LINQ介绍
LINQ是语言集成查询的缩写(Language Integrated Query)。
LINQ的提出就是为了提供一种跨越各种数据源的统一查询方式-它主要包含4个组件
- Linq to SQL:可以查询基于关系数据库的数据,微软只实现了SQLServer的查询等操作,其他的第三方也实现了很多。
- Linq to DataSet: 查询DataSet中的数据,并能对数据进行增删等操作。
- Linq to XML:该组件可以查询XML文件。
- Linq to Objects:可以查询集合数据,如数组或List等。
名称空间
System.Linq
API
LINQ查询步骤
所有 LINQ 查询操作都由以下三个不同的操作组成:
- 获取数据源
- 创建LINQ查询
-
例子:不同的查询写法
public class Program{static void Main(string[] args){int[] numbers = { 5, 4, 1, 3, 9, 8, 6, 7, 2, 0, 2, 8, 6, 6, 4, 3, 1, 7, 5, 4, 6, 2, 1, 0, 3, 0, 1 };//查询大于5的数//方法1:查询语法IEnumerable<int> result = from num in numbers where num > 5 select num;//方法2:方法语法IEnumerable<int> result2 = numbers.Where(num => num > 5);//方法3,自己写方法语法,类似Where。IEnumerable<int> result3 = myWhere(numbers, (num) => num > 5);//方法4:自己写方法语法,用yield,边处理边返回IEnumerable<int> result4 = myWhere2(numbers, (num) => num > 5);}static IEnumerable<int> myWhere(IEnumerable<int> source, Func<int, bool> func){List<int> result = new List<int>();foreach (int num in source){if (func(num)){result.Add(num);}}return result;}static IEnumerable<int> myWhere2(IEnumerable<int> source, Func<int, bool> func){foreach (int num in source){if (func(num)){yield return num;}}}}
查询语法
static void Main(string[] args){//1. 先得有数据源才行,这里用Object的数据源,LINQ都一样int[] numbers = {5,4,1,3,9,8,6,7,2,0,2,8,6,6,4,3,1,7,5,4,6,2,1,0,3,0,1};//2. 创建一个LINQ查询IEnumerable<int> lowNums = from num in numberswhere num < 7 && num >2select num;//3.1. 执行查询(延迟执行)foreach (int i in lowNums){Console.Write(i + " ");}//3.2. 立即执行 在linq查询变量后面打点int[] list = lowNums.ToArray();}
图解说明
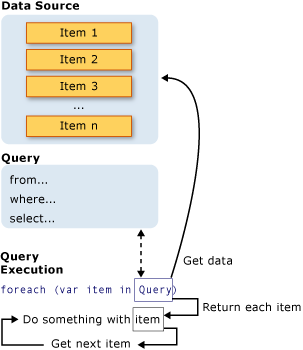
因为上面的例子是数组,我们要查询的是整型,第二步的 lowNums 其实是一个IEnumerable
类型。实现了这个接口的类才能迭代。 所以第二步的 lowNums 是包含了我们要查询的数据的迭代对象。 第三部就用foreach迭代这个对象,就获取到了值。
语法说明
查询以from关键词开头,from后面跟一个范变量(就是给你要查询的那个玩意取个名字) in 后面跟查询的数据源。 where就是查询的条件 条件可以用C#的逻辑操作符,&& || ! …….. 各种操作,和SQL差不多,排序,分组啥的,关键字的子句看官方文档 最后写selelct 后面跟 我要查的那个东西,可以用匿名对象
方法语法
Linq,Lambda,委托结合起来用
static void Main(string[] args){//1. 现在有一个学生列表,这是数据源List<Student> stulist = new List<Student>();stulist.Add(new Student(1, 13, "张飞"));stulist.Add(new Student(2, 14, "刘备"));stulist.Add(new Student(3, 11, "关羽"));stulist.Add(new Student(4, 13, "曹操"));stulist.Add(new Student(5, 12, "马超"));//2. linqvar stu = from stus in stulistwhere stus.Age == 13select stus.Name;//3. 强制执行出一个结果集,年龄等于13的学生的名字的listList<string> list = stu.ToList<string>();//3.x 这一步操作等于上面的2,3步操作list = stulist.Where<Student>(x => x.Age == 13).Select<Student, string>(y => y.Name).ToList<string>();}
语法说明
3.x那里用到了lambda和委托 Where和Select的原理,可以看上面的例子:不同的查询写法。 数据源就是当前对象,因为这是对IEnumerable
的拓展方法。这些Linq拓展方法里面,传入Func委托。这些方法遍历数据的时候调用这个委托,委托是你自己传的,所以条件,规则也是你自己定义的。最终成立,满足的就装到IEnumerable 集合中返回。因为返回的都是IEnumerable 类型,所以可以链式编程 上面的链式操作是一种极简写法。还原写法如下:
//这一步查出来了年龄等于13的学生Func<Student,bool> f1 = x => x.Age == 13;var IE = stulist.Where<Student>(f1);//这一步查询出了年龄等于13的学生的名字Func<Student, string> f2 = x => x.Name;var IE2 = IE.Select<Student, string>(f2);list = IE2.ToList<string>();

