- 1. How to Include Spring Cloud Gateway
- 2. Glossary
- 3. How It Works
- 4. Configuring Route Predicate Factories and Gateway Filter Factories
- 5. Route Predicate Factories
- 5.1. The After Route Predicate Factory
- 5.2. The Before Route Predicate Factory
- 5.3. The Between Route Predicate Factory
- 5.4. The Cookie Route Predicate Factory
- 5.5. The Header Route Predicate Factory
- 5.6. The Host Route Predicate Factory
- 5.7. The Method Route Predicate Factory
- 5.8. The Path Route Predicate Factory
- 5.9. The Query Route Predicate Factory
- 5.10. The RemoteAddr Route Predicate Factory
- 5.11. The Weight Route Predicate Factory
- 6.
GatewayFilterFactories- 6.1. The
AddRequestHeaderGatewayFilterFactory - 6.2. The
AddRequestParameterGatewayFilterFactory - 6.3. The
AddResponseHeaderGatewayFilterFactory - 6.4. The
DedupeResponseHeaderGatewayFilterFactory - 6.5. Spring Cloud CircuitBreaker GatewayFilter Factory
- 6.6. The
FallbackHeadersGatewayFilterFactory - 6.7. The
MapRequestHeaderGatewayFilterFactory - 6.8. The
PrefixPathGatewayFilterFactory - 6.9. The
PreserveHostHeaderGatewayFilterFactory - 6.10. The
RequestRateLimiterGatewayFilterFactory - 6.11. The
RedirectToGatewayFilterFactory - 6.12. The
RemoveRequestHeaderGatewayFilter Factory - 6.13.
RemoveResponseHeaderGatewayFilterFactory - 6.14. The
RemoveRequestParameterGatewayFilterFactory - 6.15. The
RewritePathGatewayFilterFactory - 6.16.
RewriteLocationResponseHeaderGatewayFilterFactory - 6.17. The
RewriteResponseHeaderGatewayFilterFactory - 6.18. The
SaveSessionGatewayFilterFactory - 6.19. The
SecureHeadersGatewayFilterFactory - 6.20. The
SetPathGatewayFilterFactory - 6.21. The
SetRequestHeaderGatewayFilterFactory - 6.22. The
SetResponseHeaderGatewayFilterFactory - 6.23. The
SetStatusGatewayFilterFactory - 6.24. The
StripPrefixGatewayFilterFactory - 6.25. The Retry
GatewayFilterFactory - 6.26. The
RequestSizeGatewayFilterFactory - 6.27. The
SetRequestHostHeaderGatewayFilterFactory - 6.28. Modify a Request Body
GatewayFilterFactory - 6.29. Modify a Response Body
GatewayFilterFactory - 6.30. Token Relay
GatewayFilterFactory - 6.31. Default Filters
- 6.1. The
3.0.3 official
This project provides an API Gateway built on top of the Spring Ecosystem, including: Spring 5, Spring Boot 2 and Project Reactor. Spring Cloud Gateway aims to provide a simple, yet effective way to route to APIs and provide cross cutting concerns to them such as: security, monitoring / metrics, and resiliency.
1. How to Include Spring Cloud Gateway
To include Spring Cloud Gateway in your project, use the starter with a group ID of org.springframework.cloud and an artifact ID of spring-cloud-starter-gateway. See the Spring Cloud Project page for details on setting up your build system with the current Spring Cloud Release Train.
If you include the starter, but you do not want the gateway to be enabled, set spring.cloud.gateway.enabled=false.
Spring Cloud Gateway is built on Spring Boot 2.x, Spring WebFlux, and Project Reactor. As a consequence, many of the familiar synchronous libraries (Spring Data and Spring Security, for example) and patterns you know may not apply when you use Spring Cloud Gateway. If you are unfamiliar with these projects, we suggest you begin by reading their documentation to familiarize yourself with some of the new concepts before working with Spring Cloud Gateway. Spring Cloud Gateway requires the Netty runtime provided by Spring Boot and Spring Webflux. It does not work in a traditional Servlet Container or when built as a WAR.
2. Glossary
- Route: The basic building block of the gateway. It is defined by an ID, a destination URI, a collection of predicates, and a collection of filters. A route is matched if the aggregate predicate is true.
- Predicate: This is a Java 8 Function Predicate. The input type is a Spring Framework
ServerWebExchange. This lets you match on anything from the HTTP request, such as headers or parameters. - Filter: These are instances of
GatewayFilterthat have been constructed with a specific factory. Here, you can modify requests and responses before or after sending the downstream request.3. How It Works
The following diagram provides a high-level overview of how Spring Cloud Gateway works: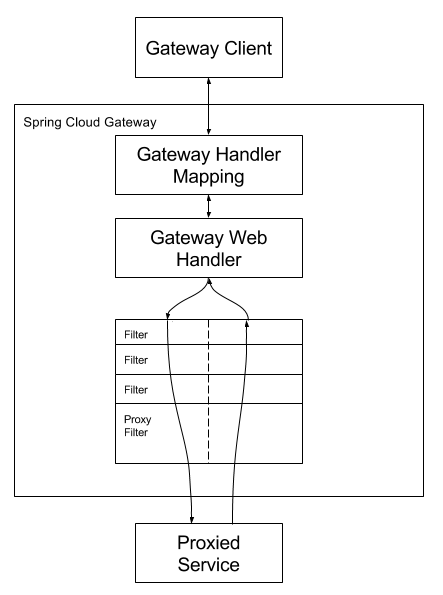
Clients make requests to Spring Cloud Gateway. If the Gateway Handler Mapping determines that a request matches a route, it is sent to the Gateway Web Handler. This handler runs the request through a filter chain that is specific to the request. The reason the filters are divided by the dotted line is that filters can run logic both before and after the proxy request is sent. All “pre” filter logic is executed. Then the proxy request is made. After the proxy request is made, the “post” filter logic is run.URIs defined in routes without a port get default port values of 80 and 443 for the HTTP and HTTPS URIs, respectively.
