1. Scrapy

2. 创建项目
初始化项目
scrapy startproject 项目名称
创建爬虫
#scrapy genspider 项目名 爬取的url域名/地址scrapy genspider dfcf “http://data.eastmoney.com/zjlx/detail.html”
项目名:作为爬虫运行时的参数
爬取的域名/地址:对爬虫设置的爬取范围,设置之后用于过滤要爬取的url,如果爬取的url与允许的域不同则会被过滤掉。
项目结构
整个工程的目录结构如下:├── scrapy.cfg #工程信息└── xy3├── __init__.py├── items.py #需要解析出来的内容├── pipelines.py #处理解析出来的items├── settings.py #爬虫的设置内容└── spiders├── dhxy3.py #解析内容,生成新的请求规则的蜘蛛└── __init__.py
- scrapy.cfg: 项目的配置文件。
- mySpider/: 项目的Python模块,将会从这里引用代码。
- mySpider/items.py: 项目的目标文件。
- mySpider/pipelines.py: 项目的管道文件。
- mySpider/settings.py: 项目的设置文件。
- mySpider/spiders/: 存储爬虫代码目录。
运行项目
在项目文件以命令行形式运行
cd tutorial#scrapy crawl 爬虫名scrapy crawl quotes
或在项目中创建一个python程序
from scrapy import cmdlinecmdline.execute('scrapy crawl txms'.split())
3. Items
数据建模
定义item文件提前规划好哪些字段需要抓取,防止写错字段名,scrapy会帮我们自动检查错误。
可以清晰自动需要抓取哪些字段
一些特定组件需要Item做支持,如scrapy的imagesPipeline管理类
class MyspiderItem(scrapy.Item):# define the fields for your item here like:name = scrapy.Field() # 名字title = scrapy.Field() # 标题desc = scrapy.Field() # 简介
其实是scrapy帮我们创建一个为空的特殊字典,如果没有指定的键时添加时会报错,不会像python字典帮我们自动创建新键。
需要注意的是:items对象无法直接当做字段来使用,需要强转为字典
item = dict(item)json_data = json.dumps(item, ensure_ascii = False)
4. Request
class scrapy.http.Request(url[, callback, method='GET', headers, body, cookies, meta, encoding='utf-8', priority=0, dont_filter=False, errback])

url(string)- 此请求的网址callback(callable)- 将使用此请求的响应(一旦下载)作为其第一个参数调用的函数。有关更多信息,请参阅下面的将附加数据传递给回调函数。如果请求没有指定回调,parse()将使用spider的 方法。请注意,如果在处理期间引发异常,则会调用errback。method(string)- 此请求的HTTP方法。默认为’GET’。meta(dict)- 属性的初始值Request.meta。如果给定,在此参数中传递的dict将被浅复制。包含此请求的任意元数据的字典。此dict对于新请求为空,通常由不同的Scrapy组件(扩展程序,中间件等)填充。因此,此dict中包含的数据取决于您启用的扩展。dont_filter(boolean)- 表示此请求不应由调度程序过滤。当您想要多次执行相同的请求时忽略重复过滤器时使用。小心使用它,或者你会进入爬行循环。默认为False。body(str或unicode)- 请求体。如果unicode传递了a,那么它被编码为 str使用传递的编码(默认为utf-8)。如果 body没有给出,则存储一个空字符串。不管这个参数的类型,存储的最终值将是一个str(不会是unicode或None)。headers(dict)- 这个请求的头。dict值可以是字符串(对于单值标头)或列表(对于多值标头)。如果 None作为值传递,则不会发送HTTP头。cookie(dict或list)- 请求cookie。这些可以以两种形式发送。
5. Response
6. pipeline管道
process_item(self,item,spider):
- 管道类中必须有的函数
- 实现对item数据的处理
- 必须return item
- open_spider(self,spider) 在爬虫开启的时候仅执行一次
- close_spider(self,spider) 在爬虫关闭时仅执行一次
pipeline使用前要在settings中开启
ITEM_PIPELINES = {# 项目名.pipelines.类名'myspider.pipelines.MyspiderPipeline': 300, # 优先级 小的先执行}
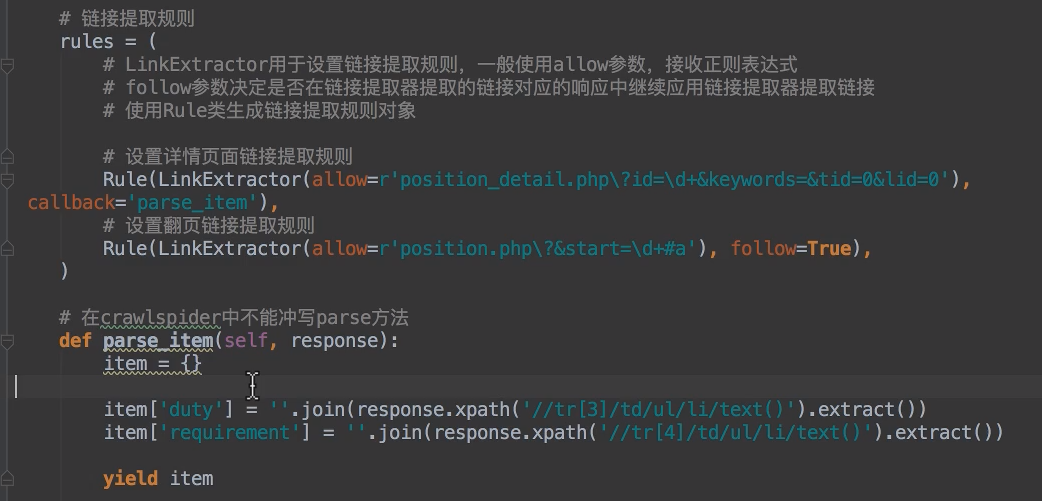
7. crawlspider爬虫
创建模板型爬虫
scrapy genspider -t crawl 项目名 域名
8. middlewares中间件
8.1. 下载中间件
process_request(self, request, spider):
