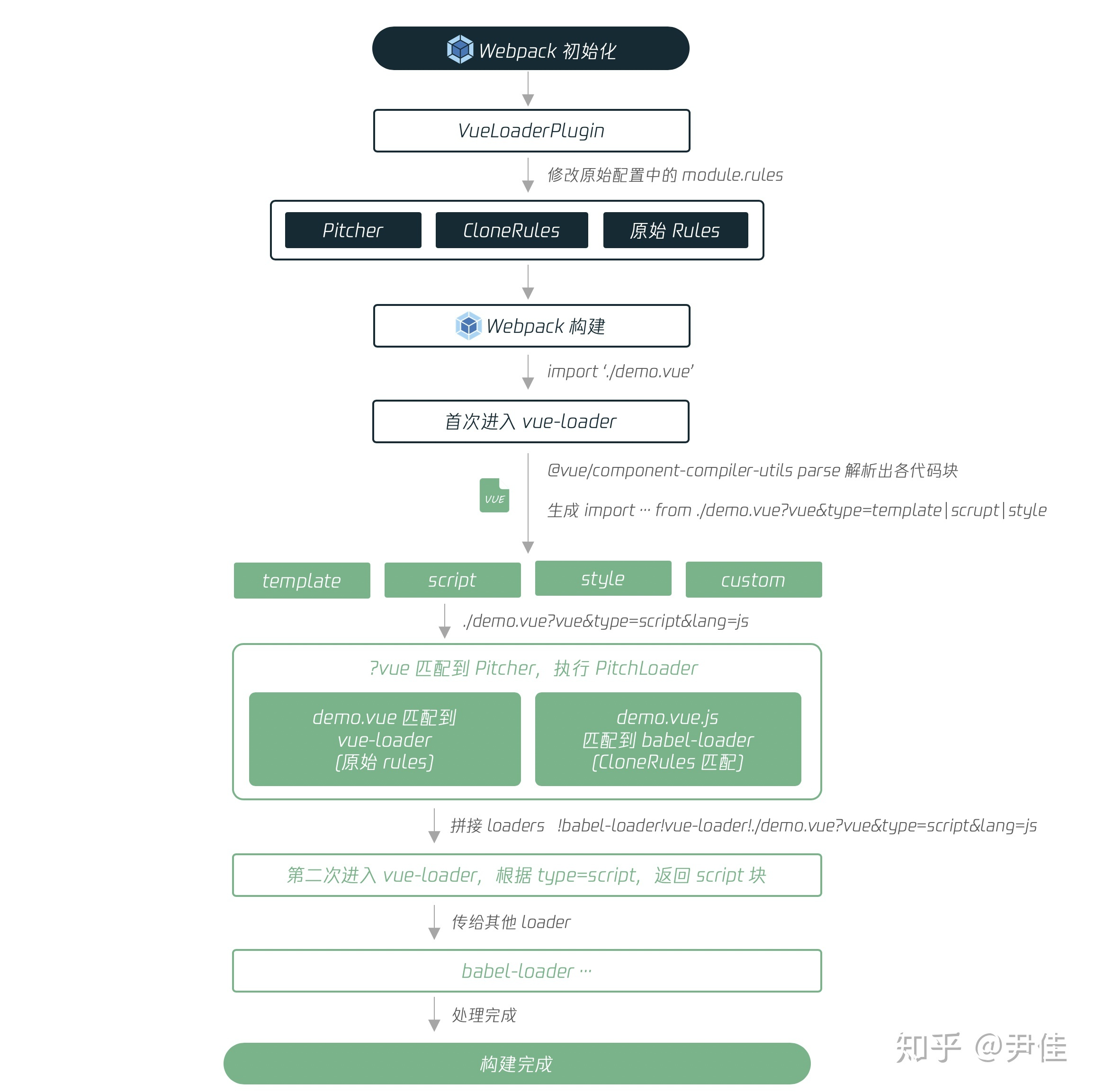
Webpack 需要增加 vue-loader 和 vueLoaderPlugin 对 SFC 进行支持。
样式: vue-style-loader、 css-loader
2、template、script、style 代码块切分
打包编译之后会被转化为 import 引入
./packages/button/src/button.vue?vue&type=template&id=ca859fb4
./packages/button/src/button-group.vue?vue&type=script&lang=js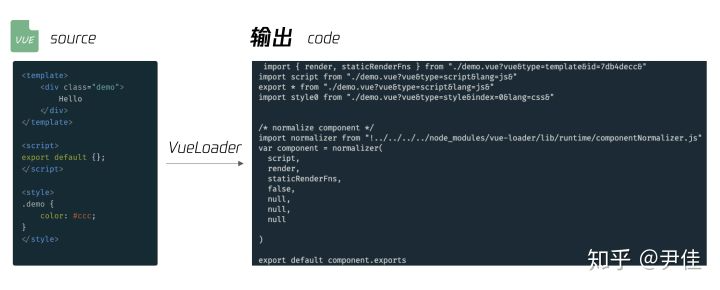
例如: foo.vue?type=template&id=xxxxx
module.exports = function (source) {// ...// 解析源码,得到描述符const descriptor = parse({ source, ... });// 处理 template 块let templateImport = `var render, staticRenderFns`let templateRequestif (descriptor.template) {const src = descriptor.template.src || resourcePathconst idQuery = `&id=${id}`const scopedQuery = hasScoped ? `&scoped=true` : ``const attrsQuery = attrsToQuery(descriptor.template.attrs)const query = `?vue&type=template${idQuery}${scopedQuery}${attrsQuery}${inheritQuery}`const request = templateRequest = stringifyRequest(src + query)templateImport = `import { render, staticRenderFns } from ${request}`}// 处理 script 块let scriptImport = `var script = {}`if (descriptor.script) {const src = descriptor.script.src || resourcePathconst attrsQuery = attrsToQuery(descriptor.script.attrs, 'js')const query = `?vue&type=script${attrsQuery}${inheritQuery}`const request = stringifyRequest(src + query)scriptImport = (`import script from ${request}\n` +`export * from ${request}` // support named exports)}// 处理 styles 块 (支持多 style 块)let stylesCode = ``if (descriptor.styles.length) {stylesCode = genStylesCode(loaderContext,descriptor.styles,id,resourcePath,stringifyRequest,needsHotReload,isServer || isShadow // needs explicit injection?)