4. Configuring Route Predicate Factories and Gateway Filter Factories
There are two ways to configure predicates and filters: shortcuts and fully expanded arguments. Most examples below use the shortcut way.
The name and argument names will be listed as code in the first sentance or two of the each section. The arguments are typically listed in the order that would be needed for the shortcut configuration.
4.1. Shortcut Configuration
Shortcut configuration is recognized by the filter name, followed by an equals sign (=), followed by argument values separated by commas (,).
application.yml
spring:cloud:gateway:routes:- id: after_routeuri: https://example.orgpredicates:- Cookie=mycookie,mycookievalue
The previous sample defines the Cookie Route Predicate Factory with two arguments, the cookie name, mycookie and the value to match mycookievalue.
4.2. Fully Expanded Arguments
Fully expanded arguments appear more like standard yaml configuration with name/value pairs. Typically, there will be a name key and an args key. The args key is a map of key value pairs to configure the predicate or filter.
application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: after_route
uri: https://example.org
predicates:
- name: Cookie
args:
name: mycookie
regexp: mycookievalue
This is the full configuration of the shortcut configuration of the Cookie predicate shown above.
5. Route Predicate Factories
Spring Cloud Gateway matches routes as part of the Spring WebFlux HandlerMapping infrastructure. Spring Cloud Gateway includes many built-in route predicate factories. All of these predicates match on different attributes of the HTTP request. You can combine multiple route predicate factories with logical and statements.
5.1. The After Route Predicate Factory
The After route predicate factory takes one parameter, a datetime (which is a java ZonedDateTime). This predicate matches requests that happen after the specified datetime. The following example configures an after route predicate:
Example 1. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: after_route
uri: https://example.org
predicates:
- After=2017-01-20T17:42:47.789-07:00[America/Denver]
This route matches any request made after Jan 20, 2017 17:42 Mountain Time (Denver).
5.2. The Before Route Predicate Factory
The Before route predicate factory takes one parameter, a datetime (which is a java ZonedDateTime). This predicate matches requests that happen before the specified datetime. The following example configures a before route predicate:
Example 2. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: before_route
uri: https://example.org
predicates:
- Before=2017-01-20T17:42:47.789-07:00[America/Denver]
This route matches any request made before Jan 20, 2017 17:42 Mountain Time (Denver).
5.3. The Between Route Predicate Factory
The Between route predicate factory takes two parameters, datetime1 and datetime2which are java ZonedDateTime objects. This predicate matches requests that happen after datetime1 and before datetime2. The datetime2 parameter must be after datetime1. The following example configures a between route predicate:
Example 3. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: between_route
uri: https://example.org
predicates:
- Between=2017-01-20T17:42:47.789-07:00[America/Denver], 2017-01-21T17:42:47.789-07:00[America/Denver]
This route matches any request made after Jan 20, 2017 17:42 Mountain Time (Denver) and before Jan 21, 2017 17:42 Mountain Time (Denver). This could be useful for maintenance windows.
5.4. The Cookie Route Predicate Factory
The Cookie route predicate factory takes two parameters, the cookie name and a regexp (which is a Java regular expression). This predicate matches cookies that have the given name and whose values match the regular expression. The following example configures a cookie route predicate factory:
Example 4. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: cookie_route
uri: https://example.org
predicates:
- Cookie=chocolate, ch.p
This route matches requests that have a cookie named chocolate whose value matches the ch.p regular expression.
5.5. The Header Route Predicate Factory
The Header route predicate factory takes two parameters, the header name and a regexp (which is a Java regular expression). This predicate matches with a header that has the given name whose value matches the regular expression. The following example configures a header route predicate:
Example 5. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: header_route
uri: https://example.org
predicates:
- Header=X-Request-Id, \d+
This route matches if the request has a header named X-Request-Id whose value matches the \d+ regular expression (that is, it has a value of one or more digits).
5.6. The Host Route Predicate Factory
The Host route predicate factory takes one parameter: a list of host name patterns. The pattern is an Ant-style pattern with . as the separator. This predicates matches the Host header that matches the pattern. The following example configures a host route predicate:
Example 6. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: host_route
uri: https://example.org
predicates:
- Host=**.somehost.org,**.anotherhost.org
URI template variables (such as {sub}.myhost.org) are supported as well.
This route matches if the request has a Host header with a value of www.somehost.org or beta.somehost.org or www.anotherhost.org.
This predicate extracts the URI template variables (such as sub, defined in the preceding example) as a map of names and values and places it in the ServerWebExchange.getAttributes() with a key defined in ServerWebExchangeUtils.URI_TEMPLATE_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE.
Those values are then available for use by GatewayFilter factories
5.7. The Method Route Predicate Factory
The Method Route Predicate Factory takes a methods argument which is one or more parameters: the HTTP methods to match. The following example configures a method route predicate:
Example 7. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: method_route
uri: https://example.org
predicates:
- Method=GET,POST
This route matches if the request method was a GET or a POST.
5.8. The Path Route Predicate Factory
The Path Route Predicate Factory takes two parameters: a list of Spring PathMatcher patterns and an optional flag called matchTrailingSlash (defaults to true). The following example configures a path route predicate:
Example 8. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: path_route
uri: https://example.org
predicates:
- Path=/red/{segment},/blue/{segment}
This route matches if the request path was, for example: /red/1 or /red/1/ or /red/blue or /blue/green.
If matchTrailingSlash is set to false, then request path /red/1/ will not be matched.
