- Mybatis 是如何将 sql 执行结果封装为目标对象并返回的?都有哪些映射形式?
- Mybatis 如何执行批量插入?
- Mybatis 动态 sql 有什么用?执行原理?有哪些动态 sql?
- Mybatis 的 Xml 映射 文件 中,不同 的 Xml 映射 文件 , id 是否 可以 重复 ?
- 为什么说 Mybatis 是半自动 ORM 映射工具?它与全自动的区别在哪里?
- Mybatis 的一对一、一对多的关联查询 ?
- MyBatis 实现一对一有几种方式?具体怎么操作的?
- MyBatis 实现一对多有几种方式,怎么操作的?
- Mybatis 是否支持延迟加载?如果支持,它的实现原理是什么?
- Mybatis 的一级、二级缓存
- 什么是 MyBatis 的接口绑定?有哪些实现方式?
- 使用 MyBatis 的 mapper 接口调用时有哪些要求?
- Mapper 编写的几种实现方式?
- 简述 Mybatis 的插件运行原理,以及如何编写一个插件?
https://juejin.cn/post/7000890438966050846
Mybatis 是如何将 sql 执行结果封装为目标对象并返回的?都有哪些映射形式?
第一种方法是使用标记逐个定义数据库列名和对象属性名之间的映射。
第二种方法是使用SQL列的别名函数将列的别名作为对象属性名写入。
使用列名和属性名之间的映射,Mybatis通过反射创建对象并使用反射对象的属性逐个赋值并返回,如果找不到映射关系,则无法完成赋值。
Mybatis 如何执行批量插入?
- 首先,创建一个简单的INSERT语句:
<insert id=”insertname”>insert into names (name) values (#{value})</insert>
然后在Java代码中执行批量插入操作: ```java list < string > names = new arraylist(); names.add(“fred”); names.add(“barney”); names.add(“betty”); names.add(“wilma”);
// 注意 executortype.batch sqlsession sqlsession =sqlsessionfactory.opensession(executortype.batch); try { namemapper mapper = sqlsession.getmapper(namemapper.class); for (string name: names) { mapper.insertname(name); } sqlsession.commit(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); sqlSession.rollback(); throw e; } finally { sqlsession.close(); }
<a name="qQyn1"></a>## Mybatis 如何获取自动生成的(主)键值?**Mapper文件insert语句设置**
useGeneratedKeys=”true” keyProperty=”id”
<a name="ejPI1"></a>## Mybatis 在 mapper 中如何传递多个参数?**第一种方案 DAO层的函数方法**
Public User selectUser(String name,String area);
<br />**对应的Mapper.xml配置文件**```xml<select id="selectUser" resultMap="BaseResultMap" parameterType="java.lang.String">select * from user_user_t where user_name = #{0} and user_area=#{1}</select>
其中,#{0}代表接收的是dao层中的第一个参数,#{1}代表dao层中第二参数,更多参数一致往后加即可。
第二种Dao层的函数方法
Public User selectUser(@param(“userName”)Stringname,@param(“userArea”)String area);
对应的Mapper.xml配置文件
<select id=" selectUser" resultMap="BaseResultMap">select * from user_user_t where user_name = #{userName,jdbcType=VARCHAR} and user_area=#{userArea,jdbcType=VARCHAR}</select>
个人觉得这种方法比较好,能让开发者看到dao层方法就知道该传什么样的参数,比较直观,个人推荐用此种方案。
Mybatis 动态 sql 有什么用?执行原理?有哪些动态 sql?