}// Vue 还支持自定义块if (descriptor.customBlocks && descriptor.customBlocks.length) { ... }// ...}
vue-loader把vue文件中的template、javascript、style代码块分别转化为相应的 import 逻辑
二:VueLoaderPlugin 的作用
?vue&type=template 的作用是什么?可以从 VueLoaderPlugin 中找出答案,首先我们先了解 Webpack 中的 Plugin 能做什么。
1. Plugin 的特性
Plugin 的作用,主要有以下两条:
- 能够 hook 到在每个编译(compilation)阶段触发的所有关键事件。
- 在插件实例的 apply 方法中,可以通过compiler.options获取 Webpack 配置,并进行修改。
VueLoaderPlugin 通过第二个特性,在初始化阶段,对 module.rules 进行动态修改。
2. VueLoaderPlugin 预处理
VueLoaderPlugin 的处理流程中,修改了module.rules,在原来的基础上加入了 pitcher 和 cloneRules这一步的作用是:新增的 rule ,能识别形如?vue&type=template的querystring,让不同语言的代码块匹配到对应的 rule。
class VueLoaderPlugin {apply (compiler) {// 标识 VueLoaderPlugin 已被加载// add NS marker so that the loader can detect and report missing pluginif (compiler.hooks) {// webpack 4compiler.hooks.compilation.tap(id, compilation => {const normalModuleLoader = compilation.hooks.normalModuleLoadernormalModuleLoader.tap(id, loaderContext => {loaderContext[NS] = true})})} else {// webpack < 4compiler.plugin('compilation', compilation => {compilation.plugin('normal-module-loader', loaderContext => {loaderContext[NS] = true})})}// 重头戏,对 Webpack 配置进行修改const rawRules = compiler.options.module.rules;const { rules } = new RuleSet(rawRules);// for each user rule (expect the vue rule), create a cloned rule// that targets the corresponding language blocks in *.vue files.const clonedRules = rules.filter(r => r !