This predicate extracts the URI template variables (such as segment, defined in the preceding example) as a map of names and values and places it in the ServerWebExchange.getAttributes() with a key defined in ServerWebExchangeUtils.URI_TEMPLATE_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE. Those values are then available for use by GatewayFilter factories
A utility method (called get) is available to make access to these variables easier. The following example shows how to use the get method:
Map<String, String> uriVariables = ServerWebExchangeUtils.getPathPredicateVariables(exchange);
String segment = uriVariables.get("segment");
5.9. The Query Route Predicate Factory
The Query route predicate factory takes two parameters: a required param and an optional regexp (which is a Java regular expression). The following example configures a query route predicate:
Example 9. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: query_route
uri: https://example.org
predicates:
- Query=green
The preceding route matches if the request contained a green query parameter.
application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: query_route
uri: https://example.org
predicates:
- Query=red, gree.
The preceding route matches if the request contained a red query parameter whose value matched the gree. regexp, so green and greet would match.
5.10. The RemoteAddr Route Predicate Factory
The RemoteAddr route predicate factory takes a list (min size 1) of sources, which are CIDR-notation (IPv4 or IPv6) strings, such as 192.168.0.1/16 (where 192.168.0.1 is an IP address and 16 is a subnet mask). The following example configures a RemoteAddr route predicate:
Example 10. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: remoteaddr_route
uri: https://example.org
predicates:
- RemoteAddr=192.168.1.1/24
This route matches if the remote address of the request was, for example, 192.168.1.10.
5.11. The Weight Route Predicate Factory
The Weight route predicate factory takes two arguments: group and weight (an int). The weights are calculated per group. The following example configures a weight route predicate:
Example 11. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: weight_high
uri: https://weighthigh.org
predicates:
- Weight=group1, 8
- id: weight_low
uri: https://weightlow.org
predicates:
- Weight=group1, 2
This route would forward ~80% of traffic to weighthigh.org and ~20% of traffic to weighlow.org
5.11.1. Modifying the Way Remote Addresses Are Resolved
By default, the RemoteAddr route predicate factory uses the remote address from the incoming request. This may not match the actual client IP address if Spring Cloud Gateway sits behind a proxy layer.
You can customize the way that the remote address is resolved by setting a custom RemoteAddressResolver. Spring Cloud Gateway comes with one non-default remote address resolver that is based off of the X-Forwarded-For header, XForwardedRemoteAddressResolver.XForwardedRemoteAddressResolver has two static constructor methods, which take different approaches to security:
XForwardedRemoteAddressResolver::trustAllreturns aRemoteAddressResolverthat always takes the first IP address found in theX-Forwarded-Forheader. This approach is vulnerable to spoofing, as a malicious client could set an initial value for theX-Forwarded-For, which would be accepted by the resolver.XForwardedRemoteAddressResolver::maxTrustedIndextakes an index that correlates to the number of trusted infrastructure running in front of Spring Cloud Gateway. If Spring Cloud Gateway is, for example only accessible through HAProxy, then a value of 1 should be used. If two hops of trusted infrastructure are required before Spring Cloud Gateway is accessible, then a value of 2 should be used.
Consider the following header value:
X-Forwarded-For: 0.0.0.1, 0.0.0.2, 0.0.0.3
The following maxTrustedIndex values yield the following remote addresses:
maxTrustedIndex |
result |
|---|---|
[Integer.MIN_VALUE,0] |
(invalid, IllegalArgumentException during initialization) |
| 1 | 0.0.0.3 |
| 2 | 0.0.0.2 |
| 3 | 0.0.0.1 |
[4, Integer.MAX_VALUE] |
0.0.0.1 |
The following example shows how to achieve the same configuration with Java:
Example 12. GatewayConfig.java
RemoteAddressResolver resolver = XForwardedRemoteAddressResolver
.maxTrustedIndex(1);
...
.route("direct-route",
r -> r.remoteAddr("10.1.1.1", "10.10.1.1/24")
.uri("https://downstream1")
.route("proxied-route",
r -> r.remoteAddr(resolver, "10.10.1.1", "10.10.1.1/24")
.uri("https://downstream2")
)
6. GatewayFilter Factories
Route filters allow the modification of the incoming HTTP request or outgoing HTTP response in some manner. Route filters are scoped to a particular route. Spring Cloud Gateway includes many built-in GatewayFilter Factories.
For more detailed examples of how to use any of the following filters, take a look at the unit tests.
6.1. The AddRequestHeader GatewayFilter Factory
The AddRequestHeader GatewayFilter factory takes a name and value parameter. The following example configures an AddRequestHeader GatewayFilter:
Example 13. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: add_request_header_route
uri: https://example.org
filters:
- AddRequestHeader=X-Request-red, blue
This listing adds X-Request-red:blue header to the downstream request’s headers for all matching requests.AddRequestHeader is aware of the URI variables used to match a path or host. URI variables may be used in the value and are expanded at runtime. The following example configures an AddRequestHeader GatewayFilter that uses a variable:
Example 14. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: add_request_header_route
uri: https://example.org
predicates:
- Path=/red/{segment}
filters:
- AddRequestHeader=X-Request-Red, Blue-{segment}
6.2. The AddRequestParameter GatewayFilter Factory
The AddRequestParameter GatewayFilter Factory takes a name and value parameter. The following example configures an AddRequestParameter GatewayFilter:
Example 15. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: add_request_parameter_route
uri: https://example.org
filters:
- AddRequestParameter=red, blue
This will add red=blue to the downstream request’s query string for all matching requests.AddRequestParameter is aware of the URI variables used to match a path or host. URI variables may be used in the value and are expanded at runtime. The following example configures an AddRequestParameter GatewayFilter that uses a variable:
Example 16. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: add_request_parameter_route
uri: https://example.org
predicates:
- Host: {segment}.myhost.org
filters:
- AddRequestParameter=foo, bar-{segment}
6.3. The AddResponseHeader GatewayFilter Factory
The AddResponseHeader GatewayFilter Factory takes a name and value parameter. The following example configures an AddResponseHeader GatewayFilter:
Example 17. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: add_response_header_route
uri: https://example.org
filters:
- AddResponseHeader=X-Response-Red, Blue
This adds X-Response-Foo:Bar header to the downstream response’s headers for all matching requests.AddResponseHeader is aware of URI variables used to match a path or host. URI variables may be used in the value and are expanded at runtime. The following example configures an AddResponseHeader GatewayFilter that uses a variable:
Example 18. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: add_response_header_route
uri: https://example.org
predicates:
- Host: {segment}.myhost.org
filters:
- AddResponseHeader=foo, bar-{segment}
6.4. The DedupeResponseHeader GatewayFilter Factory
The DedupeResponseHeader GatewayFilter factory takes a name parameter and an optional strategy parameter. name can contain a space-separated list of header names. The following example configures a DedupeResponseHeader GatewayFilter:
Example 19. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: dedupe_response_header_route
uri: https://example.org
filters:
- DedupeResponseHeader=Access-Control-Allow-Credentials Access-Control-Allow-Origin
This removes duplicate values of Access-Control-Allow-Credentials and Access-Control-Allow-Origin response headers in cases when both the gateway CORS logic and the downstream logic add them.