- 每个request通过下载中间件时 该方法被调用
- 返回Node值: 没有return也是返回Node 该request对象传递给下载器 或通过引擎传递给其他权重低的process_request方法
- 返回Rsponse对象:不再请求 把response返回给引擎
- 返回Request对象: 把request对象通过引擎给的调度器 此时将不通过其他权重低的process——request方法
process_response(self, request, response, spider):
- 当下载器完成http请求 传递响应给引擎的时候调用
- 返回Rsponse对象:通过引擎给爬虫处理或交给权重更低的其他下载中间件的process_response方法
- 返回Request对象:通过引擎交给调度器继续请求 此时将不通过其他权重低的 process_request方法
9. Xpath
1.路径查询 //:查找所有子孙节点,不考虑层级关系 / :找直接子节点
2.谓词查询 //div[@id] //div[@id="maincontent"]
3.属性查询 //@class
4.模糊查询 //div[contains(@id, "he")] //div[starts‐with(@id, "he")]
5.内容查询 //div/h1/text()
6.逻辑运算 //div[@id="head" and @class="s_down"] //title | //price
response = HtmlResponse(url='http://example.com', body=html,encoding='utf-8')hxs = HtmlXPathSelector(response)print(hxs) # selector对象hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a')print(hxs) #查找所有的a标签hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[2]')print(hxs) #查找某一个具体的a标签 取第三个a标签hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[@id]')print(hxs) #查找所有含有id属性的a标签hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[@id="i1"]')print(hxs) # 查找含有id=“i1”的a标签hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[@href="link.html"][@id="i1"]')print(hxs) # 查找含有href=‘xxx’并且id=‘xxx’的a标签hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[contains(@href, "link")]')print(hxs) # 查找 href属性值中包含有‘link’的a标签hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[starts-with(@href, "link")]')print(hxs) # 查找 href属性值以‘link’开始的a标签hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[re:test(@id, "i\d+")]')print(hxs) # 正则匹配的用法 匹配id属性的值为数字的a标签hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[re:test(@id, "i\d+")]/text()').extract()print(hxs) # 匹配id属性的值为数字的a标签的文本内容hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//a[re:test(@id, "i\d+")]/@href').extract()print(hxs) #匹配id属性的值为数字的a标签的href属性值hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('/html/body/ul/li/a/@href').extract()print(hxs)hxs = Selector(response=response).xpath('//body/ul/li/a/@href').extract_first()print(hxs)ul_list = Selector(response=response).xpath('//body/ul/li')for item in ul_list:v = item.xpath('./a/span')# 或# v = item.xpath('a/span')# 或# v = item.xpath('*/a/span')print(v)
10. 保存数据
scrapy保存信息的最简单的方法主要有四种,-o 输出指定格式的文件,命令如下:
scrapy crawl itcast -o teachers.json
json lines格式,默认为Unicode编码
scrapy crawl itcast -o teachers.jsonl
csv 逗号表达式,可用Excel打开
scrapy crawl itcast -o teachers.csv
xml格式
scrapy crawl itcast -o teachers.xml