== vueRule).map(cloneRule)// global pitcher (responsible for injecting template compiler loader & CSS// post loader)const pitcher = {loader: require.resolve('./loaders/pitcher'),resourceQuery: query => {const parsed = qs.parse(query.slice(1))return parsed.vue != null},options: {cacheDirectory: vueLoaderUse.options.cacheDirectory,cacheIdentifier: vueLoaderUse.options.cacheIdentifier}}// 替换初始 module.rules,在原有 rule 上,增加 pitcher、clonedRulescompiler.options.module.rules = [pitcher,...clonedRules,...rules];}}
VueLoaderPlugin 对 rules 的修改,用下图可以更直观地理解各部分 Rule 的作用。(这里有一个小的知识点,除了常见的Rule.test选项外,Rule.resourceQuery选项可以对资源的 querystring 进行匹配)
下图展示VueLoaderPlugin 对 module.rules 的修改: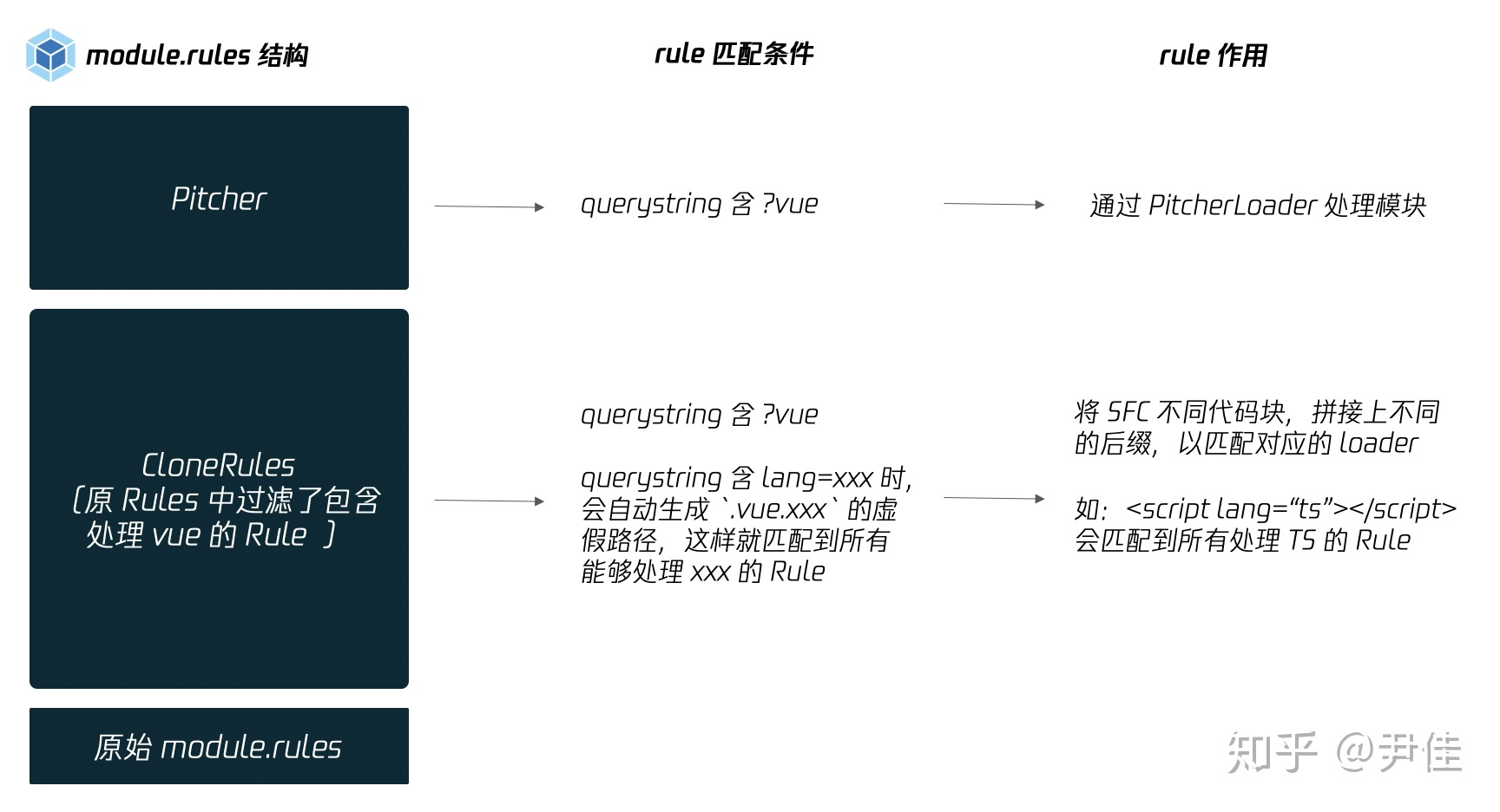
三:回到 Loader
上一节梳理了 VueLoaderPlugin 在初始化阶段的预处理,这一节我们继续回到构建阶段中,看看以 VueLoader 为中心如何协调其它 Loader ,得到每个代码块的构建结果。同样地,我们先了解一下 Webpack 的 loader 特性。
1、Webpack 的 loader 运行顺序
对于 loader ,我们知道它们的执行是有顺序的,如果是这样的配置,运行的顺序将是 c-loader -> b-loader -> a-loader。
module.exports = {module: {rules: [{...use: ['a-loader', 'b-loader', 'c-loader'],}],},};
不过,在实际(从右到左)执行 loader 之前,会先从左到右调用 loader 上的 pitch 方法。
|- a-loader `pitch`|- b-loader `pitch`|- c-loader `pitch`|- requested module is picked up as a dependency|- c-loader normal execution|- b-loader normal execution|- a-loader normal execution
并且在 loader 的 pitch 方法中,如果有实际的返回值,将会跳过后续的 loader,比如在 b-loader 的 pitch 中,如果返回了实际值,将会产生下面的执行顺序。