The DedupeResponseHeader filter also accepts an optional strategy parameter. The accepted values are RETAIN_FIRST (default), RETAIN_LAST, and RETAIN_UNIQUE.
6.5. Spring Cloud CircuitBreaker GatewayFilter Factory
The Spring Cloud CircuitBreaker GatewayFilter factory uses the Spring Cloud CircuitBreaker APIs to wrap Gateway routes in a circuit breaker. Spring Cloud CircuitBreaker supports multiple libraries that can be used with Spring Cloud Gateway. Spring Cloud supports Resilience4J out of the box.
To enable the Spring Cloud CircuitBreaker filter, you need to place spring-cloud-starter-circuitbreaker-reactor-resilience4j on the classpath. The following example configures a Spring Cloud CircuitBreaker GatewayFilter:
Example 20. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: circuitbreaker_route
uri: https://example.org
filters:
- CircuitBreaker=myCircuitBreaker
To configure the circuit breaker, see the configuration for the underlying circuit breaker implementation you are using.
The Spring Cloud CircuitBreaker filter can also accept an optional fallbackUri parameter. Currently, only forward: schemed URIs are supported. If the fallback is called, the request is forwarded to the controller matched by the URI. The following example configures such a fallback:
Example 21. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: circuitbreaker_route
uri: lb://backing-service:8088
predicates:
- Path=/consumingServiceEndpoint
filters:
- name: CircuitBreaker
args:
name: myCircuitBreaker
fallbackUri: forward:/inCaseOfFailureUseThis
- RewritePath=/consumingServiceEndpoint, /backingServiceEndpoint
The following listing does the same thing in Java:
Example 22. Application.java
@Bean
public RouteLocator routes(RouteLocatorBuilder builder) {
return builder.routes()
.route("circuitbreaker_route", r -> r.path("/consumingServiceEndpoint")
.filters(f -> f.circuitBreaker(c -> c.name("myCircuitBreaker").fallbackUri("forward:/inCaseOfFailureUseThis"))
.rewritePath("/consumingServiceEndpoint", "/backingServiceEndpoint")).uri("lb://backing-service:8088")
.build();
}
This example forwards to the /inCaseofFailureUseThis URI when the circuit breaker fallback is called. Note that this example also demonstrates the (optional) Spring Cloud LoadBalancer load-balancing (defined by the lb prefix on the destination URI).
The primary scenario is to use the fallbackUri to define an internal controller or handler within the gateway application. However, you can also reroute the request to a controller or handler in an external application, as follows:
Example 23. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: ingredients
uri: lb://ingredients
predicates:
- Path=//ingredients/**
filters:
- name: CircuitBreaker
args:
name: fetchIngredients
fallbackUri: forward:/fallback
- id: ingredients-fallback
uri: http://localhost:9994
predicates:
- Path=/fallback
In this example, there is no fallback endpoint or handler in the gateway application. However, there is one in another application, registered under [localhost:9994](http://localhost:9994).
In case of the request being forwarded to fallback, the Spring Cloud CircuitBreaker Gateway filter also provides the Throwable that has caused it. It is added to the ServerWebExchange as the ServerWebExchangeUtils.CIRCUITBREAKER_EXECUTION_EXCEPTION_ATTR attribute that can be used when handling the fallback within the gateway application.
For the external controller/handler scenario, headers can be added with exception details. You can find more information on doing so in the FallbackHeaders GatewayFilter Factory section.
6.5.1. Tripping The Circuit Breaker On Status Codes
In some cases you might want to trip a circuit breaker based on the status code returned from the route it wraps. The circuit breaker config object takes a list of status codes that if returned will cause the the circuit breaker to be tripped. When setting the status codes you want to trip the circuit breaker you can either use a integer with the status code value or the String representation of the HttpStatus enumeration.
Example 24. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: circuitbreaker_route
uri: lb://backing-service:8088
predicates:
- Path=/consumingServiceEndpoint
filters:
- name: CircuitBreaker
args:
name: myCircuitBreaker
fallbackUri: forward:/inCaseOfFailureUseThis
statusCodes:
- 500
- "NOT_FOUND"
Example 25. Application.java
@Bean
public RouteLocator routes(RouteLocatorBuilder builder) {
return builder.routes()
.route("circuitbreaker_route", r -> r.path("/consumingServiceEndpoint")
.filters(f -> f.circuitBreaker(c -> c.name("myCircuitBreaker")
.fallbackUri("forward:/inCaseOfFailureUseThis")
.addStatusCode("INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR"))
.rewritePath("/consumingServiceEndpoint", "/backingServiceEndpoint"))
.uri("lb://backing-service:8088")
.build();
}
6.6. The FallbackHeaders GatewayFilter Factory
The FallbackHeaders factory lets you add Spring Cloud CircuitBreaker execution exception details in the headers of a request forwarded to a fallbackUri in an external application, as in the following scenario:
Example 26. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: ingredients
uri: lb://ingredients
predicates:
- Path=//ingredients/**
filters:
- name: CircuitBreaker
args:
name: fetchIngredients
fallbackUri: forward:/fallback
- id: ingredients-fallback
uri: http://localhost:9994
predicates:
- Path=/fallback
filters:
- name: FallbackHeaders
args:
executionExceptionTypeHeaderName: Test-Header
In this example, after an execution exception occurs while running the circuit breaker, the request is forwarded to the fallback endpoint or handler in an application running on localhost:9994. The headers with the exception type, message and (if available) root cause exception type and message are added to that request by the FallbackHeaders filter.
