LRU全称Least Recently Used,也就是最近最少使用的意思,是一种内存管理算法,该算法最早应用于Linux操作系统。
这个算法基于一种假设:长期不被使用的数据,在未来被用到的几率也不大。因此,当数据所占内存达到一定阈值时,我们要移除掉最近最少被使用的数据。
可以使用哈希链表来实现LRU算法。
我们需要抽出一个用户系统,向各个业务系统提供用户的基本信息。
以用户信息的需求为例,来演示一下LRU算法的基本思路。
- 假设使用哈希链表来缓存用户信息,目前缓存了4个用户,这4个用户是按照被访问的时间顺序依次从链表右端插入的。
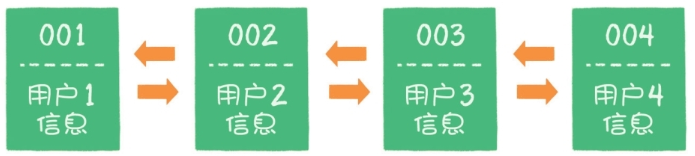
- 如果这时业务方访问用户5,由于哈希链表中没有用户5的数据,需要从数据库中读取出来,插入到缓存中。此时,链表最右端是最新被访问的用户5,最左端是最近最少被访问的用户1。
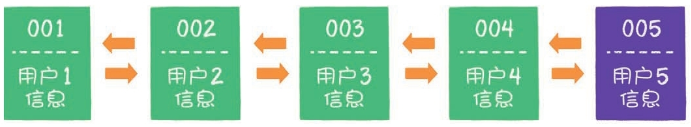
- 接下来,如果业务方访问用户2,哈希链表中已经存在用户2的数据,这时我们把用户2从它的前驱节点和后继节点之间移除,重新插入链表的最右端。此时,链表的最右端变成了最新被访问的用户2,最左端仍然是最近最少被访问的用户1。
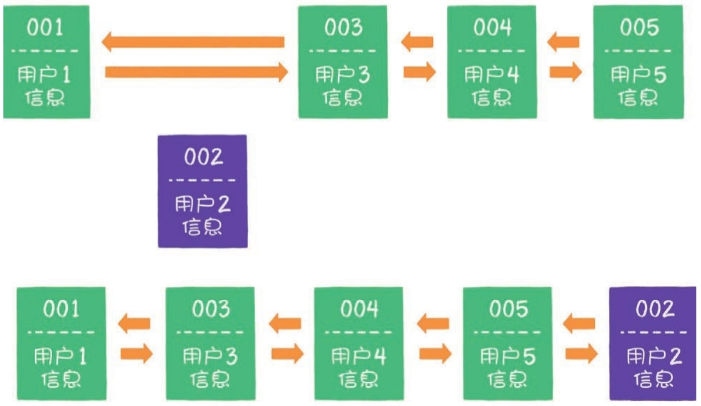
- 接下来,如果业务方请求修改用户4的信息。同样的道理,我们会把用户4从原来的位置移动到链表的最右侧,并把用户信息的值更新。这时,链表的最右端是最新被访问的用户4,最左端仍然是最近最少被访问的用户1。
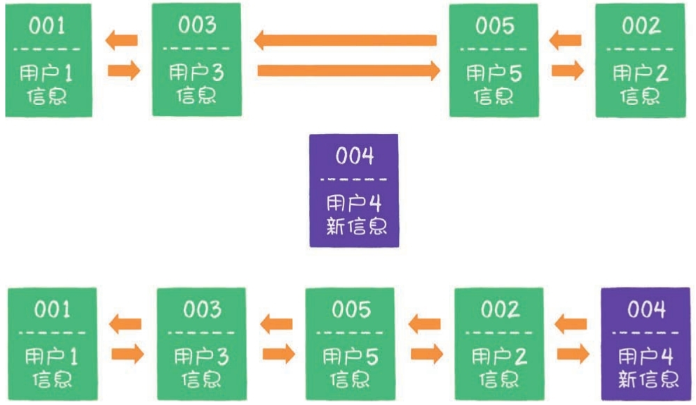
- 后来业务方又要访问用户6,用户6在缓存里没有,需要插入哈希链表中。假设这时缓存容量已经达到上限,必须先删除最近最少被访问的数据,那么位于哈希链表最左端的用户1就会被删除,然后再把用户6插入最右端的位置。
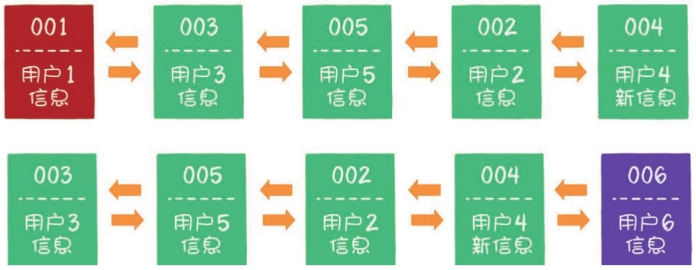
以上,就是LRU算法的基本思路。
class Node {public Node pre;public Node next;public String key;public String value;public Node(String key, String value) {this.key = key;this.value = value;}}public class LRUCache {private Node head;private Node end;// 缓存存储上限private int limit;private HashMap<String, Node> hashMap;// 删除节点private String removeNode(Node node) {if (node == head && node == end) {// 移除唯一的节点head = null;end = null;} else if (node == end) {// 移除尾结点end = end.pre;end.next = null;} else if (node == head) {// 移除头节点head = head.next;head.pre = null;} else {// 移除中间节点node.pre.next = node.next;node.next.pre = node.pre;}return node.key;}// 尾部插入节点private void addNode(Node node) {if (end != null) {end.next = node;node.pre = end;node.next = null;}end = node;if (head == null) {head = node;}}// 刷新被访问节点位置private void refreshNode(Node node) {// 如果访问的是尾节点,则无需移动节点if (node == end) return;// 移除节点removeNode(node);// 重新插入节点addNode(node);}public LRUCache(int limit) {this.limit = limit;hashMap = new HashMap<String, Node>();}public String get(String key) {Node node = hashMap.get(key);if (node == null) return null;refreshNode(node);return node.value;}public void put(String key, String value) {Node node = hashMap.get(key);if (node == null) {// 如果 key 不存在,则插入 key-valueif (hashMap.size() >= limit) {String oldKey = removeNode(head);hashMap.remove(oldKey);}node = new Node(key, value);addNode(node);hashMap.put(key, node);} else {// 如果 key 存在,则刷新 key-valuenode.value = value;refreshNode(node);}}public void remove(String key) {Node node = hashMap.get(key);removeNode(node);hashMap.remove(key);}public static void main(String[] args) {LRUCache lruCache = new LRUCache(5);lruCache.put("001", "用户1");lruCache.put("002", "用户2");lruCache.put("003", "用户3");lruCache.put("004", "用户4");lruCache.put("005", "用户5");lruCache.get("002");lruCache.put("004", "用户44");lruCache.put("006", "用户6");System.out.println(lruCache.get("001"));System.out.println(lruCache.get("006"));}}
需要注意的是,这段代码不是线程安全的代码,要想做到线程安全,需要加上synchronized修饰符。
对于用户系统的需求,你也可以使用缓存数据库Redis来实现,Redis底层也实现了类似LRU的回收算法。