# 注意 a-loader 依然会正常执行,跳过的是 c-loader|- a-loader `pitch`|- b-loader `pitch` returns a module|- a-loader normal execution
知道这个特性,有利于我们理解 SFC 中各代码块在 loader 中的处理顺序。
2、SFC 转化流程
还记得第一节生成的编译结果吗?每个代码块都导出了对应逻辑,我们以 script 块为例,结合第二节的 PitcherLoader 再次进行转化,转化后的结果为:
下图展示script 块的转化流程:
最后的 import 语句,使用了内联方式的 import 语法,我们拆分一下便于理解
# 原import-!../../node_modules/babel-loader/lib/index.js??ref--2-0!../../node_modules/vue-loader/lib/index.js??vue-loader-options!./demo.vue?vue&type=script&lang=js&";# Part1 -!# 将禁用所有已配置的 preLoader 和 loader,但是不禁用 postLoaders# Part2 ../../node_modules/babel-loader/lib/index.js??ref--2-0# 参考小节:VueLoaderPlugin 的预处理,demo.vue 会自动添加 .js 后缀,以匹配所有 js 的 Rule,这里使用 babel-loader 处理 js 模块# Part3 ../../node_modules/vue-loader/lib/index.js??vue-loader-options# /\.vue$/ 规则匹配到 demo.vue,并使用 vue-loader 处理 .vue 后缀# Part4 ./demo.vue?vue&type=script&lang=js&
3、PitchLoader
上述的转化发生在 PitchLoader 中,对 PitchLoader 的实现逻辑感兴趣的同学,可以阅读 loader/pitcher.js 的源码:
// PitcherLoader.pitch 方法,所有带 ?vue 的模块请求,都会走到这里module.exports.pitch = function (remainingRequest) {// 如 ./demo?vue&type=script&lang=js// 此时,loaders 是所有能处理 .vue 和 .xxx 的 loader 列表let loaders = this.loaders;...// 得到 -!babel-loader!vue-loader!const genRequest = loaders => { ... };// 处理 style 块 和 template 块,支持if (query.type === 'style') { ... }if (query.type === 'template') { ... }// 处理 script 块和 custom 块return `import mod from ${request}; export default mod; export * from ${request}`;}
4、再次执行 VueLoader