You can overwrite the names of the headers in the configuration by setting the values of the following arguments (shown with their default values):
executionExceptionTypeHeaderName("Execution-Exception-Type")executionExceptionMessageHeaderName("Execution-Exception-Message")rootCauseExceptionTypeHeaderName("Root-Cause-Exception-Type")rootCauseExceptionMessageHeaderName("Root-Cause-Exception-Message")
For more information on circuit breakers and the gateway see the Spring Cloud CircuitBreaker Factory section.
6.7. The MapRequestHeader GatewayFilter Factory
The MapRequestHeader GatewayFilter factory takes fromHeader and toHeader parameters. It creates a new named header (toHeader), and the value is extracted out of an existing named header (fromHeader) from the incoming http request. If the input header does not exist, the filter has no impact. If the new named header already exists, its values are augmented with the new values. The following example configures a MapRequestHeader:
Example 27. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: map_request_header_route
uri: https://example.org
filters:
- MapRequestHeader=Blue, X-Request-Red
This adds X-Request-Red:<values> header to the downstream request with updated values from the incoming HTTP request’s Blue header.
6.8. The PrefixPath GatewayFilter Factory
The PrefixPath GatewayFilter factory takes a single prefix parameter. The following example configures a PrefixPath GatewayFilter:
Example 28. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: prefixpath_route
uri: https://example.org
filters:
- PrefixPath=/mypath
This will prefix /mypath to the path of all matching requests. So a request to /hello would be sent to /mypath/hello.
6.9. The PreserveHostHeader GatewayFilter Factory
The PreserveHostHeader GatewayFilter factory has no parameters. This filter sets a request attribute that the routing filter inspects to determine if the original host header should be sent, rather than the host header determined by the HTTP client. The following example configures a PreserveHostHeader GatewayFilter:
Example 29. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: preserve_host_route
uri: https://example.org
filters:
- PreserveHostHeader
6.10. The RequestRateLimiter GatewayFilter Factory
The RequestRateLimiter GatewayFilter factory uses a RateLimiter implementation to determine if the current request is allowed to proceed. If it is not, a status of HTTP 429 - Too Many Requests (by default) is returned.
This filter takes an optional keyResolver parameter and parameters specific to the rate limiter (described later in this section).keyResolver is a bean that implements the KeyResolver interface. In configuration, reference the bean by name using SpEL.#{@myKeyResolver} is a SpEL expression that references a bean named myKeyResolver. The following listing shows the KeyResolver interface:
Example 30. KeyResolver.java
public interface KeyResolver {
Mono<String> resolve(ServerWebExchange exchange);
}
The KeyResolver interface lets pluggable strategies derive the key for limiting requests. In future milestone releases, there will be some KeyResolver implementations.
The default implementation of KeyResolver is the PrincipalNameKeyResolver, which retrieves the Principal from the ServerWebExchange and calls Principal.getName().
By default, if the KeyResolver does not find a key, requests are denied. You can adjust this behavior by setting the spring.cloud.gateway.filter.request-rate-limiter.deny-empty-key (true or false) and spring.cloud.gateway.filter.request-rate-limiter.empty-key-status-code properties.
The RequestRateLimiter is not configurable with the “shortcut” notation. The following example below is invalid:
Example 31. application.properties
# INVALID SHORTCUT CONFIGURATION
spring.cloud.gateway.routes[0].filters[0]=RequestRateLimiter=2, 2, #{@userkeyresolver}
6.10.1. The Redis RateLimiter
The Redis implementation is based off of work done at Stripe. It requires the use of the spring-boot-starter-data-redis-reactive Spring Boot starter.
The algorithm used is the Token Bucket Algorithm.
The redis-rate-limiter.replenishRate property is how many requests per second you want a user to be allowed to do, without any dropped requests. This is the rate at which the token bucket is filled.
The redis-rate-limiter.burstCapacity property is the maximum number of requests a user is allowed to do in a single second. This is the number of tokens the token bucket can hold. Setting this value to zero blocks all requests.
The redis-rate-limiter.requestedTokens property is how many tokens a request costs. This is the number of tokens taken from the bucket for each request and defaults to 1.
A steady rate is accomplished by setting the same value in replenishRate and burstCapacity. Temporary bursts can be allowed by setting burstCapacity higher than replenishRate. In this case, the rate limiter needs to be allowed some time between bursts (according to replenishRate), as two consecutive bursts will result in dropped requests (HTTP 429 - Too Many Requests). The following listing configures a redis-rate-limiter:
Rate limits bellow 1 request/s are accomplished by setting replenishRate to the wanted number of requests, requestedTokens to the timespan in seconds and burstCapacity to the product of replenishRate and requestedTokens, e.g. setting replenishRate=1, requestedTokens=60 and burstCapacity=60 will result in a limit of 1 request/min.
Example 32. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: requestratelimiter_route
uri: https://example.org
filters:
- name: RequestRateLimiter
args:
redis-rate-limiter.replenishRate: 10
redis-rate-limiter.burstCapacity: 20
redis-rate-limiter.requestedTokens: 1
The following example configures a KeyResolver in Java:
Example 33. Config.java
@Bean
KeyResolver userKeyResolver() {
return exchange -> Mono.just(exchange.getRequest().getQueryParams().getFirst("user"));
}
This defines a request rate limit of 10 per user. A burst of 20 is allowed, but, in the next second, only 10 requests are available. The KeyResolver is a simple one that gets the user request parameter (note that this is not recommended for production).
