简介
Koa 是一个新的 web 框架,由 Express 幕后的原班人马打造, 致力于成为 web 应用和 API 开发领域中的一个更小、更富有表现力、更健壮的基石。 通过利用 async 函数,Koa 帮你丢弃回调函数,并有力地增强错误处理。 Koa 并没有捆绑任何中间件, 而是提供了一套优雅的方法,帮助您快速而愉快地编写服务端应用程序。
特点:
- 轻量,无捆绑
- 中间件架构
- 优雅的API设计
- 增强的错误处理
安装使用
安装
# node < 7.6 版本的 Koa 中使用 async 方法需要使用 babel 处理代码npm install koa || yarn add koa
基本使用
// 基本代码const Koa = require('koa');const app = new Koa();app.use(async ctx => {ctx.body = 'Hello World';});app.listen(3000);
Koa原理
一个基于nodejs的入门级http服务,类似于下面的代码:
const http = require('http')const server = http.createServer((req, res)=>{res.writeHead(200)res.end('hi kaikeba')js})server.listen(3000, ()=>{console.log('Example app listening on port 3000!');})
koa的目标是用更简单化、流程化、模块化的方式实现回调部分
// koa.js 封装一个自定义的 Koa 类const http = require('http')class Koa {listen(...args) {const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {this.callback(req, res)})server.listen(...args)}use(callback) {this.callback = callback}}module.exports = Koa// app.jsconst Koa = require("./koa");const app = new Koa();app.use((req, res) => {res.writeHead(200);res.end("Hello World");});app.listen(3000, () => {console.log('Example app listening on port 3000!');});
context
koa 为了能简化API,引入上下文 context 的概念,将原始请求对象 req 和响应对象 res 封装并挂载到 context 上,并且在 context 上设置 getter 和 setter,从而简化操作。
// app.jsapp.use((ctx) => {ctx.body = "Hello World"});
具体实现:封装request、response和context (官方源码)
// request.jsmodule.exports = {get url () {return this.req.url},get method () {return this.req.method.toLowerCase()}}// response.jsmodule.exports = {get body () {return this._body},set body(val) {this._body = val}}// context.jsmodule.exports = {get url () {return this.request.url},get body () {return this.response.body},set body (val) {this.response.body = val},get method () {return this.request.method}}// koa.js 中导入这三个文件const http = require('http')const context = require("./context")const request = require("./request")const response = require("./response")class Koa {listen(...args) {const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {// 构建上下文对象let ctx = this.createContext(req, res)this.callback(ctx)// 响应res.end(ctx.body)})server.listen(...args)}// 构建上下文, 把res和req都挂载到ctx之上,并且在ctx.req和ctx.request.req同时保存createContext (req, res) {const ctx = Object.create(context)ctx.request = Object.create(request)ctx.response = Object.create(response)ctx.req = ctx.request.req = reqctx.res = ctx.response.res = res// console.log(ctx)// console.log('ctx', Object.getPrototypeOf(ctx))return ctx}use(callback) {this.callback = callback}}module.exports = Koa
中间件机制
Koa中间件机制就是函数组合的概念,将一组需要顺序执行的函数复合为一个函数,外层函数的参数实际是内层函数的返回值。洋葱圈模型可以形象表示这种机制,是源码中的精髓和难点。
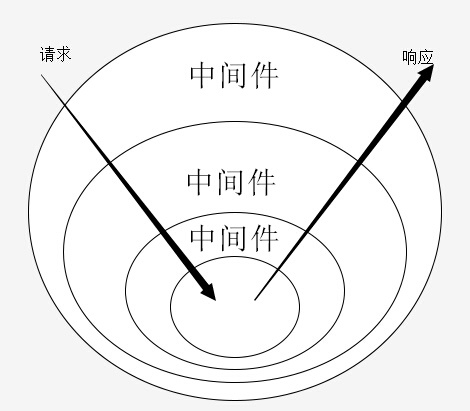
异步中间件
// Koa 中间件的实现(核心)function compose (middlewares) {return function () {// 执行第 0 个return dispatch(0)function dispatch(i) {let fn = middlewares[i]if (!fn) {return Promise.resolve()}return Promise.resolve(fn(function next () {// promise 完成后,再执行下一个return dispatch(i +1)}))}}}async function fn1(next) {console.log('fn1')next()console.log('end fn1')}async function fn2(next) {console.log('fn2')next()console.log('end fn2')}function fn3(next) {console.log('fn3')} jsconst middlewares = [fn1, fn2, fn3]const finalFn = compose(middlewares)finalFn()
Koa中使用compose
const http = require('http')const context = require("./context")const request = require("./request")const response = require("./response")class Koa {constructor () {this.middlewares = []}listen(...args) {const server = http.createServer(async (req, res) => {// 构建上下文对象let ctx = this.createContext(req, res)// 中间件合成const fn = this.compose(this.middlewares)// 执行合成函数并传入上下文await fn(ctx)// 响应res.end(ctx.body)})server.listen(...args)}// 构建上下文createContext (req, res) {const ctx = Object.create(context)ctx.request = Object.create(request)ctx.response = Object.create(response)ctx.req = ctx.request.req = reqctx.res = ctx.response.res = res// console.log(ctx)return ctx}use(middleware) {this.middlewares.push(middleware)}// 合成函数compose (middlewares) {return function (ctx) { // 传入上下文// 执行第 0 个return dispatch(0)function dispatch(i) {let fn = middlewares[i]if (!fn) {return Promise.resolve()}return Promise.resolve(fn(ctx, function next () { // 将上下文传入中间件,middleware(ctx,next)return dispatch(i +1)}))}}}}module.exports = Koa