细心的同学可能发现了,在 PitchLoader 的转化结果中,还是会以 vue-loader 作为第一个处理的 loader,但 vue-loader 不是一开始就转化过了吗 ?与第一次不同的是,这次 vue-loader 的作用,仅仅是把 SFC 中语法块的源码提取出来,并交给后面的 loader 进行处理
下图展示第二次进入 vue-loader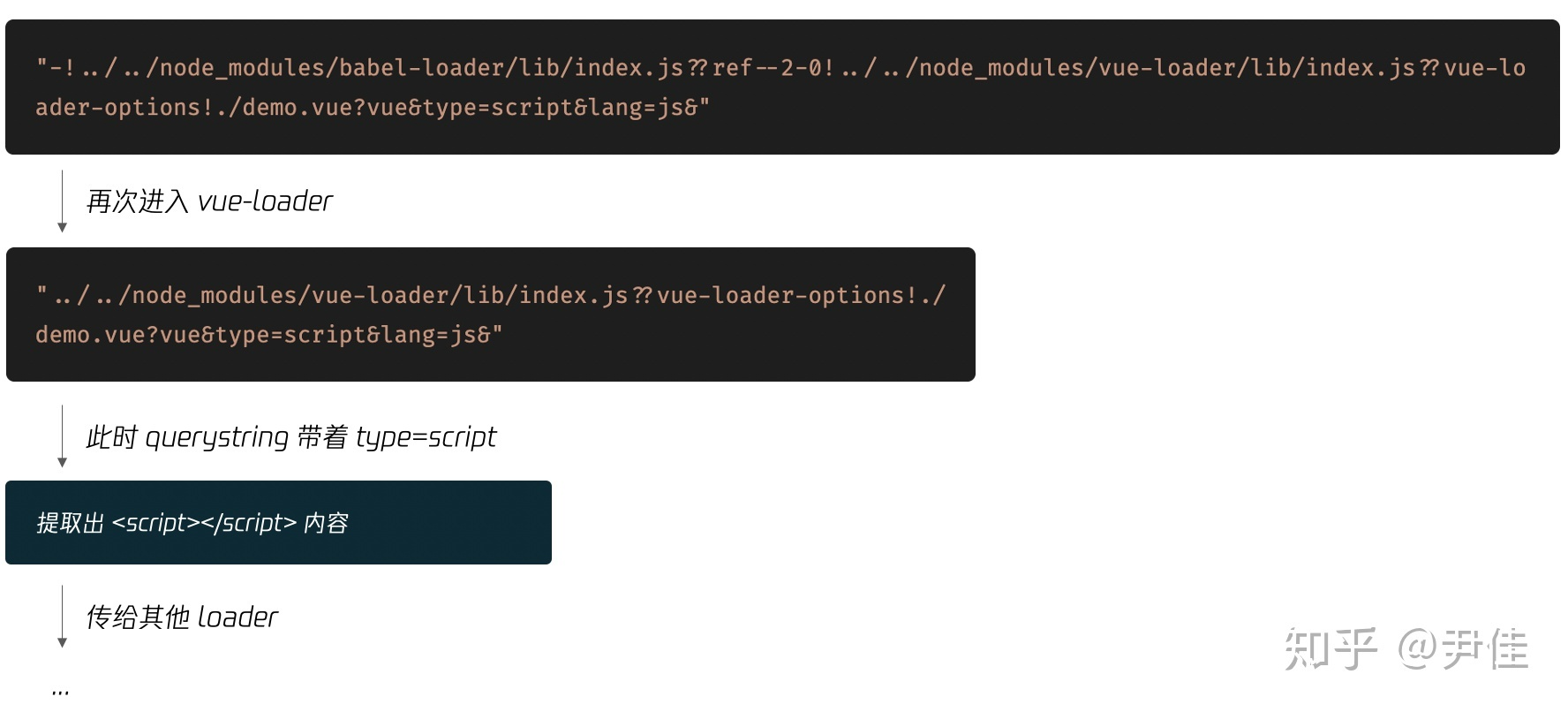
const selectBlock = require('./select')// if the query has a type field, this is a language block request// e.g. foo.vue?type=template&id=xxxxx// and we will return early// 如果querystring 包含了 type 参数,则直接返回该块的代码if (incomingQuery.type) {return selectBlock(descriptor,loaderContext,incomingQuery,!!options.appendExtension)}
module.exports = function selectBlock (descriptor,loaderContext,query,appendExtension) {// templateif (query.type === `template`) {if (appendExtension) {loaderContext.resourcePath += '.' + (descriptor.template.lang || 'html')}loaderContext.callback(null,descriptor.template.content,descriptor.template.map)return}// scriptif (query.type === `script`) {if (appendExtension) {loaderContext.resourcePath += '.' + (descriptor.script.lang || 'js')}loaderContext.callback(null,descriptor.script.content,descriptor.script.map)return}// stylesif (query.type === `style` && query.index != null) {const style = descriptor.styles[query.index]if (appendExtension) {loaderContext.resourcePath += '.' + (style.lang || 'css')}loaderContext.callback(null,style.content,style.map)return}// customif (query.type === 'custom' && query.index != null) {const block = descriptor.customBlocks[query.index]loaderContext.callback(null,block.content,block.map)return}}
至此,vue-loader 里面的处理逻辑基本已经梳理完成~各部分代码块也传入后续的 loader 中进行解析和转化。
四、总结