You can also define a rate limiter as a bean that implements the RateLimiter interface. In configuration, you can reference the bean by name using SpEL.#{@myRateLimiter} is a SpEL expression that references a bean with named myRateLimiter. The following listing defines a rate limiter that uses the KeyResolver defined in the previous listing:
Example 34. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: requestratelimiter_route
uri: https://example.org
filters:
- name: RequestRateLimiter
args:
rate-limiter: "#{@myRateLimiter}"
key-resolver: "#{@userKeyResolver}"
6.11. The RedirectTo GatewayFilter Factory
The RedirectTo GatewayFilter factory takes two parameters, status and url. The status parameter should be a 300 series redirect HTTP code, such as 301. The url parameter should be a valid URL. This is the value of the Location header. For relative redirects, you should use uri: no://op as the uri of your route definition. The following listing configures a RedirectTo GatewayFilter:
Example 35. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: prefixpath_route
uri: https://example.org
filters:
- RedirectTo=302, https://acme.org
This will send a status 302 with a Location:https://acme.org header to perform a redirect.
6.12. The RemoveRequestHeader GatewayFilter Factory
The RemoveRequestHeader GatewayFilter factory takes a name parameter. It is the name of the header to be removed. The following listing configures a RemoveRequestHeader GatewayFilter:
Example 36. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: removerequestheader_route
uri: https://example.org
filters:
- RemoveRequestHeader=X-Request-Foo
This removes the X-Request-Foo header before it is sent downstream.
6.13. RemoveResponseHeader GatewayFilter Factory
The RemoveResponseHeader GatewayFilter factory takes a name parameter. It is the name of the header to be removed. The following listing configures a RemoveResponseHeader GatewayFilter:
Example 37. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: removeresponseheader_route
uri: https://example.org
filters:
- RemoveResponseHeader=X-Response-Foo
This will remove the X-Response-Foo header from the response before it is returned to the gateway client.
To remove any kind of sensitive header, you should configure this filter for any routes for which you may want to do so. In addition, you can configure this filter once by using spring.cloud.gateway.default-filters and have it applied to all routes.
6.14. The RemoveRequestParameter GatewayFilter Factory
The RemoveRequestParameter GatewayFilter factory takes a name parameter. It is the name of the query parameter to be removed. The following example configures a RemoveRequestParameter GatewayFilter:
Example 38. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: removerequestparameter_route
uri: https://example.org
filters:
- RemoveRequestParameter=red
This will remove the red parameter before it is sent downstream.
6.15. The RewritePath GatewayFilter Factory
The RewritePath GatewayFilter factory takes a path regexp parameter and a replacement parameter. This uses Java regular expressions for a flexible way to rewrite the request path. The following listing configures a RewritePath GatewayFilter:
Example 39. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: rewritepath_route
uri: https://example.org
predicates:
- Path=/red/**
filters:
- RewritePath=/red/?(?<segment>.*), /$\{segment}
For a request path of /red/blue, this sets the path to /blue before making the downstream request. Note that the $ should be replaced with $\ because of the YAML specification.
6.16. RewriteLocationResponseHeader GatewayFilter Factory
The RewriteLocationResponseHeader GatewayFilter factory modifies the value of the Location response header, usually to get rid of backend-specific details. It takes stripVersionMode, locationHeaderName, hostValue, and protocolsRegex parameters. The following listing configures a RewriteLocationResponseHeader GatewayFilter:
Example 40. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: rewritelocationresponseheader_route
uri: http://example.org
filters:
- RewriteLocationResponseHeader=AS_IN_REQUEST, Location, ,
For example, for a request of POST [api.example.com/some/object/name](https://api.example.com/some/object/name), the Location response header value of [object-service.prod.example.net/v2/some/object/id](https://object-service.prod.example.net/v2/some/object/id) is rewritten as [api.example.com/some/object/id](https://api.example.com/some/object/id).
The stripVersionMode parameter has the following possible values: NEVER_STRIP, AS_IN_REQUEST (default), and ALWAYS_STRIP.
NEVER_STRIP: The version is not stripped, even if the original request path contains no version.AS_IN_REQUESTThe version is stripped only if the original request path contains no version.ALWAYS_STRIPThe version is always stripped, even if the original request path contains version.
The hostValue parameter, if provided, is used to replace the host:port portion of the response Location header. If it is not provided, the value of the Host request header is used.
The protocolsRegex parameter must be a valid regex String, against which the protocol name is matched. If it is not matched, the filter does nothing. The default is http|https|ftp|ftps.
6.17. The RewriteResponseHeader GatewayFilter Factory
The RewriteResponseHeader GatewayFilter factory takes name, regexp, and replacement parameters. It uses Java regular expressions for a flexible way to rewrite the response header value. The following example configures a RewriteResponseHeader GatewayFilter:
Example 41. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: rewriteresponseheader_route
uri: https://example.org
filters:
- RewriteResponseHeader=X-Response-Red, , password=[^&]+, password=***
For a header value of /42?user=ford&password=omg!what&flag=true, it is set to /42?user=ford&password=***&flag=true after making the downstream request. You must use $\ to mean $ because of the YAML specification.
6.18. The SaveSession GatewayFilter Factory
The SaveSession GatewayFilter factory forces a WebSession::save operation before forwarding the call downstream. This is of particular use when using something like Spring Session with a lazy data store and you need to ensure the session state has been saved before making the forwarded call. The following example configures a SaveSession GatewayFilter:
Example 42. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: save_session
uri: https://example.org
predicates:
- Path=/foo/**
filters:
- SaveSession
If you integrate Spring Security with Spring Session and want to ensure security details have been forwarded to the remote process, this is critical.
6.19. The SecureHeaders GatewayFilter Factory
The SecureHeaders GatewayFilter factory adds a number of headers to the response, per the recommendation made in this blog post.