Mybatis 动态 sql 可以在 Xml 映射文件内,以标签的形式编写动态 sql,
执行原理是根据表达式的值 完成逻辑判断并动态拼接 sql 的功能。
动态 sql有九种、具体是:trim | where | set | foreach | if | choose| when | otherwise | bind。
具体九种动态SQL举例:
if标签
<!-- 查询学生list,like姓名 --><select id=" getStudentListLikeName " parameterType="StudentEntity" resultMap="studentResultMap">SELECT * from STUDENT_TBL ST<if test="studentName!=null and studentName!='' ">WHERE ST.STUDENT_NAME LIKE CONCAT(CONCAT('%', #{studentName}),'%')</if></select>
where标签
<!-- 查询学生list,like姓名,=性别 --><select id="getStudentListWhere" parameterType="StudentEntity" resultMap="studentResultMap">SELECT * from STUDENT_TBL ST<where><if test="studentName!=null and studentName!='' ">ST.STUDENT_NAME LIKE CONCAT(CONCAT('%', #{studentName}),'%')</if><if test="studentSex!= null and studentSex!= '' ">AND ST.STUDENT_SEX = #{studentSex}</if></where></select>
set标签
<!-- 更新学生信息 --><update id="updateStudent" parameterType="StudentEntity">UPDATE STUDENT_TBL<set><if test="studentName!=null and studentName!='' ">STUDENT_TBL.STUDENT_NAME = #{studentName},</if><if test="studentSex!=null and studentSex!='' ">STUDENT_TBL.STUDENT_SEX = #{studentSex},</if><if test="studentBirthday!=null ">STUDENT_TBL.STUDENT_BIRTHDAY = #{studentBirthday},</if><if test="classEntity!=null and classEntity.classID!=null and classEntity.classID!='' ">STUDENT_TBL.CLASS_ID = #{classEntity.classID}</if></set>WHERE STUDENT_TBL.STUDENT_ID = #{studentID};</update>
trim标签
<!-- 查询学生list,like姓名,=性别 --><select id="getStudentListWhere" parameterType="StudentEntity" resultMap="studentResultMap">SELECT * from STUDENT_TBL ST<trim prefix="WHERE" prefixOverrides="AND|OR"><if test="studentName!=null and studentName!='' ">ST.STUDENT_NAME LIKE CONCAT(CONCAT('%', #{studentName}),'%')</if><if test="studentSex!= null and studentSex!= '' ">AND ST.STUDENT_SEX = #{studentSex}</if></trim></select>
choose when otherwise标签
<!-- 查询学生list,like姓名、或=性别、或=生日、或=班级,使用choose --><select id="getStudentListChooseEntity" parameterType="StudentEntity" resultMap="studentResultMap">SELECT * from STUDENT_TBL ST<where><choose><when test="studentName!=null and studentName!='' ">ST.STUDENT_NAME LIKE CONCAT(CONCAT('%', #{studentName}),'%')</when><when test="studentSex!= null and studentSex!= '' ">AND ST.STUDENT_SEX = #{studentSex}</when><when test="studentBirthday!=null">AND ST.STUDENT_BIRTHDAY = #{studentBirthday}</when><when test="classEntity!=null and classEntity.classID !=null and classEntity.classID!='' ">AND ST.CLASS_ID = #{classEntity.classID}</when><otherwise></otherwise></choose></where></select>
foreach
<select id="getStudentListByClassIDs" resultMap="studentResultMap">SELECT * FROM STUDENT_TBL STWHERE ST.CLASS_ID IN<foreach collection="list" item="classList" open="(" separator="," close=")">#{classList}</foreach></select>
Mybatis 的 Xml 映射 文件 中,不同 的 Xml 映射 文件 , id 是否 可以 重复 ?
不同的Xml映射文件 ,如果配置了namespace,那么id可以重复;
如果没有配置namespace,那么id不能重复;原因就是namespace+id是作为Map
有了namespace,自然id就可以重复 ,namespace不同 ,namespace+id自然也就不同 。
为什么说 Mybatis 是半自动 ORM 映射工具?它与全自动的区别在哪里?
Hibernate属于全自动ORM映射工具 ,使用Hibernate查询关联对象或者关联集合对象时,可以根据对象关系模型直接获取 ,所以它是全自动的。而Mybatis在查询关联对象或关联集合对象时,需要手动编写sql来完成,所以 ,称之为半自动ORM映射工具。
Mybatis 的一对一、一对多的关联查询 ?
一对一关联查询
<mapper namespace="com.lcb.mapping.userMapper"><!--association 一对一关联查询 --><select id="getClass" parameterType="int" resultMap="ClassesResultMap">select * from class c,teacher t where c.teacher_id=t.t_id and c.c_id=#{id}</select><resultMap type="com.lcb.user.Classes" id="ClassesResultMap"><!-- 实体类的字段名和数据表的字段名映射 --><id property="id" column="c_id"/><result property="name" column="c_name"/><association property="teacher" javaType="com.lcb.user.Teacher"><id property="id" column="t_id"/><result property="name" column="t_name"/></association></resultMap></mapper>
一对多关联查询
<!--collection 一对多关联查询 --><select id="getClass2" parameterType="int" resultMap="ClassesResultMap2">select * from class c,teacher t,student s where c.teacher_id=t.t_id and c.c_id=s.class_id and c.c_id=#{id}</select><resultMap type="com.lcb.user.Classes" id="ClassesResultMap2"><id property="id" column="c_id"/><result property="name" column="c_name"/><association property="teacher" javaType="com.lcb.user.Teacher"><id property="id" column="t_id"/><result property="name" column="t_name"/></association><collection property="student" ofType="com.lcb.user.Student"><id property="id" column="s_id"/><result property="name" column="s_name"/></collection></resultMap>
MyBatis 实现一对一有几种方式?具体怎么操作的?