中间件的实现
中间件的规范
- 一个 async 函数
- 接收 ctx 和 next 两个参数
- 任务结束需要执行next
const mid = async (ctx, next) => {// 来到中间件,洋葱圈左边next() // 进入其他中间件// 再次来到中间件,洋葱圈右边};
中间件常见任务
请求拦截
// iptable.jsmodule.exports = async function(ctx, next) {const { req } = ctx;const blackList = ["127.0.0.1"]const ip = getClientIP(req)if (blackList.includes(ip)) {//出现在黑名单中将被拒绝ctx.body = "not allowed"} else {await next()}}function getClientIP(req) {return (req.headers["x-forwarded-for"] || // 判断是否有反向代理 IPreq.connection.remoteAddress || // 判断 connection 的远程 IPreq.socket.remoteAddress || // 判断后端的 socket 的 IPreq.connection.socket.remoteAddress)}// app.jsapp.use(require("./interceptor"));app.listen(5000, '0.0.0.0', () => {console.log("监听端口3000");});
日志
// app.js// 利用koa的洋葱模型打印访问日志app.use(async (ctx, next) => {let start = new Date().getTime()console.log(`start ${ctx.url}`)next()let end = new Date().getTime()console.log(`请求耗时:${end - start} ms`)})
静态文件服务
- 配置绝对资源目录地址,默认为static
- 获取文件或者目录信息
- 静态文件读取
- 返回
// static.jsconst fs = require("fs");const path = require("path");module.exports = (dirPath = "./public") => {return async (ctx, next) => {if (ctx.url.indexOf("/public") === 0) {// public开头 读取文件const url = path.resolve(__dirname, dirPath);const filepath = url + ctx.url.replace("/public", "");try {stats = fs.statSync(filepath);console.log(stats)if (stats.isDirectory()) {const dir = fs.readdirSync(filepath);const ret = ['<div style="padding-left:20px">'];dir.forEach(filename => {// 简单认为不带小数点的格式,就是文件夹,实际应该用statSyncif (filename.indexOf(".") > -1) {ret.push(`<p><a style="color:black" href="${ctx.url}/${filename}">${filename}</a></p>`);} else {// 文件ret.push(`<p><a href="${ctx.url}/${filename}">${filename}</a></p>`);}});ret.push("</div>");ctx.body = ret.join("");} else {const content = fs.readFileSync(filepath);ctx.body = content;}} catch (e) {// 报错了 文件不存在ctx.body = "404, not found";}} else {// 否则不是静态资源,直接去下一个中间件await next();}};};// app.jsconst static = require('./static')app.use(static(__dirname + '/public'));
路由
// router.jsclass Router {constructor() {this.stack = [];}register(path, methods, middleware) {let route = {path, methods, middleware}this.stack.push(route);}// 现在只支持get和post,其他的同理get(path,middleware){this.register(path, 'get', middleware);}post(path,middleware){this.register(path, 'post', middleware);}routes() {let stock = this.stack;return async function(ctx, next) {let currentPath = ctx.url;let route;for (let i = 0; i < stock.length; i++) {let item = stock[i];if (currentPath === item.path && item.methods.indexOf(ctx.method) >= 0) {// 判断path和methodroute = item.middleware;break;}}if (typeof route === 'function') {route(ctx, next);return;}await next();};}}module.exports = Router;
router.routes()的返回值是一个中间件,由于需要用到method,所以需要挂载method到ctx之上
// request.jsmodule.exports = {get method(){return this.req.method.toLowerCase()}}// context.jsmodule.exports = {get method() {return this.request.method}}
测试
// app.jsconst Koa = require('./source/koa')const Router = require('./source/router')const router = new Router()router.get('/index', async ctx => {ctx.body = "index page"})router.get('/post', async ctx => {ctx.body = "post page"})router.get('/list', async ctx => {ctx.body = "list page"})app.use(router.routes())