The following headers (shown with their default values) are added:
X-Xss-Protection:1 (mode=block)Strict-Transport-Security (max-age=631138519)X-Frame-Options (DENY)X-Content-Type-Options (nosniff)Referrer-Policy (no-referrer)Content-Security-Policy (default-src 'self' https:; font-src 'self' https: data:; img-src 'self' https: data:; object-src 'none'; script-src https:; style-src 'self' https: 'unsafe-inline)'X-Download-Options (noopen)X-Permitted-Cross-Domain-Policies (none)
To change the default values, set the appropriate property in the spring.cloud.gateway.filter.secure-headers namespace. The following properties are available:
xss-protection-headerstrict-transport-securityx-frame-optionsx-content-type-optionsreferrer-policycontent-security-policyx-download-optionsx-permitted-cross-domain-policies
To disable the default values set the spring.cloud.gateway.filter.secure-headers.disable property with comma-separated values. The following example shows how to do so:
spring.cloud.gateway.filter.secure-headers.disable=x-frame-options,strict-transport-security
The lowercase full name of the secure header needs to be used to disable it..
6.20. The SetPath GatewayFilter Factory
The SetPath GatewayFilter factory takes a path template parameter. It offers a simple way to manipulate the request path by allowing templated segments of the path. This uses the URI templates from Spring Framework. Multiple matching segments are allowed. The following example configures a SetPath GatewayFilter:
Example 43. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: setpath_route
uri: https://example.org
predicates:
- Path=/red/{segment}
filters:
- SetPath=/{segment}
For a request path of /red/blue, this sets the path to /blue before making the downstream request.
6.21. The SetRequestHeader GatewayFilter Factory
The SetRequestHeader GatewayFilter factory takes name and value parameters. The following listing configures a SetRequestHeader GatewayFilter:
Example 44. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: setrequestheader_route
uri: https://example.org
filters:
- SetRequestHeader=X-Request-Red, Blue
This GatewayFilter replaces (rather than adding) all headers with the given name. So, if the downstream server responded with a X-Request-Red:1234, this would be replaced with X-Request-Red:Blue, which is what the downstream service would receive.SetRequestHeader is aware of URI variables used to match a path or host. URI variables may be used in the value and are expanded at runtime. The following example configures an SetRequestHeader GatewayFilter that uses a variable:
Example 45. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: setrequestheader_route
uri: https://example.org
predicates:
- Host: {segment}.myhost.org
filters:
- SetRequestHeader=foo, bar-{segment}
6.22. The SetResponseHeader GatewayFilter Factory
The SetResponseHeader GatewayFilter factory takes name and value parameters. The following listing configures a SetResponseHeader GatewayFilter:
Example 46. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: setresponseheader_route
uri: https://example.org
filters:
- SetResponseHeader=X-Response-Red, Blue
This GatewayFilter replaces (rather than adding) all headers with the given name. So, if the downstream server responded with a X-Response-Red:1234, this is replaced with X-Response-Red:Blue, which is what the gateway client would receive.SetResponseHeader is aware of URI variables used to match a path or host. URI variables may be used in the value and will be expanded at runtime. The following example configures an SetResponseHeader GatewayFilter that uses a variable:
Example 47. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: setresponseheader_route
uri: https://example.org
predicates:
- Host: {segment}.myhost.org
filters:
- SetResponseHeader=foo, bar-{segment}
6.23. The SetStatus GatewayFilter Factory
The SetStatus GatewayFilter factory takes a single parameter, status. It must be a valid Spring HttpStatus. It may be the integer value 404 or the string representation of the enumeration: NOT_FOUND. The following listing configures a SetStatus GatewayFilter:
Example 48. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: setstatusstring_route
uri: https://example.org
filters:
- SetStatus=BAD_REQUEST
- id: setstatusint_route
uri: https://example.org
filters:
- SetStatus=401
In either case, the HTTP status of the response is set to 401.
You can configure the SetStatus GatewayFilter to return the original HTTP status code from the proxied request in a header in the response. The header is added to the response if configured with the following property:
Example 49. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
set-status:
original-status-header-name: original-http-status
6.24. The StripPrefix GatewayFilter Factory
The StripPrefix GatewayFilter factory takes one parameter, parts. The parts parameter indicates the number of parts in the path to strip from the request before sending it downstream. The following listing configures a StripPrefix GatewayFilter:
Example 50. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: nameRoot
uri: https://nameservice
predicates:
- Path=/name/**
filters:
- StripPrefix=2
When a request is made through the gateway to /name/blue/red, the request made to nameservice looks like [nameservice/red](https://nameservice/red).
6.25. The Retry GatewayFilter Factory
The Retry GatewayFilter factory supports the following parameters:retries: The number of retries that should be attempted.statuses: The HTTP status codes that should be retried, represented by using org.springframework.http.HttpStatus.methods: The HTTP methods that should be retried, represented by using org.springframework.http.HttpMethod.series: The series of status codes to be retried, represented by using org.springframework.http.HttpStatus.Series.exceptions: A list of thrown exceptions that should be retried.backoff: The configured exponential backoff for the retries. Retries are performed after a backoff interval of firstBackoff * (factor ^ n), where n is the iteration. If maxBackoff is configured, the maximum backoff applied is limited to maxBackoff. If basedOnPreviousValue is true, the backoff is calculated byusing prevBackoff * factor.