有联合查询和嵌套查询,
联合查询是几个表联合查询,只查询一次,通过在resultMap里面配置association节点配置一对一的类就可以完成;
嵌套查询是先查一个表,根据这个表里面的结果的外键id,去再另外一个表里面查询数据,也是通过association配置,但另外一个表的查询通过select属性配置
MyBatis 实现一对多有几种方式,怎么操作的?
有联合查询和嵌套查询。
联合查询是几个表联合查询,只查询一次,通过在resultMap里面的collection节点配置一对多的类就可以完成;嵌套查询是先查一个表,根据这个表里面的结果的外键id,去再另外一个表里面查询数据,也是通过配置collection,但另外一个表的查询通过select节点配置。
Mybatis 是否支持延迟加载?如果支持,它的实现原理是什么?
**Mybatis仅支持association关联对象和collection关联集合对象的延迟加载** **,association指的就是一对一,collection指的就是一对多查询。在Mybatis配置文件中,可以配置是否启用延迟加载lazyLoadingEnabled=true|false。**<br />**它的原理是,使用CGLIB创建目标对象的代理对象,当调用目标方法时,进入拦截器方法,比如调用a.getB().getName(),拦截器invoke()方法发现a.getB()是null值,那么就会单独发送事先保存好的查询关联B对象的sql,把B查询上来,然后调用a.setB(b),于是a的对象b属性就有值了,接着完成a.getB().getName()方法的调用。这就是延迟加载的基本原理。**<br />**当然了,不光是Mybatis,几乎所有的包括Hibernate,支持延迟加载的原理都是一样的。**
Mybatis 的一级、二级缓存
一级缓存:
Mybatis支持缓存,但在没有配置的情况下,默认情况下它只启用一级缓存。级别1缓存只对相同的SqlSession启用。因此,如果SQL参数一模一样,我们使用相同的SqlSession对象调用映射方法,通常只执行SQL一次,因为第一个查询使用SelSession MyBatis将把它放在缓存中,和将来查询,如果没有声明需要刷新,如果缓存中没有,SqlSession将获取当前缓存的数据,并且不会再次向数据库发送SQL
二级缓存:
MyBatis的二级缓存是Application级别的缓存,它可以提高对数据库查询的效率,以提高应用的性能。二级缓存与一级缓存其机制相同,默认也是采用PerpetualCache,HashMap存储,不同在于其存储作用域为Mapper(Namespace),并且可自定义存储源,如Ehcache。默认不打开二级缓存,要开启二级缓存,使用二级缓存属性类需要实现Serializable序列化接口(可用来保存对象的状态),可在它的映射文件中配置;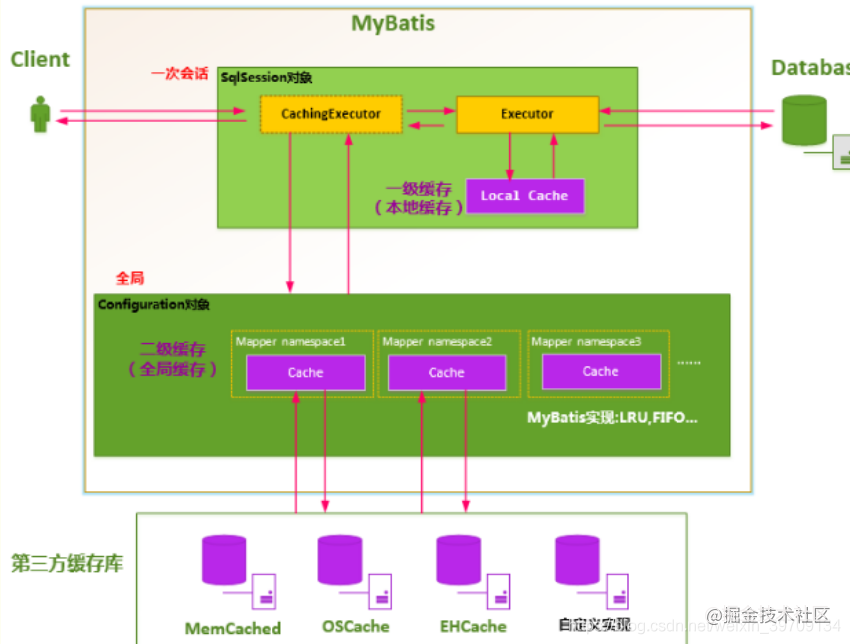
对于缓存数据更新机制,当某一个作用域(一级缓存Session/二级缓存Namespaces)的进行了C/U/D操作后,默认该作用域下所有select中的缓存将被clear。
什么是 MyBatis 的接口绑定?有哪些实现方式?