The following defaults are configured for Retry filter, if enabled:retries: Three timesseries: 5XX seriesmethods: GET methodexceptions: IOException and TimeoutExceptionbackoff: disabled
The following listing configures a Retry GatewayFilter:
Example 51. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: retry_test
uri: http://localhost:8080/flakey
predicates:
- Host=*.retry.com
filters:
- name: Retry
args:
retries: 3
statuses: BAD_GATEWAY
methods: GET,POST
backoff:
firstBackoff: 10ms
maxBackoff: 50ms
factor: 2
basedOnPreviousValue: false
When using the retry filter with a
forward:prefixed URL, the target endpoint should be written carefully so that, in case of an error, it does not do anything that could result in a response being sent to the client and committed. For example, if the target endpoint is an annotated controller, the target controller method should not returnResponseEntitywith an error status code. Instead, it should throw anExceptionor signal an error (for example, through aMono.error(ex)return value), which the retry filter can be configured to handle by retrying. When using the retry filter with any HTTP method with a body, the body will be cached and the gateway will become memory constrained. The body is cached in a request attribute defined byServerWebExchangeUtils.CACHED_REQUEST_BODY_ATTR. The type of the object is aorg.springframework.core.io.buffer.DataBuffer.
6.26. The RequestSize GatewayFilter Factory
When the request size is greater than the permissible limit, the RequestSize GatewayFilter factory can restrict a request from reaching the downstream service. The filter takes a maxSize parameter. The maxSize is aDataSizetype, so values can be defined as a number followed by an optionalDataUnitsuffix such as 'KB' or 'MB'. The default is 'B' for bytes. It is the permissible size limit of the request defined in bytes. The following listing configures aRequestSize`GatewayFilter:
Example 52. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: request_size_route
uri: http://localhost:8080/upload
predicates:
- Path=/upload
filters:
- name: RequestSize
args:
maxSize: 5000000
The RequestSize GatewayFilter factory sets the response status as 413 Payload Too Large with an additional header errorMessage when the request is rejected due to size. The following example shows such an errorMessage:
errorMessage` : `Request size is larger than permissible limit. Request size is 6.0 MB where permissible limit is 5.0 MB
The default request size is set to five MB if not provided as a filter argument in the route definition.
6.27. The SetRequestHostHeader GatewayFilter Factory
There are certain situation when the host header may need to be overridden. In this situation, the SetRequestHostHeader GatewayFilter factory can replace the existing host header with a specified vaue. The filter takes a host parameter. The following listing configures a SetRequestHostHeader GatewayFilter:
Example 53. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: set_request_host_header_route
uri: http://localhost:8080/headers
predicates:
- Path=/headers
filters:
- name: SetRequestHostHeader
args:
host: example.org
The SetRequestHostHeader GatewayFilter factory replaces the value of the host header with example.org.
6.28. Modify a Request Body GatewayFilter Factory
You can use the ModifyRequestBody filter filter to modify the request body before it is sent downstream by the gateway.
This filter can be configured only by using the Java DSL.
The following listing shows how to modify a request body GatewayFilter:
@Bean
public RouteLocator routes(RouteLocatorBuilder builder) {
return builder.routes()
.route("rewrite_request_obj", r -> r.host("*.rewriterequestobj.org")
.filters(f -> f.prefixPath("/httpbin")
.modifyRequestBody(String.class, Hello.class, MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE,
(exchange, s) -> return Mono.just(new Hello(s.toUpperCase())))).uri(uri))
.build();
}
static class Hello {
String message;
public Hello() { }
public Hello(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
}
if the request has no body, the
RewriteFilterwill be passednull.Mono.empty()should be returned to assign a missing body in the request.
6.29. Modify a Response Body GatewayFilter Factory
You can use the ModifyResponseBody filter to modify the response body before it is sent back to the client.
This filter can be configured only by using the Java DSL.
The following listing shows how to modify a response body GatewayFilter:
@Bean
public RouteLocator routes(RouteLocatorBuilder builder) {
return builder.routes()
.route("rewrite_response_upper", r -> r.host("*.rewriteresponseupper.org")
.filters(f -> f.prefixPath("/httpbin")
.modifyResponseBody(String.class, String.class,
(exchange, s) -> Mono.just(s.toUpperCase()))).uri(uri))
.build();
}
if the response has no body, the
RewriteFilterwill be passednull.Mono.empty()should be returned to assign a missing body in the response.
6.30. Token Relay GatewayFilter Factory
A Token Relay is where an OAuth2 consumer acts as a Client and forwards the incoming token to outgoing resource requests. The consumer can be a pure Client (like an SSO application) or a Resource Server.
Spring Cloud Gateway can forward OAuth2 access tokens downstream to the services it is proxying. To add this functionlity to gateway you need to add theTokenRelayGatewayFilterFactory like this:
App.java
@Bean
public RouteLocator customRouteLocator(RouteLocatorBuilder builder) {
return builder.routes()
.route("resource", r -> r.path("/resource")
.filters(f -> f.tokenRelay())
.uri("http://localhost:9000"))
.build();
}
or this
application.yaml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: resource
uri: http://localhost:9000
predicates:
- Path=/resource
filters:
- TokenRelay=
and it will (in addition to logging the user in and grabbing a token) pass the authentication token downstream to the services (in this case/resource).
To enable this for Spring Cloud Gateway add the following dependencies
org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-oauth2-client
How does it work? The {githubmaster}/src/main/java/org/springframework/cloud/gateway/security/TokenRelayGatewayFilterFactory.java[filter] extracts an access token from the currently authenticated user, and puts it in a request header for the downstream requests.
For a full working sample see this project.
A
TokenRelayGatewayFilterFactorybean will only be created if the properspring.security.oauth2.client.*properties are set which will trigger creation of aReactiveClientRegistrationRepositorybean. The default implementation ofReactiveOAuth2AuthorizedClientServiceused byTokenRelayGatewayFilterFactoryuses an in-memory data store. You will need to provide your own implementationReactiveOAuth2AuthorizedClientServiceif you need a more robust solution.
6.31. Default Filters
To add a filter and apply it to all routes, you can use spring.cloud.gateway.default-filters. This property takes a list of filters. The following listing defines a set of default filters:
Example 54. application.yml
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
default-filters:
- AddResponseHeader=X-Response-Default-Red, Default-Blue
- PrefixPath=/httpbin