**接口绑定** **,就是在MyBatis中任意定义接口,然后把接口里面的方法和SQL语句绑定,我们直接调用接口方法就可以,这样比起原来了SqlSession提供的方法我们可以有更加灵活的选择和设置。**<br />**接口绑定有两种实现方式,一种是通过注解绑定,就是在接口的方法上面加上@Select、@Update等注解,里面包含Sql语句来绑定;**<br />**另外一种就是通过xml里面写SQL来绑定,在这种情况下,要指定xml映射文件里面的namespace必须为接口的全路径名。**<br />**当Sql语句比较简单时候,用注解绑定,当SQL语句比较复杂时候,用xml绑定,一般用xml绑定的比较多。**
使用 MyBatis 的 mapper 接口调用时有哪些要求?
Mapper接口方法名和mapper.xml中定义的每个sql的id相同;
Mapper接口方法的输入参数类型和mapper.xml中定义的每个sql的parameterType的类型相同;
Mapper接口方法的输出参数类型和mapper.xml中定义的每个sql的resultType的类型相同;
Mapper.xml文件中的namespace即是mapper接口的类路径。
Mapper 编写的几种实现方式?
第一、接口实现类继承 SqlSessionDaoSupport:使用此种方法需要编写mapper 接口,mapper 接口实现类、mapper.xml 文件。
1、在 sqlMapConfig.xml 中配置 mapper.xml 的位置
<mappers><mapper resource="mapper.xml 文件的地址" /><mapper resource="mapper.xml 文件的地址" /></mappers>
2、定义 mapper 接口.
3、实现类集成 SqlSessionDaoSupportmapper 方法中可以this.getSqlSession()进行数据增删改查。
4、spring 配置
<bean id=" " class="mapper 接口的实现"><property name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactory"></property></bean>
第二、使用 org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperFactoryBean:
1、在 sqlMapConfig.xml 中配置 mapper.xml 的位置,如果 mapper.xml 和mappre 接口的名称相同且在同一个目录,这里可以不用配置
<mappers><mapper resource="mapper.xml 文件的地址" /><mapper resource="mapper.xml 文件的地址" /></mappers>
2、定义 mapper 接口:
2.1、mapper.xml 中的 namespace 为 mapper 接口的地址
2.2、mapper 接口中的方法名和 mapper.xml 中的定义的 statement 的 id 保持一致
2.3、Spring 中定义
<bean id="" class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperFactoryBean"><property name="mapperInterface" value="mapper 接口地址" /><property name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactory" /></bean>
第三、使用 mapper 扫描器:
1、mapper.xml 文件编写:mapper.xml 中的 namespace 为 mapper 接口的地址;mapper 接口中的方法名和 mapper.xml 中的定义的 statement 的 id 保持一致;如果将 mapper.xml 和 mapper 接口的名称保持一致则不用在 sqlMapConfig.xml中进行配置。
2、定义 mapper 接口:注意 mapper.xml 的文件名和 mapper 的接口名称保持一致,且放在同一个目录
3、配置 mapper 扫描器:
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer"><property name="basePackage" value="mapper 接口包地址"></property><property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName"value="sqlSessionFactory"/></bean>
4、使用扫描器后从 spring 容器中获取 mapper 的实现对象
简述 Mybatis 的插件运行原理,以及如何编写一个插件?
**Mybatis只能为ParameterHandler, ResultSetHandler,StatementHandler和Executor接口。Mybatis使用JDK的动态生成为需要被拦截的接口生成代理对象,以便在执行这4种类型时实现接口方法拦截Invoke (), Invoke (), Invoke ()、当然,方法只会拦截那些您指定需要拦截的方法。**<br />**编写插件:实现Mybatis的Interceptor接口**
public interface Interceptor {Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable;default Object plugin(Object target) {return Plugin.wrap(target, this);}default void setProperties(Properties properties) {// NOP}}
复制intercept()方法插件会编写注解来指定要拦截接口的哪些方法。记住不要忘记配置文本配置你编写的插件哈。
public class Invocation {private final Object target;private final Method method;private final Object[] args;public Invocation(Object target, Method method, Object[] args) {this.target = target;this.method = method;this.args = args;}public Object getTarget() {return target;}public Method getMethod() {return method;}public Object[] getArgs() {return args;}public Object proceed() throws InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {return method.invoke(target, args);}}
方法说明:这个东西包含了四个概念:
- target 拦截的对象
- method 拦截target中的具体方法,也就是说Mybatis插件的粒度是精确到方法级别的。
- args 拦截到的参数。
- proceed 执行被拦截到的方法,你可以在执行的前后做一些事情。

